KINS 1224 Lab- Lab 4- Blood Pressure (Lab Exam 2)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
blood pressure
the force that the blood exerts against a vessel wall
systolic blood pressure
pressure produced while the ventricles are contracted
diastolic blood pressure
pressure produced when the ventricles are relaxing
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure; represents both systolic as a single number
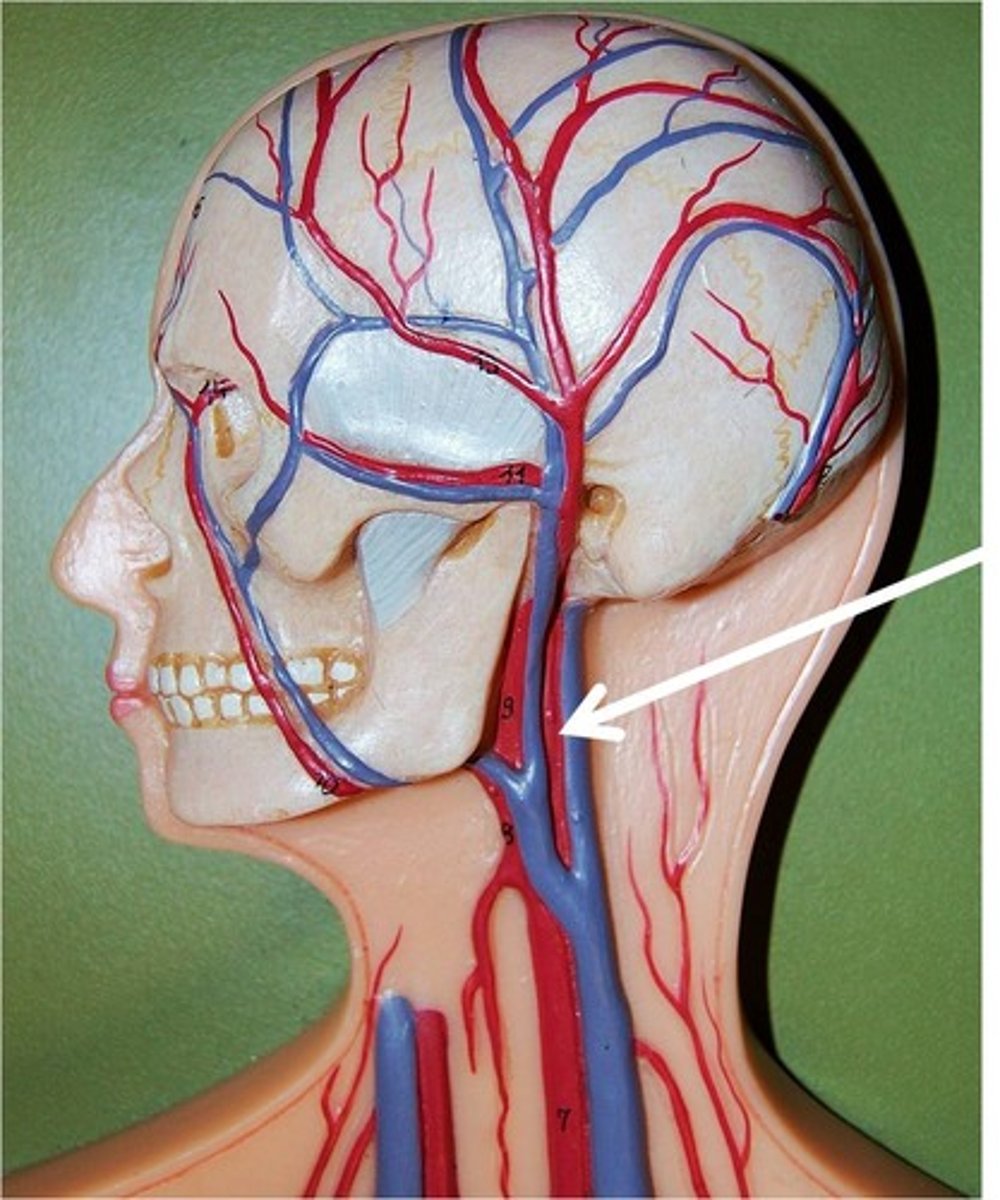
carotid artery
artery on each side of the neck that supplies blood to the head
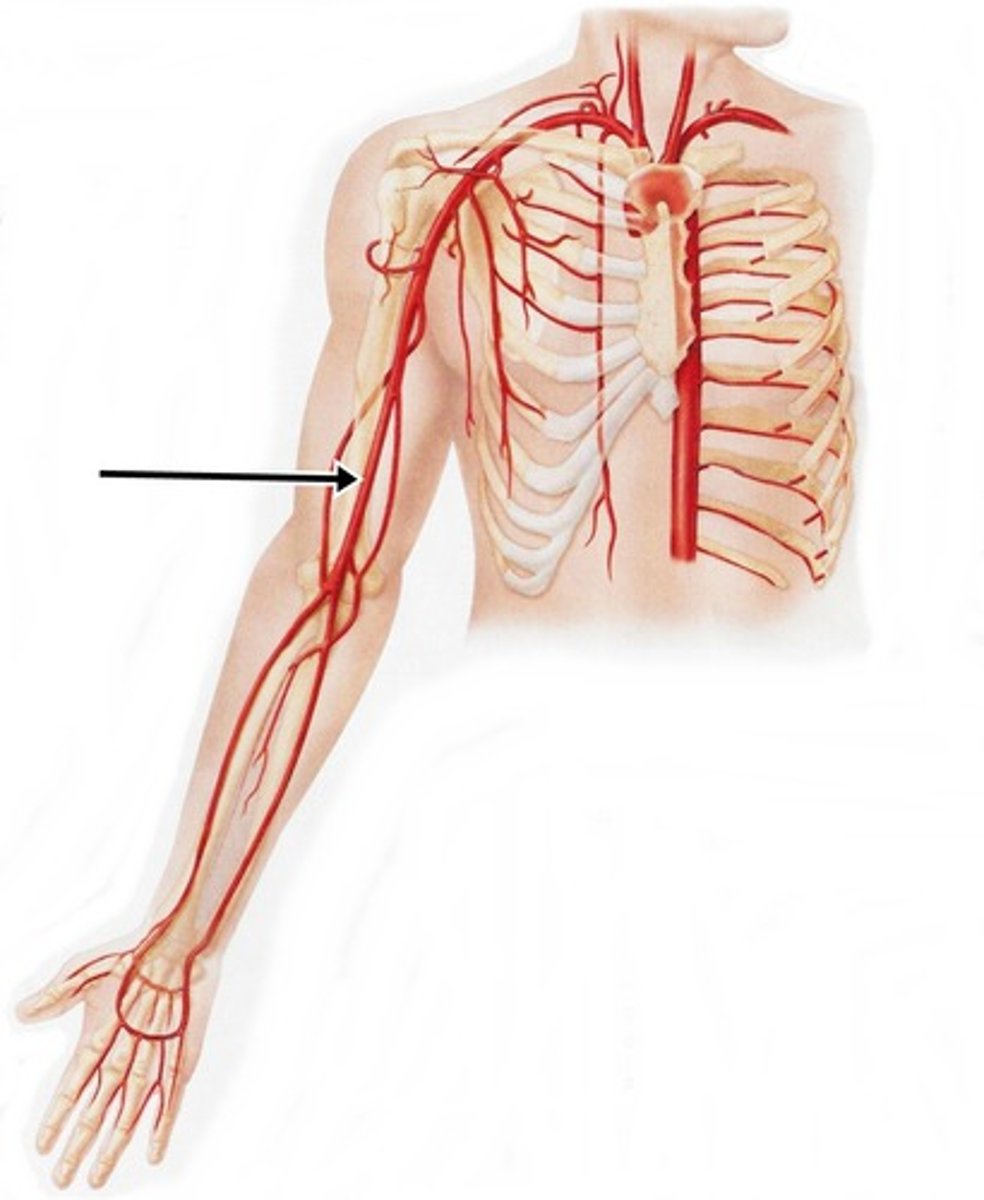
brachial artery
The major vessel in the upper extremity that supplies blood to the arm.
