d. Knee Pathologies
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
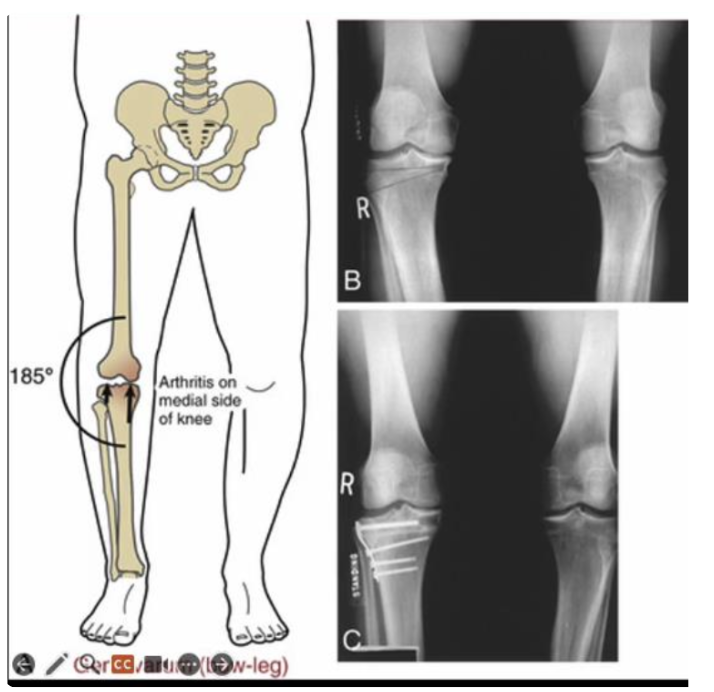
What is the vicious cycle in Genu Varum (bow-legged) deformity?
Deformity →
increased medial joint loading →
greater loss of joint space →
greater tibial adduction →
increased strain on LCL →
increased medial joint load
What management strategies are used for Genu Varum?
High tibial (wedge) osteotomy
valgus knee brace
lateral wedge insole
gait modification
decrease walking speed
strengthen glute max & TFL
How much does varus torque increase at the knee during walking in Genu Varum, and how does it affect arthritis risk?
20% increase in varus torque → 6-fold increase in risk of medial compartment arthritis
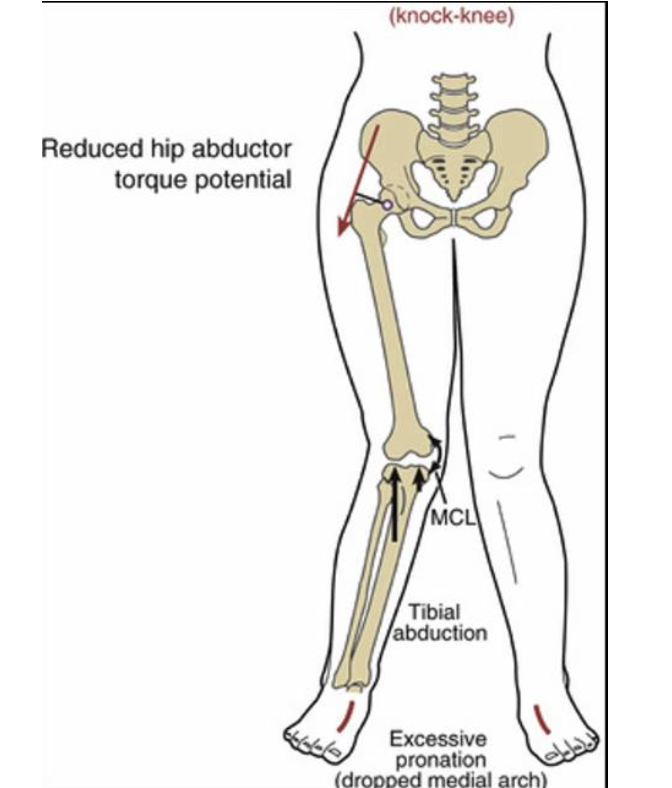
What are the detrimental effects of Genu Valgum (knock-kneed)?
