Week 3 - Spinothalamic Tract and pathways
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards covering the spinothalamic tract and dorsal column-medial lemniscus, including key functions, pathways, and comparison of the two tracts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
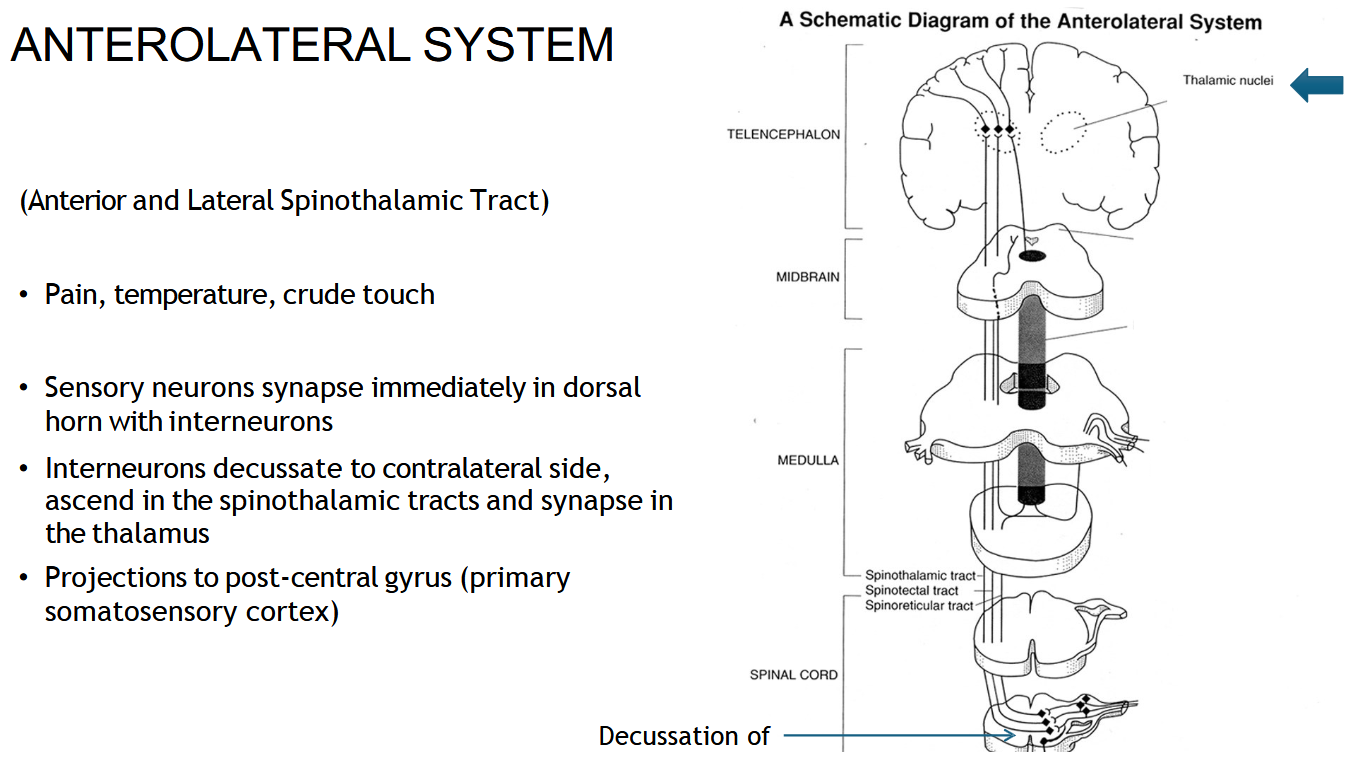
What information does the spinothalamic tract carry?
Pain, temperature, and crude touch.
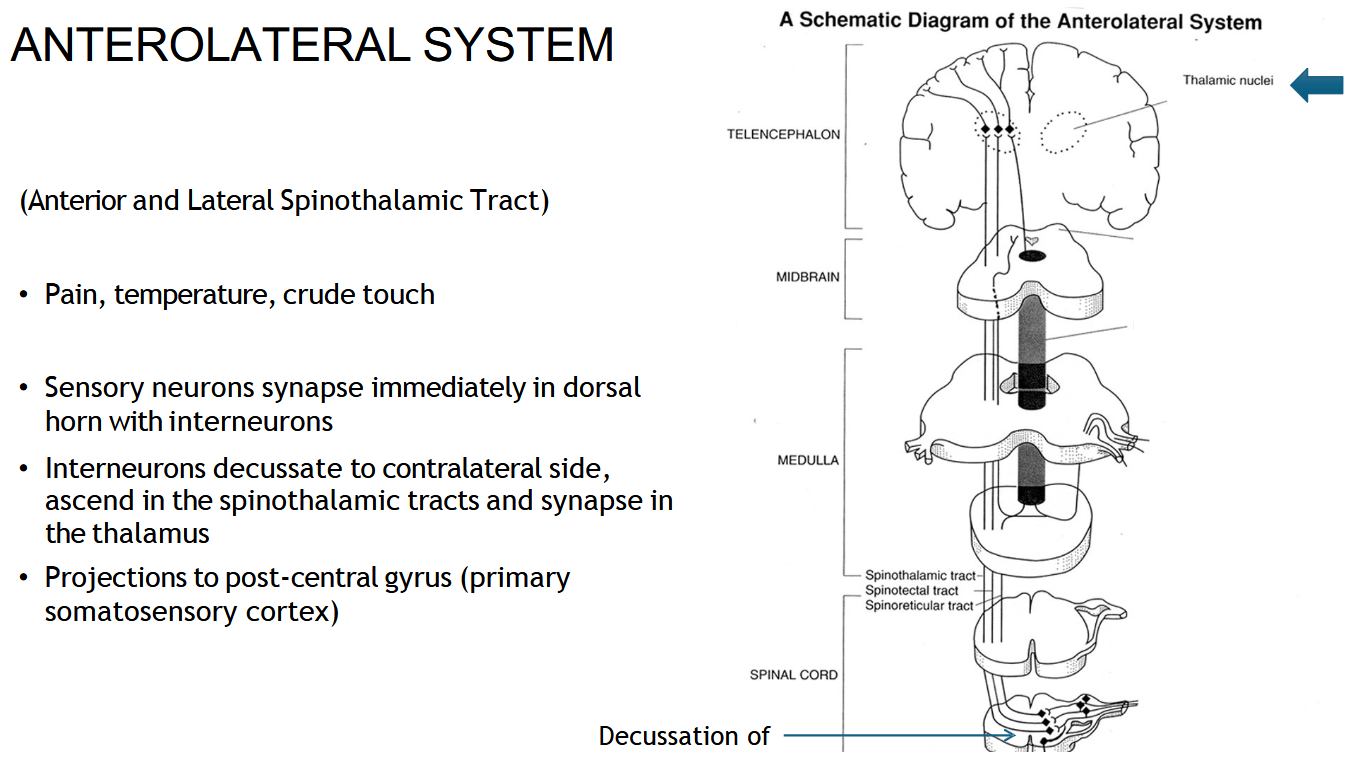
Where does the spinothalamic (AnteroLateral) tract start?
