Unit 4 Skeletal System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
functions of the skeleton
support, protection, movement, blood cell production, mineral storage
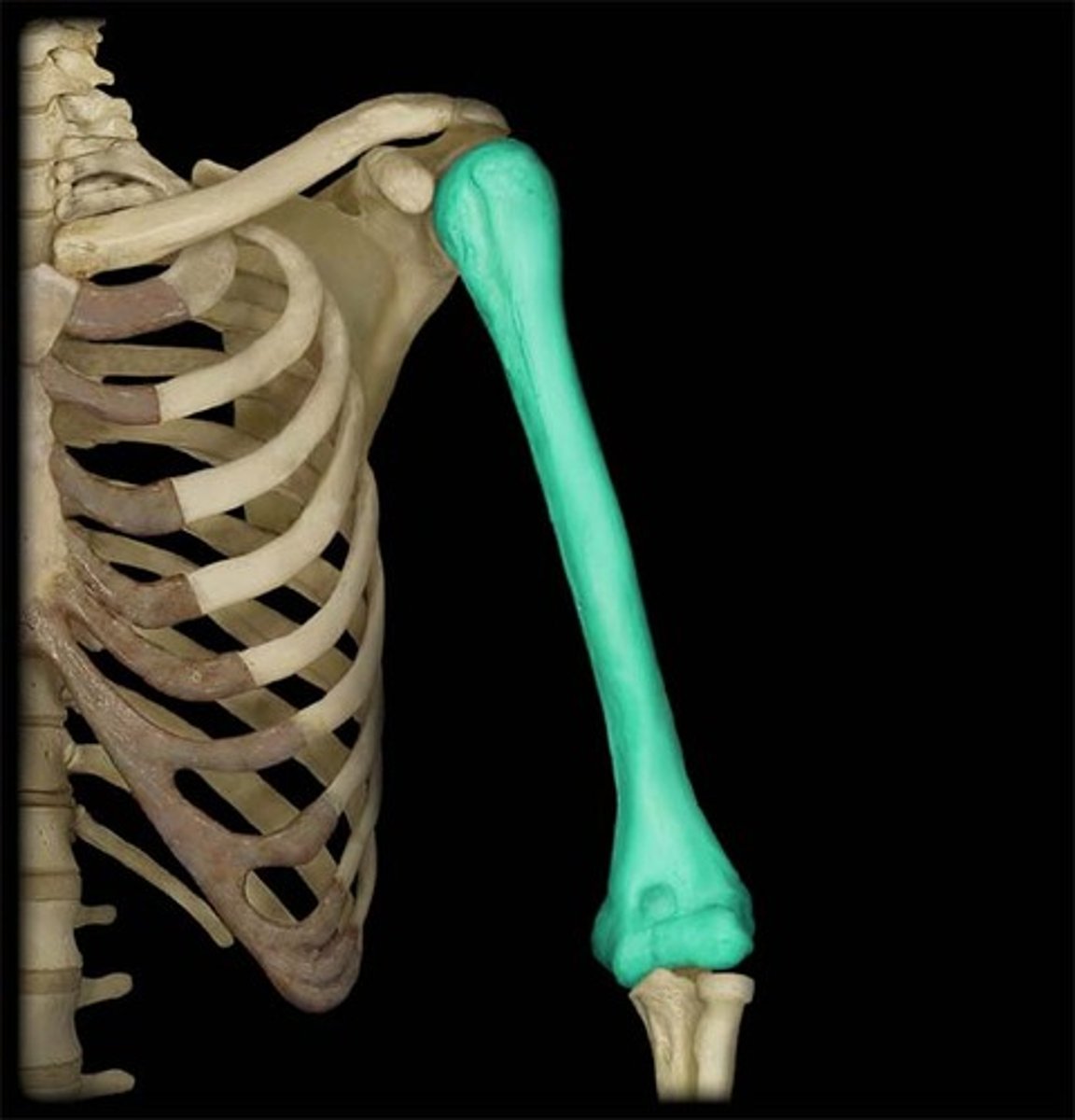
long bones
support the weight of the body and facilitate movement
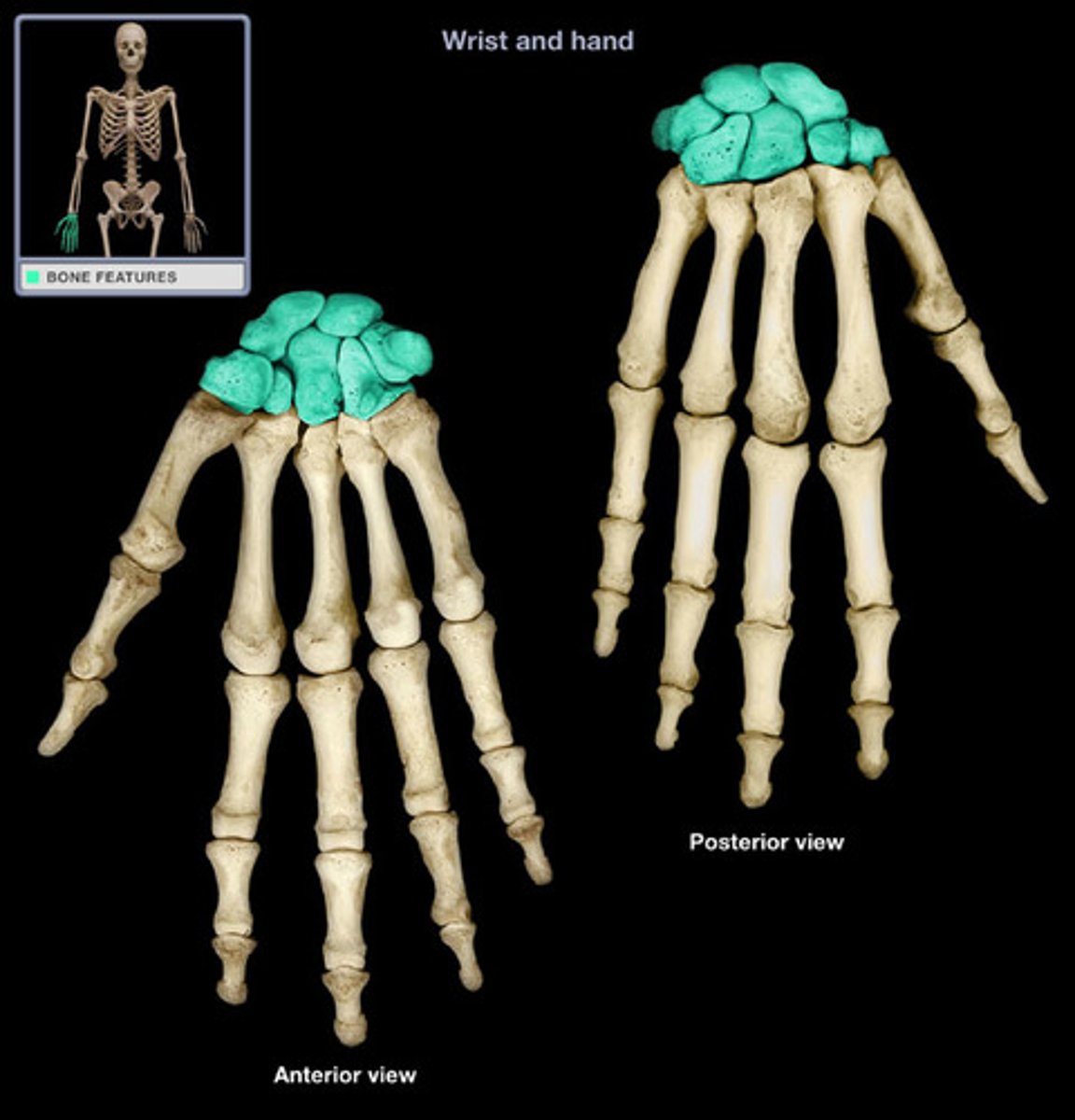
short bones
provide support and stability in areas of the body that need to be compact and strong, and where range of motion is less important
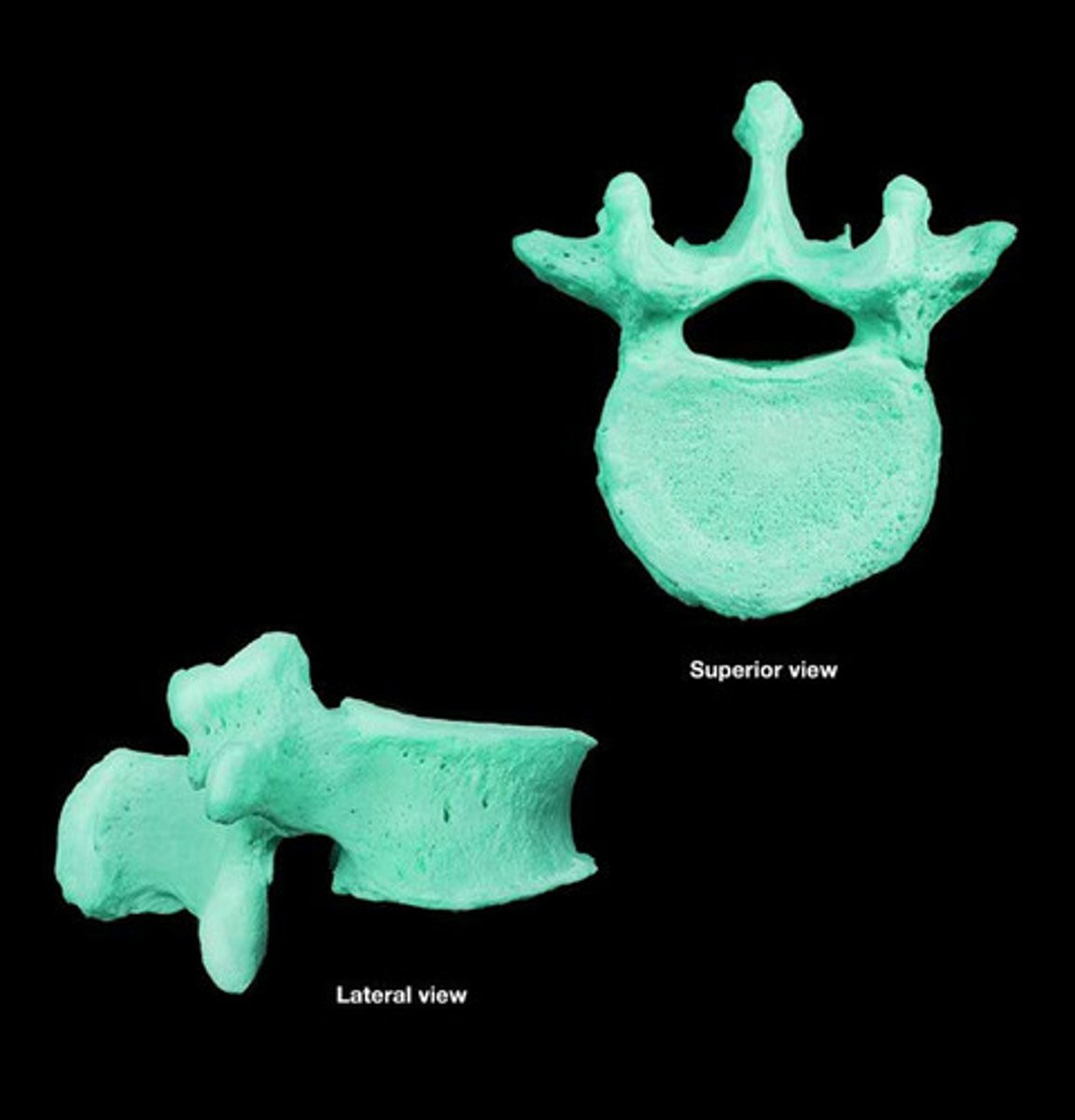
irregular bones
serve various purposes such as protection of nervous tissues, affording multiple anchor points for skeletal muscle attachment and tongue attachment
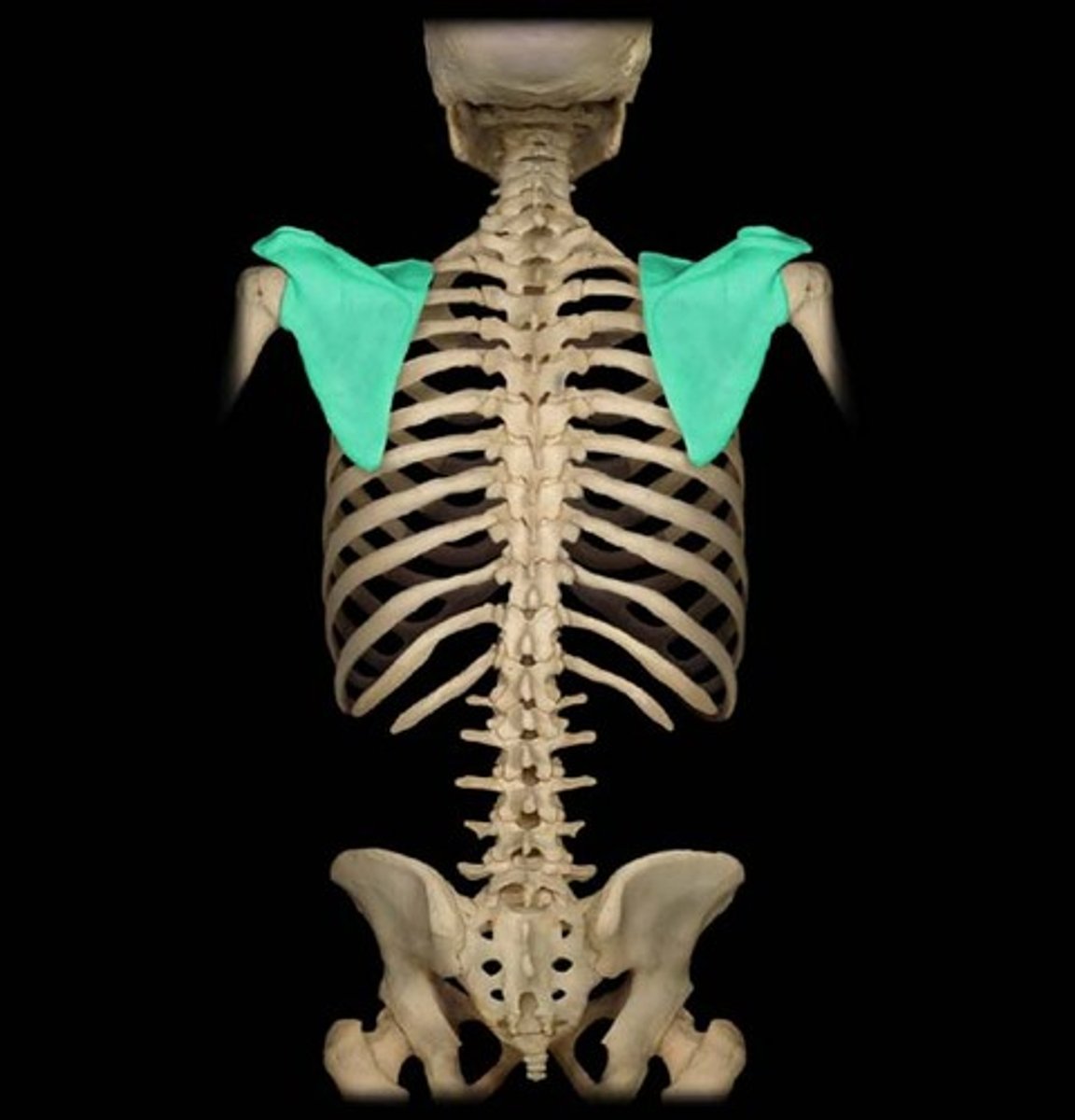
flat bones
protect internal organs such as the brain, heart and pelvic organs
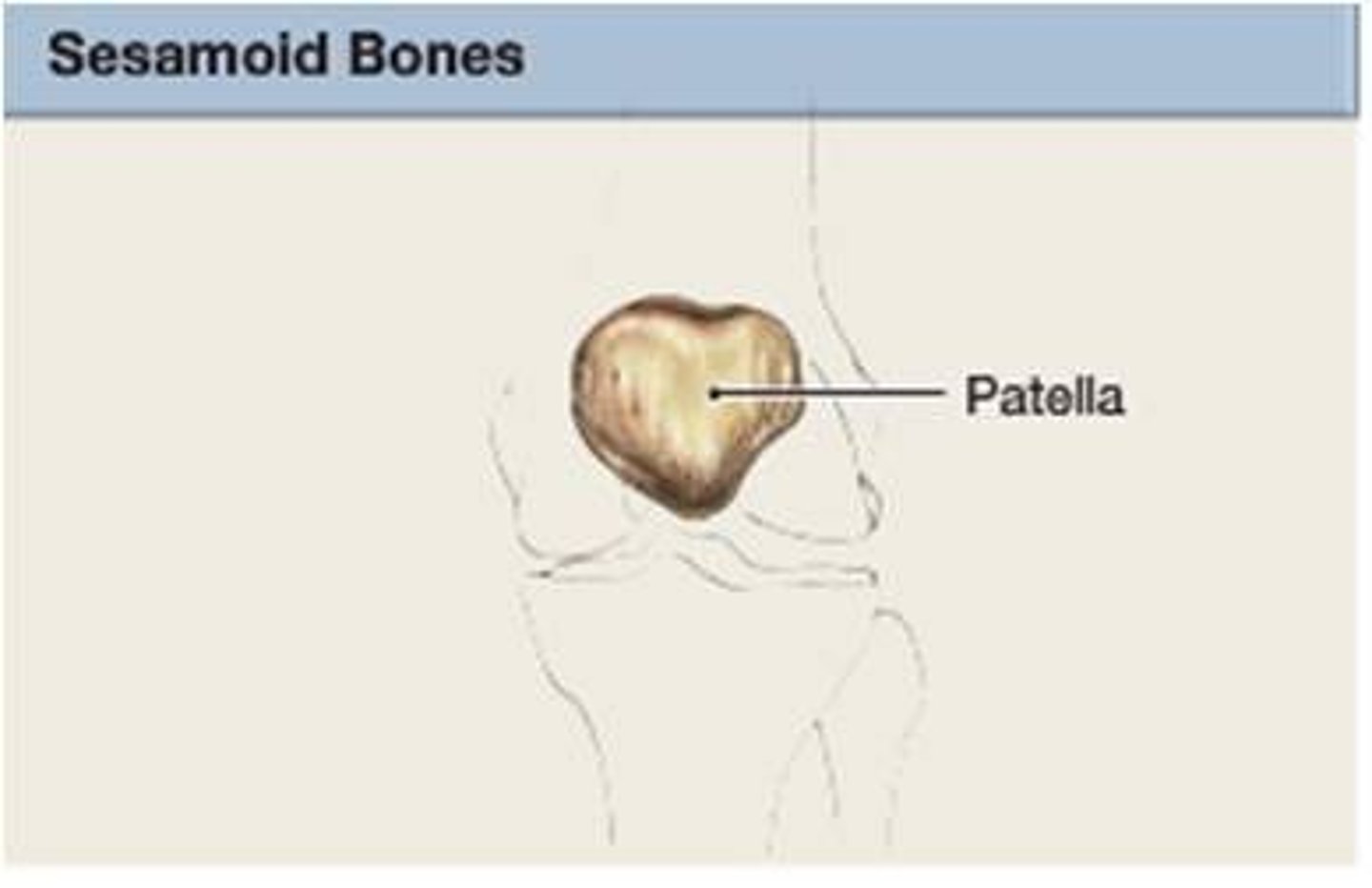
sesamoid bones
relieve tension with muscles and tendons, allowing for increased weight-bearing and tolerance by redistributing forces throughout muscle or tendons
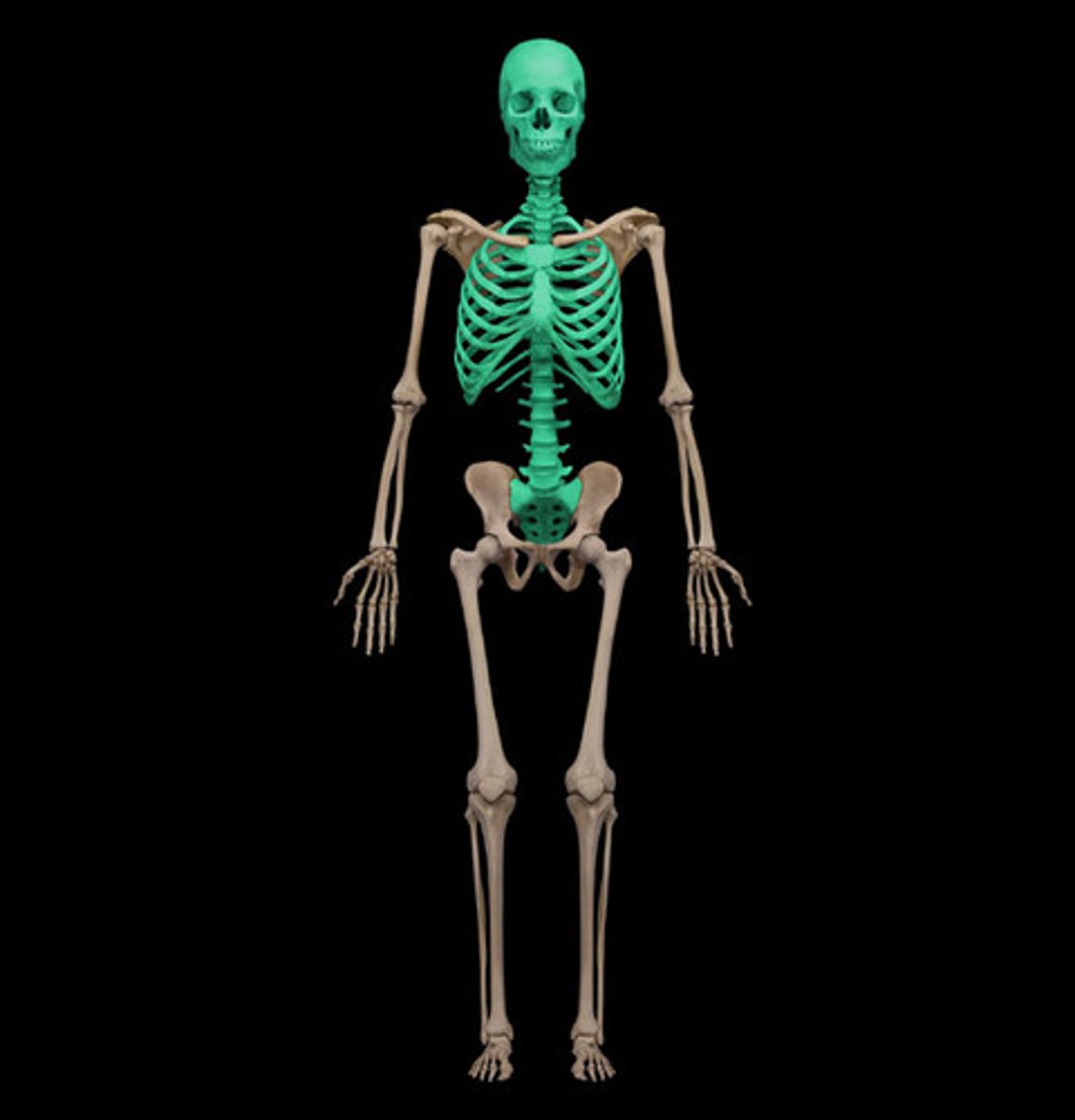
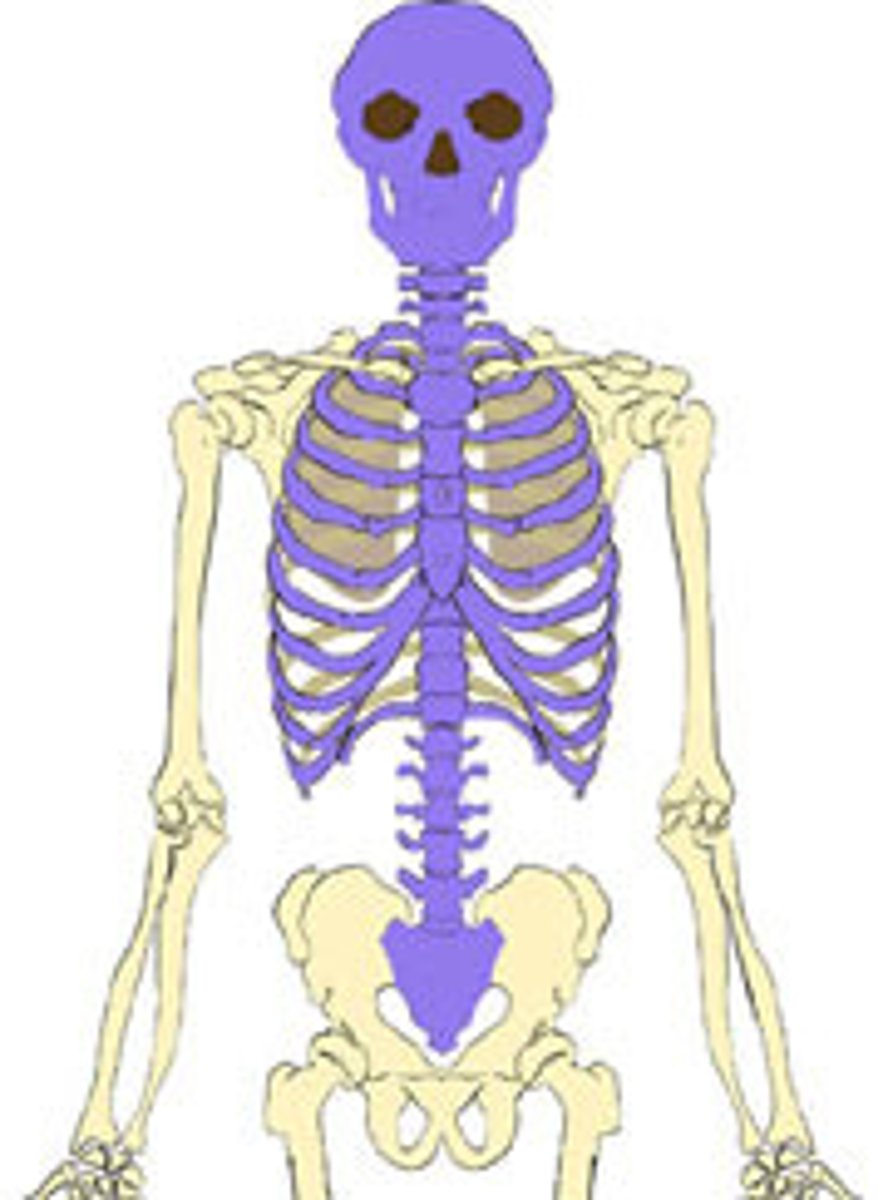
axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column. -form axis of the body
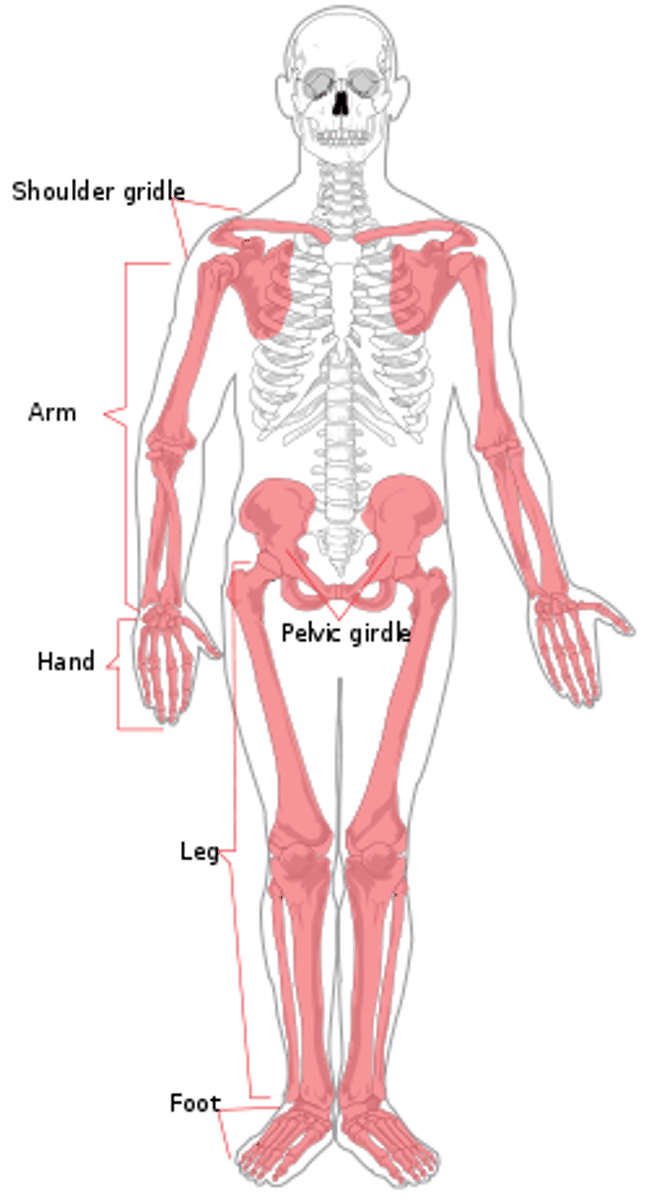
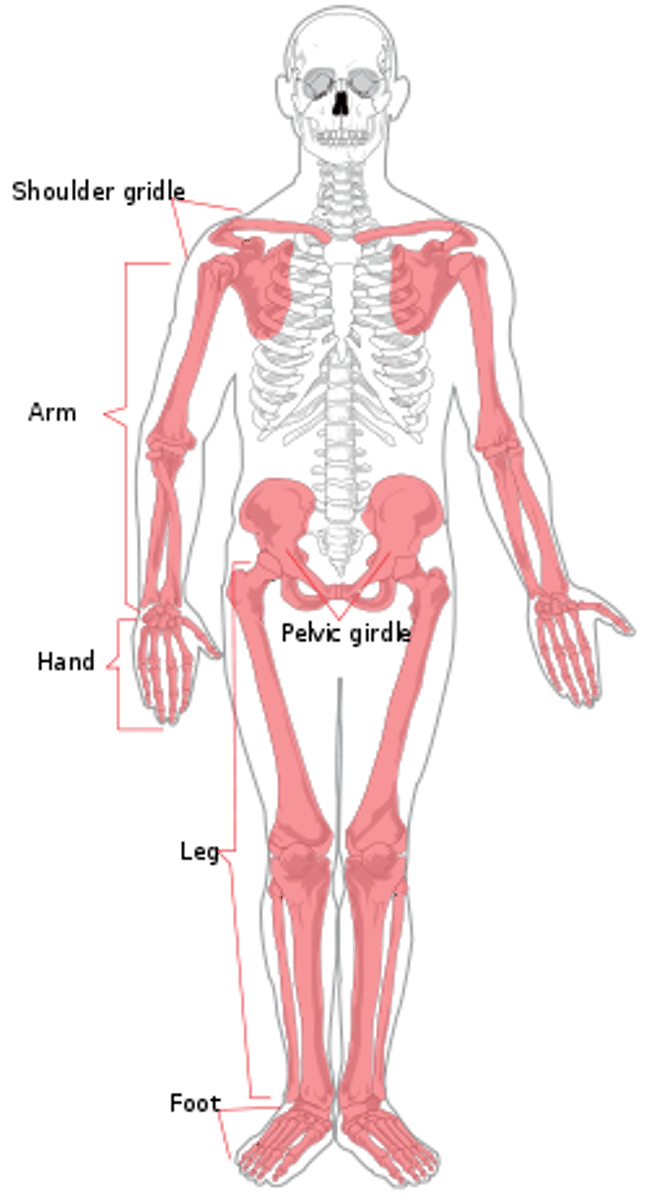
appendicular skeleton
Bones that anchor appendages to axial skeleton (arms/legs)