ACL stress
MCL & medial capsule stress
patellar mal-tracking
lateral compartment osteoarthritis (OA)
possible knee replacement surgery
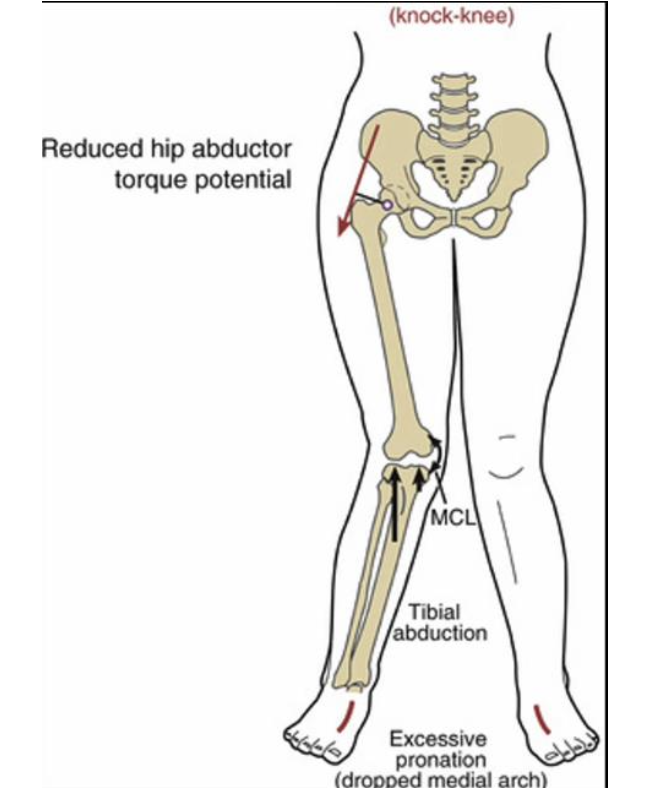
What are some potential causes of Genu Valgum?
Previous injury
genetic predisposition
high BMI
ligament laxity
weak hip abductors
excessive foot pronation
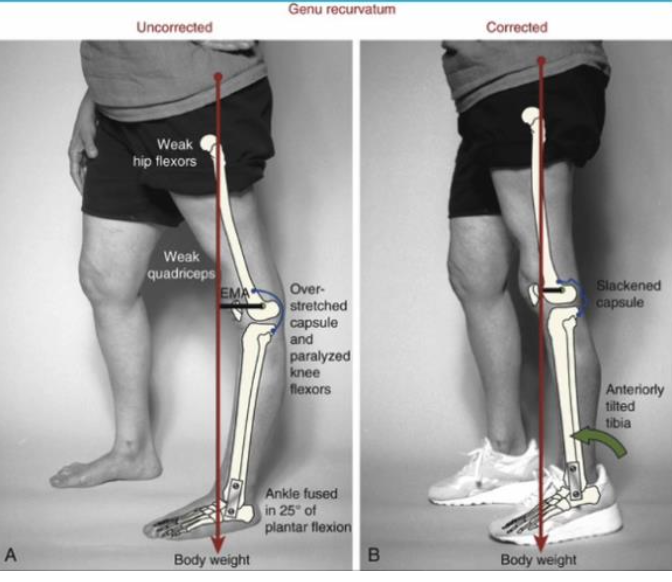
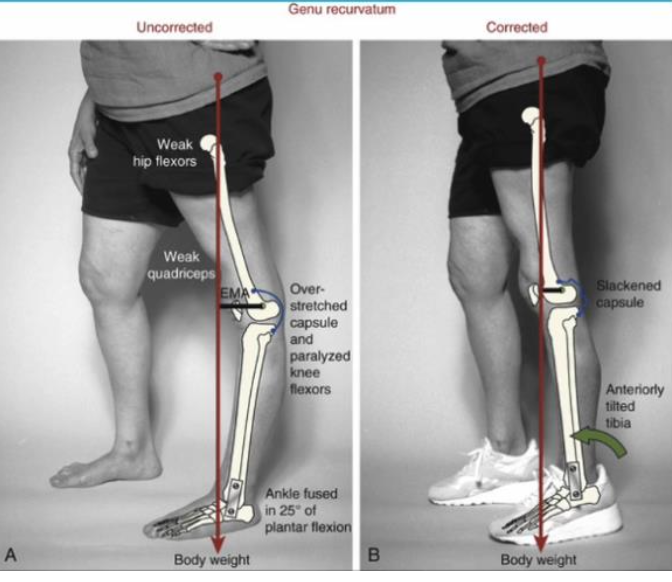
What defines Genu Recurvatum?