In the sensory neurons that enter the spinal cord through the dorsal horn.
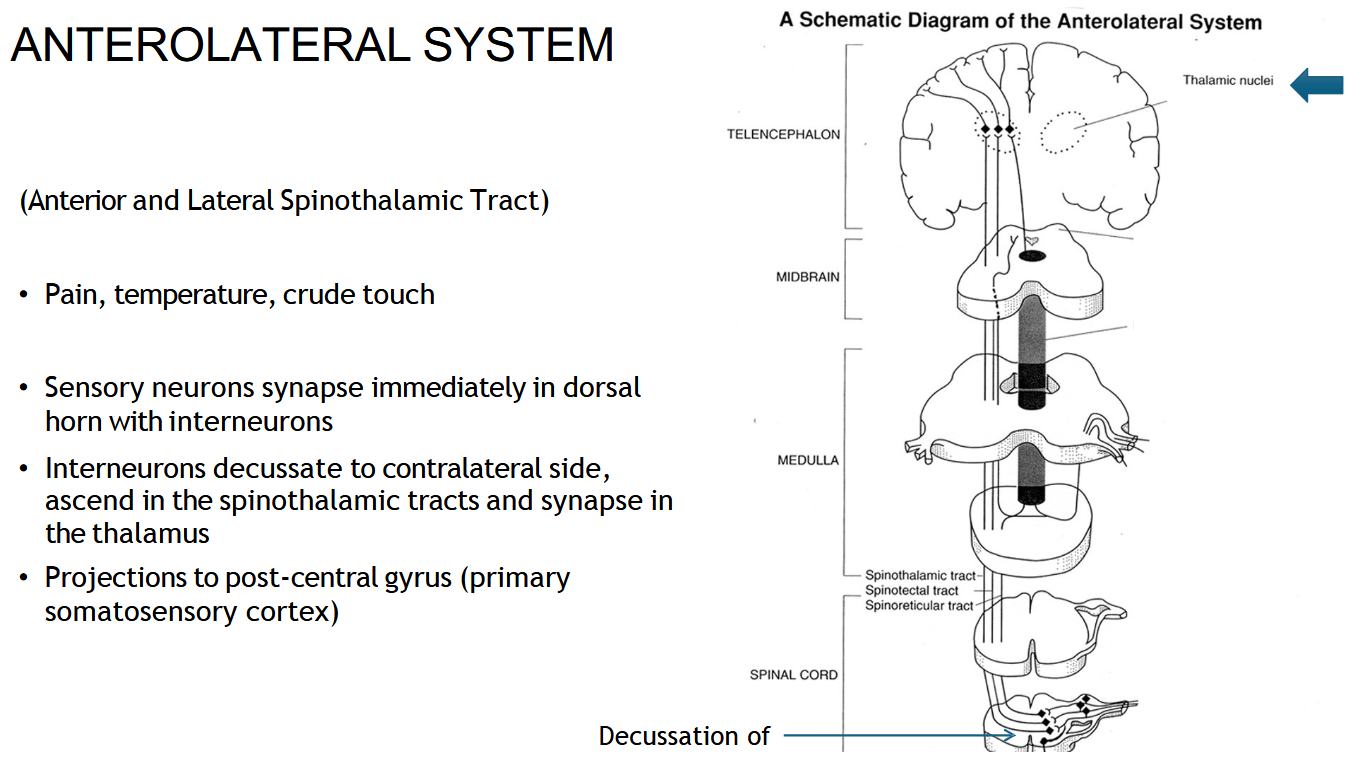
Where does the spinothalamic (Anterolateral) tract cross (decussate)?
In the spinal cord, about 1–2 levels above where it enters.
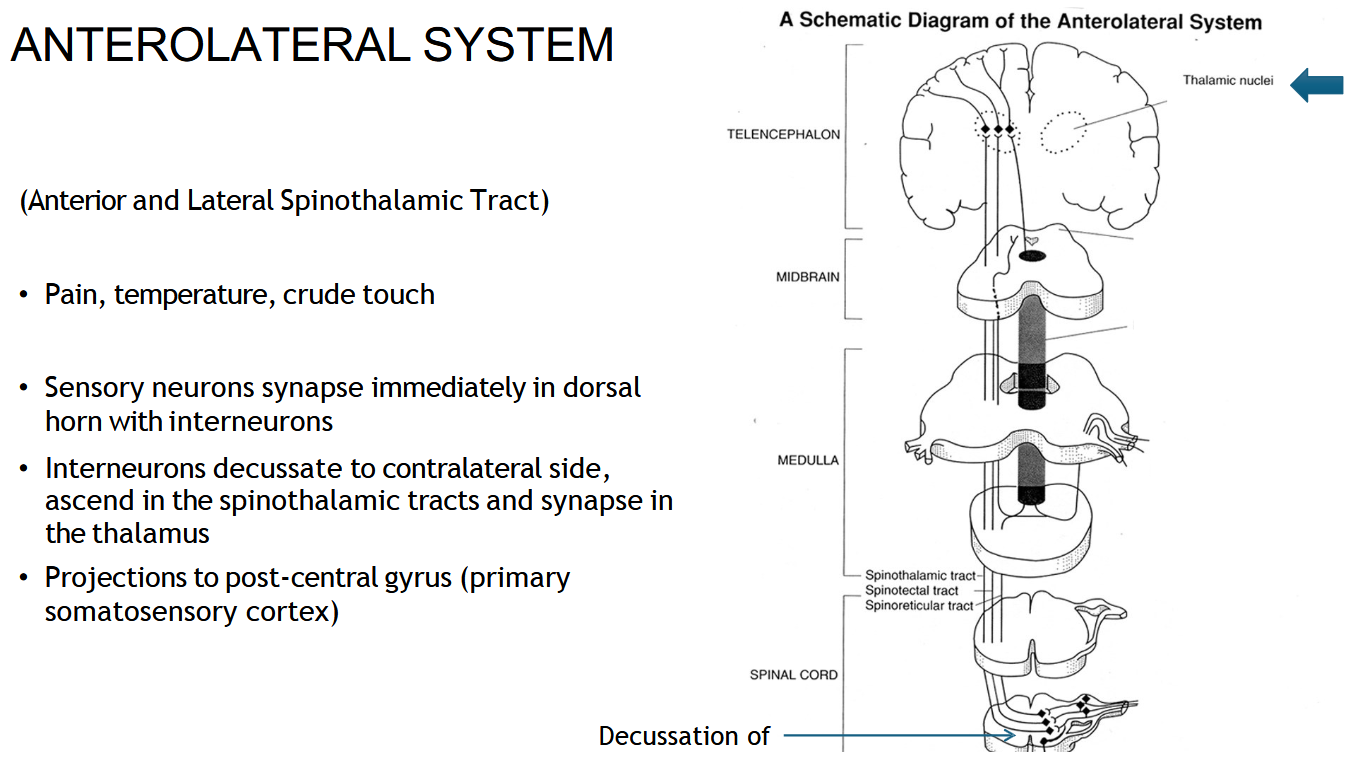
After crossing, which side does the spinothalamic (anterolateral) tract travel up?
