Biology - Patterns of Inheritance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
Last updated 6:22 PM on 1/29/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
1
New cards
the science of heredity:
genetics
2
New cards
Gregor Mendel was from:
Austria
3
New cards
What did Mendel discover?
the basic principles of heredity by breeding garden peas
4
New cards
what is another name for mendel?
the father of genetics
5
New cards
what are some advantages of using pea plants to study?
distinct features, controlled mating, gamete-producing organs, and cross-pollination
6
New cards
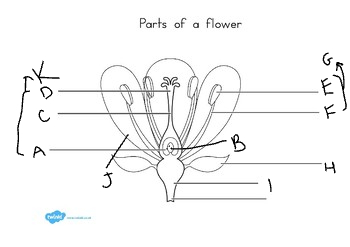
A:
ovary
7
New cards
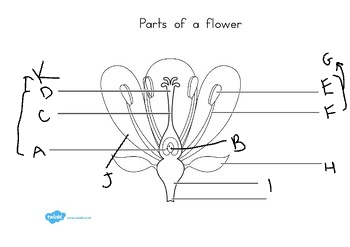
B:
ovule
8
New cards
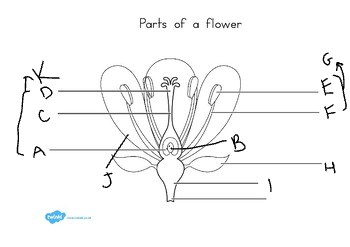
C:
style
9
New cards
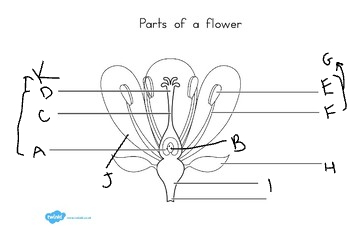
D:
stigma
10
New cards
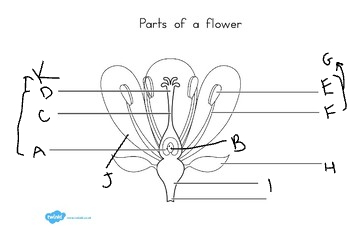
E:
anther
11
New cards
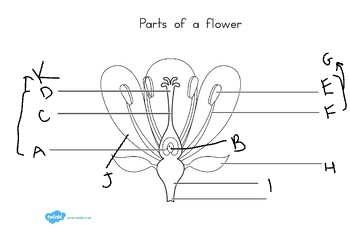
F:
filament
12
New cards
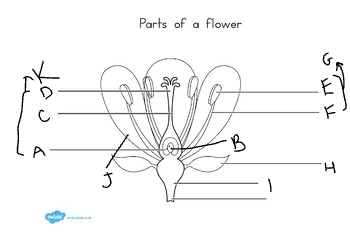
G:
stamen
13
New cards
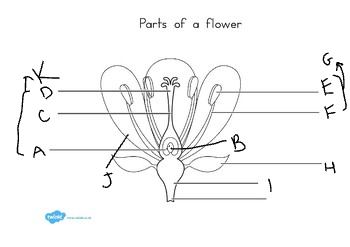
H:
sepal
14
New cards
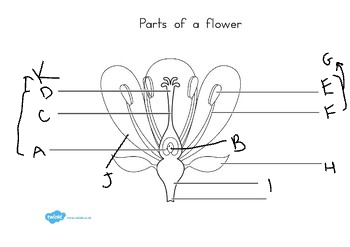
I:
receptacle
15
New cards
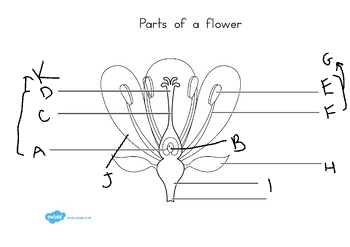
J:
petal
16
New cards
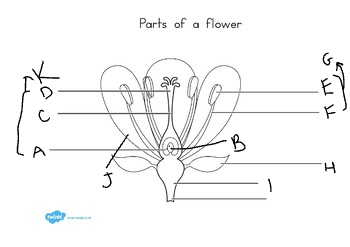
K:
carpel
17
New cards
at the base of the flower, are usually green, enclose the flower before it opens:
sepal
18
New cards
these are important in attracting pollinators:
petals
19
New cards
the stamen is made up of:
filament and anther
20
New cards
stamens are the ____ part:
male
21
New cards
what grows in the anther?
pollen grains
22
New cards
the carpel consists of:
style, stigma, and ovary
23
New cards
usually, plants:
self-pollinate
24
New cards
how did mendel ensure that self-pollination would occur?
he covered the flower with a bag.