Knee hyperextension >10 degrees beyond neutral
what is normal knee hyperextension?
5-10° beyond neutral
How does gravity affect the knee in normal hyperextension?
Gravity creates a slight extension torque that helps lock the knee in hyperextension, allowing the quadriceps to relax
This is opposed by passive tension in the:
posterior capsule
knee flexors
gastrocnemius
What causes Genu Recurvatum?
Posterior structure laxity
Chronic overpowering/excessive knee extensor torque due to poor postural control
Neuromuscular disease (spastic quads or paralyzed/weak knee flexors)
What is Jumper’s Knee (Patellar Tendinopathy)?
Chronic pain in the patellar ligament, common in athletes who do repetitive explosive jumping
no inflammation so it is a “-osis” or “-opathy,” not “-itis”
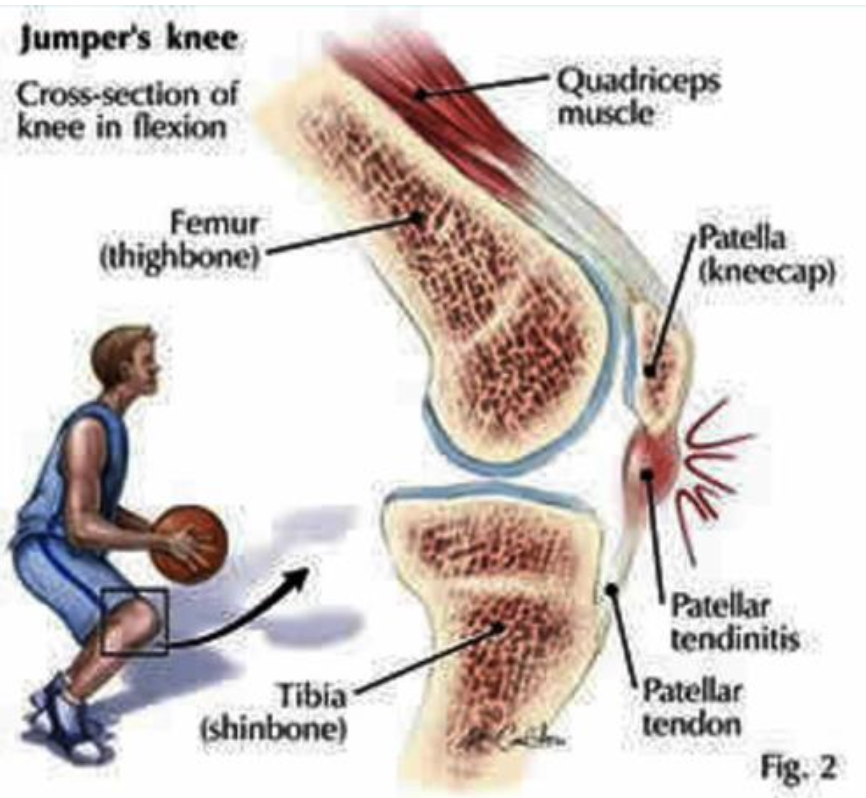
Which athletes are most commonly affected by Jumper’s Knee?