The opposite (contralateral) side of the spinal cord.
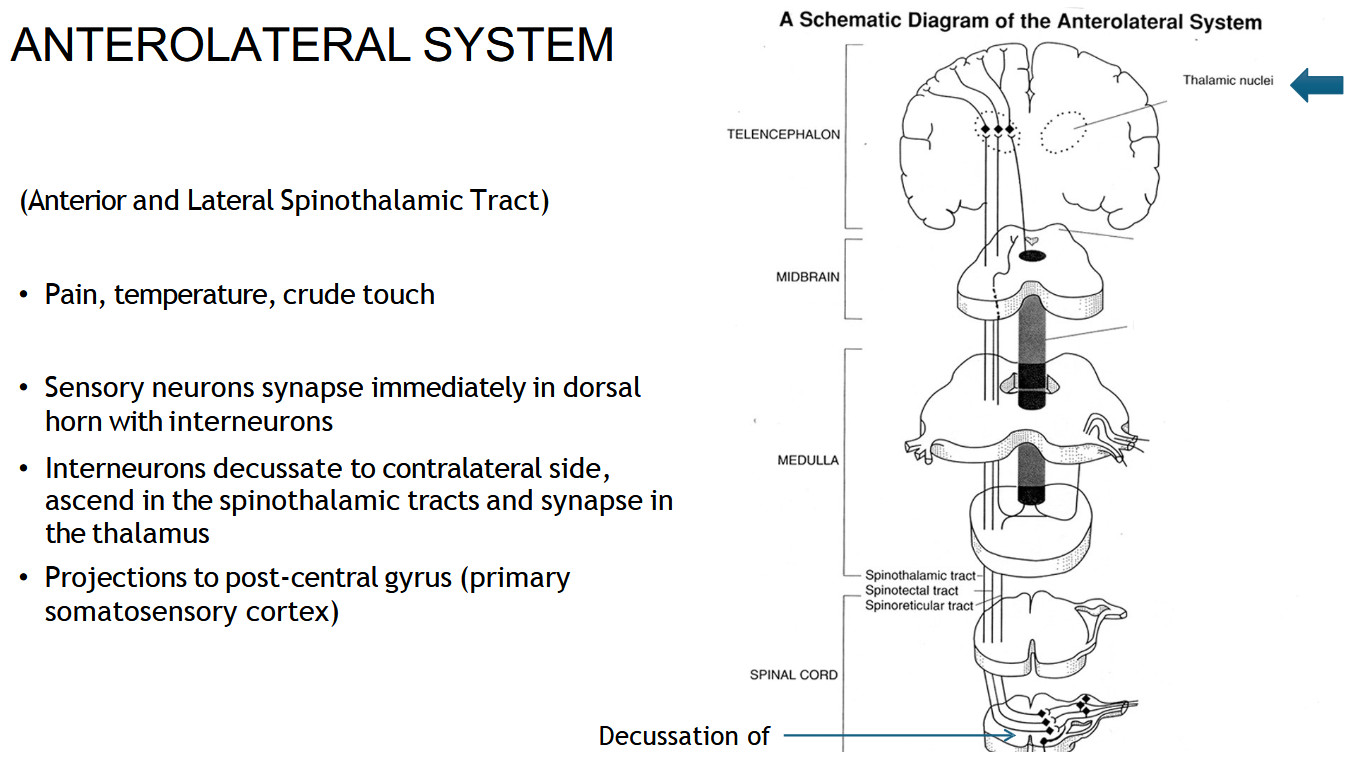
Where does the spinothalamic tract end?
In the thalamus, then the signal goes to the sensory cortex.
What is an easy way to remember the pathway of the spinothalamic tract?