25
New cards
how did mendel ensure that cross-fertilization would occur?
cut off the stamen of one plant and dusted its carpel powder with another plant.
26
New cards
true breeds are:
offspring with identical traits to those of the parents: homozygous
27
New cards
in mendels experiment, the true-breed generation was called:
P generation
28
New cards
in mendels experiment, the hybrid offspring of the P generation were called:
F1 generation
29
New cards
F1 stands for:
first filial
30
New cards
F2 was a result of:
F1 self-pollinating
31
New cards
what phenotypic ratio did mendel discover in the F2 generation?
3 purple to 1 white flower
32
New cards
purple is a ___ trait, while white is a ____ trait
dominant, recessive
33
New cards
flower color ratio:
3\.15 purple: 1 white
34
New cards
flower position ratio:
3\.14 axial: 1 terminal
35
New cards
seed color ratio:
3\.01 yellow: 1 green
36
New cards
seed shape ratio:
2\.96 round: 1 wrinkled
37
New cards
pod shape ratio:
2\.95 inflated: 1 constricted
38
New cards
pod color ratio:
2\.82 green: 1 yellow
39
New cards
stem length ratio:
2\.84 tall: 1 short
40
New cards
mendel’s model is made up of:
four concepts
41
New cards
mendel’s first concept:
alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters
42
New cards
allele:
alternate variation of a gene
43
New cards
mendel’s second concept:
for each character an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent
44
New cards
mendel’s third concept:
if the two alleles at a locus differ, then the dominant allele determines the organism’s appearance, and the recessive allele has no noticeable effect on appearance
45
New cards
upper case letters represent these alleles:
dominant
46
New cards
lower case letters represent these alleles:
recessive
47
New cards
mendel’s fourth concept:
the sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited trait because allele pairs separate from each other during the production of gametes.