-upper & lower extremities shoulder & pelvic girdles
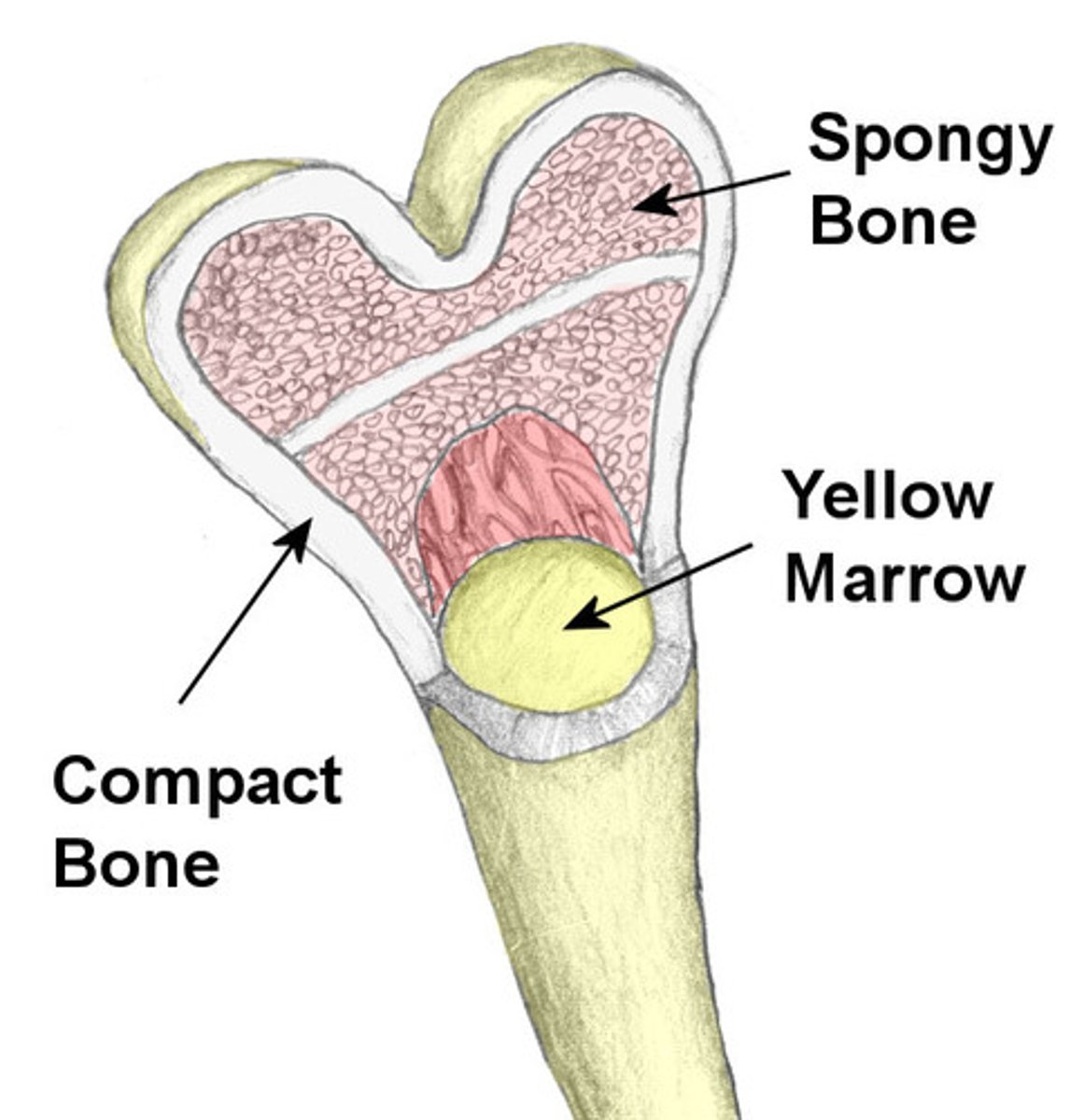
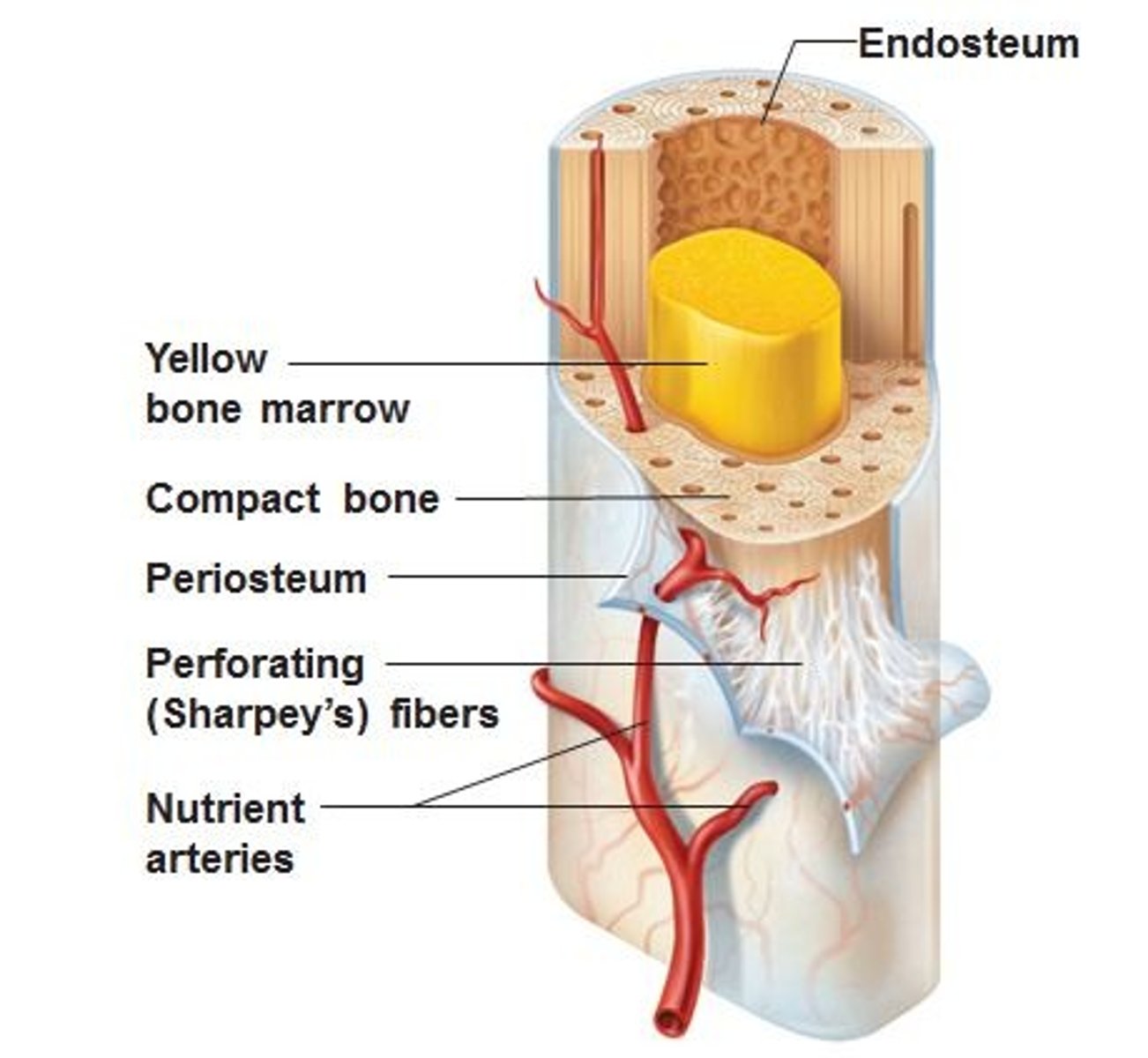
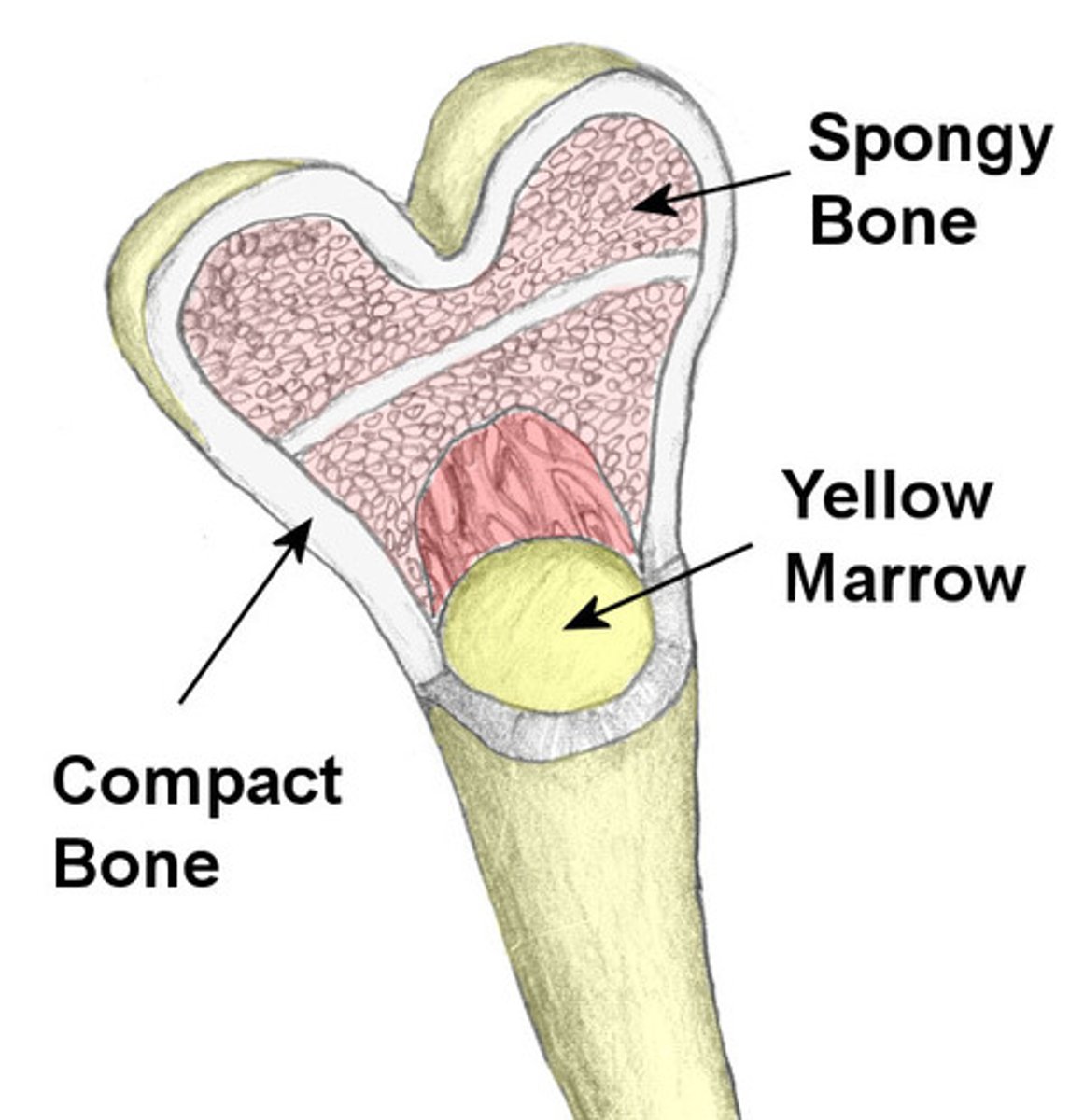
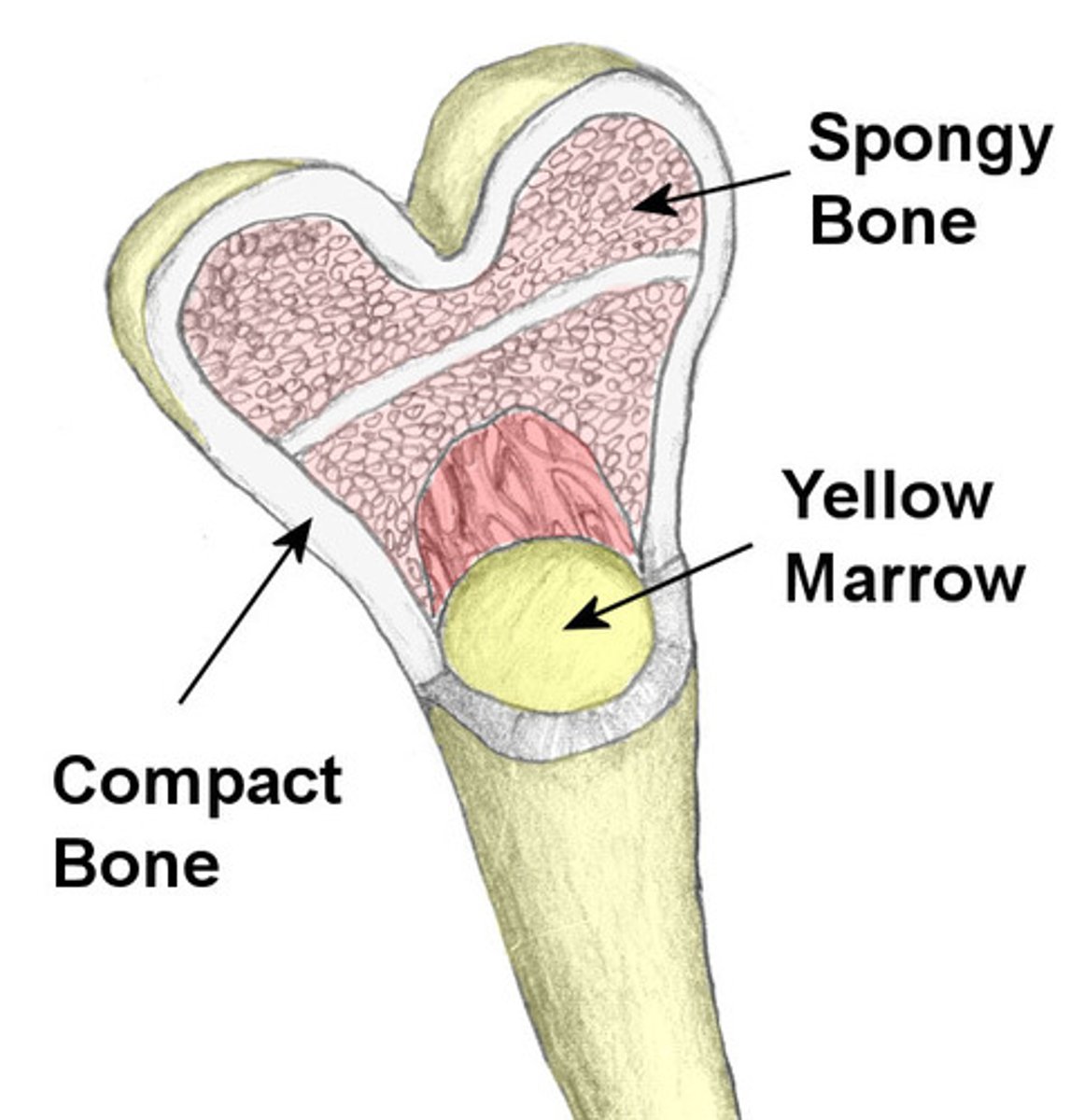
compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone. 80% total bone mass in adults
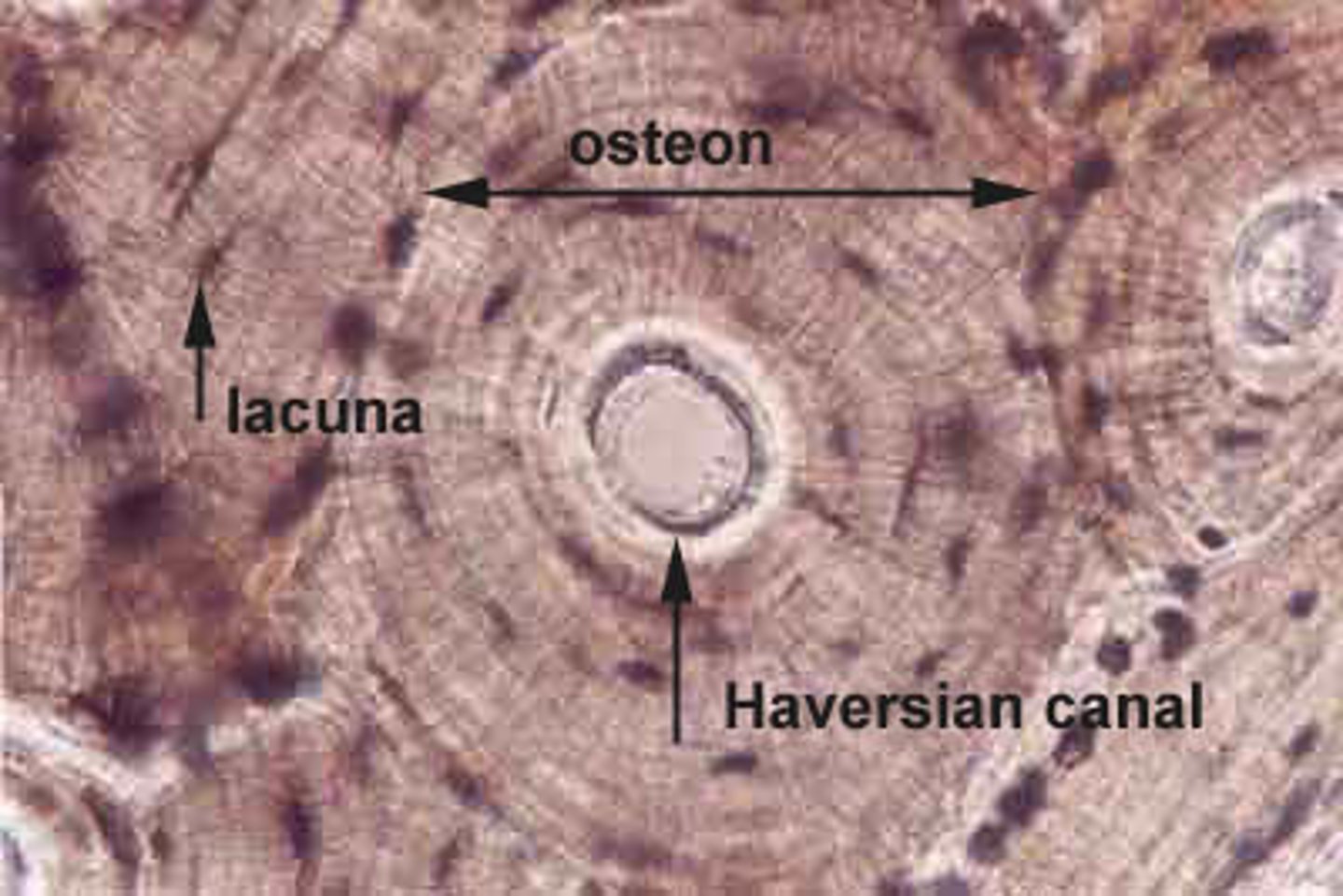
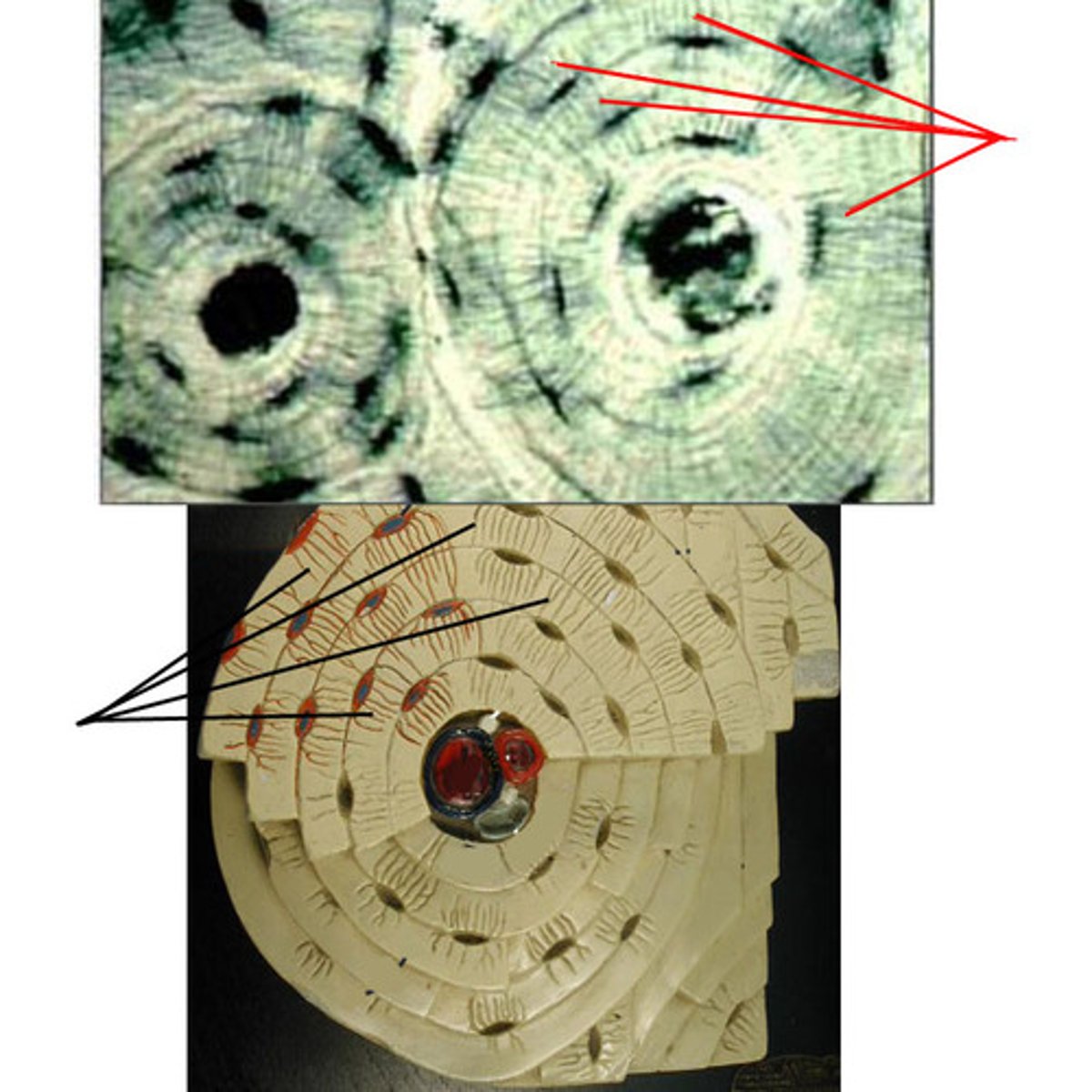
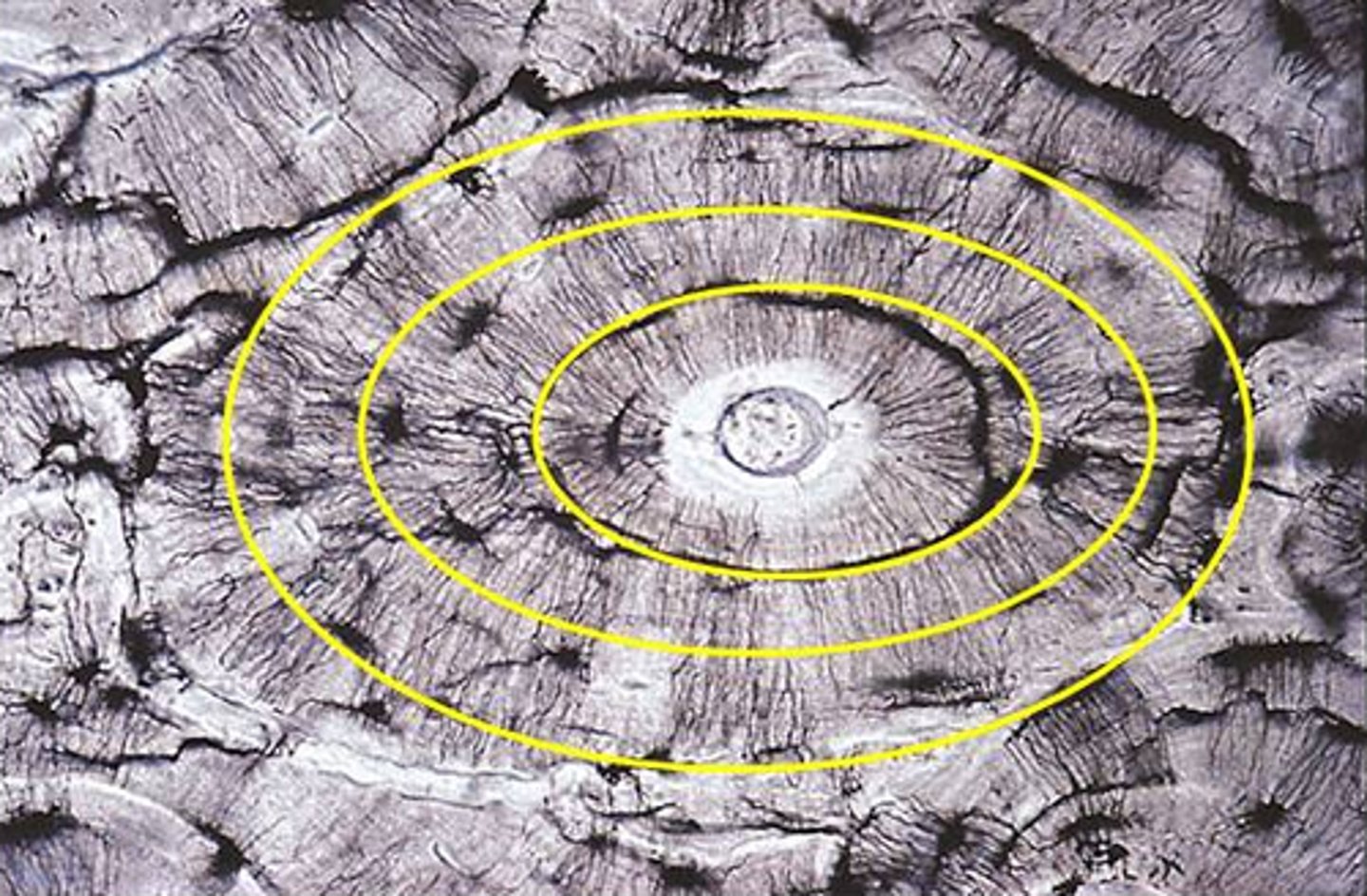
osteon
structural unit of compact bone. cylindar shaped and surrounds a central canal
central canal
a fluid-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord that helps with delivery of nutirents
lamellae
rings around the central canal, sites of lacunae. A thin layer, membrane, or plate of tissue in bone
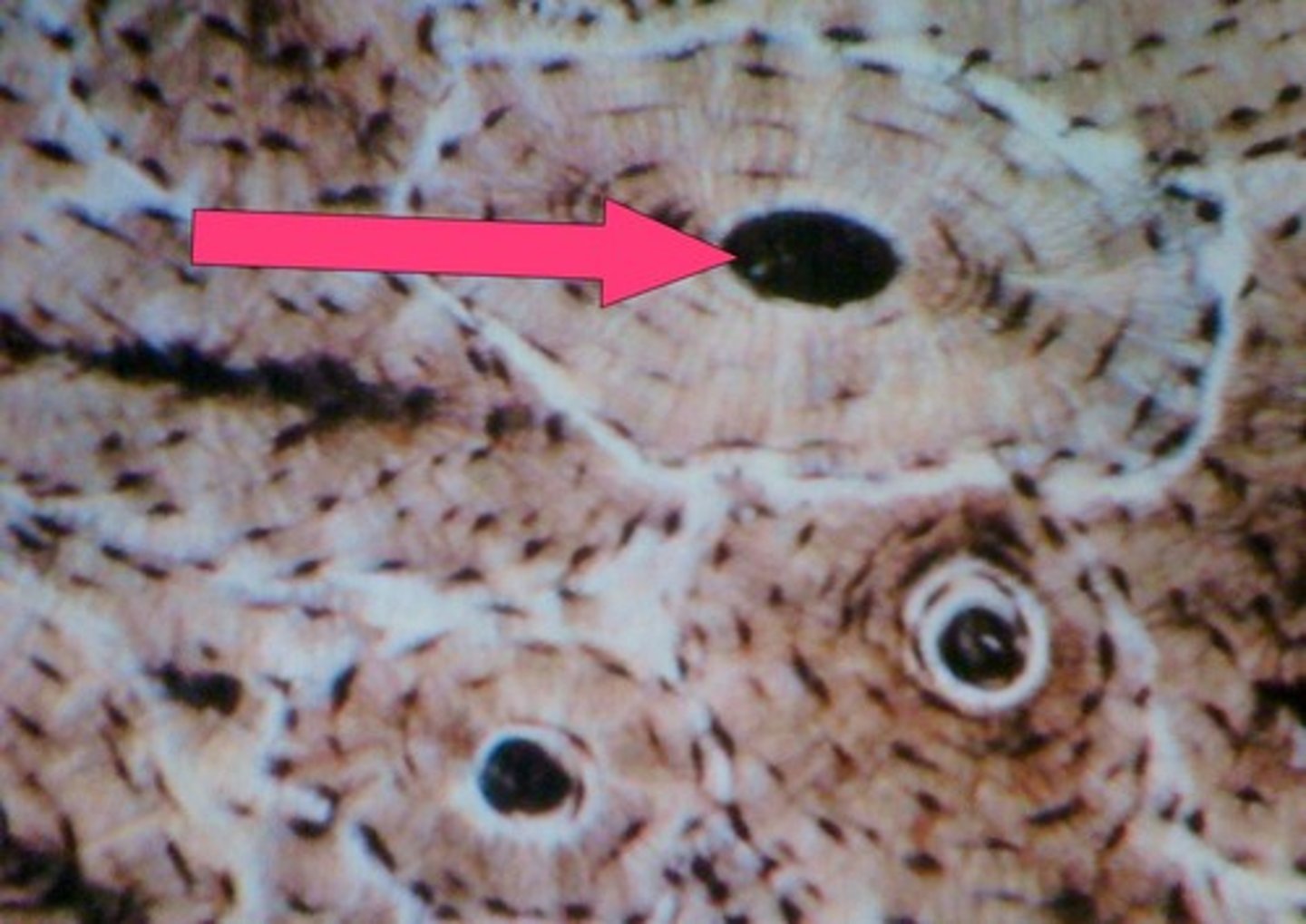
Lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes. House and keep cells alive and functional
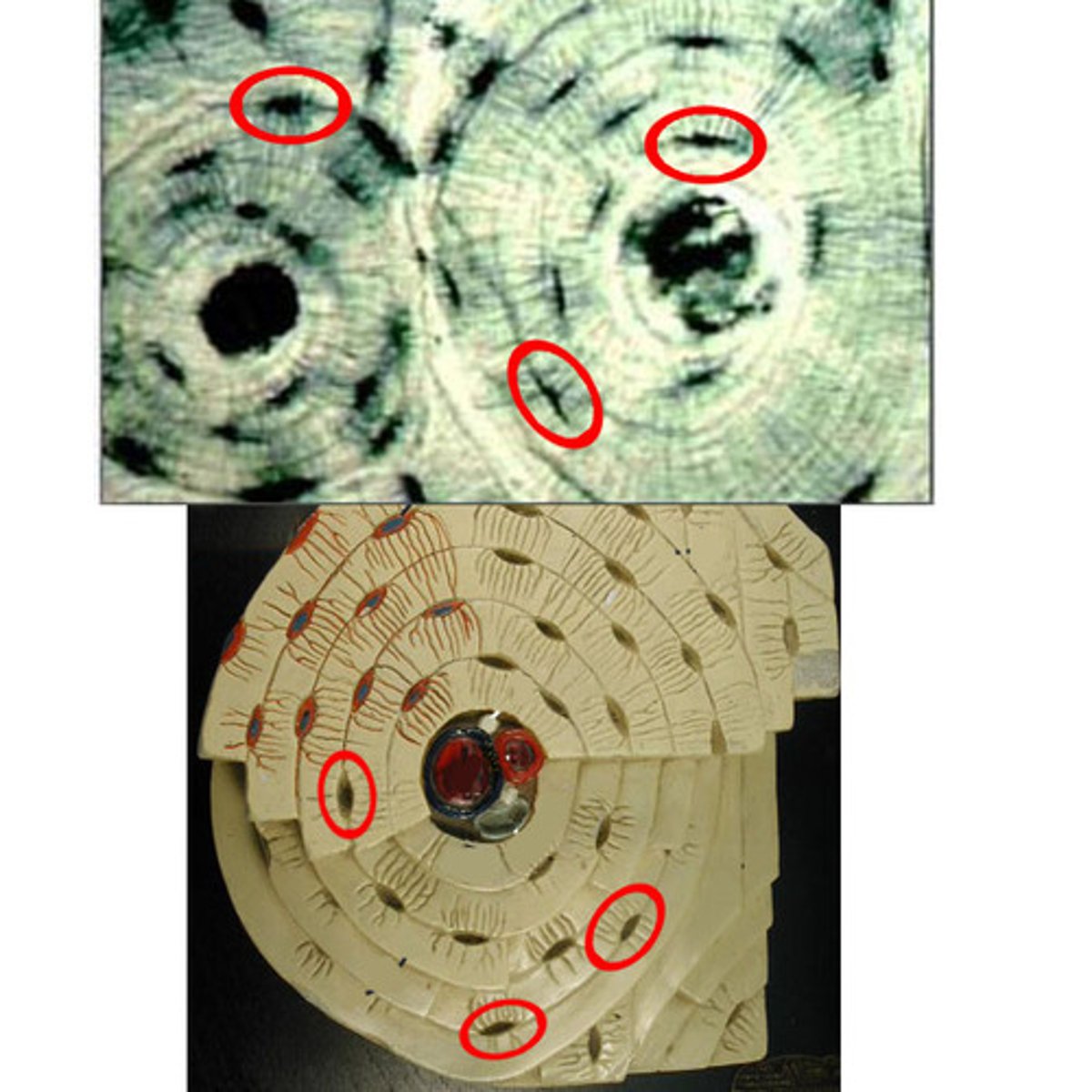
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
transverse canals
they allow blood vessels and nerves to travel through them to supply osteocytes
-as a tube, its length varies widely and in small-bodied taxa it may be very short and essentially non-existent
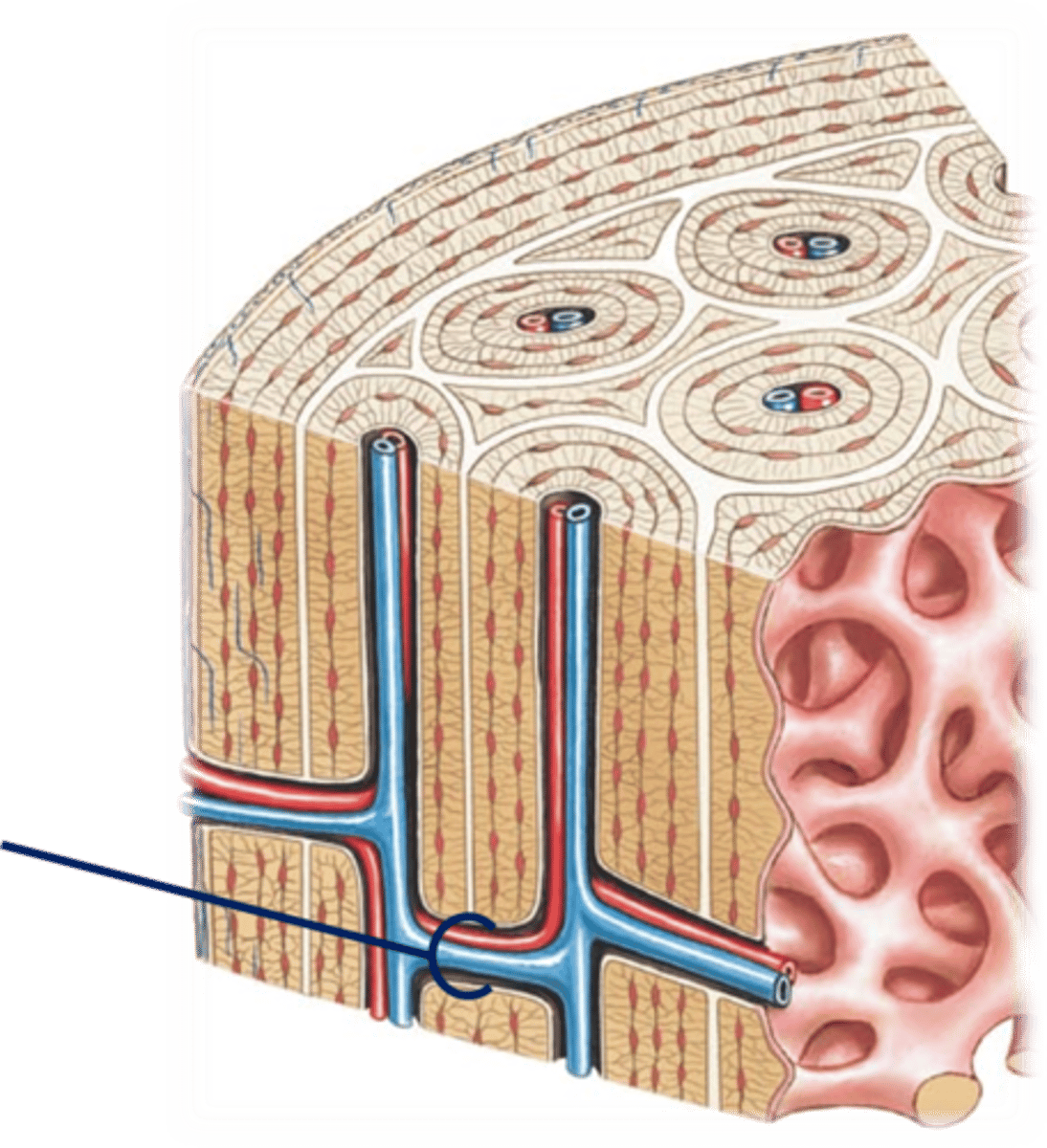
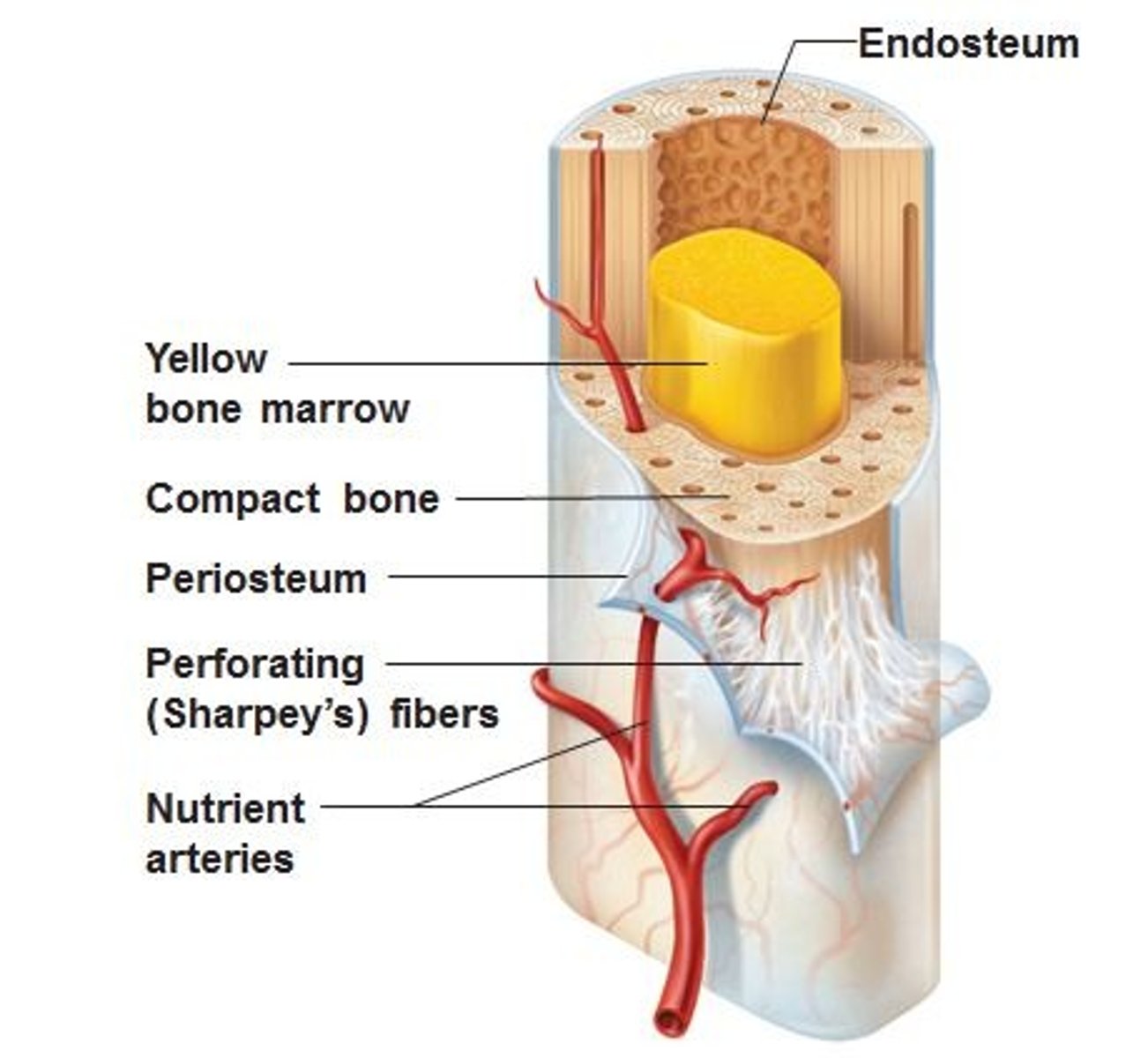
endosteum