“Pain crosses low and goes high.” (crosses in spinal cord, goes up to brain)
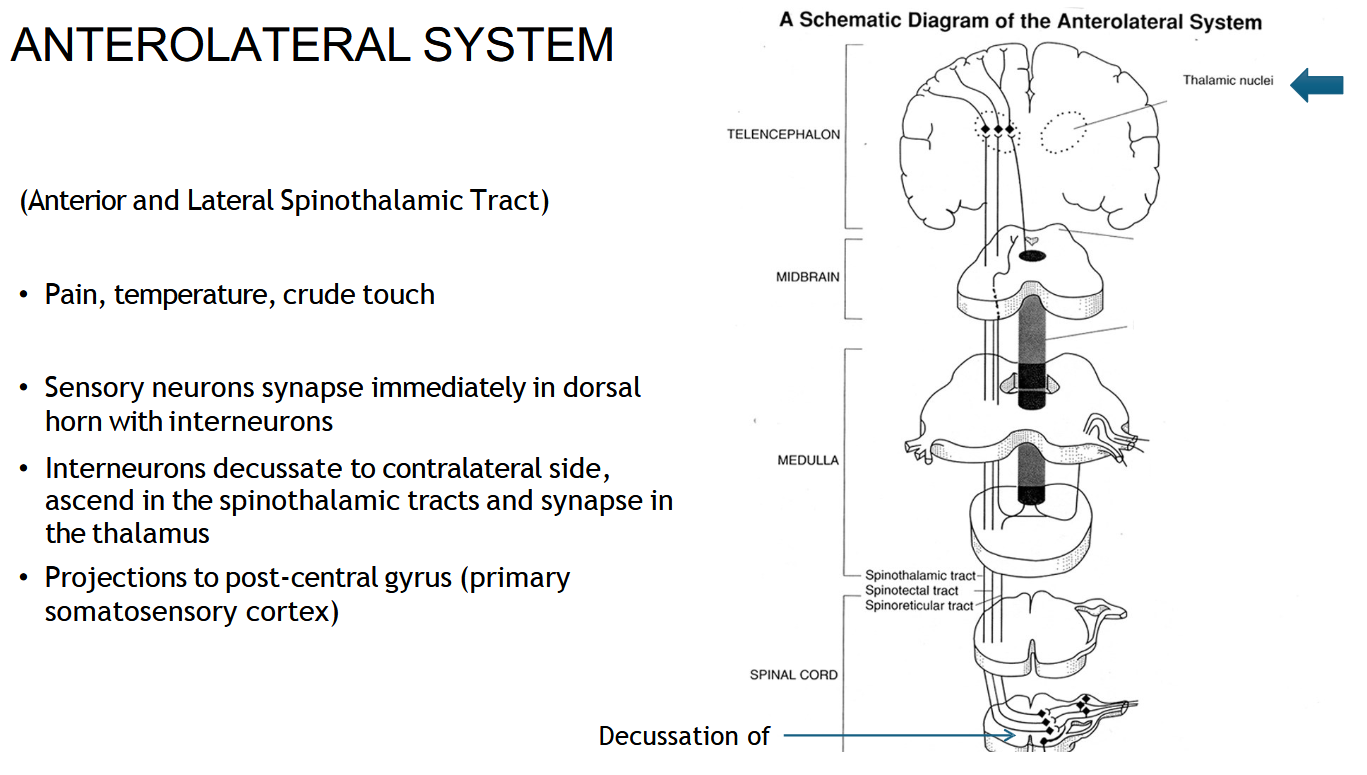
If there’s a right-sided spinal cord injury, which side loses pain and temperature?
The left side (because it already crossed).
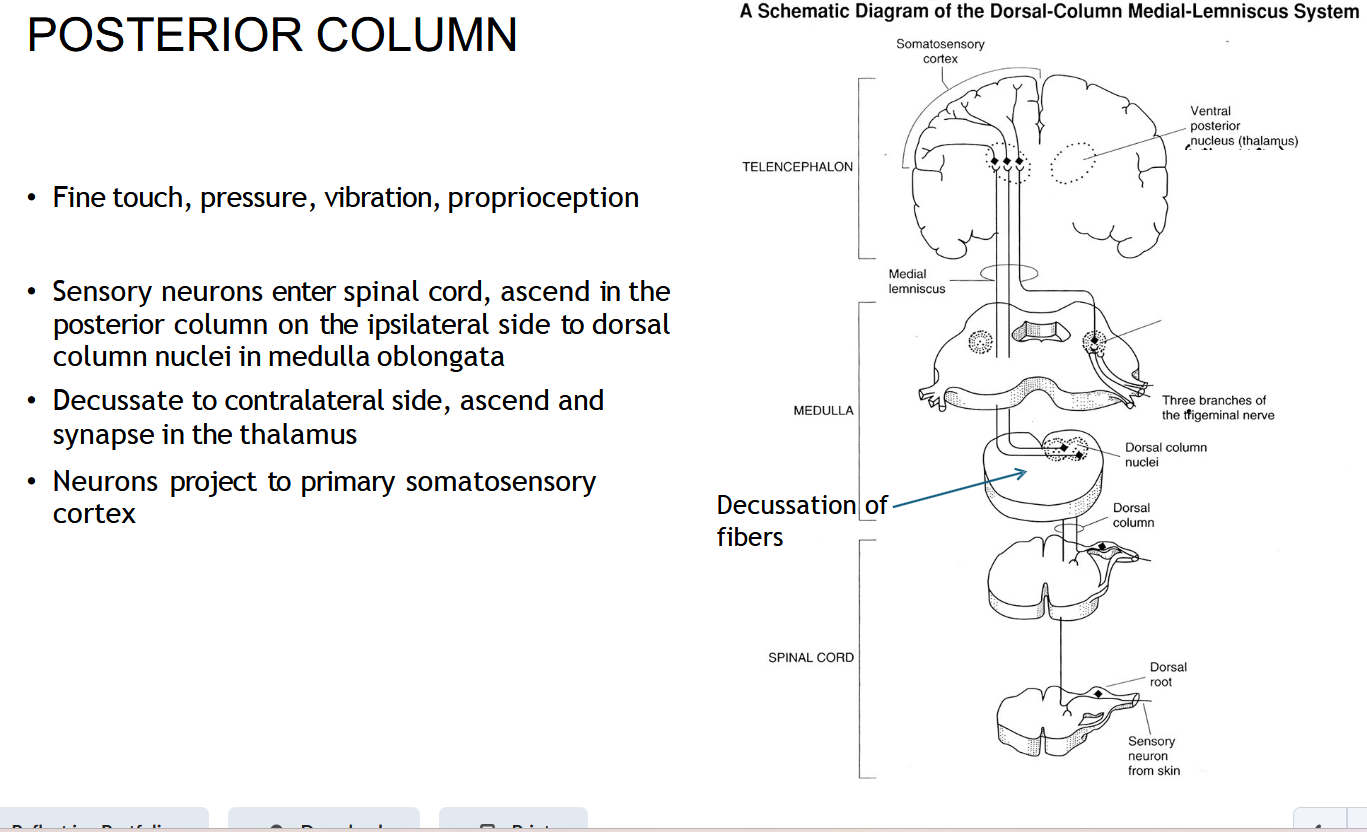
What information does the POSTERIOR COLUMN ( Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus (DCML) carry?
Fine touch, vibration, and proprioception (body position).