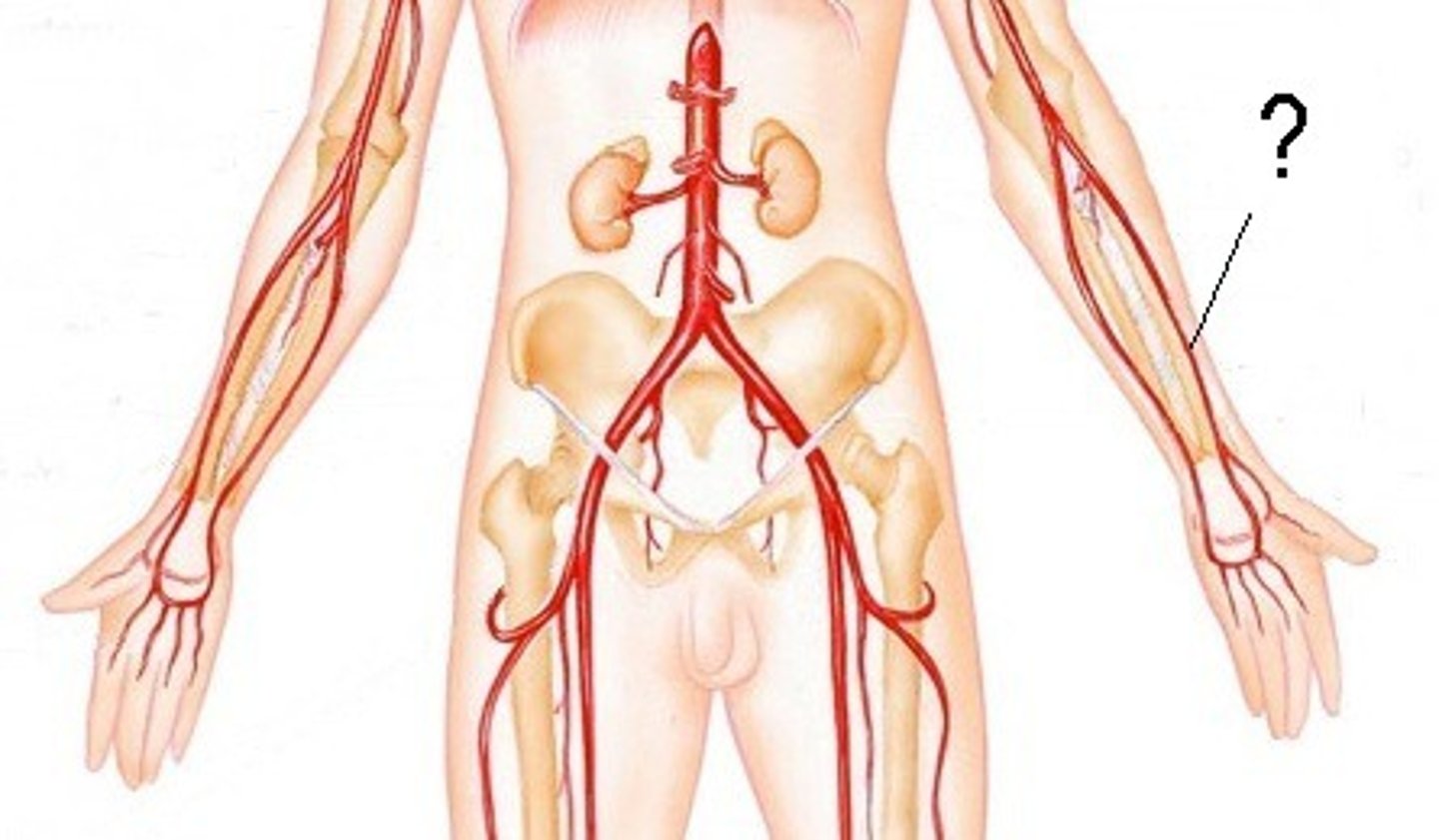
radial artery
The major artery in the forearm; it is palpable at the wrist on the thumb side.