a thin membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of a bone, specifically the medullary cavity
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
concentric lamellae
cylinder-shaped layers of calcified matrix around the central canal. rich in collagen
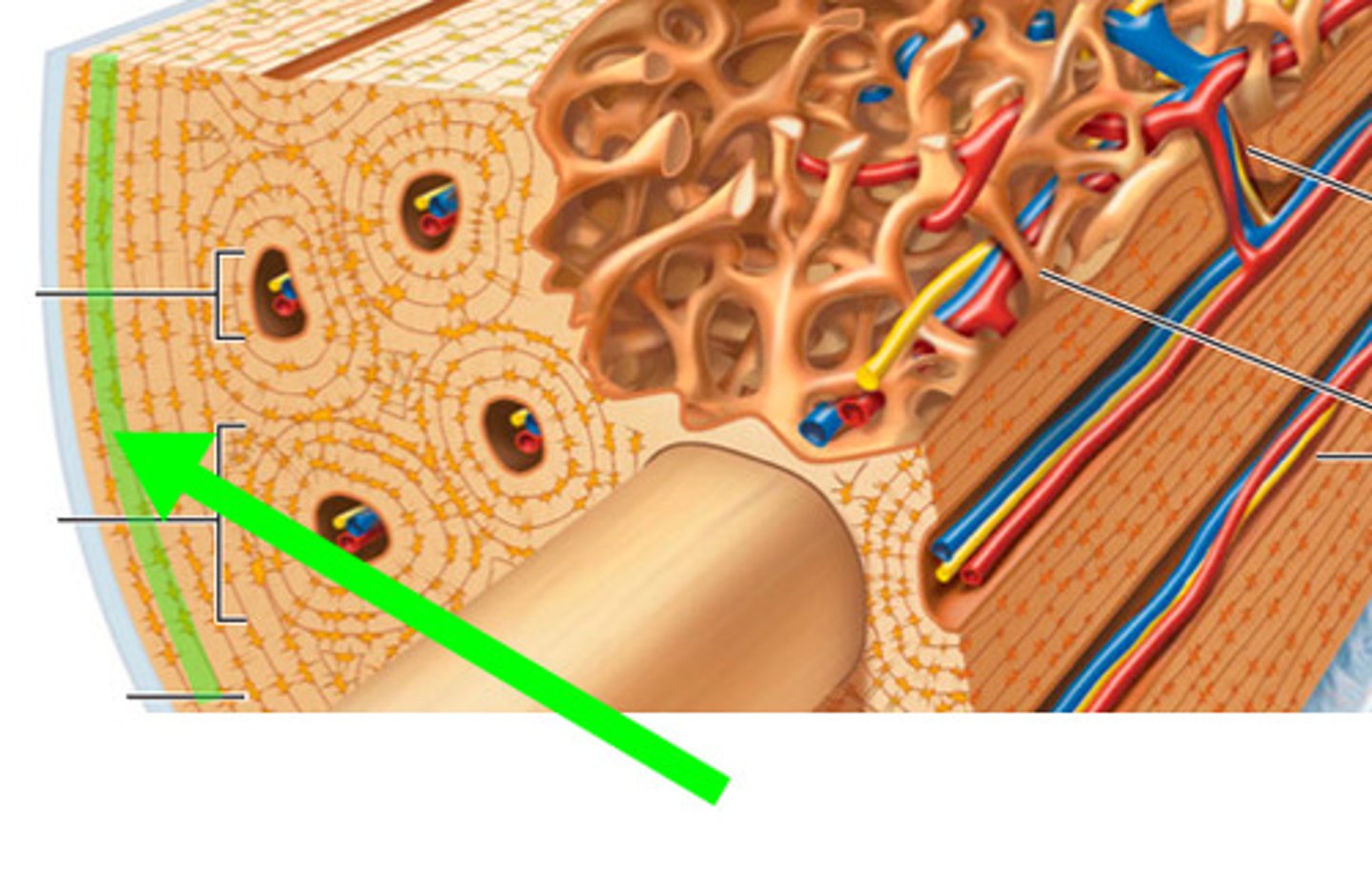
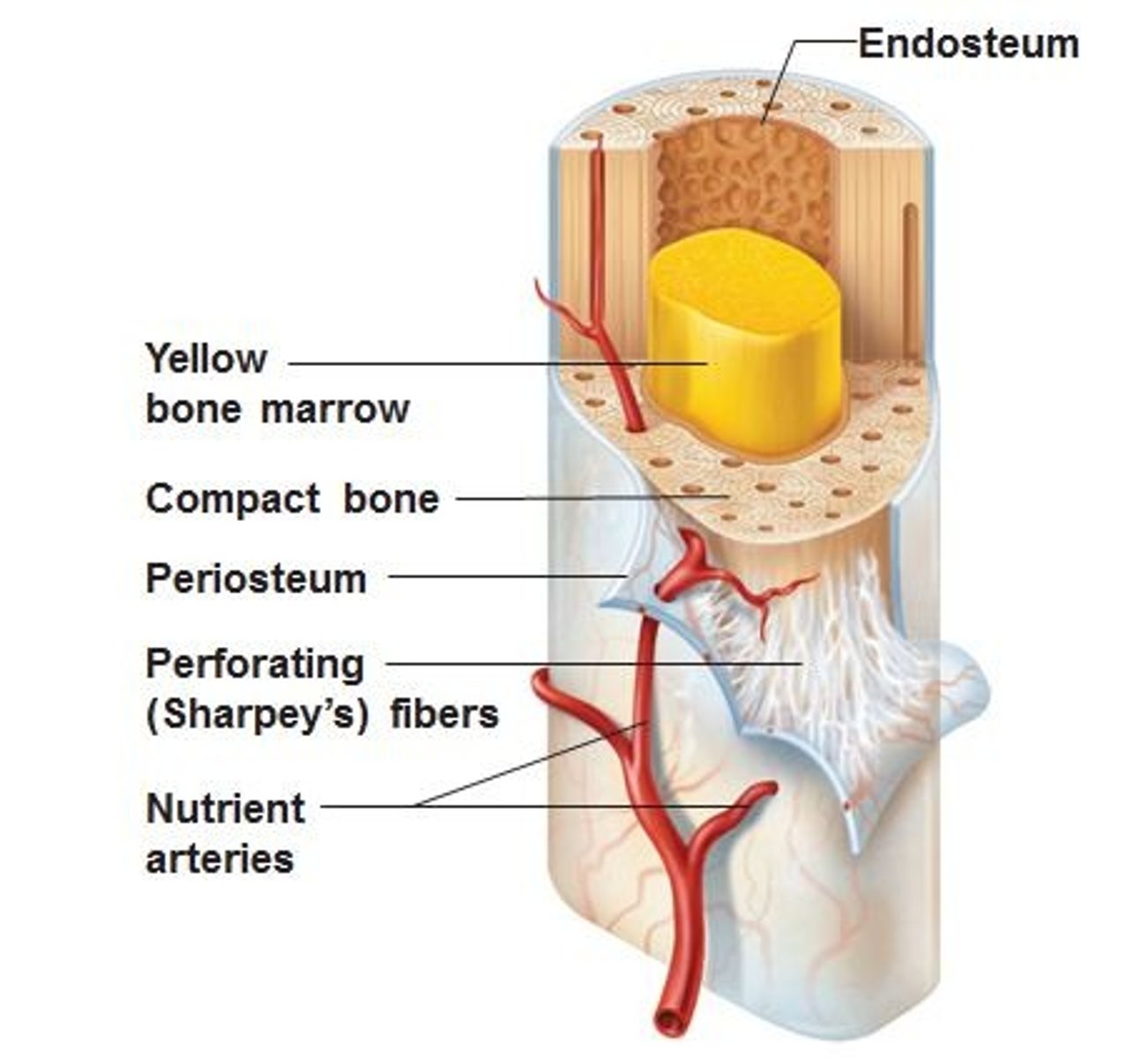
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
axial skeleton function
provides support and cushioning for brain, spinal cord, and organs
appendicular skeleton function
provides internal support and positioning of the limbs; supports and moves axial skeleton
Epiphysis
bone end, space near joints for muscle attachment
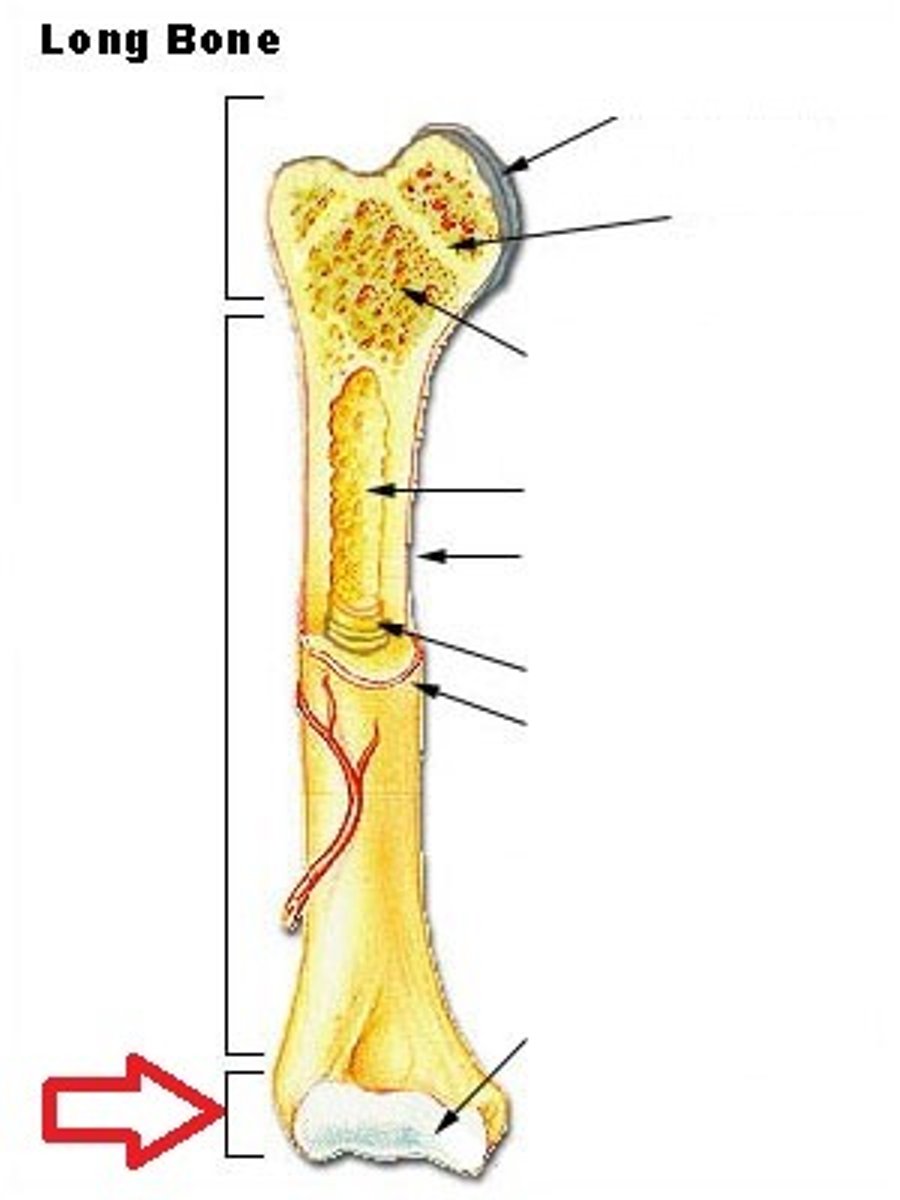
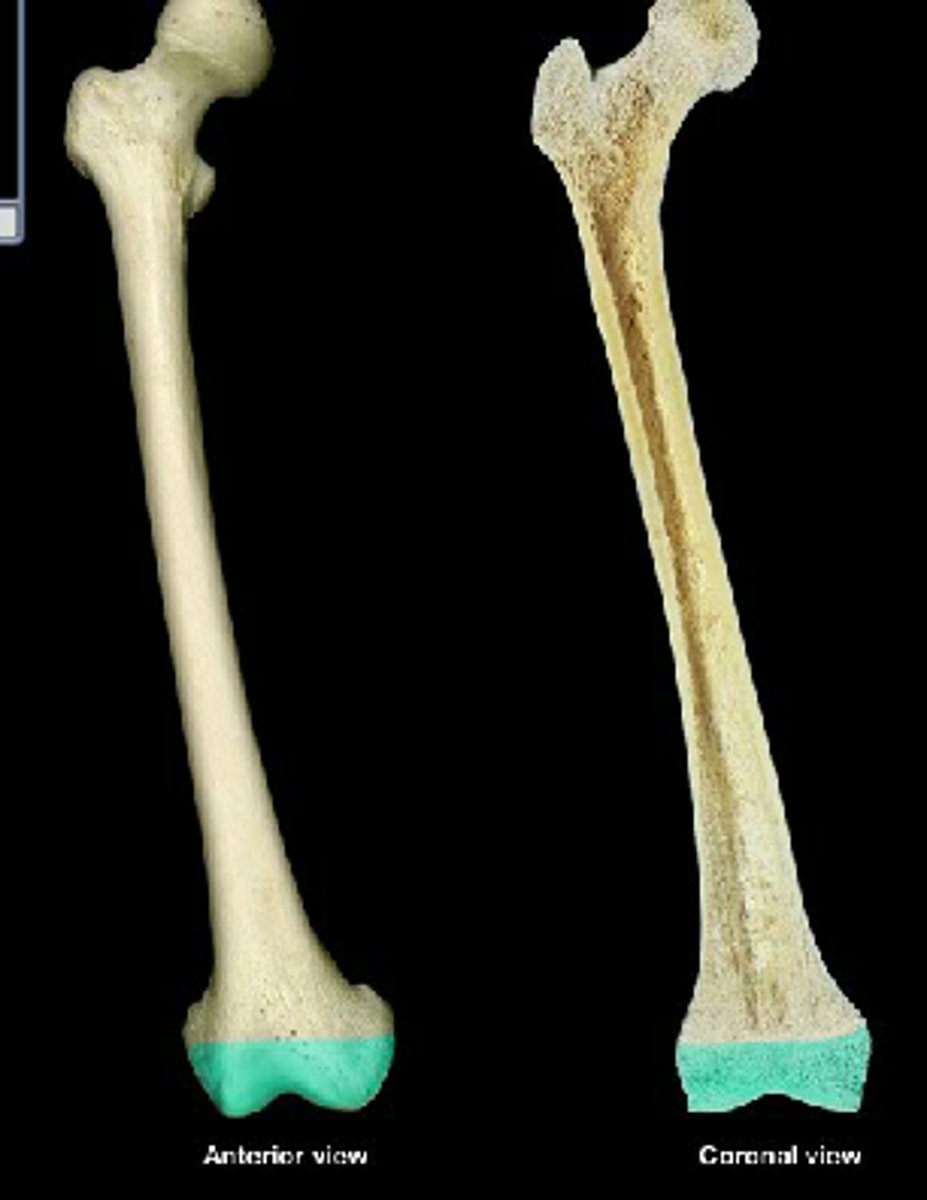
diaphysis
the bone's shaft or body - the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone. Supports without adding any additional weight to the bone
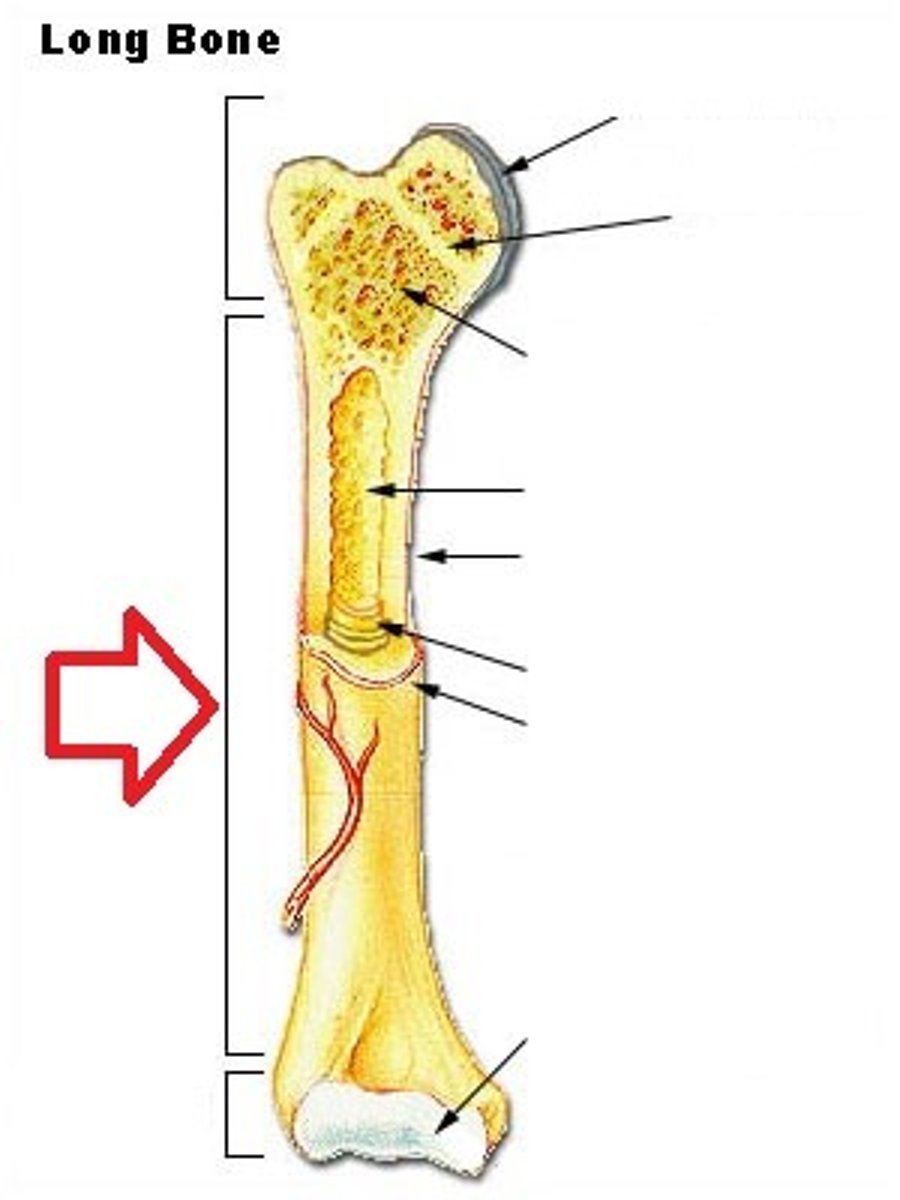
medullary cavity
marrow cavity serves to lighten bone weight and provide space for its marrow
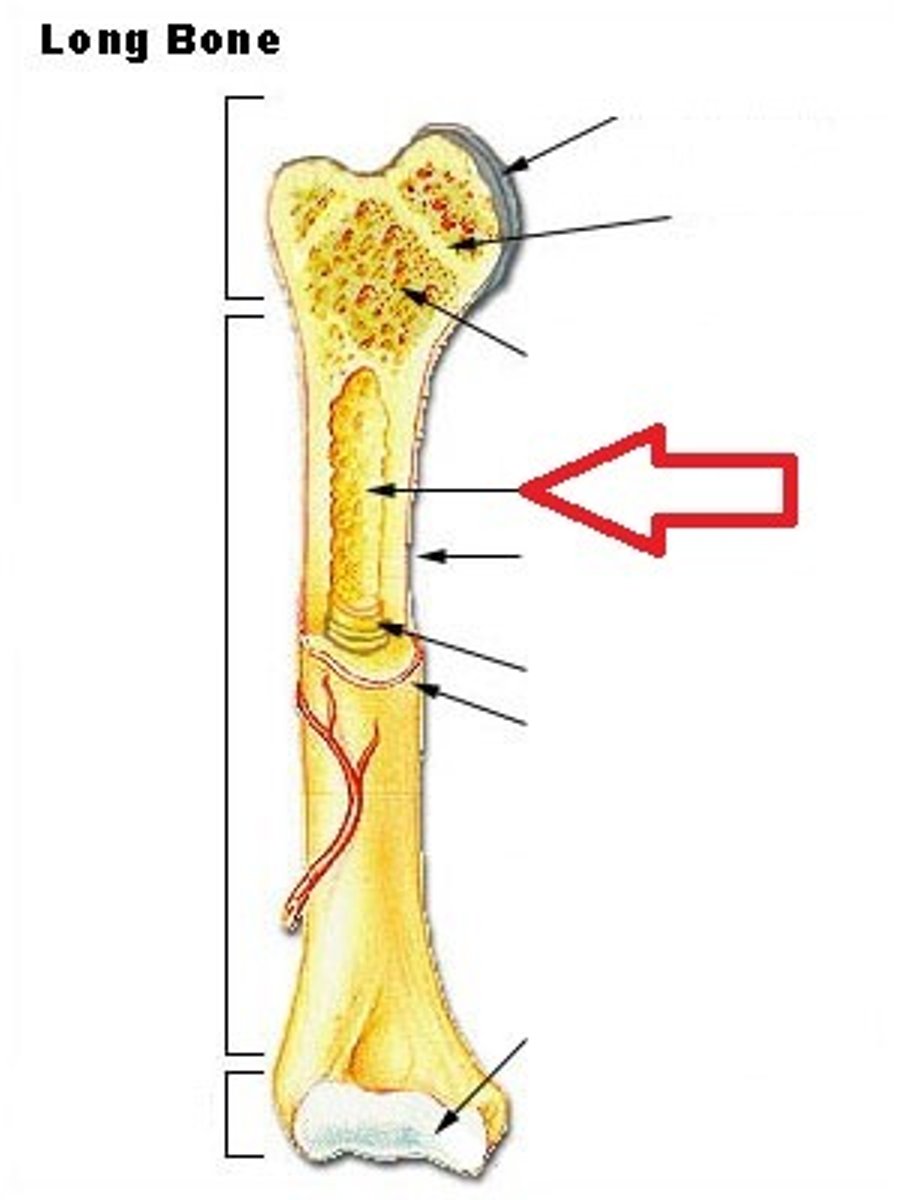
periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
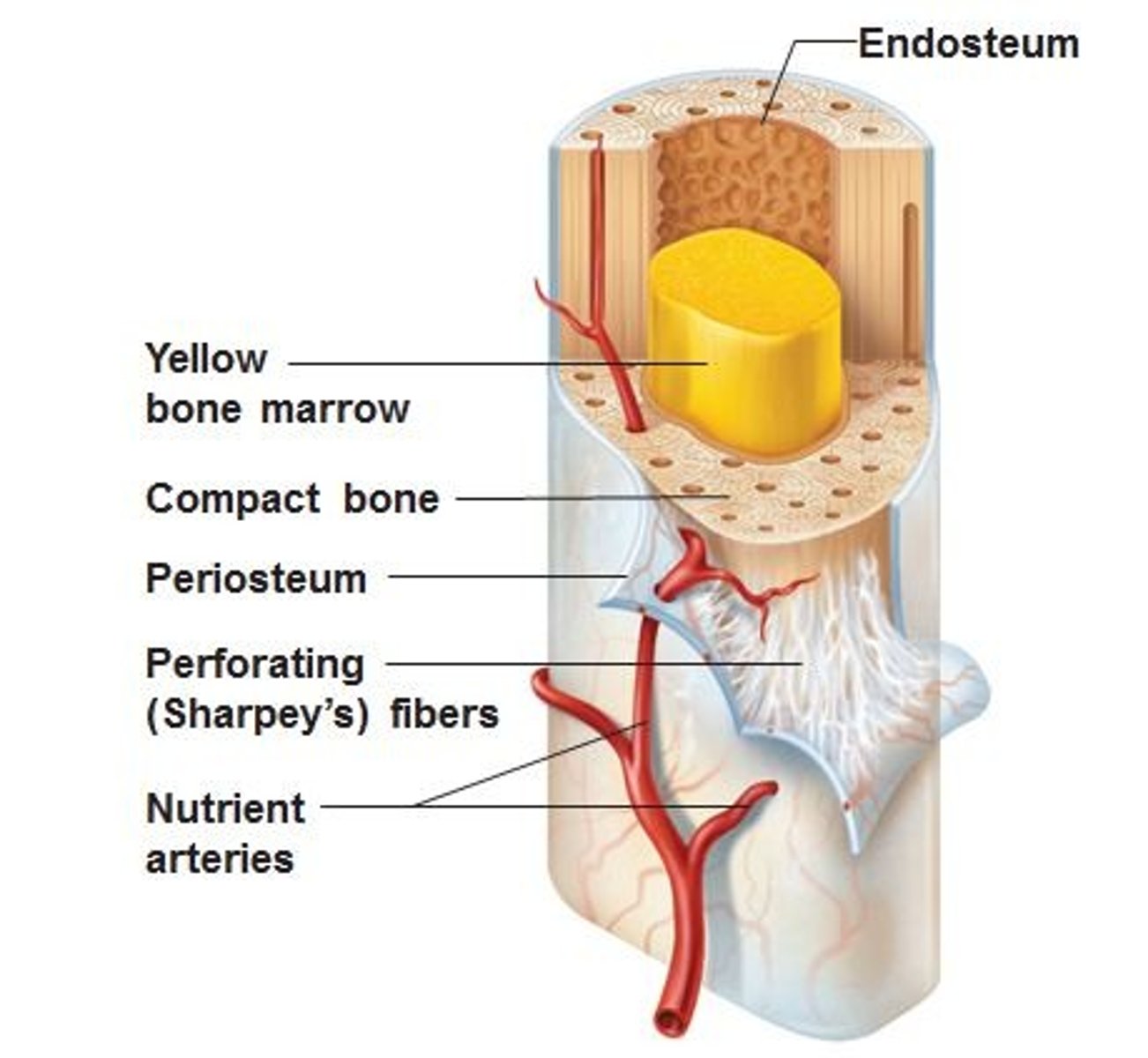
Endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone. Fibrous tissue, internal covering of the medullary cavity
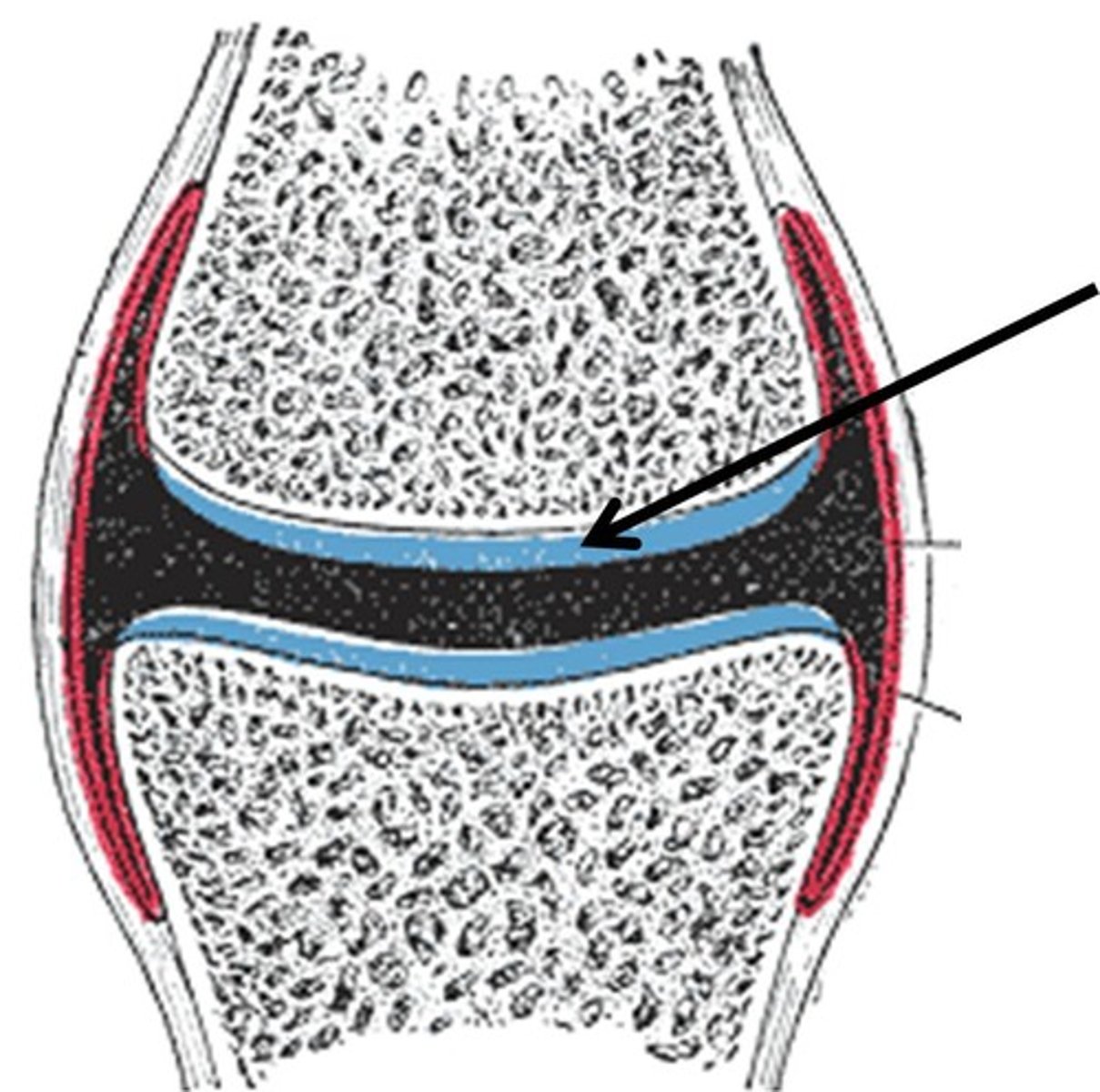