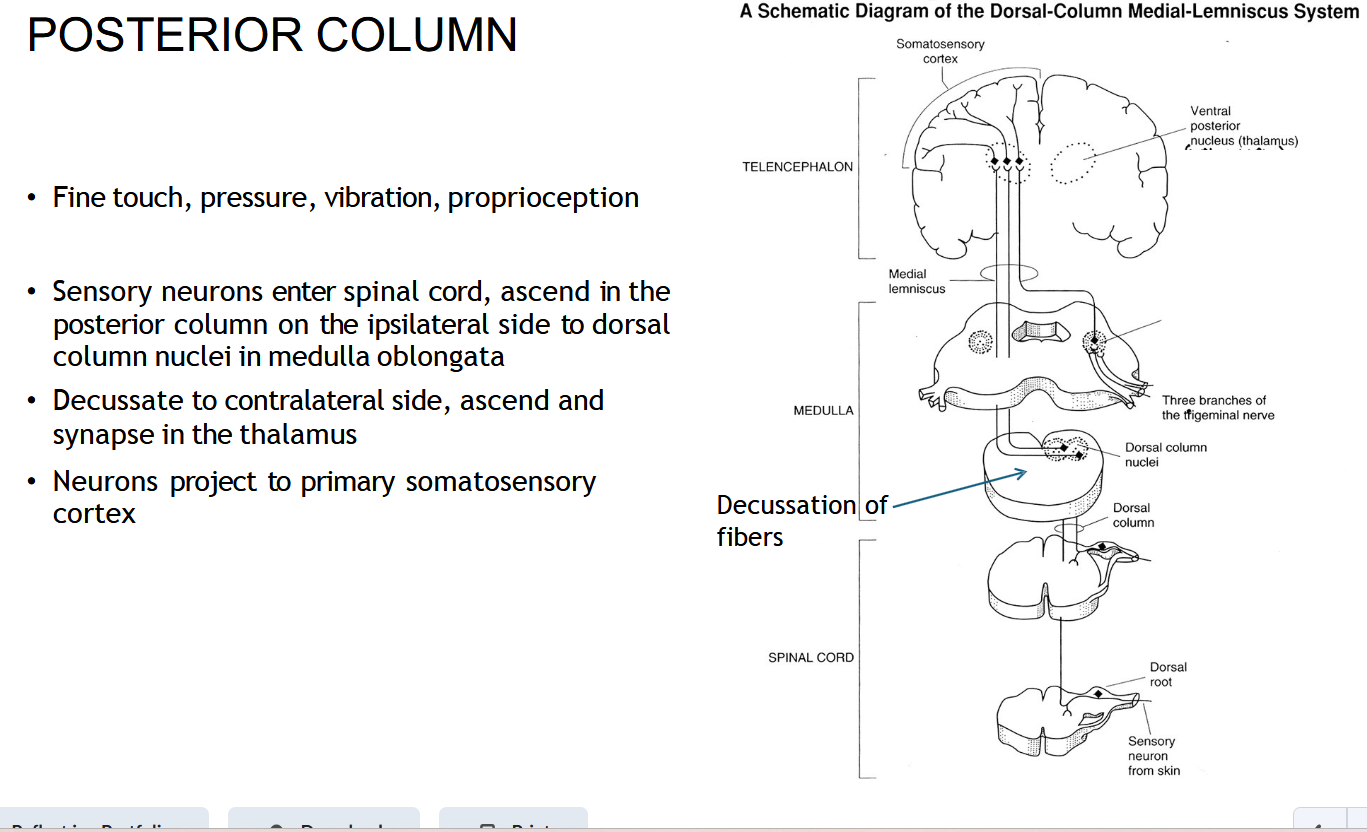
Where does the DCML ( POSTERIOR COLUMN () start?
In sensory neurons entering the spinal cord through the dorsal root.
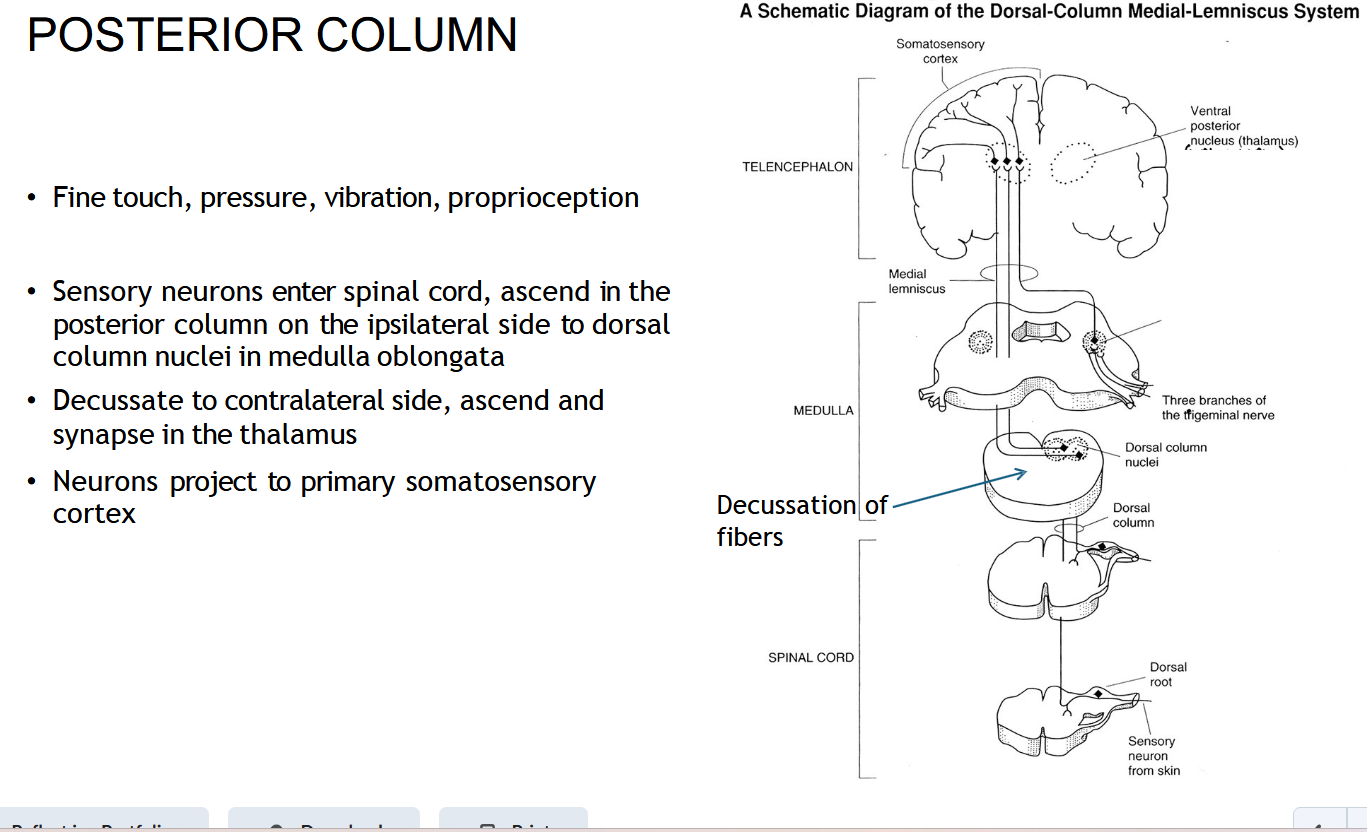
Does the DCML (POSTERIOR COLUMN) Cross right away?
