Week 3 (Language and thought)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Language
the primary mode of communication for humans it consists of a combination of symbols, sounds, with meanings and rules
Symbolic
arbitrary symbols i.e letters, characters etc
Semantic
has meaning
Structured
grammar
Generative
Productivity infinite number of combinations
Phonemes
Smallest unit of sound information (p, b, m, f)
Morphemes
smallest unit of meaning (words, suffixes and prefixes)
Syntax
rules that govern the placement of words and phrases within a language
Chomsky grammar
a system for generating acceptable language utterances and identifying unacceptable ones
Development of language 0-3 months
Coos, gurgles, and orients to sound
Development of language 4-6 months
Responds to name; emits vowel and consonant sounds, babbles and cries
Development of language 7-18 months
Copies gestures; specialises native language; responds to gestures
Development of language 2-3 years
Uses short sentences; matches objects to names, follows instructions
Development of language 4-5 years
Uses proper simple grammar, memorises simple songs, clearer speach
Development of language 10+ years
Stored 50-10,000 words; can speak 2-4 words per-second
B.F Skinner view on language
humans learn language through conditioning (Nurture)
Chomsky’s view on language
impossible to learn all the words and grammar that fast so he suggested that universal grammar is innate and language acquisition parts of the brain
Nature vs Nurture on language
Genetic predisposition to create language and environmental factors specialise language advancement
Broca’s area
important for speech production and grammar
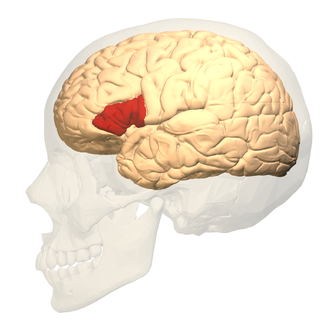
Broca’s aphasia (non-fluent)
difficult speech
slight deficit with grammar
comprehension may be relatively well preserved
Wernicke’s area
recognising speech sounds/ words meaning
Wernicke’s aphasia (fluent)
normal speech rhythm
Incorrect use and/or pronounciation of words
Algorithms
systematic rules/procedure that vary by context
Heuristics
a rule of thumb that provides a best-guess solution including trial and error or shortcuts
barriers to problem solving
mental set, functional fixedness and confirmation bias
mental set
using the same strategies
functional fixedness
inability to use ab object in an unfamiliar way
confirmation bias
search for confirmation of what they already believe and overlook conflicting information
decision making
Define the problem
define alternatives
decide on criteria
pros and cons
make the decision
Heuristics in decision making
representative → people categorise by matching similar things and ignore probability
negatively impact ability to think statistically
Availability → events that are more easily remembered are judged to be more probable than events that are harder to remember
problem solving
Process of transforming one situation into another to meet a goal, the Initial state → Operators → Goal state