Chemistry Unit 3 Topic 2 (Redox Reactions)
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Redox reactions
transfer of electrons
What is more likely to be a reducing agent
fewer valence electrons
low ionization energy
low electronegativity
Metals
What is more likely to be an oxidizing agent
more valence electrons
high ionization energy
high electronegativity
non-metals
more reactive a metal is, the more likely it is to
oxidise
Identify metals with set oxidation state and their exception
fluorine = -1 (most electronegative)
hydrogen = +1 (except metal hydrides…metal + hydrogen)
oxygen = -2 (h2O2)
element oxidation state by itself
0
oxidation sates in monatomic ions
equals to their charge
sum of oxidation states in polyatomic ions
=polyatomic ion charge
the most electronegative atom in a molecule, their oxidation state is always
negative
when molecule/atom is oxidized, oxidation state
increases
how to determine oxidation number from transition metal
represented by their pronumeral
when molecule/atom is reduced, oxidation state
Decreases
when molecule/atom is reduced, oxidation state
increases
Type of reactions that can be redox
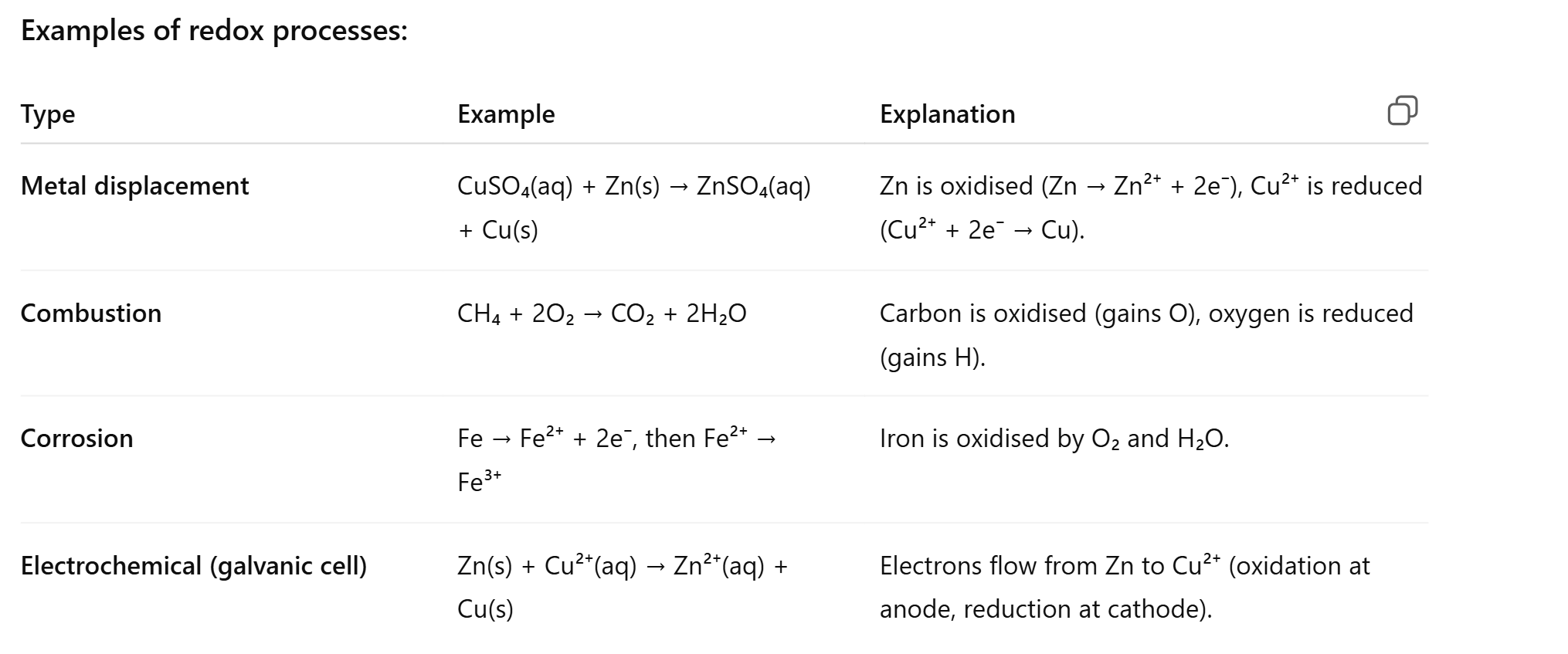

how to balance redox reaction under acidic conditions
oxidation number for every atom
determine which is the reducing and oxidising agent
Split into unbalanced half equations
balance all atoms through coefficient except O and H first