No — it stays on the same (ipsilateral) side until it reaches the medulla.
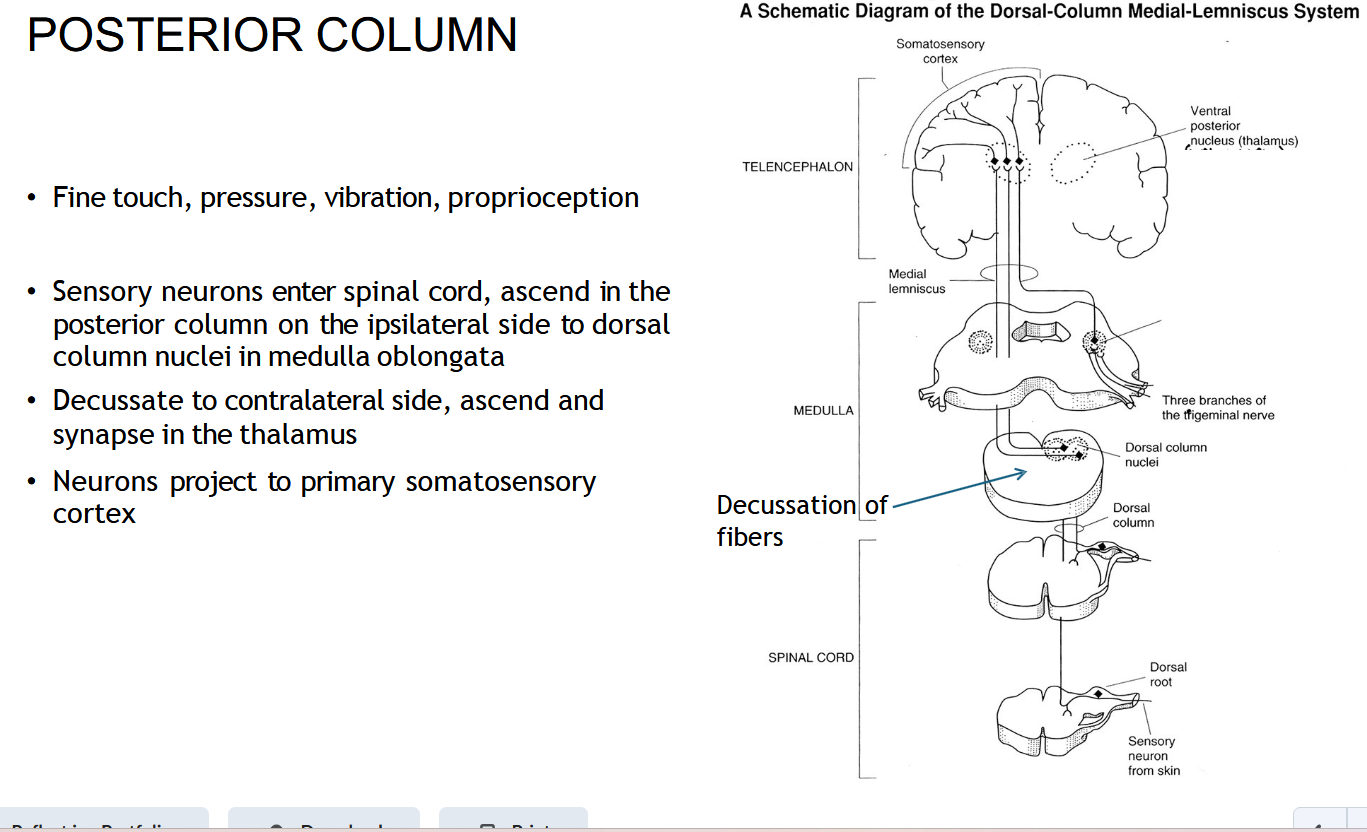
Where does the DCML ( POSTERIOR COLUMN) cross (decussate)?
In the medulla oblongata.
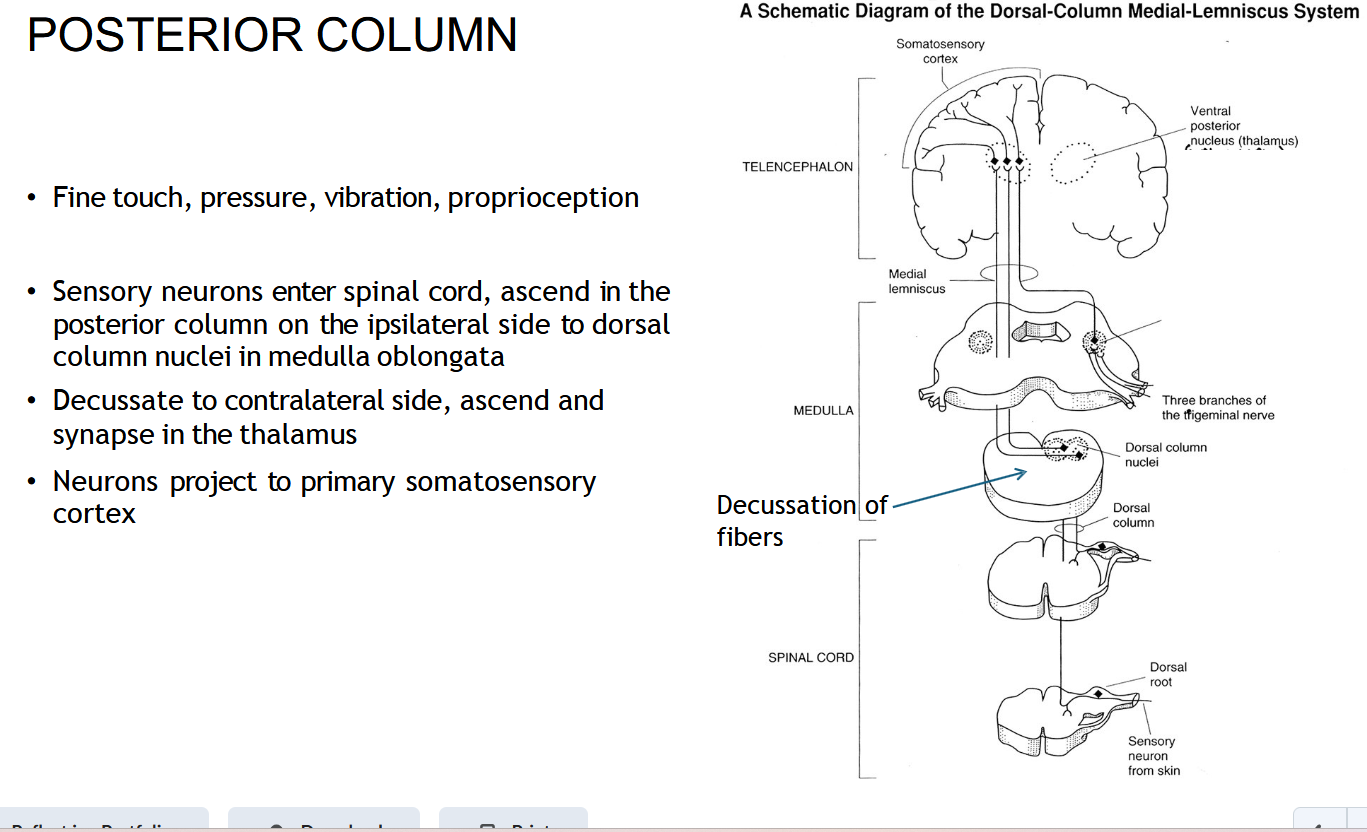
After crossing, where does the DCML ( POSTERIOR COLUMN) go?