Basketball and volleyball players (those who perform explosive and repetitive jumping)
Chase Budinger couldn’t chase or jump the volleyball or basketball ‘cause his patellar tendon/lig took a fall

What extrinsic factors contribute to Jumper’s Knee?
Training intensity
Playing surface
Footwear
What intrinsic factors contribute to Jumper’s Knee?
patellar hypermobility
patella alta
male gender
Strength
endurance
flexibility
skill level
tendon elasticity
body weight & height
How much force can the patellar ligament experience during landing from a jump?
Up to 7x body weight

What biomechanical factors help disperse kinetic injury when landing a jump?
DF rate and magnitude
eccentric activation of quadriceps and PFs
What does PFPS stand for?
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
What is Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)?
Diffuse peripatellar or retropatellar pain with insidious onset
spread-out pain around and behind patella. not sharp
worse with
squatting
stair climbing
prolonged sitting with knees flexed (movie goers sign)
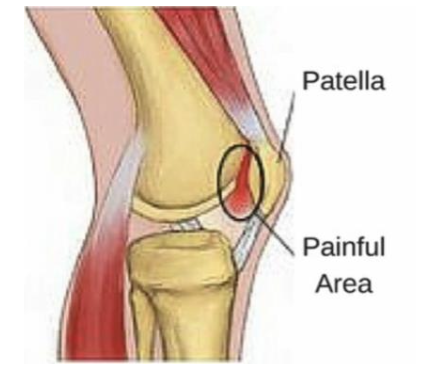
What activities worsen PFPS pain?
Squatting
Stair climbing
Prolonged sitting with knees flexed (movie goers sign)