Balance O by adding H2O to one side
balance H by adding it to H+ ion
balance charge by adding electrons to the side with more positive charge
combining electrons
ensure electron lost through oxidation = electron gained in reduction which can be down by multiplying to a common factor
simplify by cancelling out like terms on the reactant and product side
Galvanic/voltaic cell is
spontanous: a reaction that can occur without external energy input
anode in galvanic/voltaic cell is
negative
anode in galvanic/voltaic cell is
positive
electrolytic cell is
non-spontaneous: requires a continuous supple of external energy to proceed
anode in electrolyic cell is
positive
cathode in electrolyic cell is
negative
similarities between galvanic and electrolytic
oxidation occurs at anode
reduction occurs at cathode
e flow from anode to cathode
anions more towards anode
cations move towards cathode
anode and cathode are electrodes
a more positive standard electrode potential means a
stronger oxidizing agent(left) and weaker reducing agent (right)
how to represent galvanic cell in cell diagram
Zn(s) | Zn²⁺(aq) || Cu²⁺(aq) | Cu(s)
Left side = anode (oxidation)
Right side = cathode (reduction)
“|” separates phases, “||” = salt bridge
what is salt bridge in galvanic cell
A tube filled with a neutral ionic solution used to balance the charge and keep the reactions going.
If they are multiple ions which types of ions gets oxidized at the anode