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that covers ends of bones in synovial joints to cushion and top break down
cancellous (spongy) bone
tiny beams of the bone that resist the stresses of weight and postural changes as well as muscular development
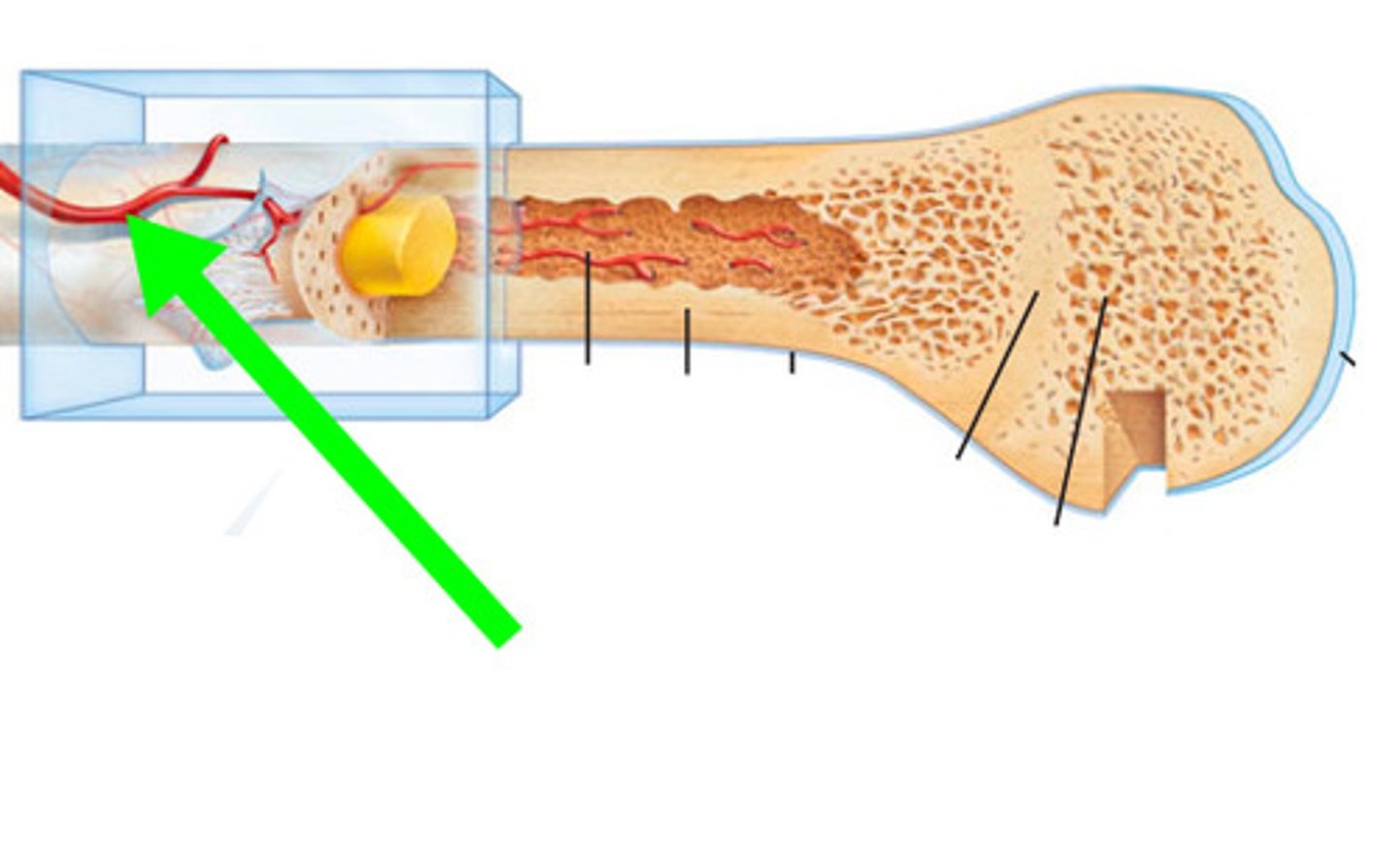
nutrient artery
an oblique tunnel in a bones shaft for the passage or the artery that enters through the medullary cavity
epiphysis
the end part of a long bone, initially growing separately from the shaft. Filled with spongy bone and red bone marrow. widens out to connect to other bones
epiphyseal plate
cells actively divide so bones grow in length
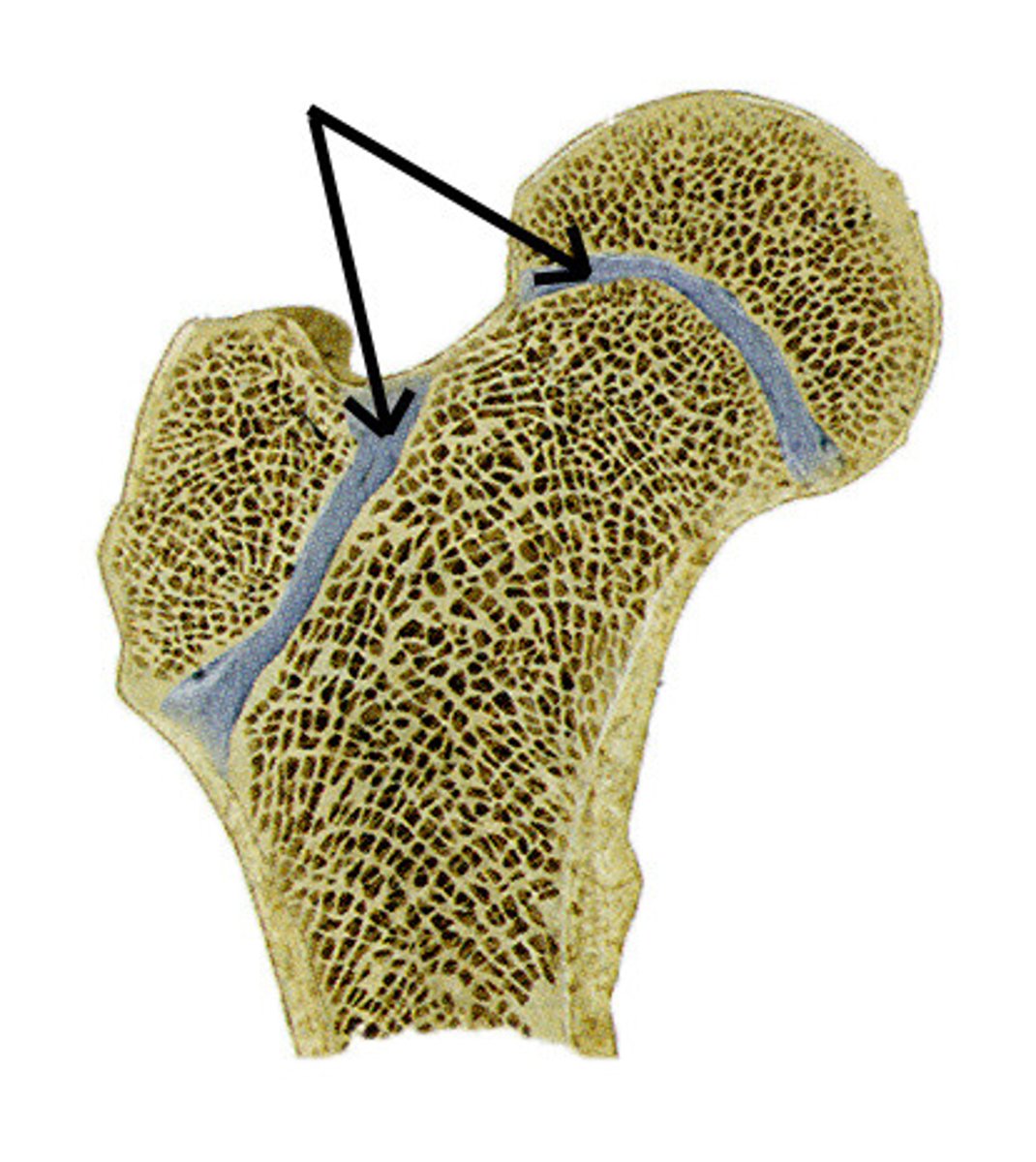
metaphysis
where the bone widens out toward the end

nerves
carry electrical impulses or signals from the brain back to the bone
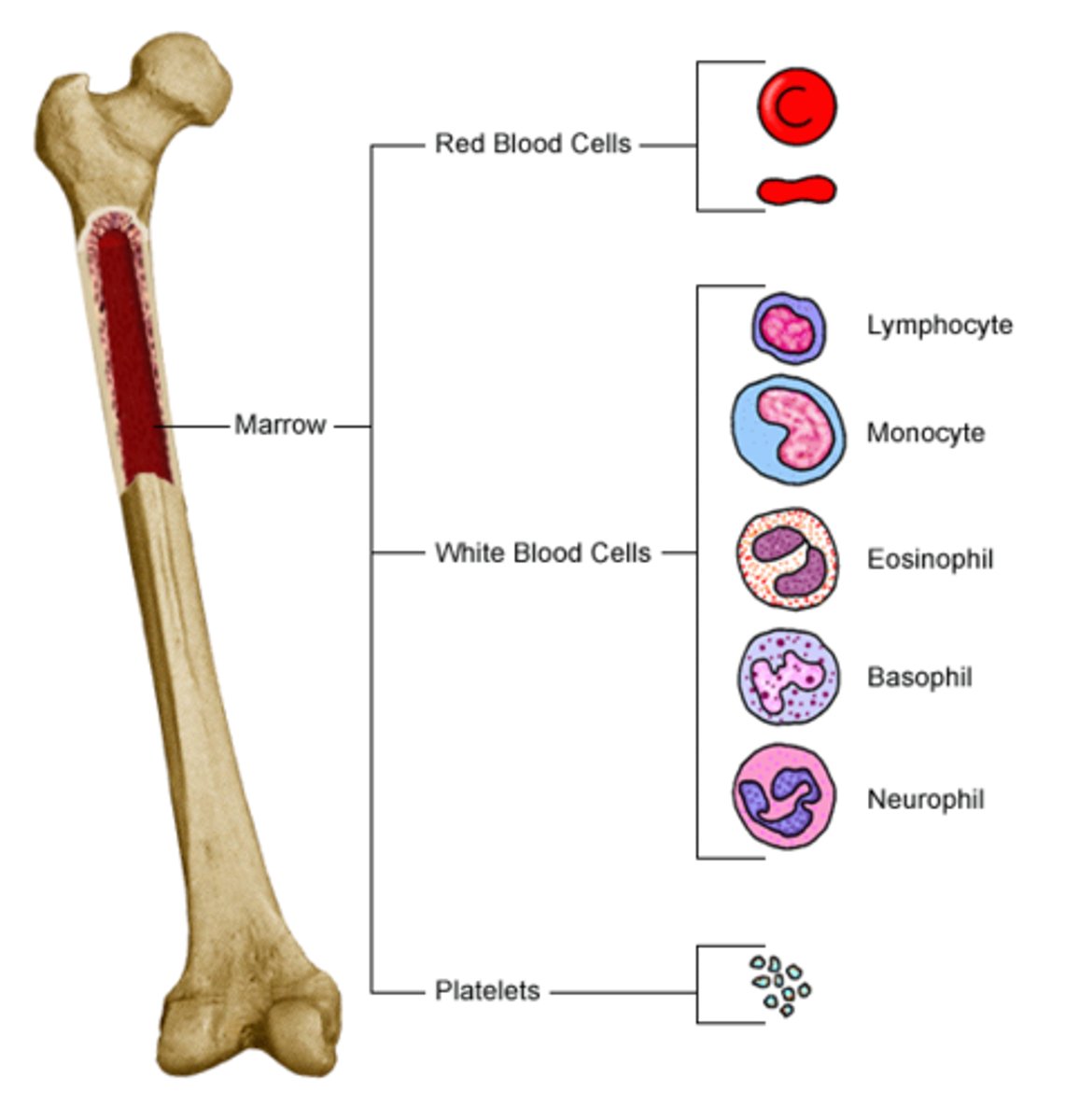
red bone marrow
red fluid that fills spongy bone holes, red blood cells are made
vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart. Carries Co2 and waste away from bone cells
yellow bone marrow
stores fat and nutrients for bone cells
hydrokya patite
mineral composed of phosporus and calcium, found in human bones and teeth
osteoblasts
synthesize and secrete and organic matrix called osteoid. form new bones and grow/heal existing bones
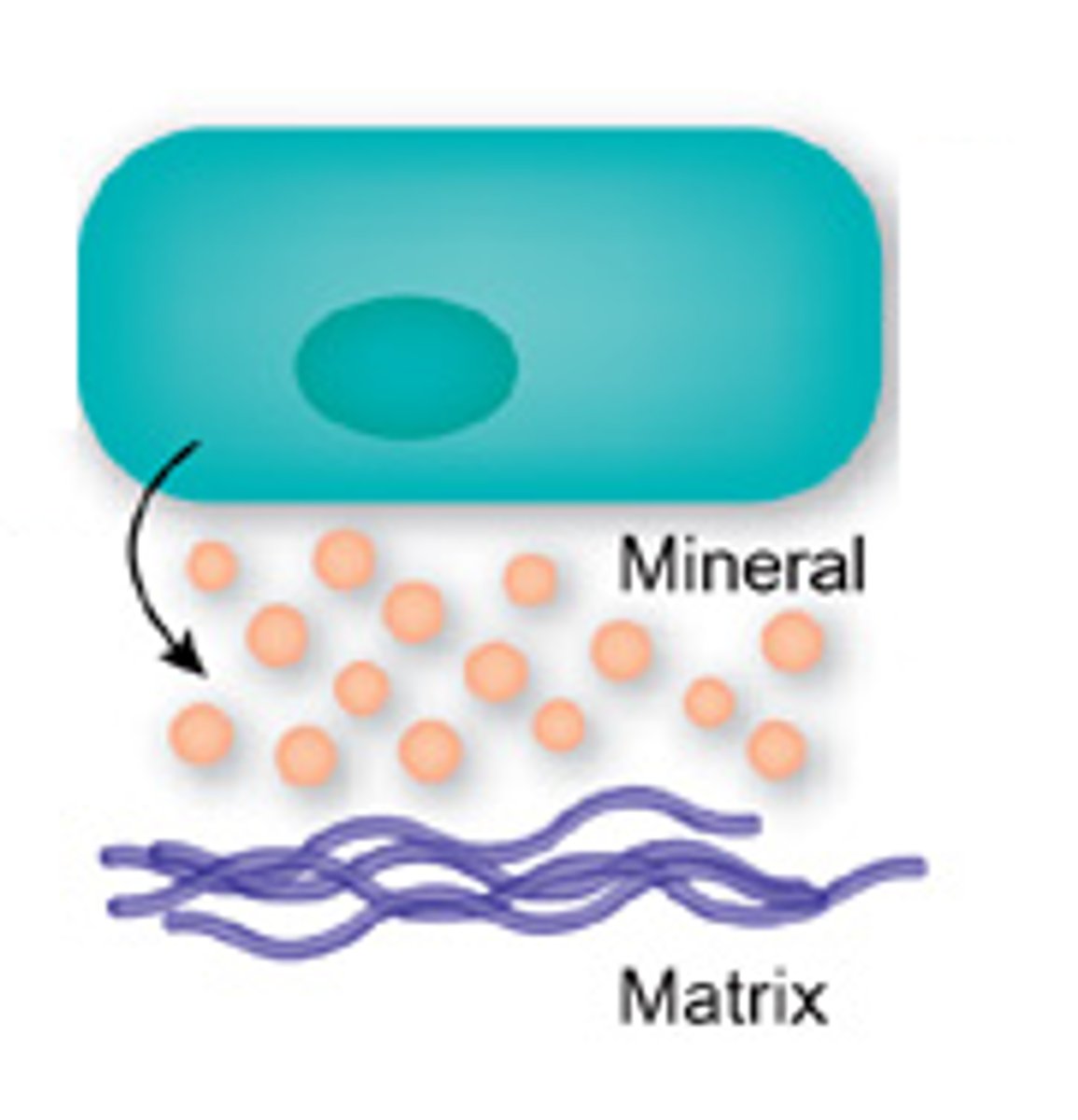
