Measures of Association
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Define Association
relationship b/w 2 variables that renders them statistically dependent
positive or negative
association does NOT equal causation
What measures are absolute measures?
Risk Difference (RD)
absolute risk reduction (ARR)
absolute risk increase (ARI)
Number needed to treat (NNT)
number needed to harm (NNH)
What measures are relative measures?
Risk Ratio (RR)
relative risk reduction (RRR) and relative risk increase (RRI)
Odds Ratio (OR)
Steps in measuring association
summarize data in table
calculate measures of disease frequency
calculate measures of association
Table to summarize data:
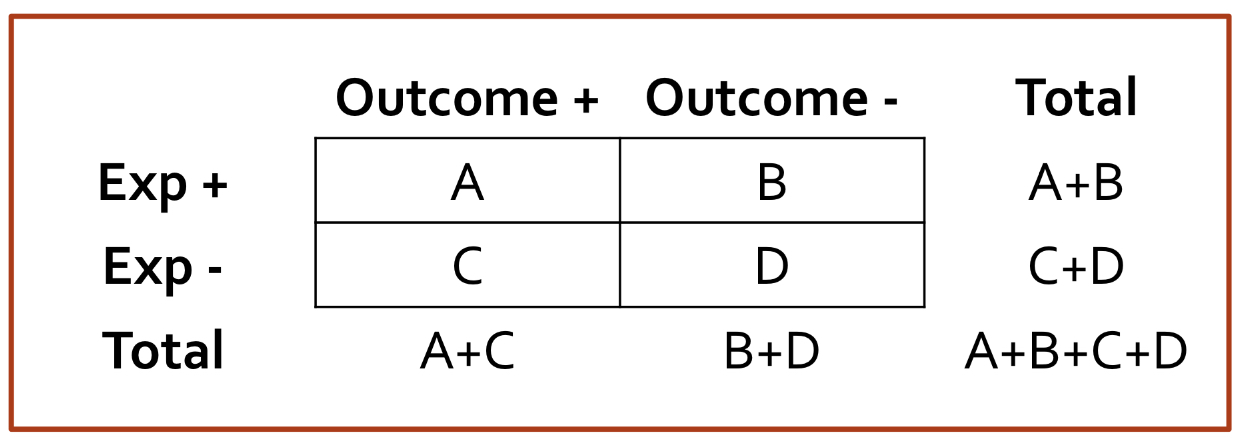
How to calculate cumulative incidence of outcome among exposed/tx group

How to calculate cumulative incidence of outcome among unexposed/tx group