the stronger reducing agent
If they are multiple ions which types of ions gets reduced at the cathode
the stronger oxidizing agent
If the difference in E is small for oxidizing agents, how do you determine which one gets oxidized at the anode
The one with the higher concentration
standard Hydrogen Electrode
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is the reference electrode against which all other electrode potentials are measured.
E is the tendency of the reactant to be reduced, with a more positive indicating its more likely to be reduced?
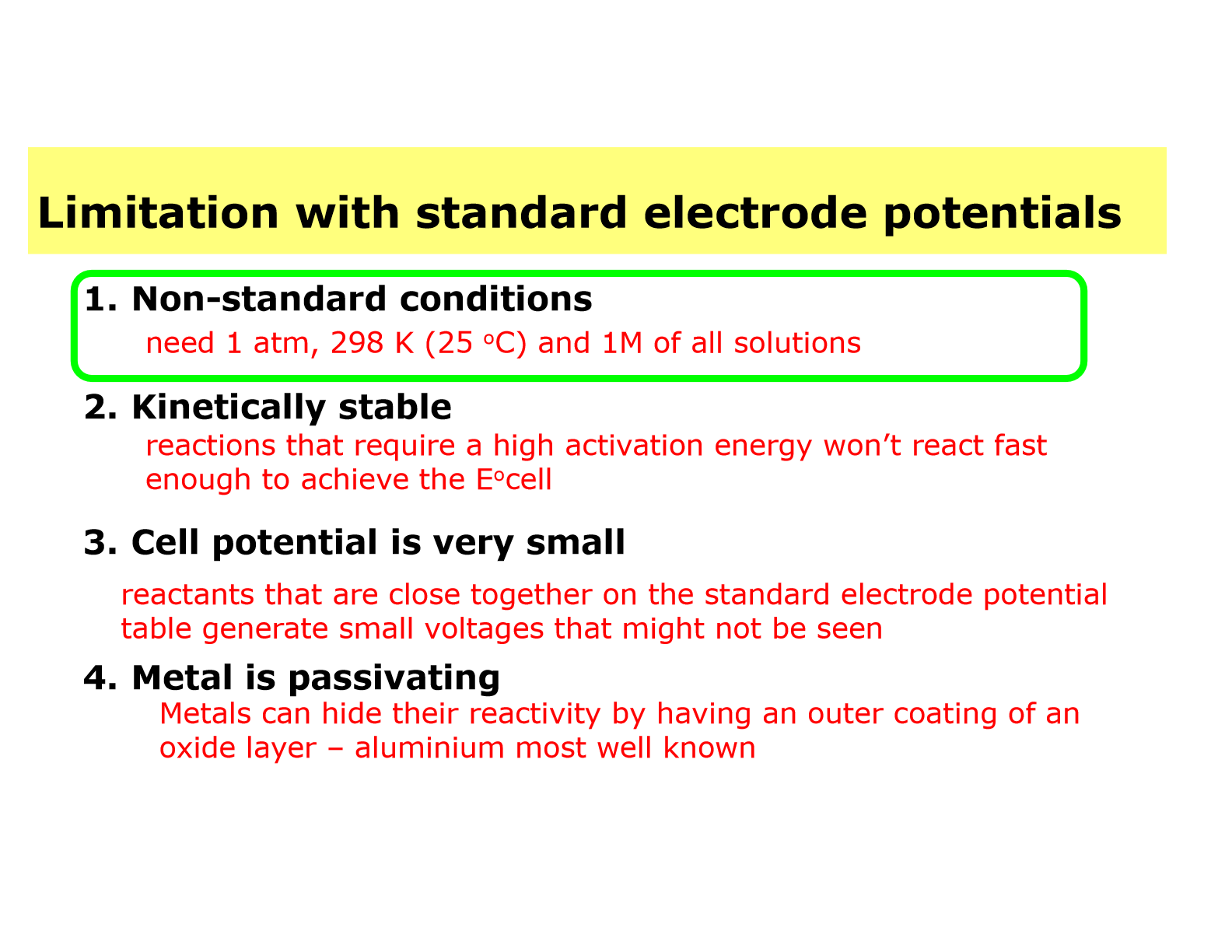
Identify the limitations associated with standard electrode (reduction) potentials, E°.

standard electrode (reduction) potential, E°
The standard electrode potential (E°) is the voltage measured when a half-cell is connected to the standard hydrogen electrode, under standard conditions:
Calculate cell potential, E°cell
E°cell=E°reduction(cathode)−E°oxidation(anode)
Predicting Spontaneity using E° of cell
If E°cell > 0, the reaction is spontaneous.
If E°cell < 0, the reaction is non-spontaneous.
Describe electrolysis plating
impure metal attached to anode.
A stronger reducing agent than the metal dissolve at the anode, but dont reduce at cathode
Less reactive metals than metal dont oxidise so they fall off the electrode.