Collagen strands
located in the osteoid and are a framework for the formation of hydroxyapatite crystals
hydroxyapatite crystals
Calcium compound which bonds to collagen to make bone tissue very strong
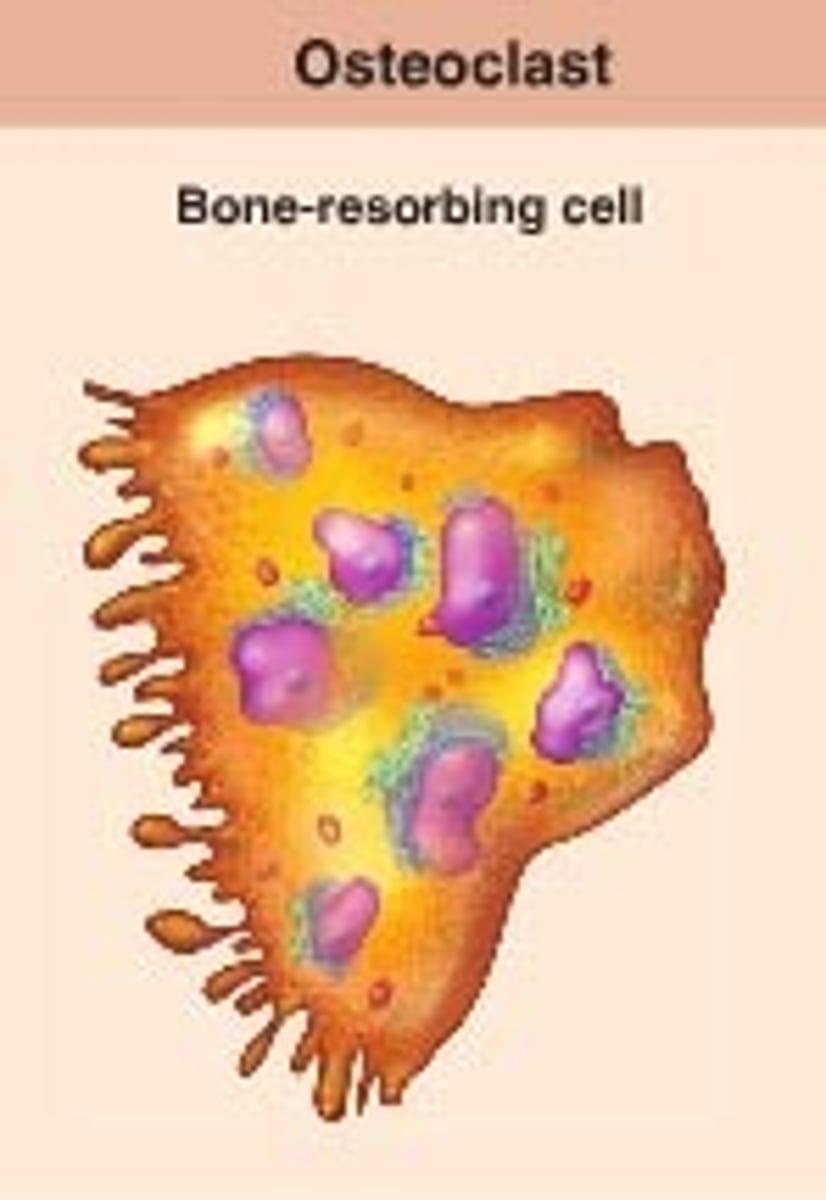
osteoclasts
Bone-destroying cells. Multinucleate cells responsible for the erosion of bone
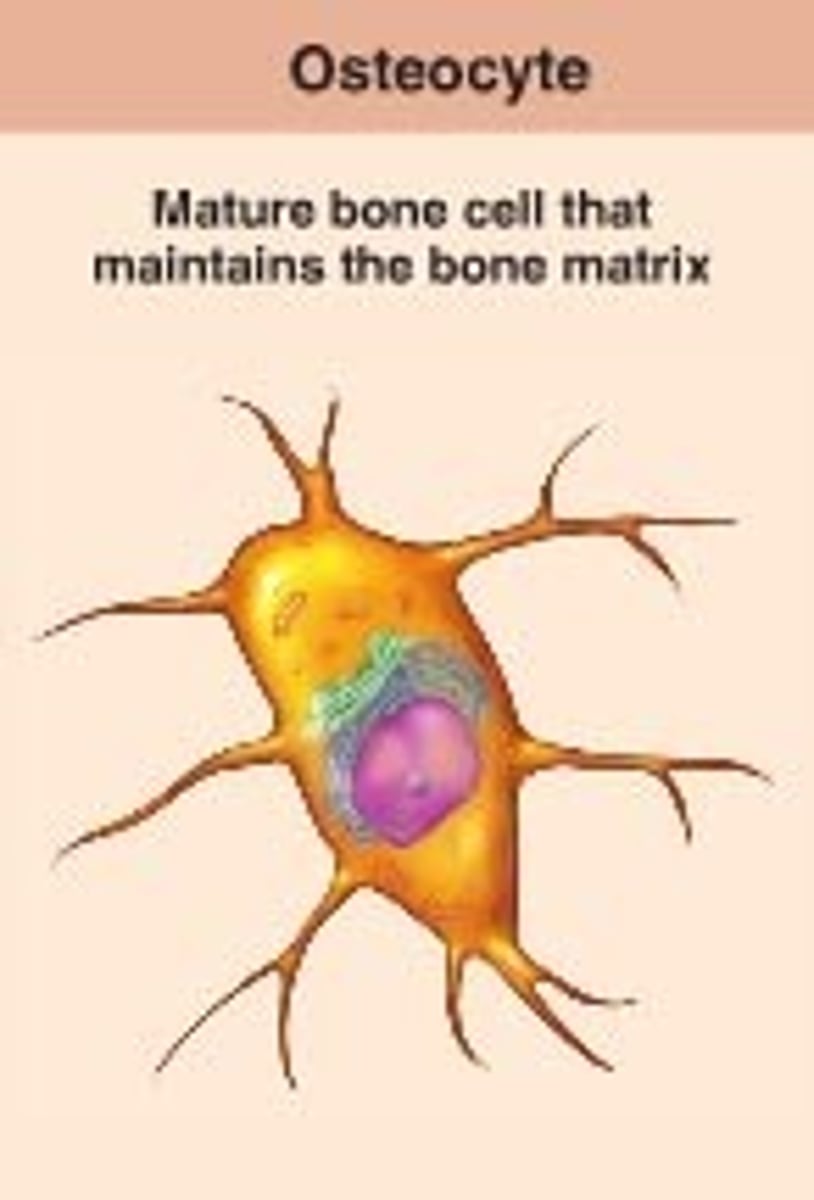
osteocytes
mature bone cells surrounded by matrix. Play a key role in remodeling, adaption, and homeostasis
osteogenic stem cells
undifferentiated cells and can become any kind of cell needed for bone formation
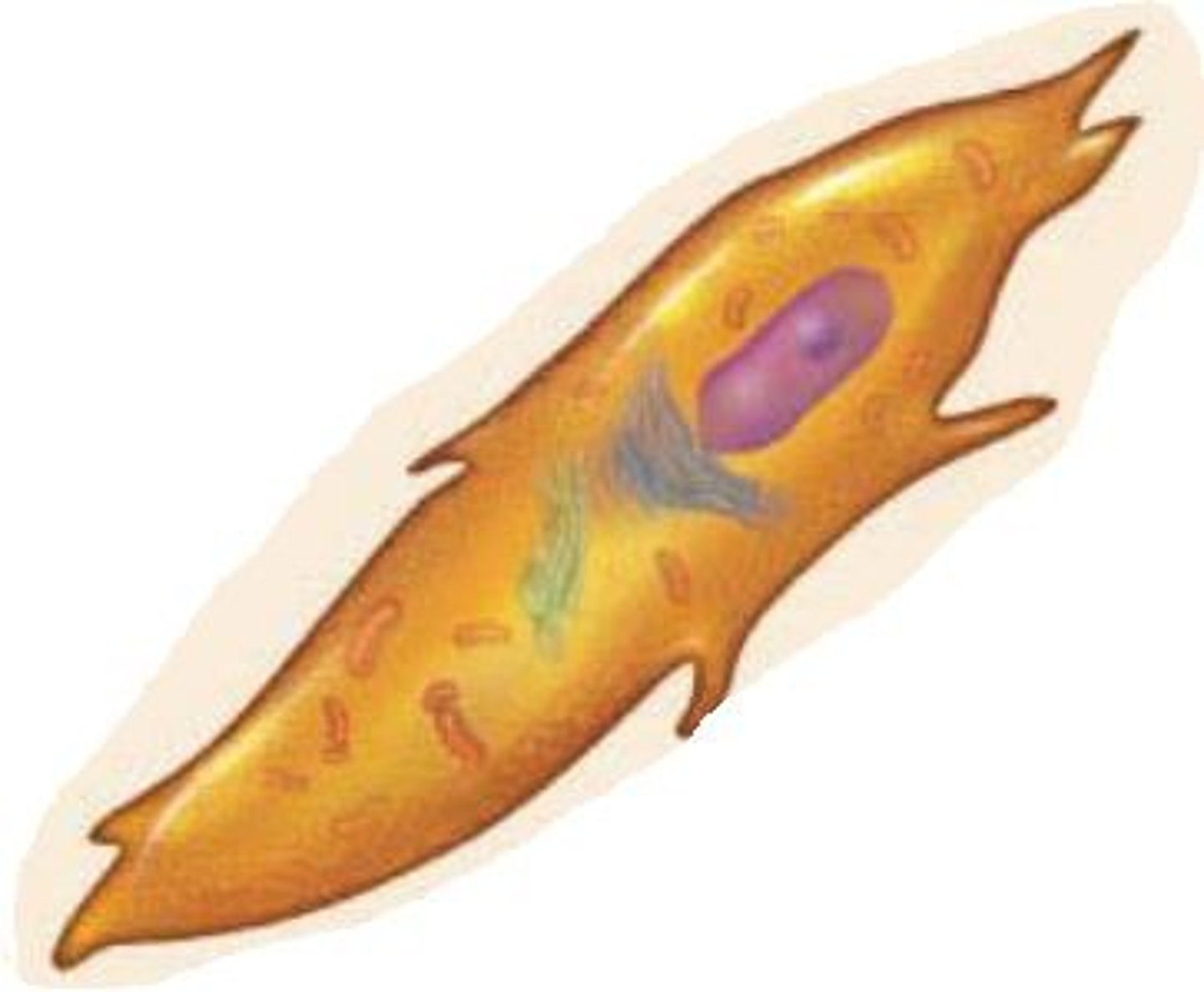
resisting cartilage (1)
joins epiphysis to diaphysis, anchor point
-small inactive cells
proliferating zone (2)
mitosis; plate lengthens. Chondroblasts quickly divide and push the epiphysis away from diaphysis, lengthening the bone
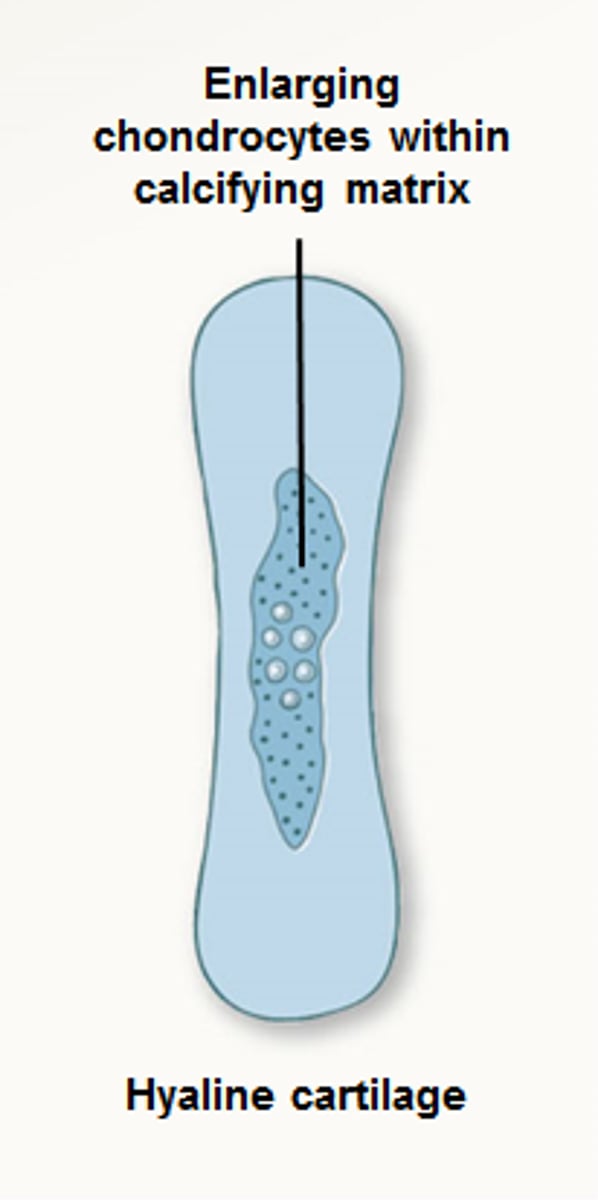
hypertrophy zone (3)
older, degenerative cells. Older chondrocytes enlarge and signal the surrounding matrix to calcify- enlarging, take in nutrients, lengthens disphysis
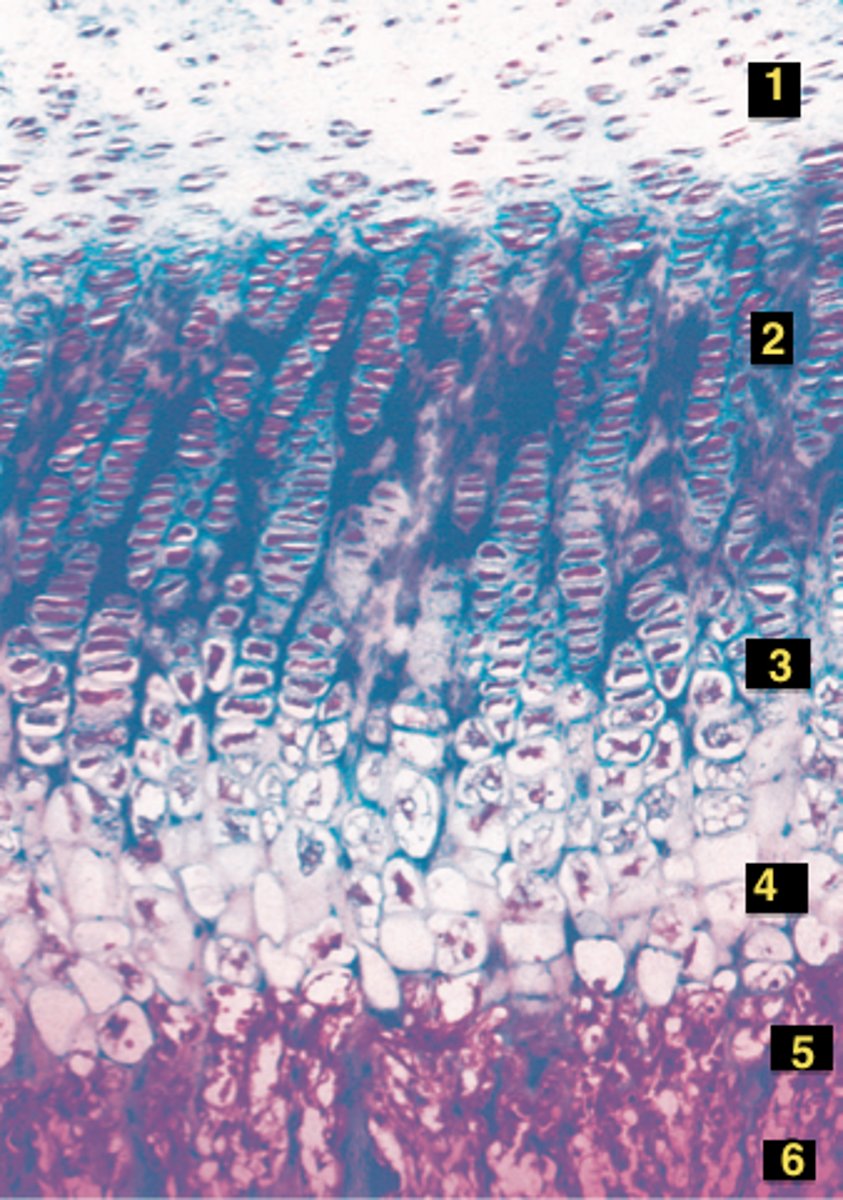
calcification zone (4)
thin, rapid calcification-fills with new bone- matrix becomes calcified, chondrocytes die, leaving behind trabeculae shaped calcified cartilage
ossification zone