48
New cards
mendel’s fourth concept is known today as:
the law of segregation
49
New cards
a punnet square is used to:
show the results of random fertilization
50
New cards
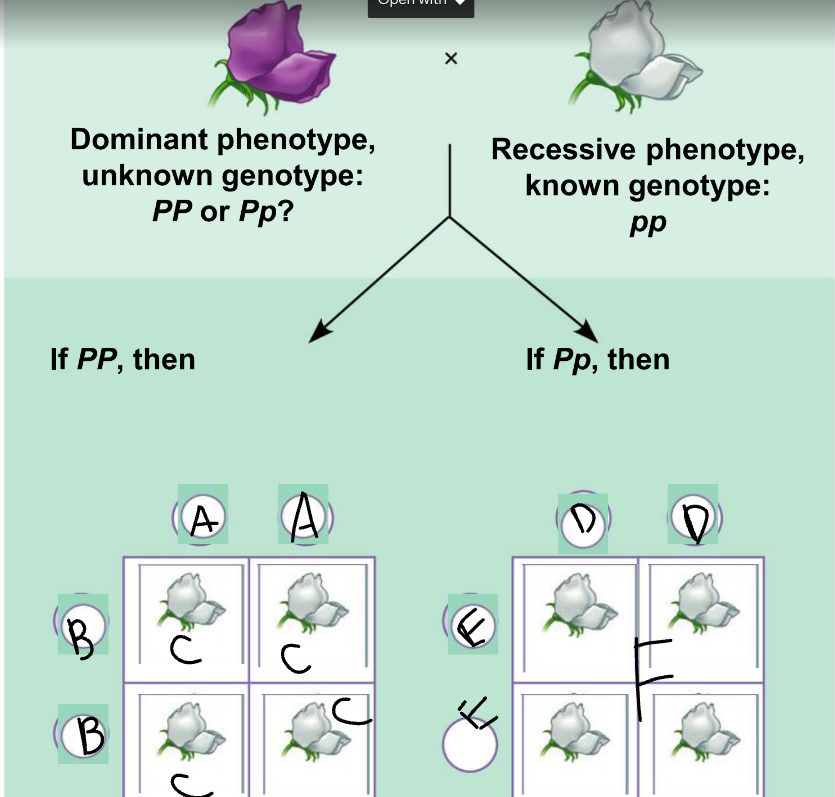
A:
PP
51
New cards
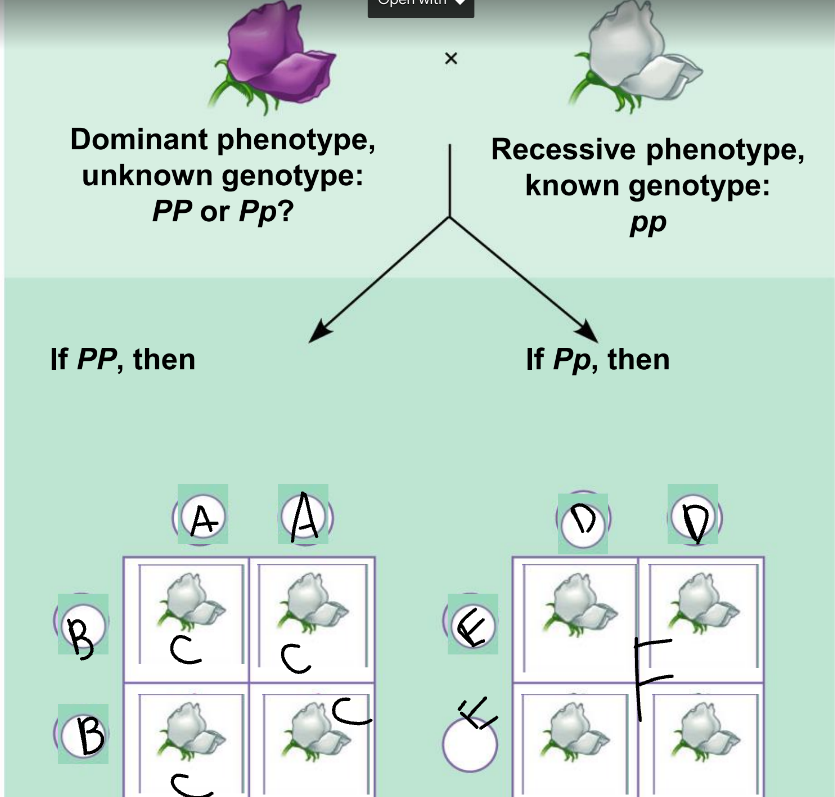
B:
pp
52
New cards
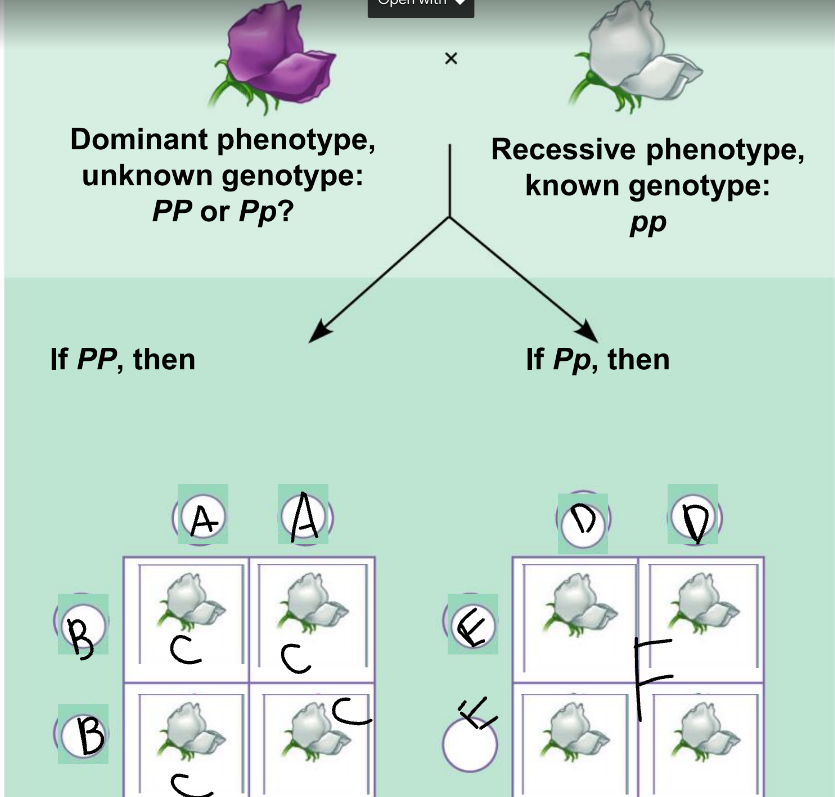
C:
Pp
53
New cards
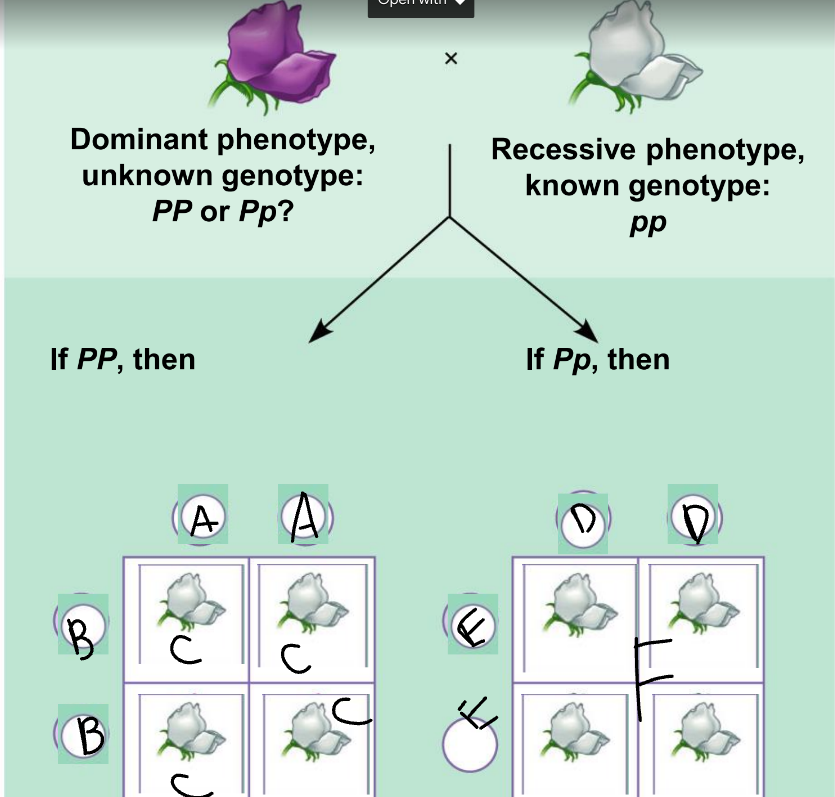
D:
Pp
54
New cards
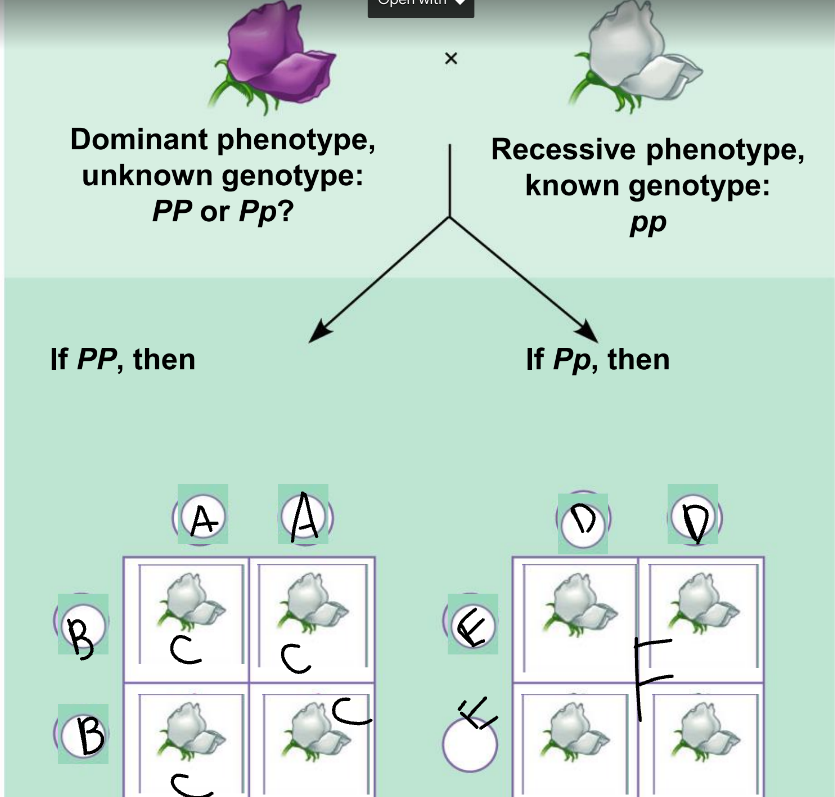
E:
pp
55
New cards
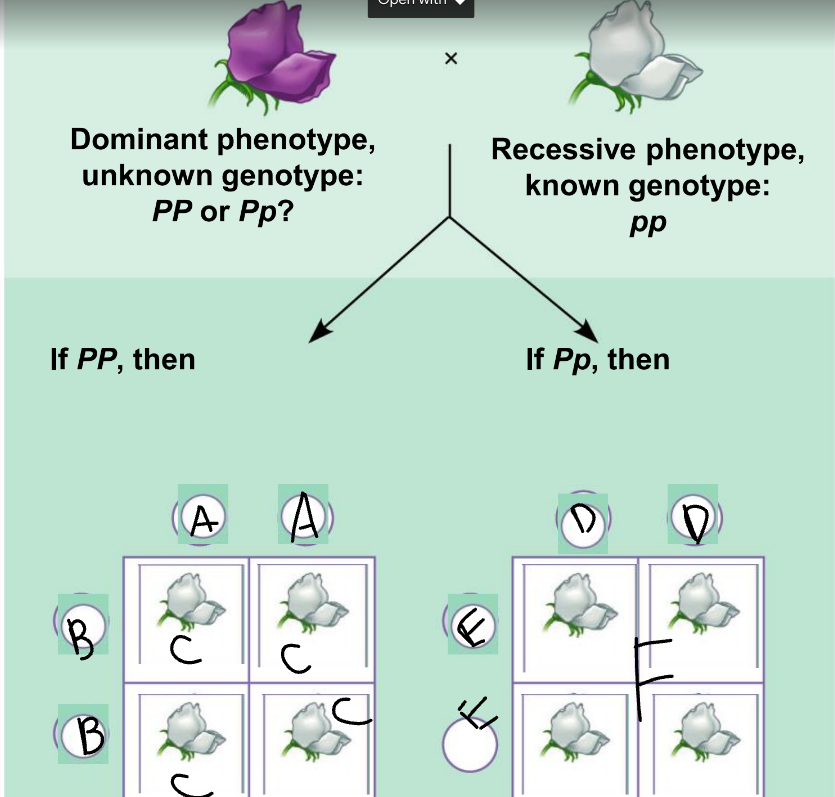
F:
Pp and pp
56
New cards
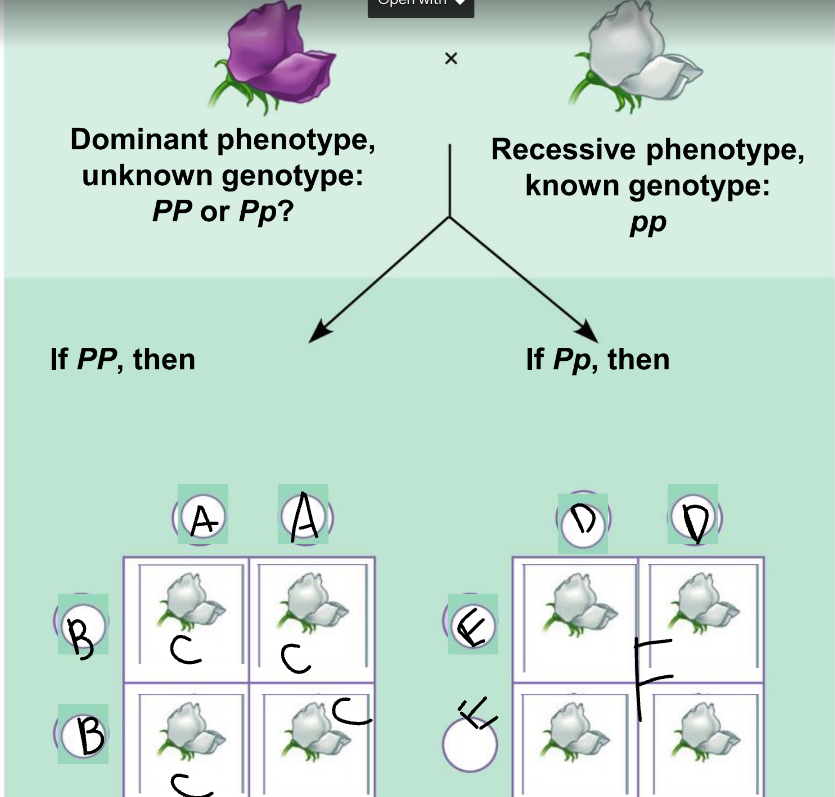
phenotypic ratio of the left:
100% purple
57
New cards
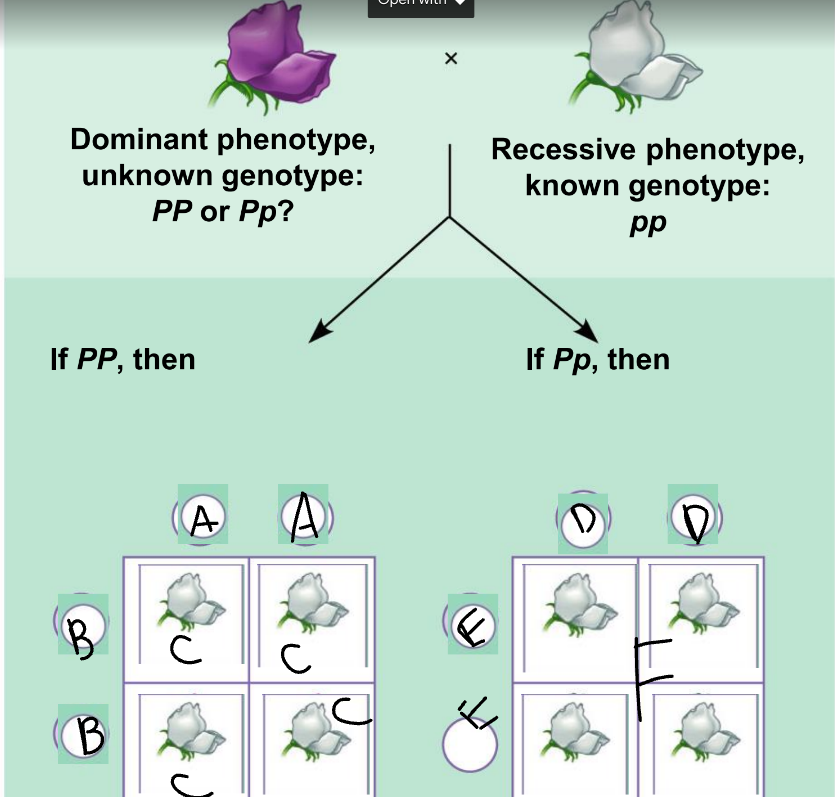
genotypic ratio of the left:
4 Pp
58
New cards
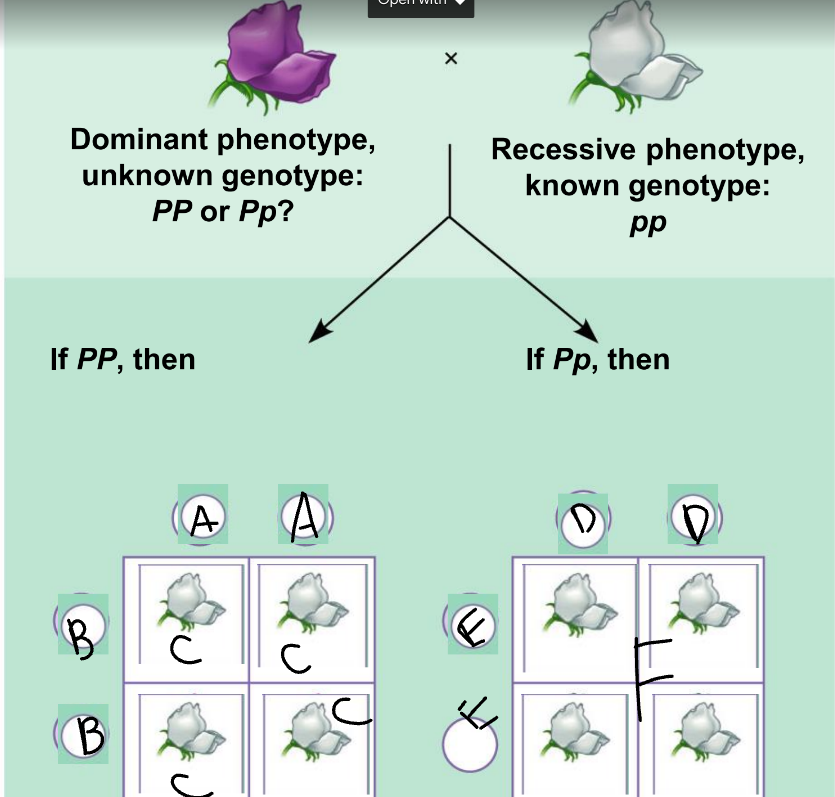
phenotypic ratio of the right:
50% purple, 50% white
59
New cards
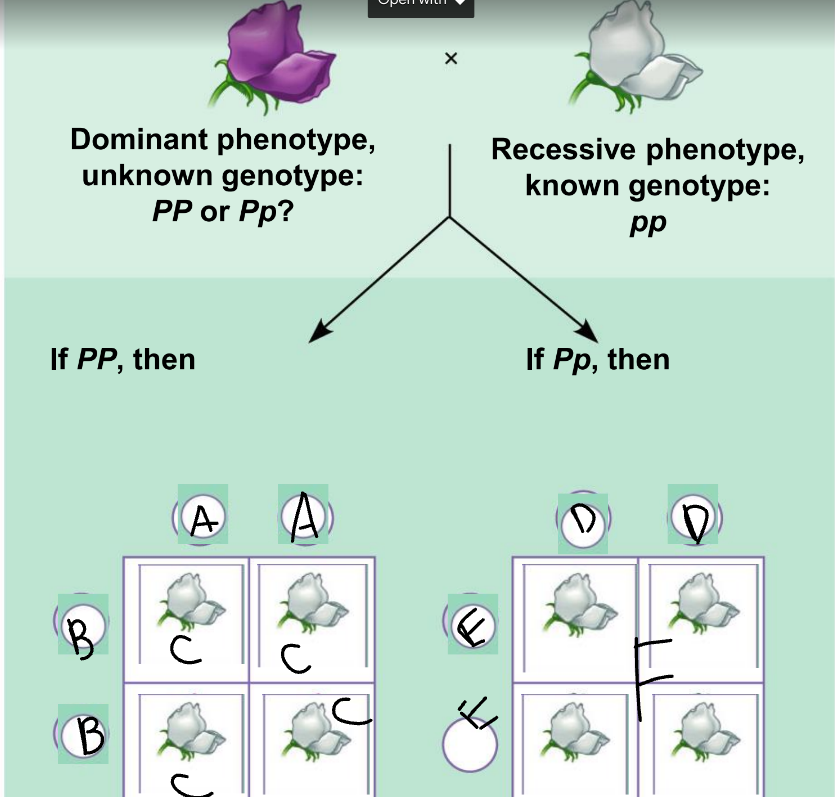
genotypic ratio of the right:
2 Pp: 2 pp
60
New cards
a monohybrid cross is a:
one trait cross
61
New cards
a homozygous organism has:
two identical alleles
62
New cards
a heterozygous organism has:
two different alleles
63
New cards
an organism’s physical appearance:
phenotype
64
New cards
an organism’s genetic makeup:
genotype
65
New cards
you can determine the genotype of an organism with the dominant phenotype by carrying out a:
testcross
66
New cards
in a test cross:
an individual of unknown genotype mates with a recessive homozygous individual
67
New cards
the law of independent assortment states that:
each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation
68
New cards
genes that are located near each other on the same chromosome are called:
linked genes
69
New cards
non-linked alleles exhibit:
independent assortment
70
New cards
linked alleles exhibit:
dependent assortment
71
New cards
the rule of addition states:
the probability that an event can occur in two or more alternative ways is the sum of the separate probabilities of the different ways.
72
New cards
the multiplication rule states:
the probability that two or more independent events will occur together is the product of their individual probabilities
73
New cards
True or False: dominant alleles are always more common:
False
74
New cards
extra fingers and toes are called:
polydactly
75
New cards
A person with achondroplasia has a __% chance of passing the condition on to any children.
50
76
New cards
Huntington’s disease is a degenerative disease of the:
nervous system
77
New cards
People who exhibit Huntington’s disease’s symptoms usually die __ to __ years later:
10, 20
78
New cards
this is the most common lethal genetic disease in the united states:
cystic fibrosis
79
New cards
symptoms of cystic fibrosis:
excessive secretion of very thick mucus from the lungs, pancreas, and other organs
80
New cards
Sickle-cell disease affects __out of __ African-Americans