THIS IS HOW METAL PLATING WORK BECAUSE EVEN THOUGH STRONGER REDUCING IMPURITY WILL OXIDISE AT ANODE FIRST IT WILL NOT BE REDUCED BECAUSE IT WILL BE A WEAKER OXIDISING AGENT.
Strong reducing agent ↔ weak oxidising agent (and vice versa).
Metal plating relies on this:
More reactive metals (strong reducers like Zn, Ni) dissolve at the anode but do not plate out.
Less reactive metals (weak reducers, strong oxidisers like Cu²⁺, Ag⁺) are the ones that get reduced and deposit as pure metal.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
a type of electrochemical cell which combines hydrogen and oxygen to form water
In Acidic Hydrogen fuel cells what is oxidized at anode and reduced at cathode
Hydrogen at anode
Oxygen at cathode
What happens at the cathode in Acidic Hydrogen fuel cell
oxygen reacts with positive hydrogen that came from the anode through the center and electron producing water
What is the electrolyte in acidic hydrogen fuel cell (the ions that moves through the center)
Positive hydrogen aka proton
In Alkaline Hydrogen fuel cells what species react at the anode
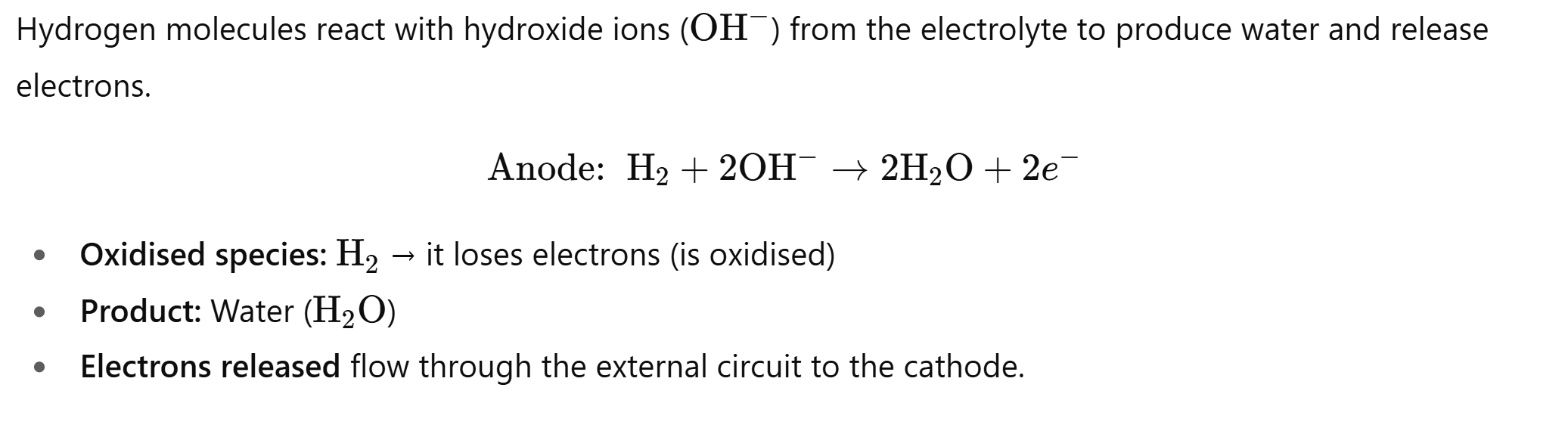

In Alkaline Hydrogen fuel cells what species react at the anode
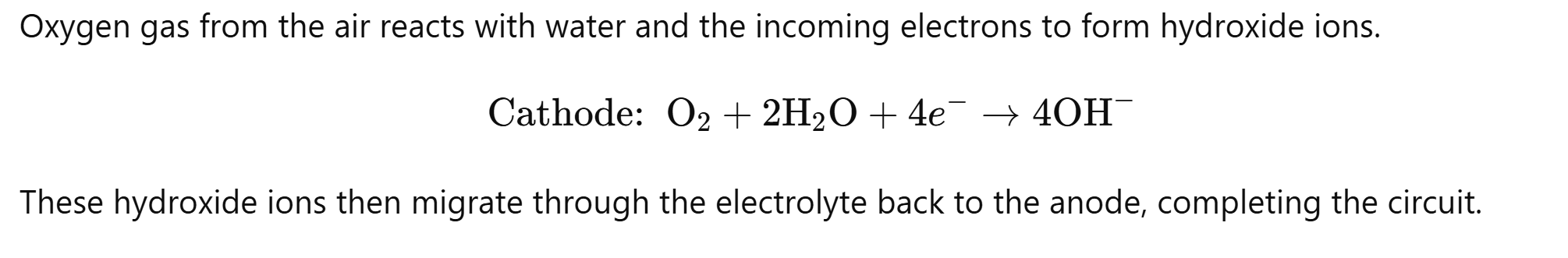
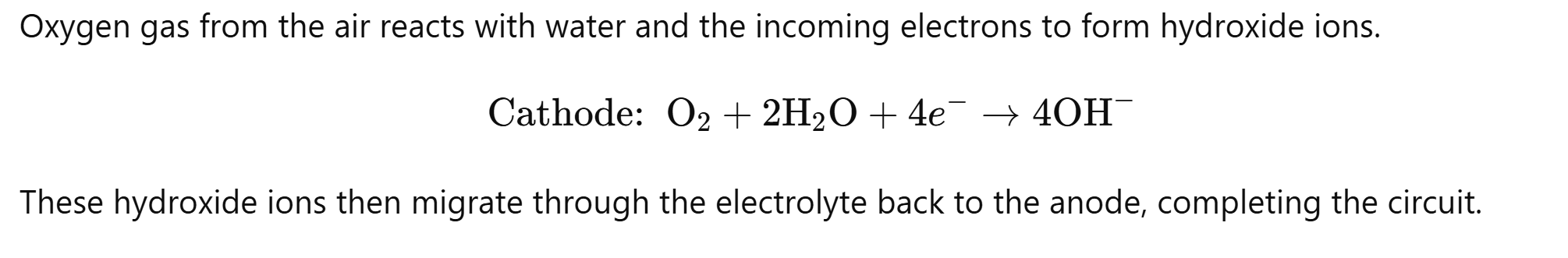
What is the electrolyte in alkaline hydrogen fuel cell (the ions that moves through the center)
Hydroxide ions
In electrolysis plating is the impure metal attached to anode or cathode
anode