osteoclasts digest the calcified cartilage and osteoblasts replace it with actual bone tissue in the shape of the calcified cartilage--->resulting in bone trabeculae
dead bone cells role
act as a mechanism to remove unnecessary or damaged cells, allowing for proper shaping of organs and tissues
endochondral ossification
process in which bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
-occurs during fetal development and is primary method for healing fractures
steps of endochondral ossification
1. Development of cartilage model
2. Growth of cartilage model
3. Development of primary ossification center
4. Development of medullary cavity
5. Development of secondary ossification center
6. Formation of articular cartilage & epiphyseal plate
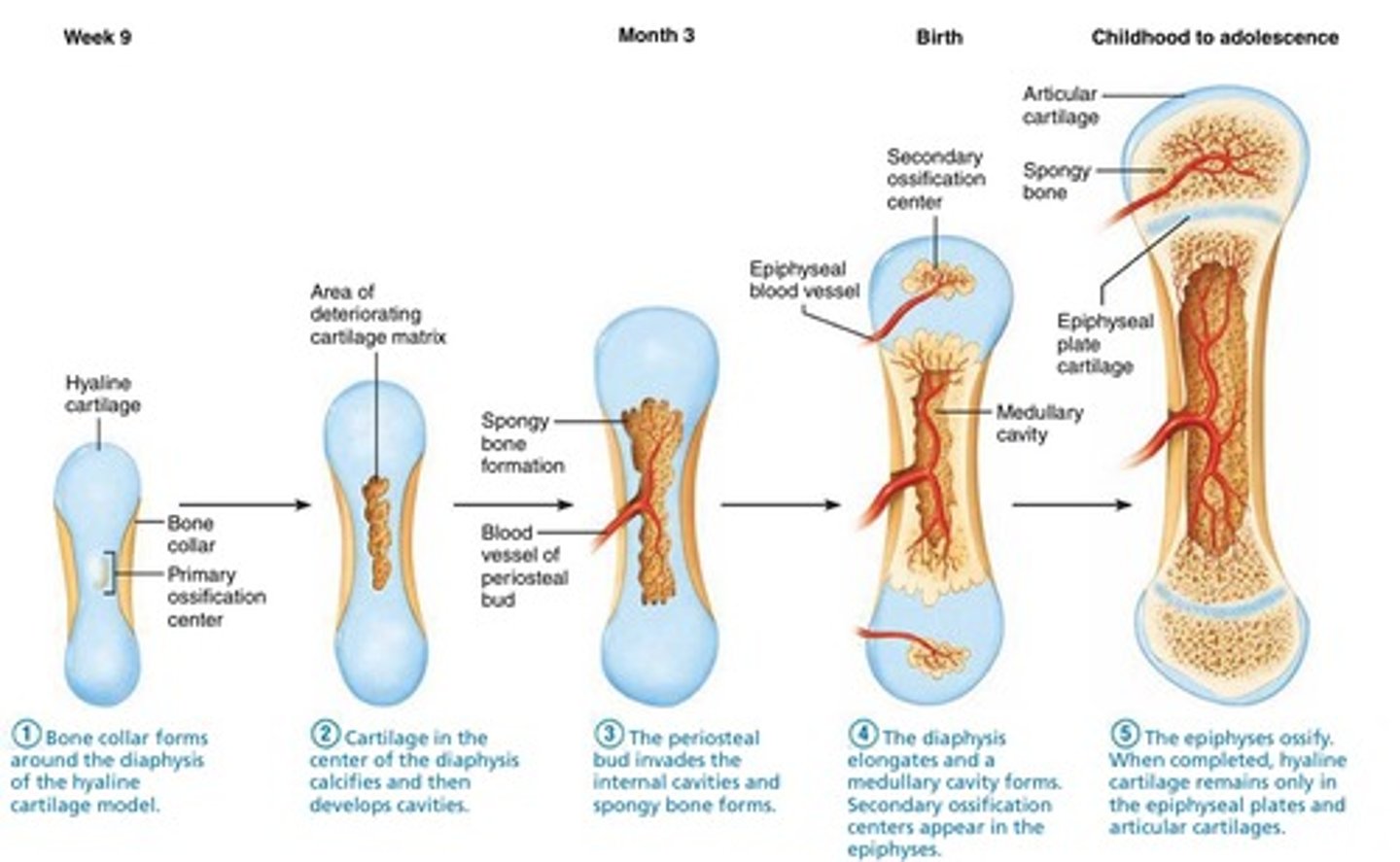
first step of endochondral ossification
bone collar forms around the diaphysis of the hyaline cartilage model
2nd step of endochondral ossification
cartilage in the center of the diaphysis calcifies and then develops cavities
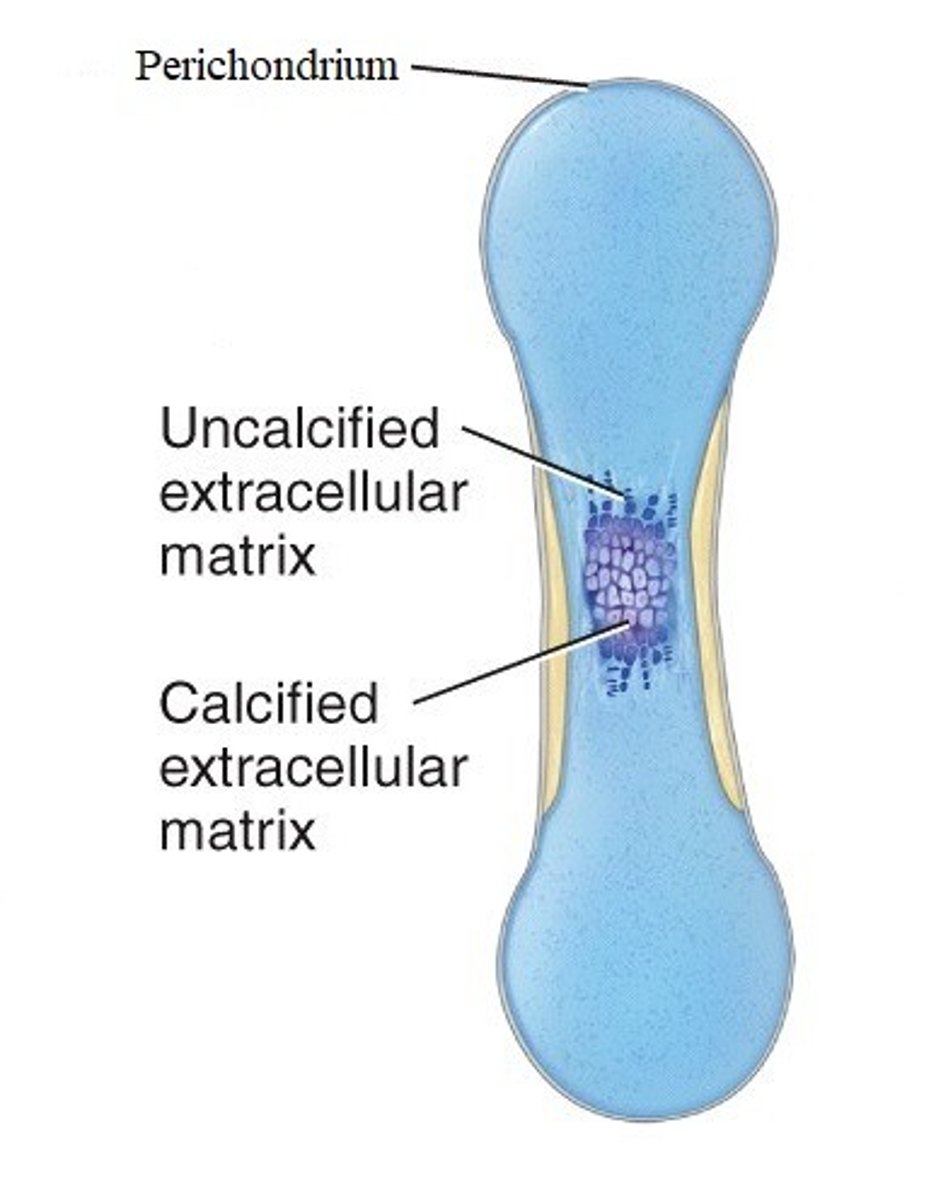
3rd step of endochondral ossification
the periosteal bud invades the internal cavities and spongy bone forms
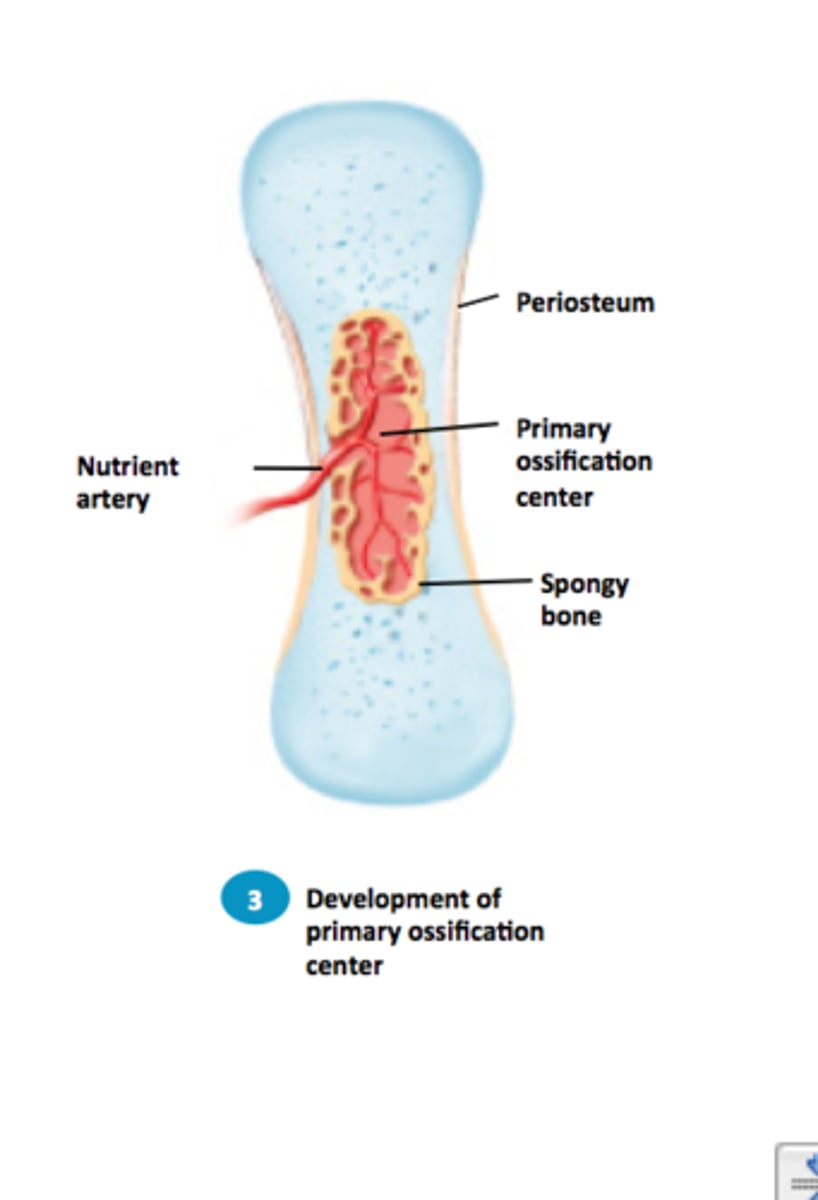
4th step of endochondral ossification
The diaphysis elongates and a medullary cavity forms. Secondary ossification centers appear in the epiphyses.