Define Risk Difference
measures difference in the risk (CI) of developing the disease b/w 2 groups
Harmful effect means
absolute risk increase (ARI)
risk in tx group > risk in control group
RD is POSITIVE
Beneficial effect means
absolute risk reduction (ARR)
risk in tx group < risk in control group
RD is NEGATIVE
No association means
risk in tx group = risk in control group
Risk Difference Equation
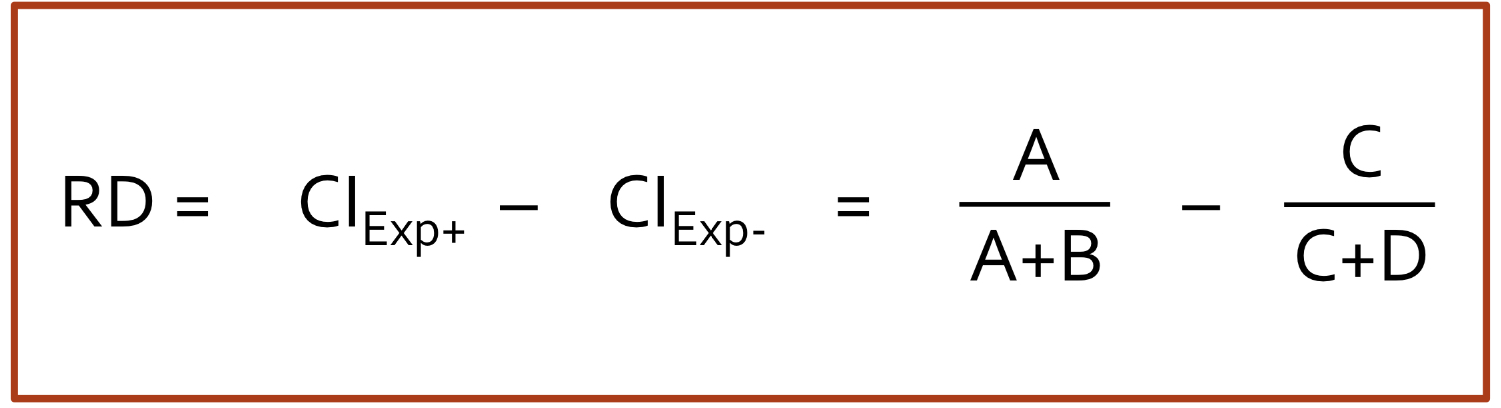
Define number needed to treat (NNT)
# of individuals who would have to receive the tx for one outcome to be prevented
NNT = 1/RD (ARR)
SMALLER NNT = BETTER
Define number needed to harm (NNH)
# of individuals who would have to receive tx for one outcome to be experienced
NNH = 1/RD (ARI)
LARGER NNH = BETTER
Define risk ratio
measures ratio of risk (CI)
Risk Ratio Equation
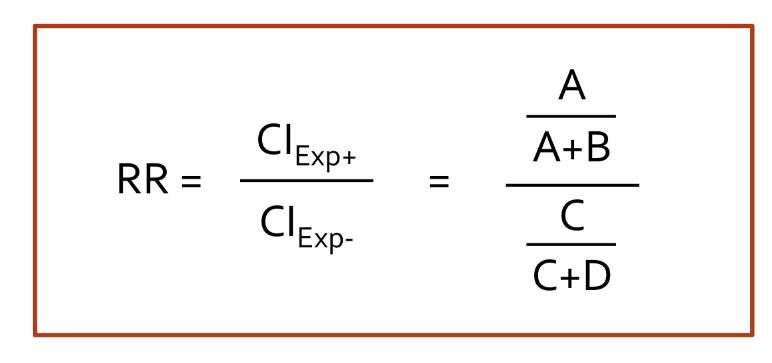
If RR < 1, the risk is ____
decreased