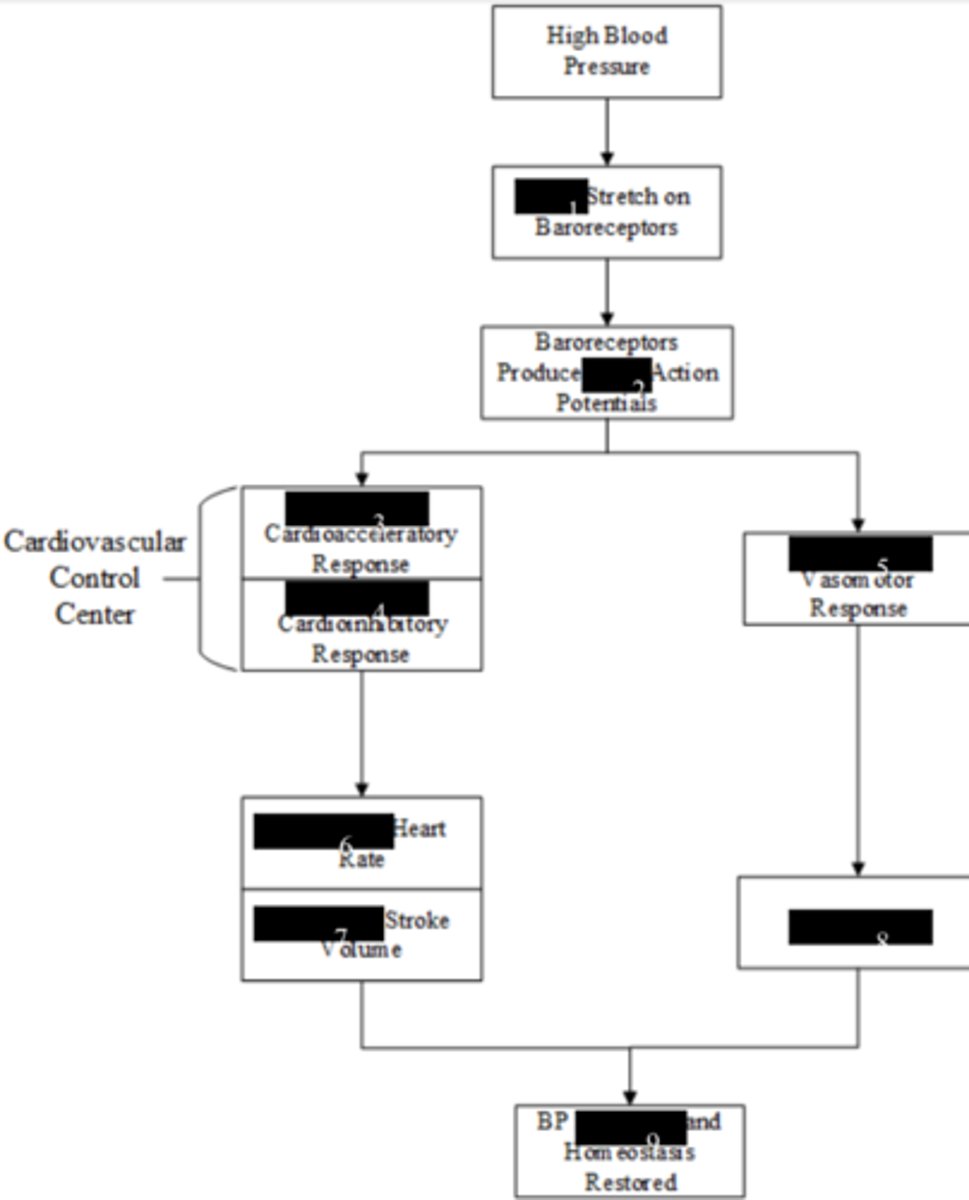
medulla oblongata; baroreceptor
The ____________________ of the brain integrates ______________ info and can activate the cardioacceleratory center, the cardioinhibitory center, and the vasomotor center.
cardioacceleratory center, the cardioinhibitory center, and the vasomotor center
3 centers activated by baroreceptor info via the medulla oblongata
baroreceptors
mechanoreceptors that monitor BP; found in aorta and carotid arteries
cardioacceleratory center and vasomotor center
Center(s) activated by low BP
cardioinhibitory center
Center(s) activated by high BP
1- More
2- More
3- Decreased
4- Increased
5- Decreased
6- Decreased
7- Decreased
8- Vasodilation
9- Decreased
(all would be opposite for low blood pressure)
Label 1-9 (high blood pressure)
heart rate (HR)
number of heart beats per minute
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure
Sounds of Korotkoff
sounds that indicate the resumption of blood flow into the forearm when taking blood pressure.
stroke volume (SV)
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction (each heartbeat)
cardiac output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
cardioacceleratory center
controls sympathetic neurons that increase the heart rate
cardioinhibitory center
controls the parasympathetic neurons that slow the heart rate
vasomotor center
adjusts blood vessel diameter for blood pressure regulation
vasoconstriction
narrowing of blood vessels
vasodilation
widening of blood vessels
systole
phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers contract, pumping blood out of the chambers
diastole
phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart muscles relax and the chambers fill with blood; the ventricles fill with blood
Arteries--> particularly those closest to the heart (aorta)
Where is blood pressure highest?
Veins --> particularly those closest to the heart (vena cava)
Where is blood pressure lowest?
decreases
Blood pressure ________________ as the distance from the heart increases.
pulse
rhythmic expansion and contraction of an artery as blood is pumped through it by the heart.
90 mmHg (180-90)
You are a clinician and you find that your patients blood pressure is 180/90 mmHg. What is their pulse pressure?
120 mmHg (90 + 1/3 (90))
You are a clinician and you find that your patients blood pressure is 180/90 mmHg. What is their mean arterial pressure (MAP)?