1.1B Kinetic Theory
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
All matter can exist in different forms called ______ __ ______. What does it depend on?
states of matter
it depends on temperature and pressure
States of matter are characterized by what?; the average kinetic energy is directly related to the ___________ of the system
energy of the particles
temperature
What is Temperature?
a measure of the average kinetic energy (Ek)of the particles of a substance
What is the State of Matter at a given temperature and pressure is determined by?
the strength of the inter-particle forces (forces between the particles)
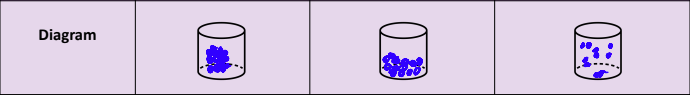
Tell me the qualities of solids, liquids, and gases.
Solid | Liquid | Gas | |
Packing | Particles close packed | Particles more spaced | Particles spread out |
Inter-Particle Forces | Strong (more attraction) | Weaker | Negligible |
Particle Motion | Particles vibrate in position | Particles slide over each other, vibrate, rotate, translate | Particles move freely, vibrate, rotate, translate (faster than liquid) |
Shape | Fixed shape | No fixed shape (takes shape of container) | No fixed shape (expands and occupies available space) |
Volume | Fixed volume | Fixed volume (don't compress easily) | No fixed volume |
What is another term for gases and liquids? Why are they called that?
fluids due to their ability to flow
What is Diffusion?
process by which particles of a substance become evenly distributed, as a result of random movement
What is Kinetic Energy? What is its symbol? How do you calculate it?
the energy associated with movement or motion (Ek)
Ek=1/2 mv2
m = mass in grams
v = velocity in m/s
Kinetic energy of various particles at the same temperature is _____. This gives the inverse relationship between ________ and ____
equal
velocity and mass
(if 2 different particles have the same kinetic energy, their temp. will be the same. That means regardless of the their size or speed [velocity], they have the same amount of energy)
(remember E =1/2mv2)
Since kinetic energy increases with temperature, as particles move faster, what happens to the particles?
they can overcome inter-particle forces and change state
State changes occur at a fixed ___________ and ________ for each substance
temperature and pressure
What is the relationship between states of matter?
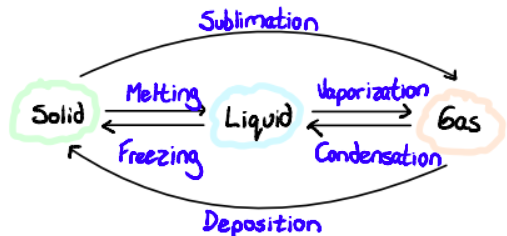
Define Sublimation
direct inter-conversion solid to gas without going through the liquid phase. Characteristic at atmospheric pressure of some substances like dry ice.
Define Deposition
reverse of sublimation, changes from gas to solid (like frosting)
Define Vaporization
the change in state of matter from liquid to gas. It can be accomplished through evaporation or boiling
Define Evaporation
change in state that occurs only at the surface of a liquid and at a temperature below the boiling point.
When heat is absorbed from the surroundings, particles at the surface acquire enough kinetic energy to vaporize and escape.
Define Boiling
volume phenomenon, happens throughout a liquid
characterized by particles leaving throughout the body of the liquid
forming bubbles
Define Boiling Point
when all molecules in a liquid have enough kinetic energy to change into a gas.
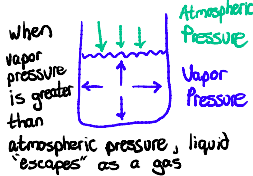
Define Vapour Pressure. What is its relation to Evaporation and Boiling?
the pressure exerted by a liquid on the walls of a container.
During evaporation, vaporization is slow because the vapor pressure is less than atmospheric pressure.
Boiling occurs when vapor pressure = atmospheric pressure