If RR > 1, the risk is _____
increased
If the RR = 1, then
there is no difference b/w the 2 groups
Define Relative Risk Reduction
measures extent to which tx REDUCES a risk compared to the control group
Relative Risk Reduction Equation
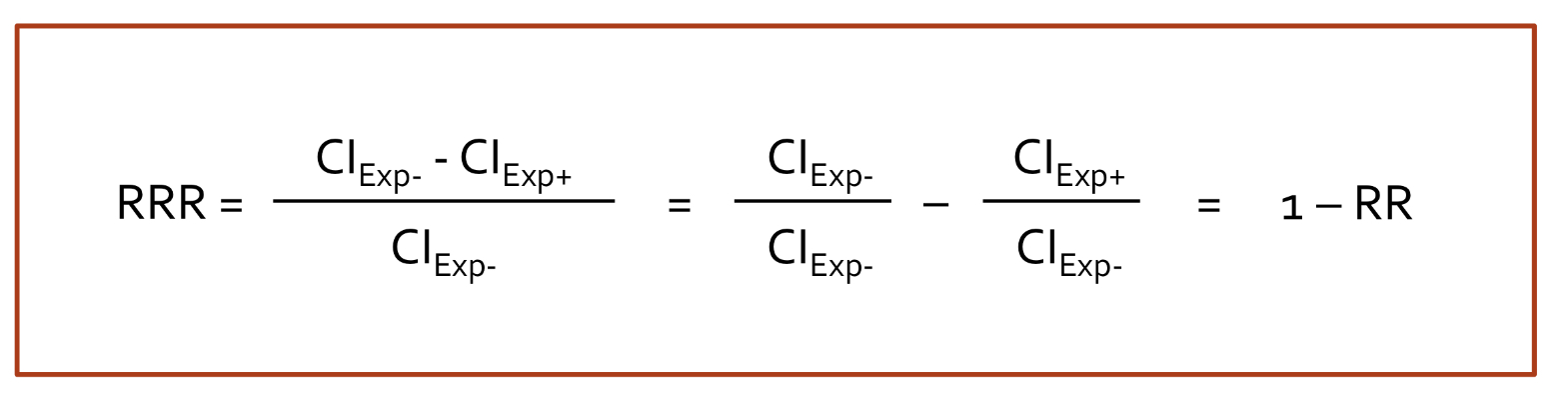
Define relative risk increase (RRI)
measures extent to which tx group INCREASES a risk compared to control group
relative risk increase equation
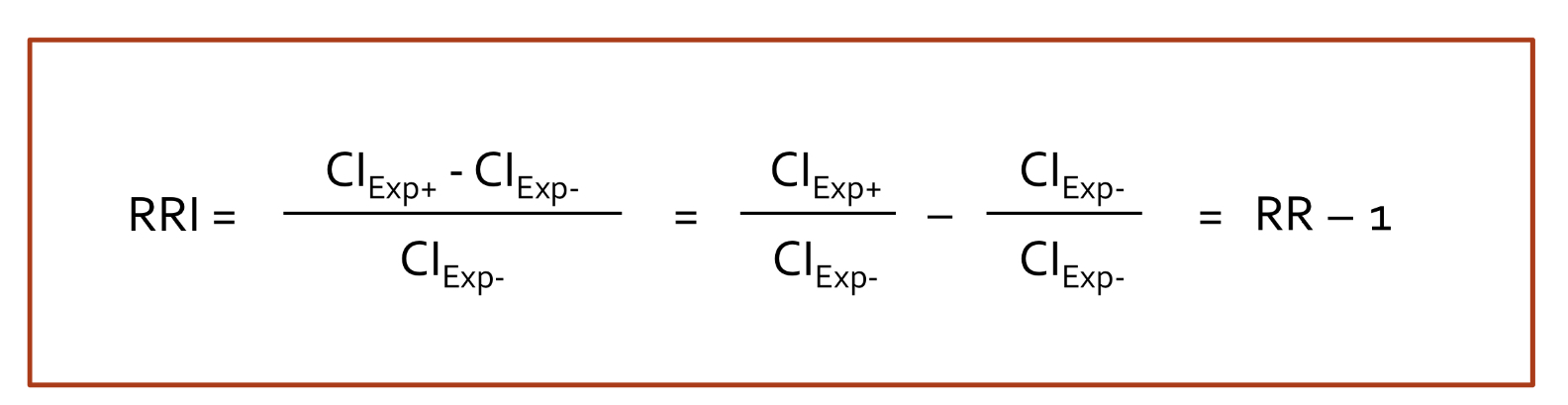
Define Odds Ratio
measures the likelihood of an event occurring
ratio of odds of event in tx group to control group
Odds Ratio equation
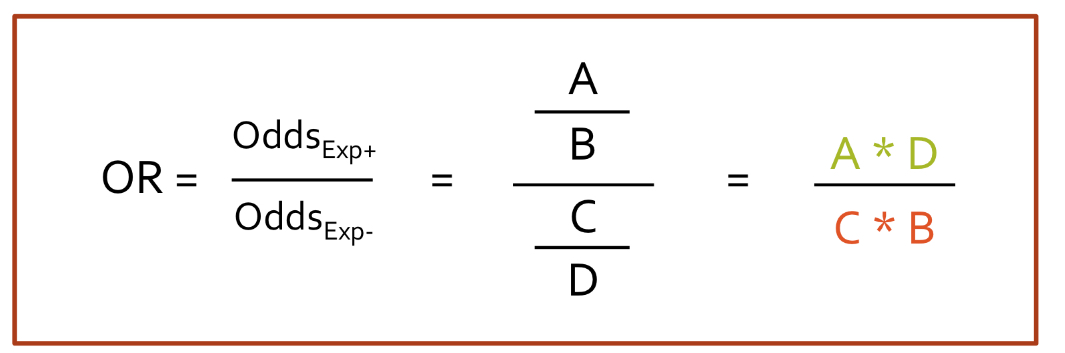
If OR < 1, the odds will be
decreased
If OR = 1, then
there is no difference in the odds
If OR > 1, then the odds will be
increased
the higher the prevalence, the more OR ____ the RR
overestimates
When the outcome (disease) is rare, then
OR ≈ RR