L30 Microbes & Energy Flow Vocabulary
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on the lecture notes about Microbes & Energy Flow.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Natural environments “unseen majority”
Most organisms can not or have not been isolated in pure culture. Identification now done using genetic ‘fingerprints’. Currently, millions of unique 16 rRNA sequences (molecular barcode) available in databases. Uncultured microbial world is far greater than cultured.
Microbial ecology
The study of interrelationships among microorganisms and their environment.
Traditional microbiology
Was driven by pathology. A lot of microbes cultured and characterised, and mostly identified pathogens or fast growing organisms. Ignoring complex interactions and fact that most organisms live in communities (auxotrophs)
Population
Individual microbial cells of a species proliferate forming this.
Communities
Formed from populations interacting/communicating.
Microbiome
Molecular tools gave rise to this term. All microorganisms, and their genes, within a particular environment (can change microbe behaviour).
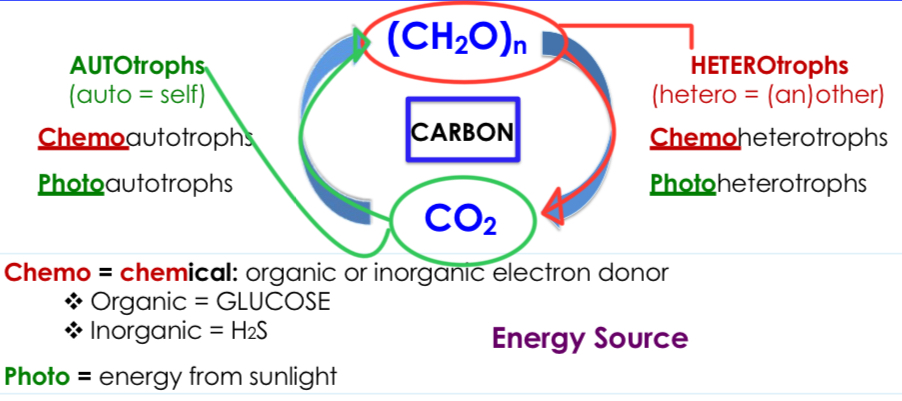
Chemoautotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain energy from chemical compounds (either organic or inorganic) and use carbon dioxide as their carbon source.
Chemoheterotrophs
Microorganisms that obtain energy and carbon from organic chemical compounds.
Photoautotrophs
Microorganisms that use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds.
Photoheterotrophs
Microorganisms that use light for energy but cannot use carbon dioxide as their sole carbon source; they must obtain organic carbon from the environment.
Autotrophs
Primary producers; self-sufficient organisms that fix CO2 and do not require organic carbon.
Heterotrophs
Decomposers; organisms that need fixed carbon and cannot use CO2 directly, depending on primary producers.
Trophic group summary
Redox Reaction
A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred between two reactants allowing for energy transfer in cells.
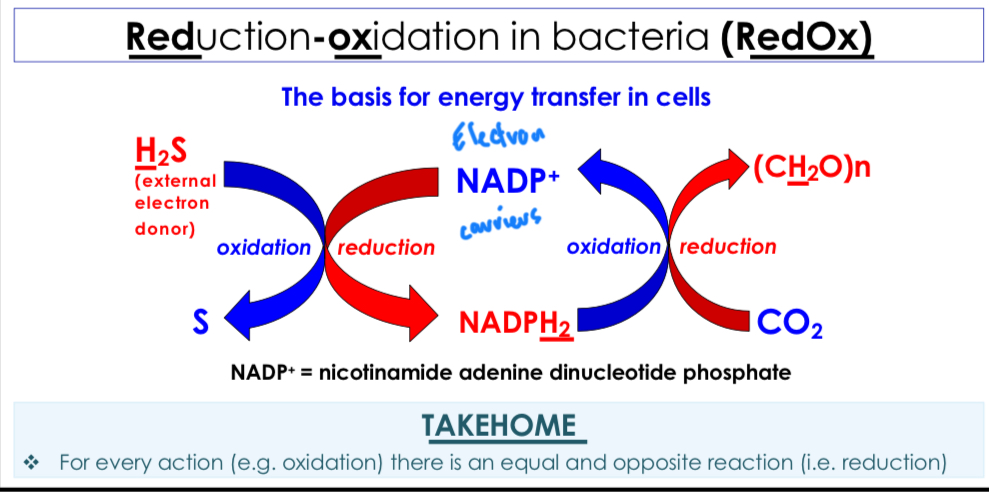
Basis for energy transfer in cell
Energy harvested from environment converted to ‘local currency’ inside cell. NADH/NADPH serve as intermediates to transfer energy inside of cell. NAD+ and NADH facilitate redox reactions without being consumed (recycled)
Hoe so many different microbes share the same metabolism
Light is a common resource, microbes avoid compition by tuning their antenna to different wave lengths.
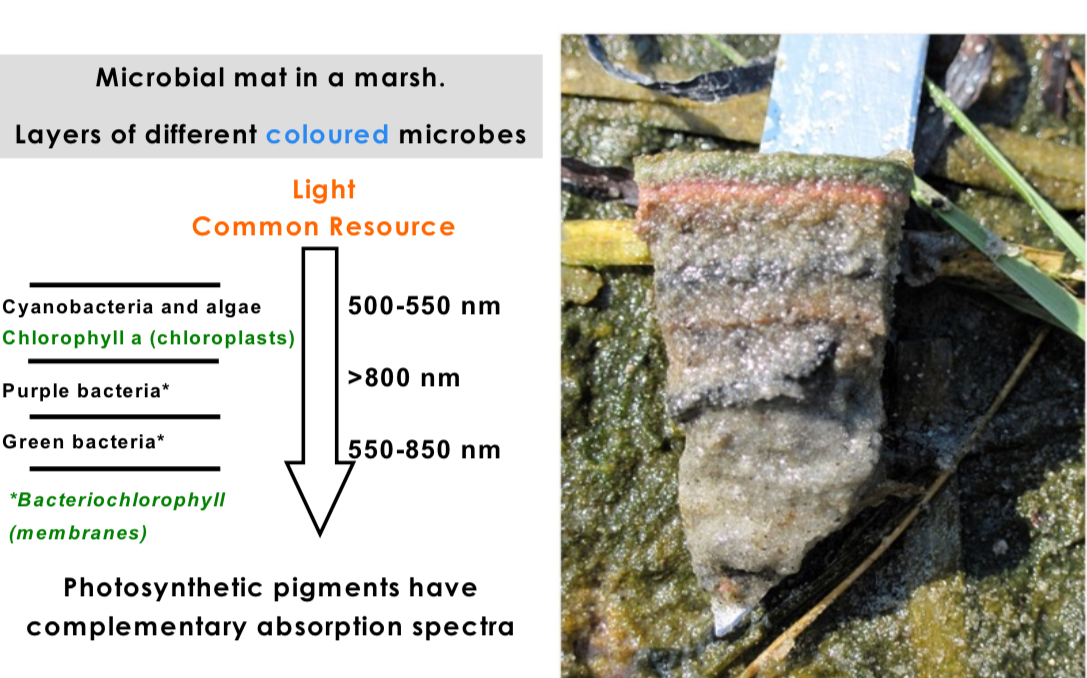
Importance of redox and metabolism
Different redox gradients select for different microbes. Reox reactions control the flow of energy, and breakdown/build up of molecules.
Organisms need
Energy and carbon (building vlocks). Energy must be harvested from something, if one energy source is missing there must be another one. Find it and communities redox profile will match it.