To the thalamus, then to the somatosensory cortex.
What is an easy way to remember the pathway of the DCML ( POSTERIOR COLUMN)?
“Fine crosses high.” (Fine touch, crosses in medulla — high up.)
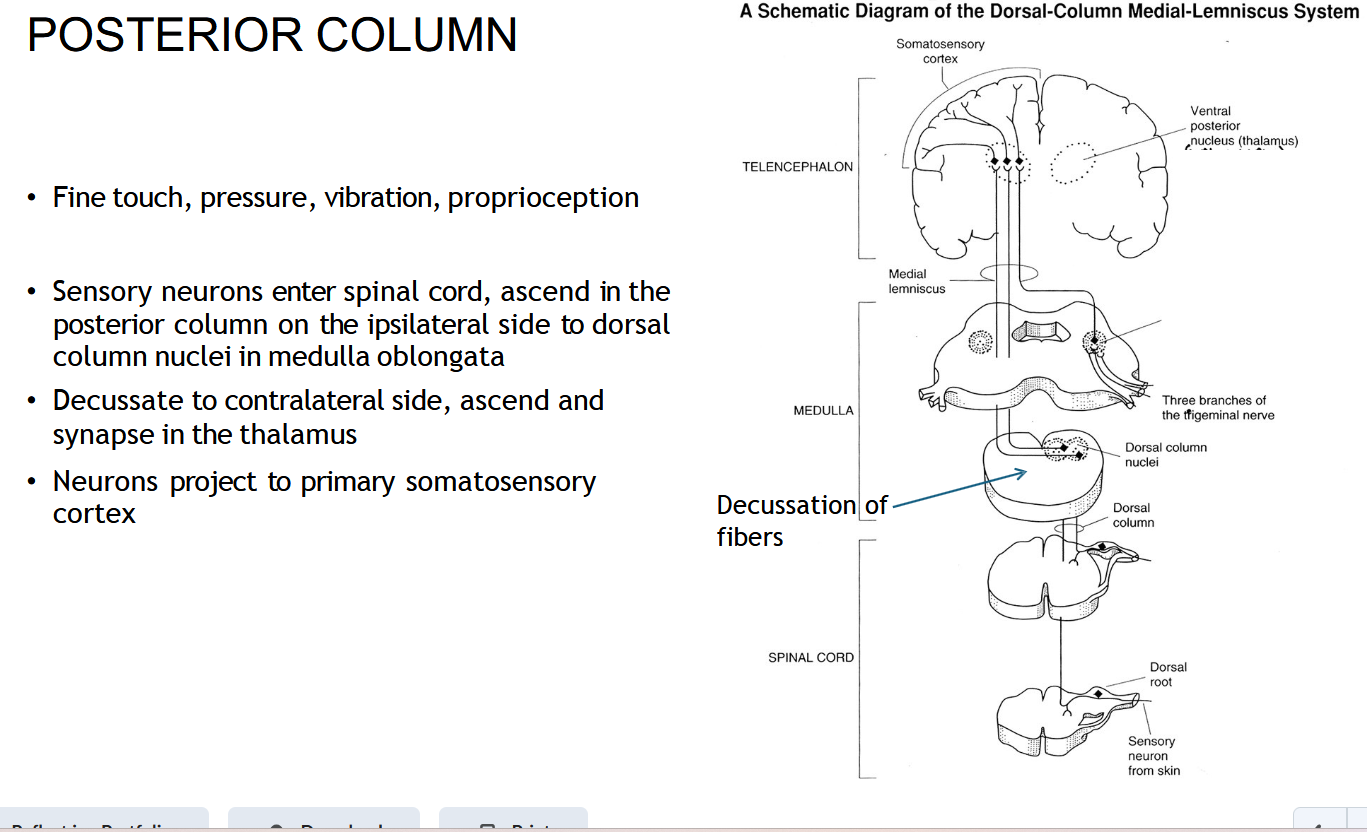
If there’s a right-sided spinal cord injury, which side loses fine touch and vibration?
The right side (because it hasn’t crossed yet).
What’s the main difference between the spinothalamic tract and the DCML?
Spinothalamic crosses in the spinal cord, DCML crosses in the medulla.