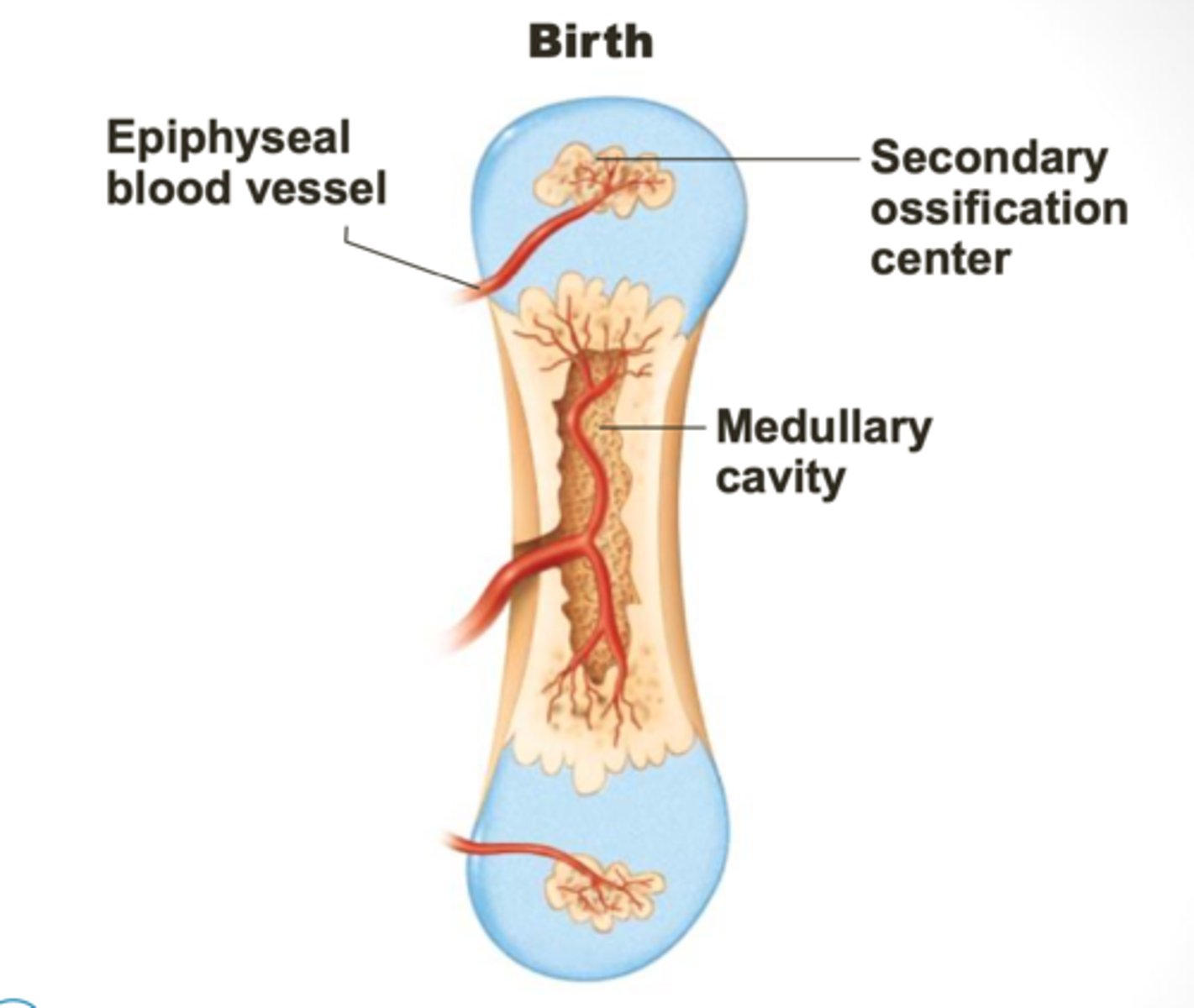
5th step of endochondral ossification
ossification of epiphyses (childhood to adulthood); cartilage in secondary ossification centers calcify and deteriorate; cartilage remains in two places : epiphyseal surfaces (articular cartilage) and epiphyseal plates (epiphysis-diaphysis interface)
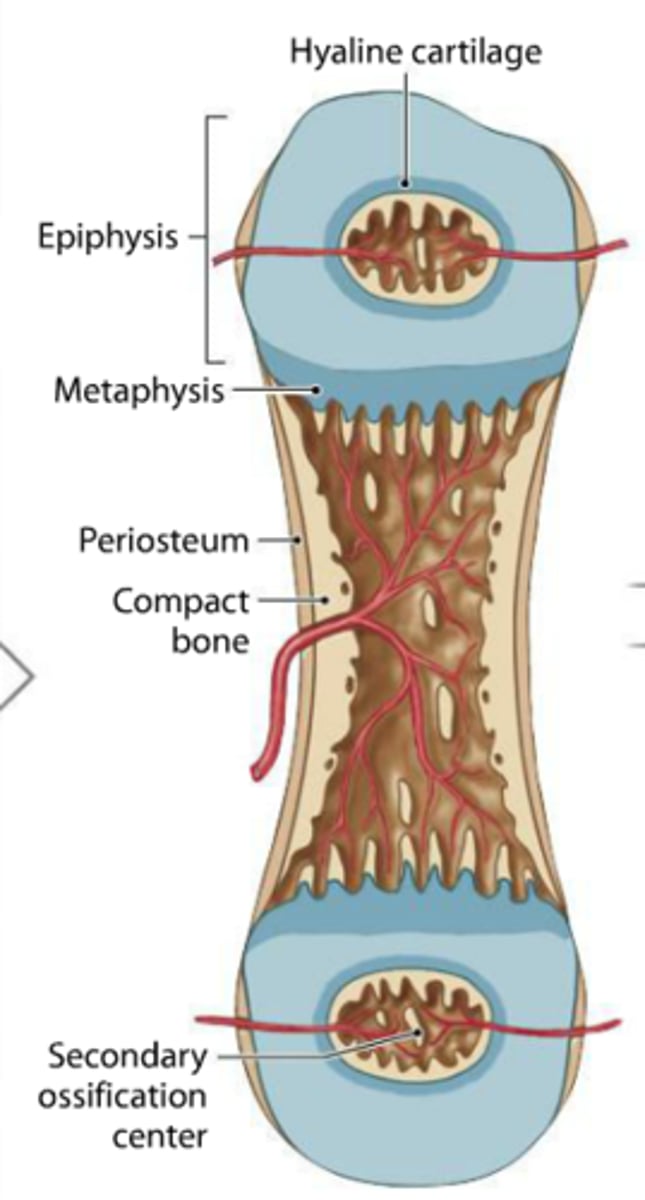
6th step of endochondral ossification
epiphyseal plates ossify and form epiphyseal lines
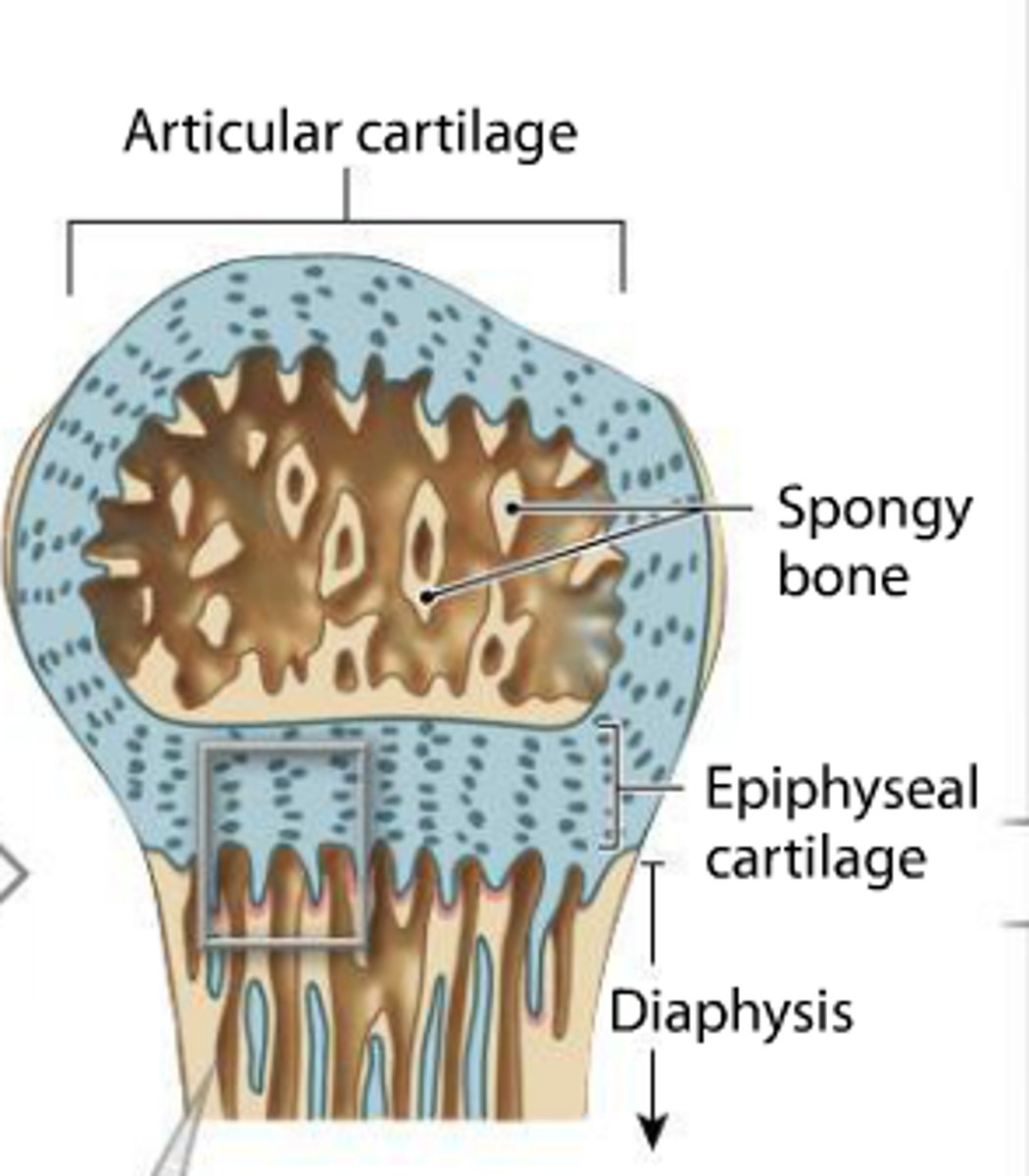
7th step of endochondral ossification
Bone grows in length at the epiphyseal cartilage
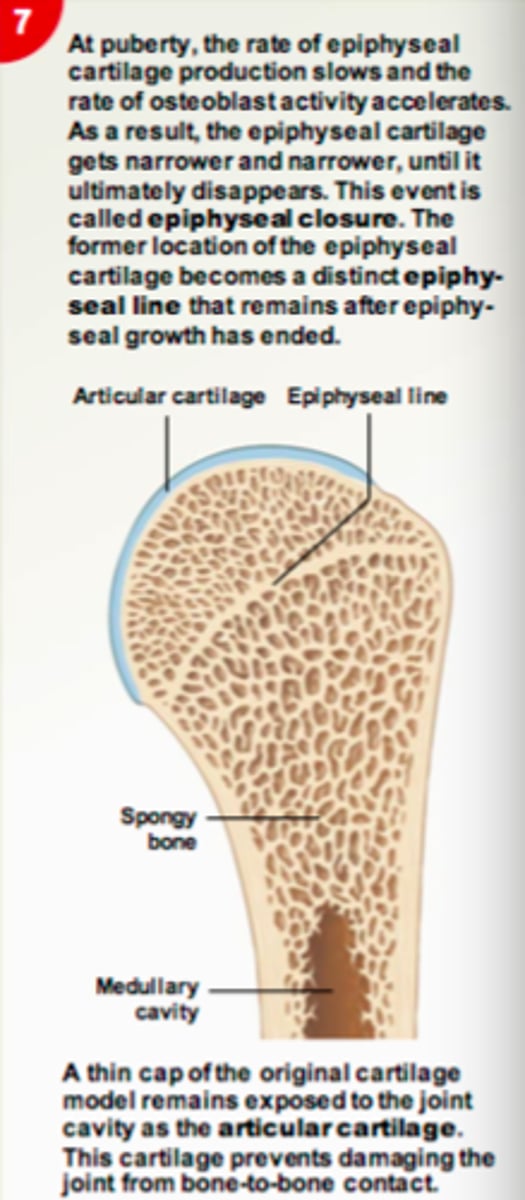
Perichondrium
Dense irregular connective tissue membrane covering cartilage
primary ossification center
region, deep in the periosteal collar, where bone development starts during endochondral ossification
blood vessels in ossification center
blood vessels penetrate cavities formed from chondrocyte death, and bring osteogenic cells into these spaces
-spaces combine and become the medullary cavity and osteoblasts brought in by blood vessels begin to deposit bone into these spaces
2nd part of primary ossification center
the cartilage template continues to grow as cartilage is laid down by chondrocytes above and below the primary ossification center, which is replaced by bone
secondary ossification center
this develops in the epiphyses of bone (ends of bone) during endochondral ossification
what do both the primary and secondary ossification center have
both have a thin cartilage between them called the epiphyseal growth plate
-chondrocytes in plate continue to proliferate and form new cartilage which is replaced by bone
Diaphysis vs Epiphysis (of a long bone)
the diaphysis grows wider while the epiphysis grows the bone longer
role of calcium
the primary mineral component that forms the bone matrix
-essentially hardening the cartilage template by binding to the osteoid, produced by osteoblasts, and transforming it into solid bone tissue during the process of bone development
location of blood vessels
located in perichondrium, POC, metaphysis/disphysis, epiphysis, and bone marrow
role of blood vessels
play a vital role in bone formation, maintenance, and regeneration
-release signaling molecules that regulate the formation of bone precursor cells
1st step of healing a fractured bone
blood flows from any vessel torn by the fracture
-the blood begins to clot and 6-8 hours after fracture, the swelling has formed a hematoma (swelling of clotted blood)
2nd step of healing a fractured bone
blood clots are replaced by fibrocartilage and cartilage is secreted
3rd step of healing a fractured bone
osteoblasts create bony callus. New blood vessels and cells in them are involved in osteogenesis. Osteoblasts build bone and connective tissue
4th step of healing a fractured bone
osteoclasts resorb the dead bone while osteoblasts build around the fracture (remodeling)
importance of diet and exercise for the skeleton
foods like yogurt, cheese, and milk all contain calcium which provides the building blocks for growth, repair, and remodeling of the bones
-exercise is crucial to help build strong bones, prevent bone loss, increase bone density, and reduce the risk of falling