1,400
81
New cards
sickle cell disease is caused by the _____ of a single amino acid in the hemoglobin sequence:
substitution
82
New cards
sickle cell disease symptoms:
physical weakness, pain, organ damage, paralysis
83
New cards
mating of close relatives:
inbreeding
84
New cards
close relatives’ offspring is more likely to have a genetic disorder because:
both relatives are more likely to carry the same recessive allele
85
New cards
sex linked genes are located on:
the sex chromosomes
86
New cards
X-O system (which organisms have it, male, female)
some insects, XO, XX
87
New cards
Z-W system (which organisms have it, male, female)
some fishes, birds, and butterflies, ZZ, ZW
88
New cards
a pedigree is:
a family tree that describes the interrelationships of parents and children
89
New cards
pedigrees can be used to:
trace inheritance patterns and make predictions about future offspring
90
New cards
fathers transmit their X and Y alleles to which children?
X allele to daughter, Y allele to son
91
New cards
mothers transmit their X alleles to which children?
both children get one X allele
92
New cards
squares in pedigrees mean:
male
93
New cards
circles in pedigrees mean:
female
94
New cards
if an affected individual has 2 unaffected parents, the disease is:
recessive
95
New cards
founding parents:
male and female in the first generation
96
New cards
founding children:
children of the founding parents
97
New cards
when an affected founding daughter has two unaffected parents, the disease is:
autosomal recessive
98
New cards
when an affected founding son has two unaffected parents, the disease is:
recessive (autosomal or x-linked)
99
New cards
when an affected non-founding son has two unaffected parents, the disease is:
x-linked recessive
100
New cards
when an affected son has a non-founding father who is also affected, the disease is:
autosomal dominant