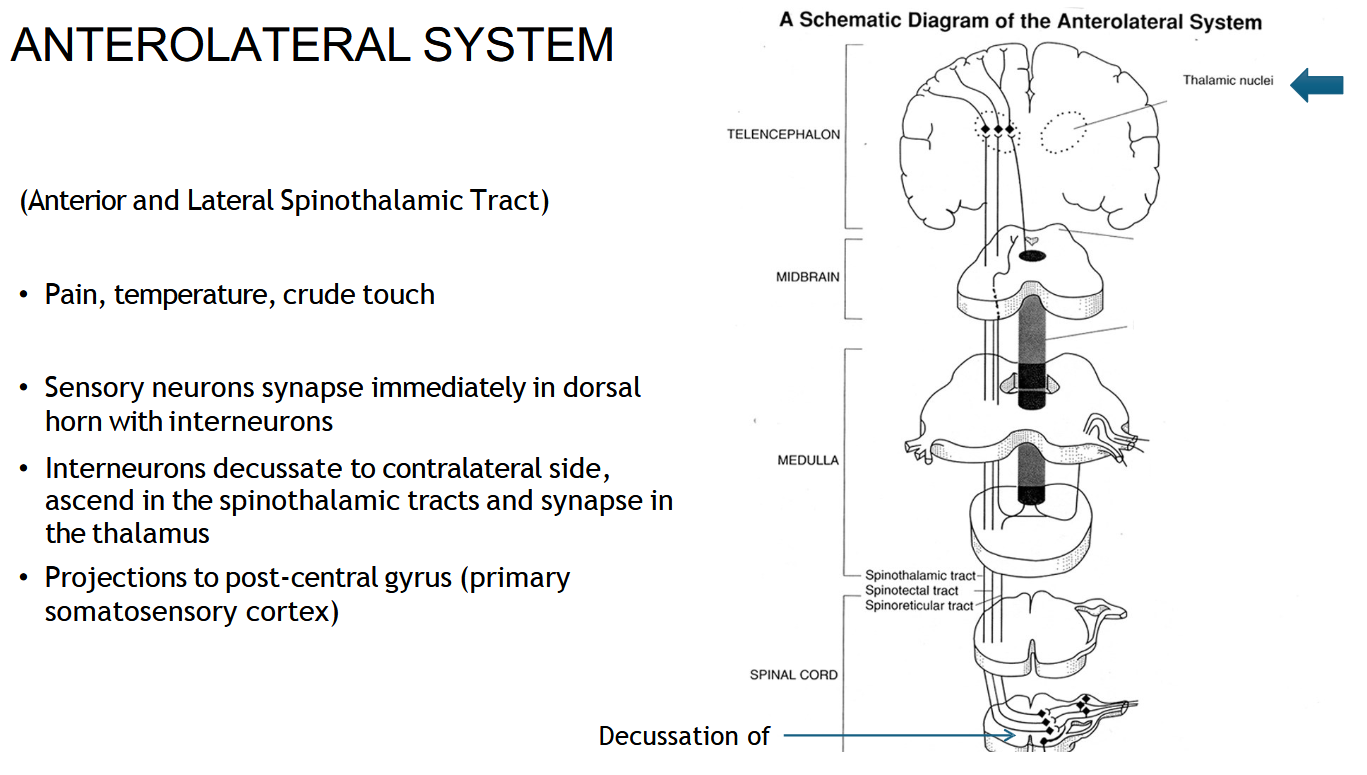
Which tract carries ‘pain and temperature’?
Spinothalamic tract.
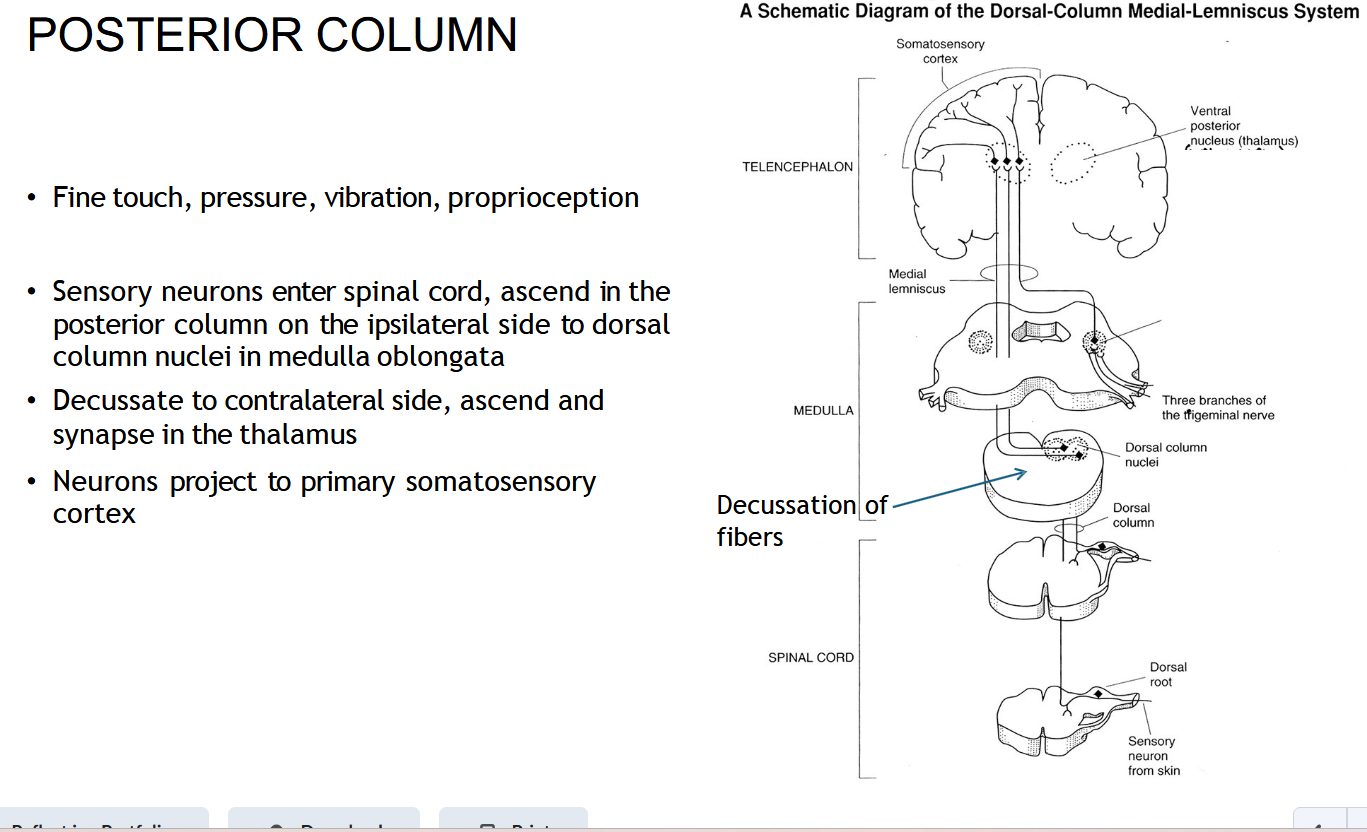
Which tract carries ‘fine touch and vibration’?
Dorsal column–medial lemniscus tract. ( POSTERIOR COLUMN)
What is an easy overall memory phrase for these tracts?
“Pain crosses low, fine crosses high.”
Where do both the spinothalamic tract and DCML eventually end?
In the thalamus, then signals go to the primary somatosensory cortex.
What happens if the thalamus is damaged?
Sensory information from both pathways won’t reach the cortex — leading to loss of sensation on the opposite side of the body.