skeletal disease causes
aging, genetics, hormonal changes and nutritional deficiencies
Role of Vitamin D
increases absorption rate of calcium in the intestines
-
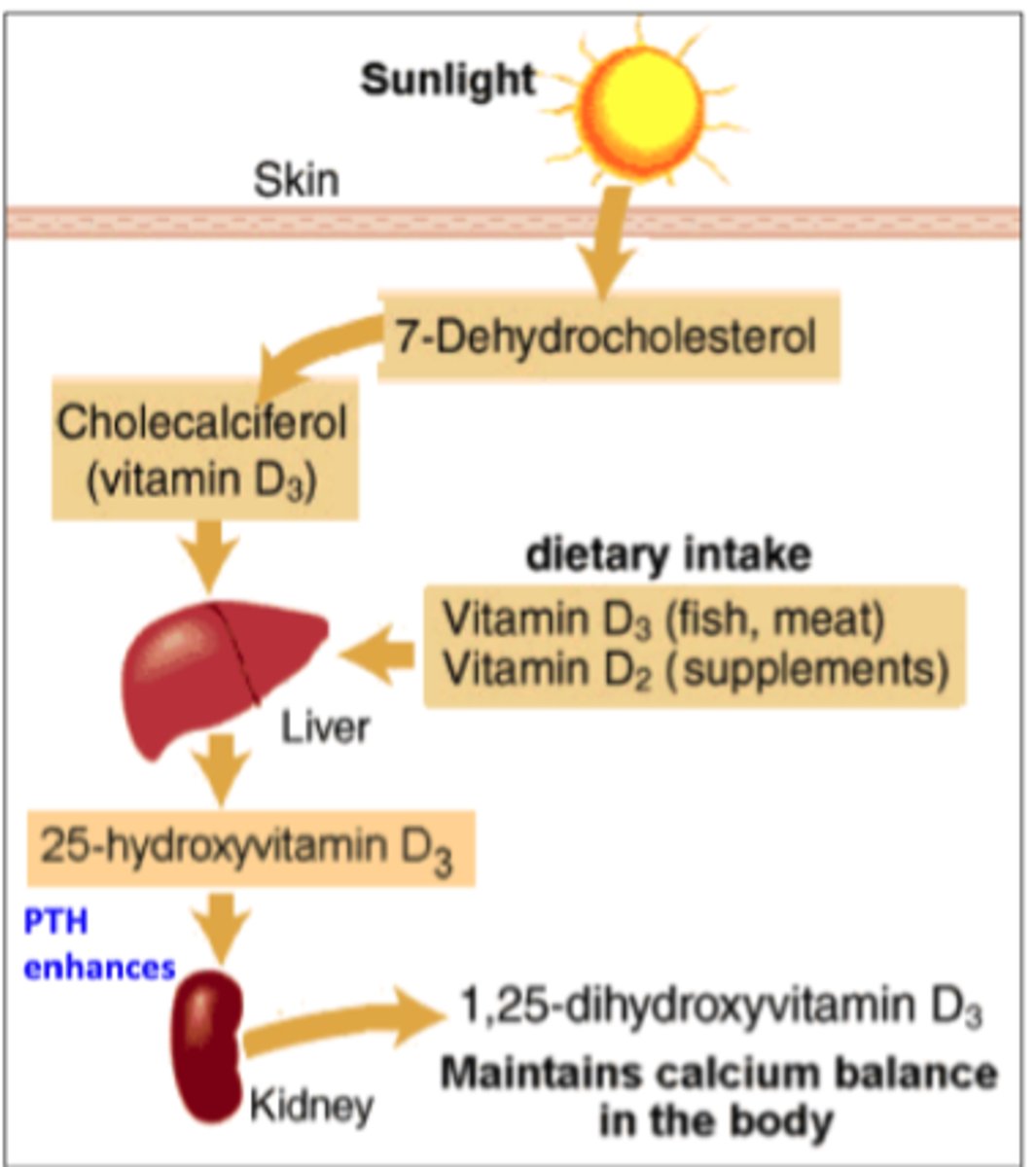
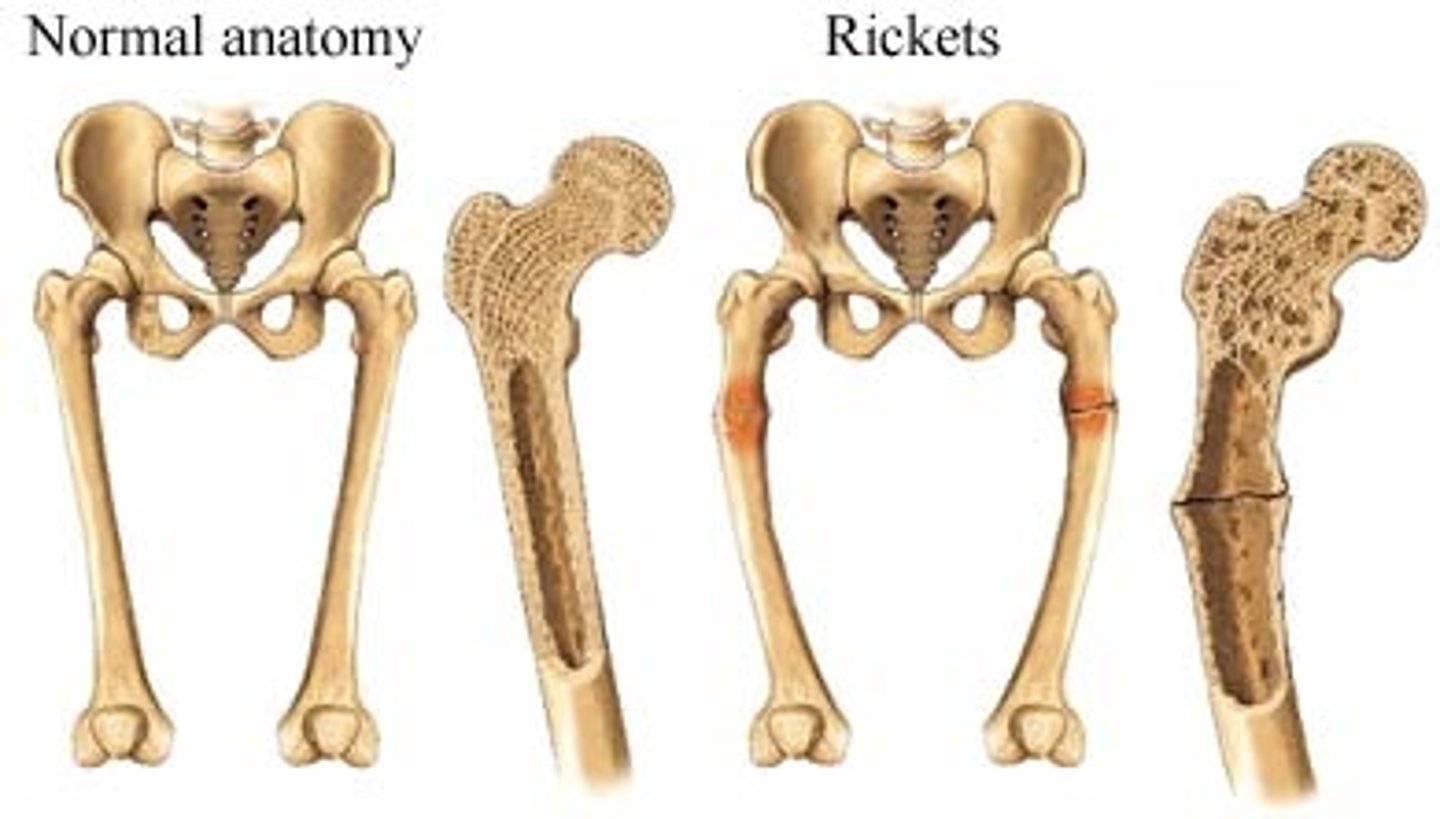
Vitamin D deficiency
rickets, osteomalacia
-a persons ability to build strong bones is lowered
(Disney Knees)
role of phosporus
key building block for bones (especially teeth)
-plays important role in how the body uses carbohydrates and fats
Calcium homeostasis
Maintenance of a stable level of calcium in the blood
-regulated by hormones and other processes that control the movement of calcium in the bones, kidneys, and gut
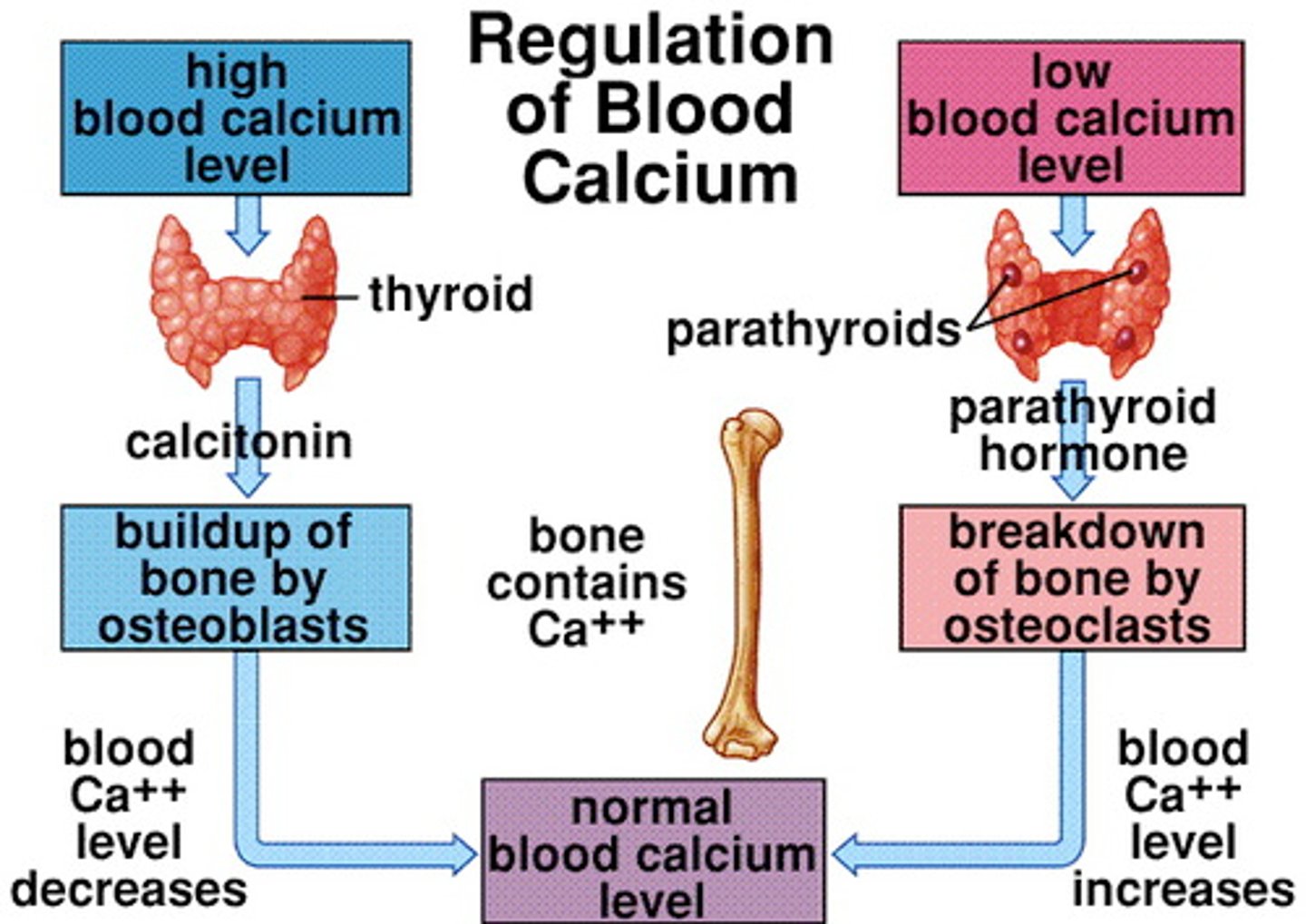
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism
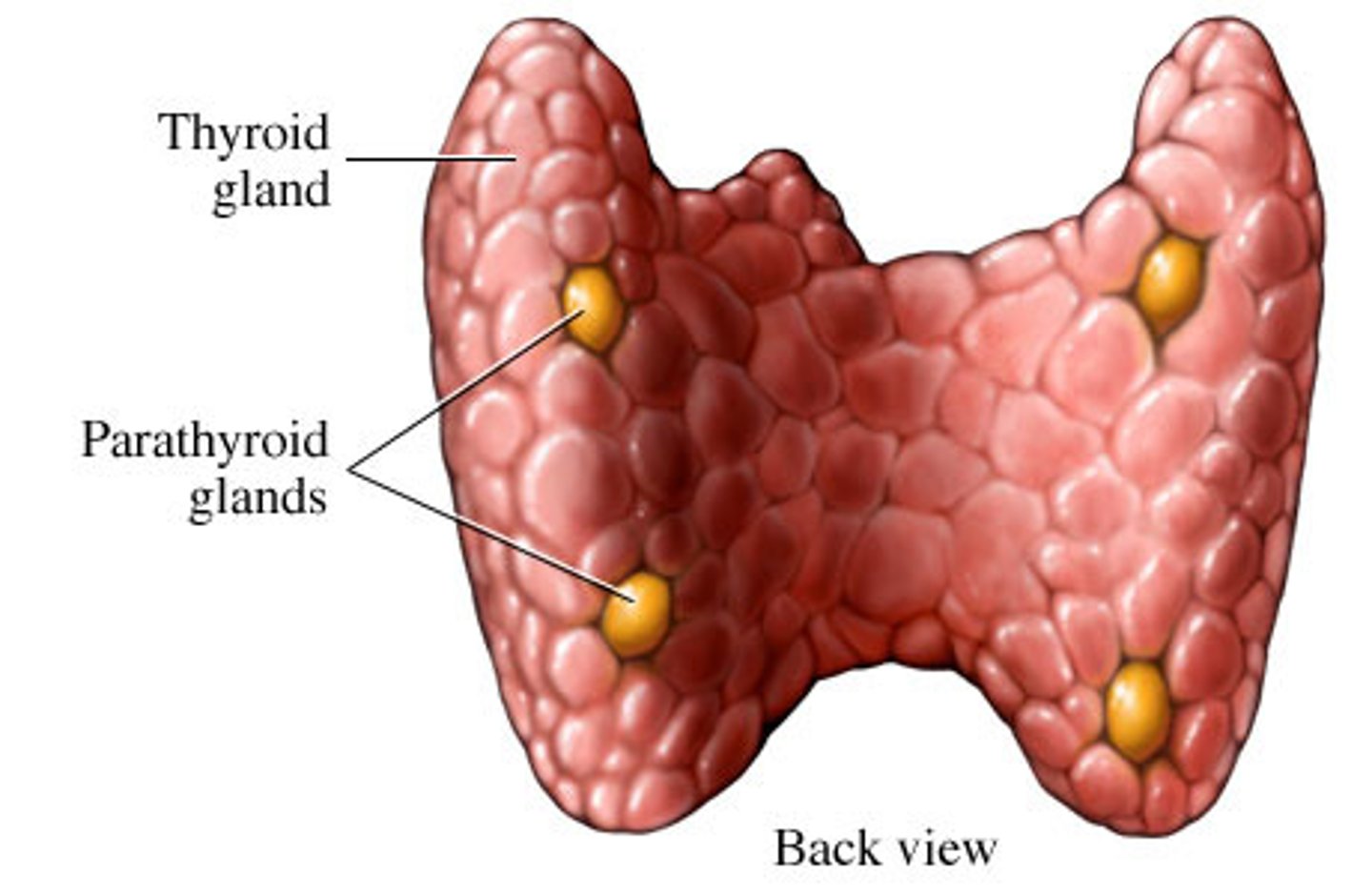
Calcitonin (CT)
Secreted by the thyroid gland; inhibits bone resorption by osteoclasts.
-a hormone that the thyroid gland makes and releases to help regulate calcium levels in your blood by decreasing it
growth hormone
hormone secreted by anterior pituitary gland that stimulates growth of bones
thyroid hormone
modulates the activity of growth hormones, ensuring proper proportions
-affects the bodys metabolic rate, influencing how quickly the body uses energy and impacting functions like heart rate and body temp
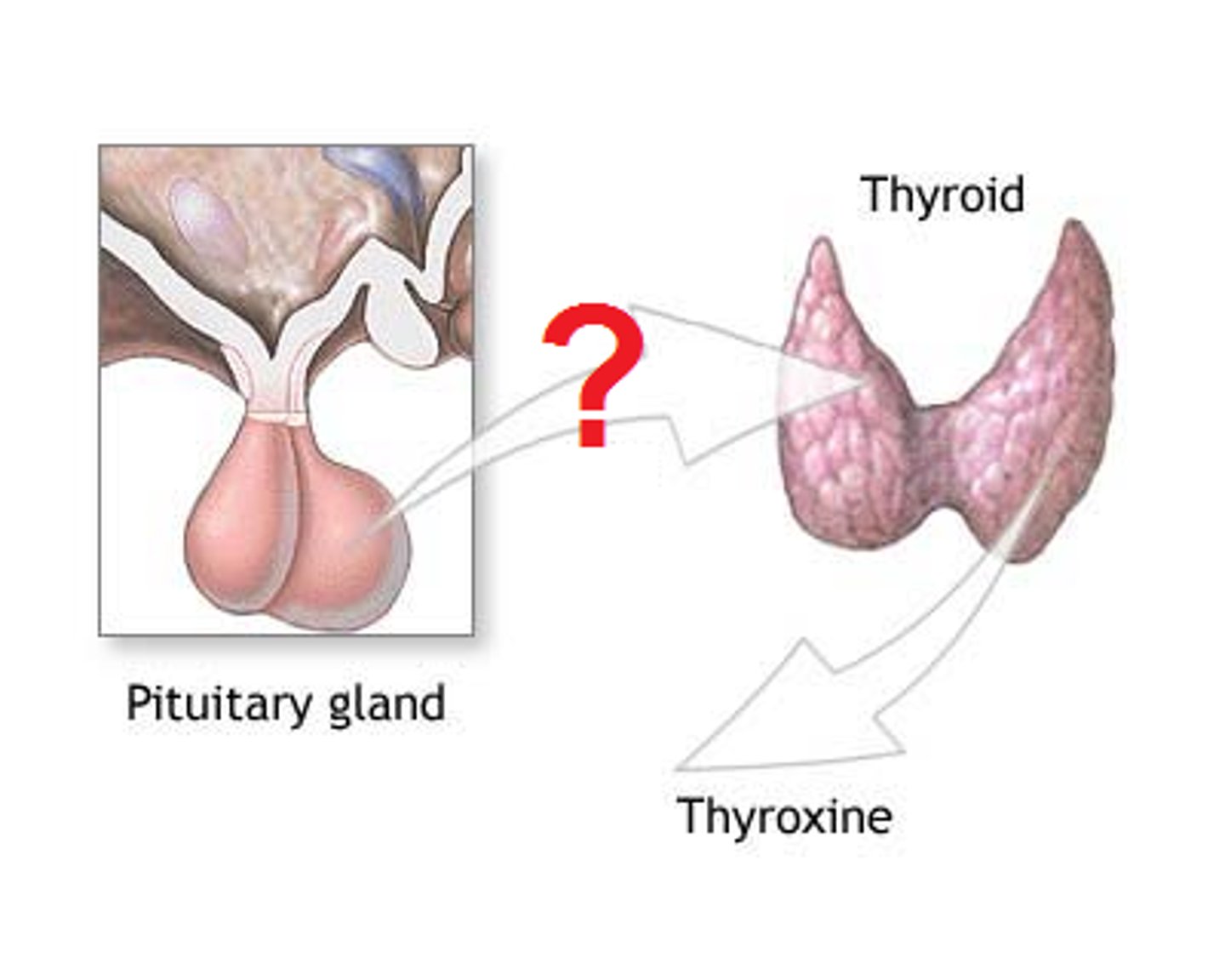
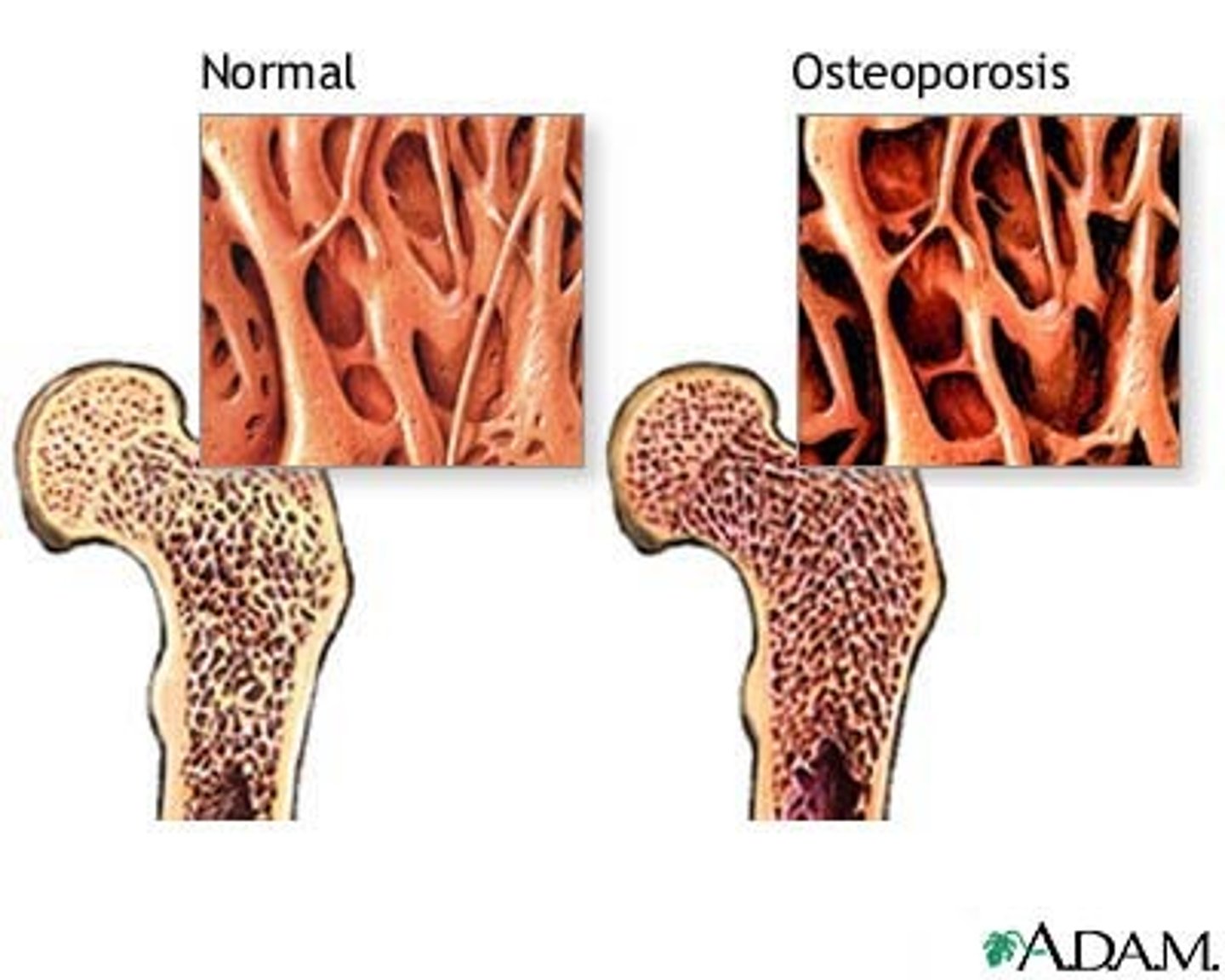
osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily.
-new bone creation doesnt keep up with old bone removal
estrogen
A sex hormone, secreted in greater amounts by females than by males. Regulates the menstrual cycle, fertility, and bone health
testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
-regulates muscle mass and bone density
role of vitamin a
stimulate the formation of bone resorbing osteoclasts but also inhibit their formation
role of vitamin c
helps to grow and repair tissues and bones. Also used to form collagen and heals wounds
Effects of Excercise on Bone
Mineral recycling allows bones to adapt to stress
Heavily stressed bones become thicker and stronger
-positively impacts joints by improving lubrication, flexibility and range of motion
articulations
Joints; points where two bones meet.
Synathrosis (fibrous joint)
immovable joint
-sutures
amphiarthrosis (cartilaginous joint)
slightly movable joint (intervertebral discs)
Diarthroses (synovial joints)
freely moveable
knee, shoulder, hip, elbow
pivot joint (uniaxial)
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
-dens of axis rotating against atlas
hinge (uniaxial)
a joint on a lid or door that allows it to swing open or shut
-elbow joint
Saddle (Biaxial) Joint
in thumb
-thumb bone articulates with trapezium -opposable
condyloid joint (biaxial)
oval shaped projection of one bone fits into the oval shaped depression of another bone, allowing movement on 2 axes.
-fits into elliptical socket
Ball & socket (multiaxial) joint
most freedom in movement (shoulder joint, hip joint)
Gliding (multiaxial)
joints between articular surfaces of successive vertebrae
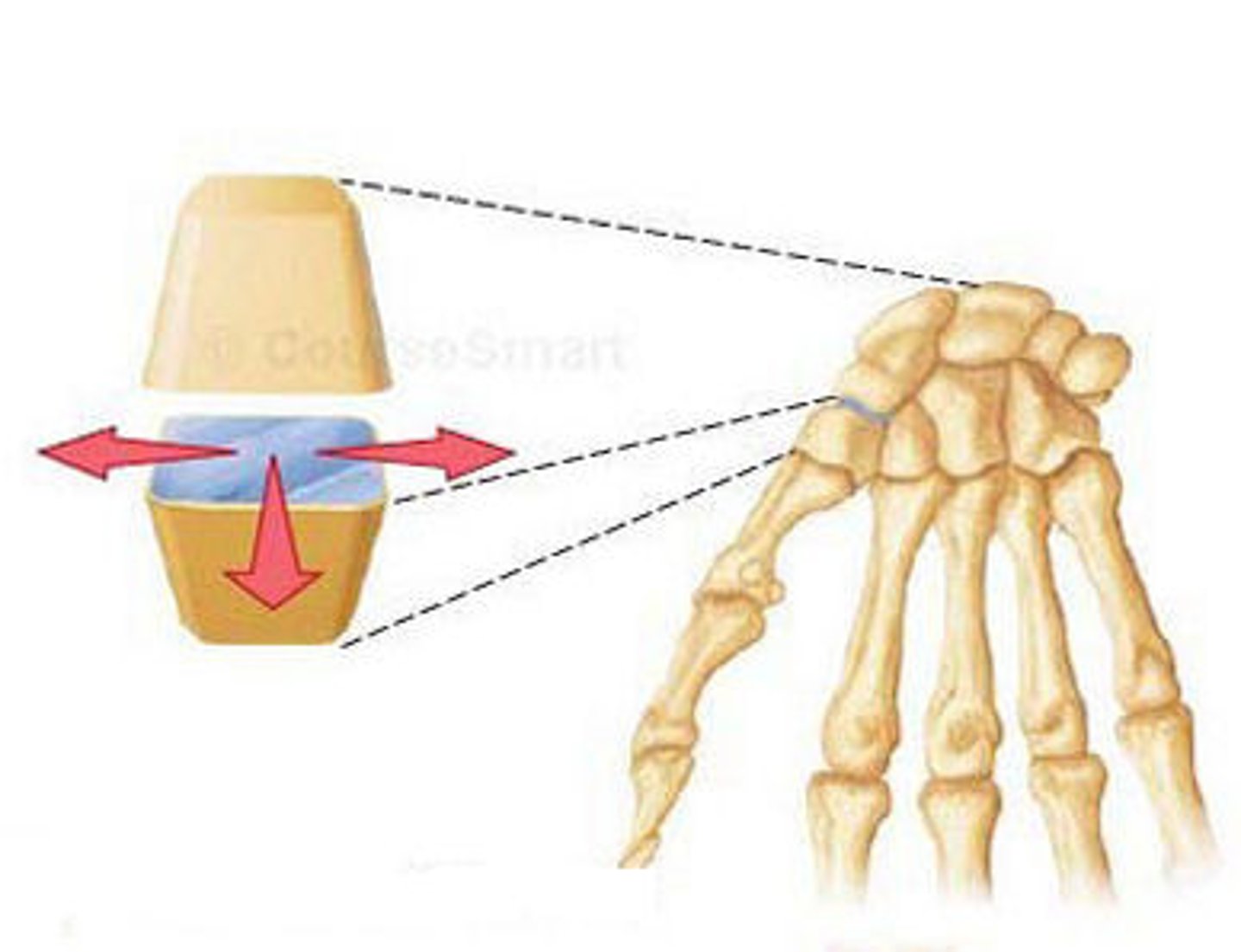
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
tendons
Connect muscle to bone