What are some causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome?
Genetic
Neurologic
Neuromuscular
Biomechanical factors
GNNB = Good Night, Night Bitch PFPS

How does a biomechanical cause contribute to PFPS?
Abnormal patellar tracking in the trochlear groove increases stress on the articular cartilage and innervated subchondral bone → leading to pain
Abnormal patellar tracking causes uneven pressure in the knee joint, irritating the cartilage and the bone underneath, which leads to pain in PFPS
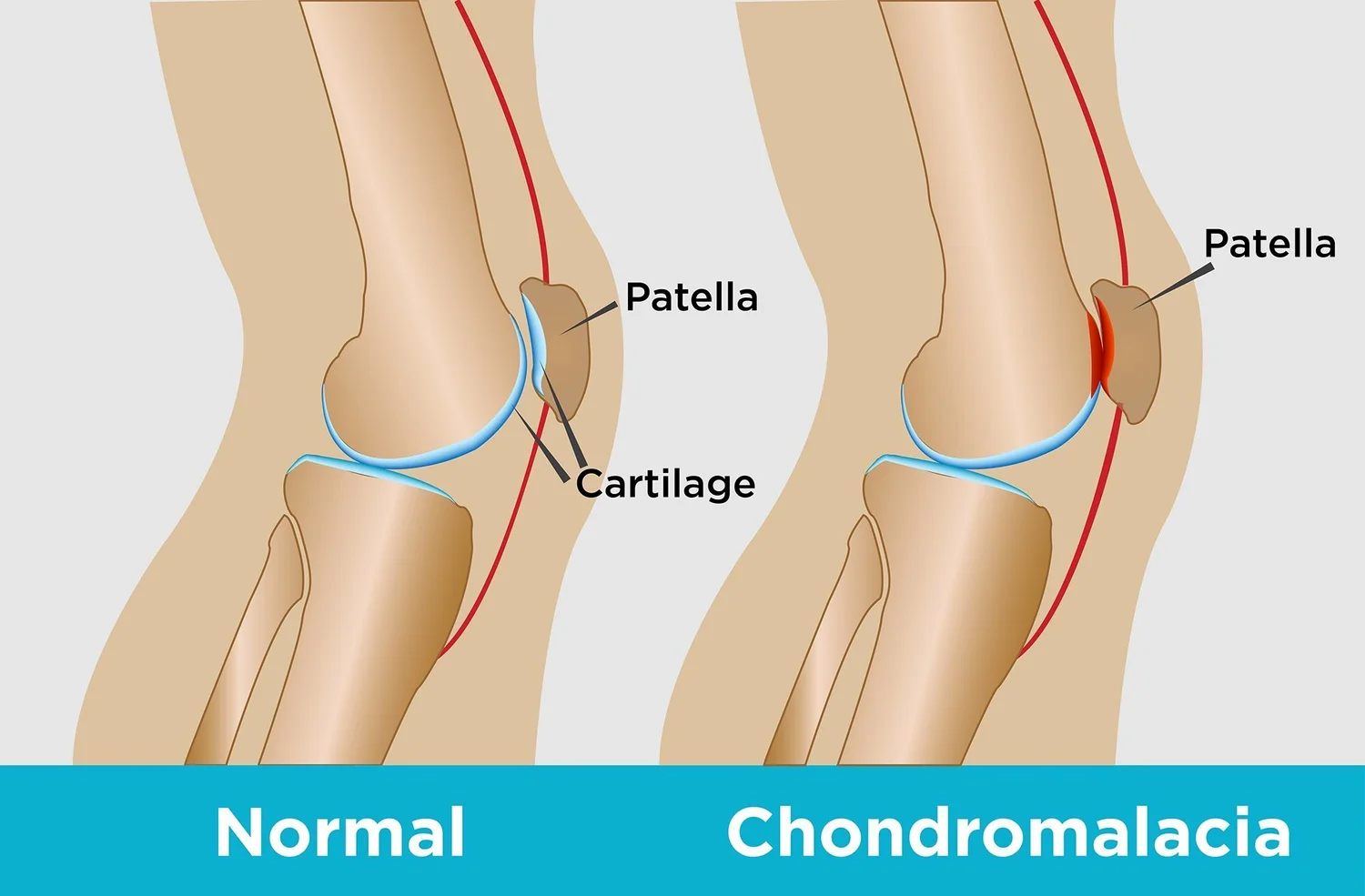
What degenerative change can occur in PFPS?
Softening of the cartilage, called Chondromalacia Patella
what is Chondromalacia Patella?
softening and breakdown of the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap, causing knee pain and irritation
Chondro- = cartilage
-malacia = softening
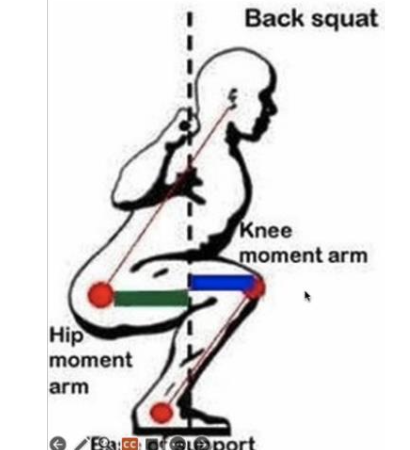
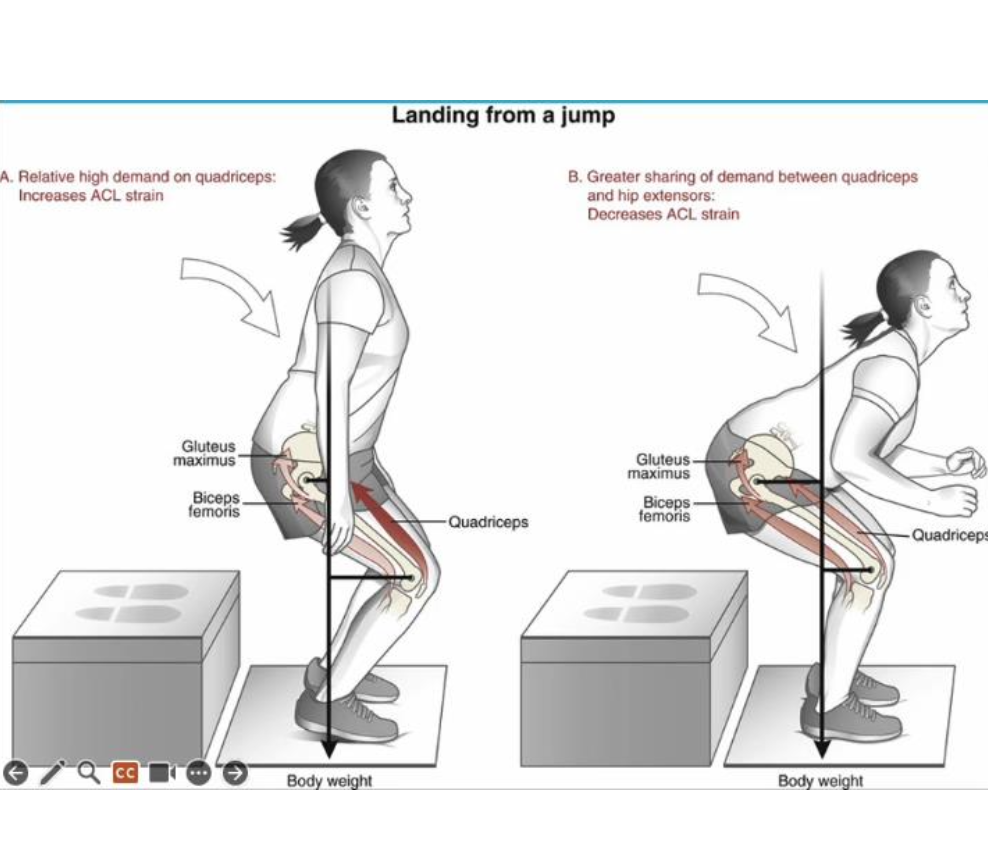
How should someone with PFPS be instructed to squat?
Keep the knees behind the toes to decrease the moment arm for the quadriceps and increase the moment arm for the hip extensors, shifting force transmission to the hips
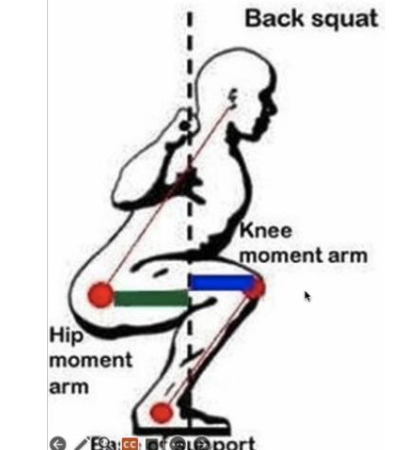
Why is keeping the knees behind the toes important in squatting with PFPS?
It decreases the external moment arm for the quads and increases it for the hip extensors, reducing stress on the patellofemoral joint
What is the common mechanism of injury for meniscal tears?
Forceful axial rotation of the femoral condyles over a flexed and weight-bearing knee, pinching and dislodging the meniscus
Which meniscus is more commonly injured and why?
medial meniscus
because axial rotation + valgus force stresses the MCL and posterior-medial capsule, which are connected to the medial meniscus
Can meniscal tears be acute or degenerative?
Yes, meniscal tears can be either acute or degenerative
What contributes to degenerative meniscal tears?
Repetitive WB activities in knee flexion cause wear and tear on the posterior aspect of the meniscus
What are some risk factors for degenerative meniscal tears?
Age over 60
male gender
repetitive kneeling
squatting
stair climbing
60 y.o. M bending his knees → meniscal tears

What can degenerative meniscal tears lead to if untreated?
Osteoarthritis (OA)
What is a meniscectomy?
Surgical removal of the torn portion of the meniscus
What is a potential consequence of a partial meniscectomy?
Increased risk of osteoarthritis
due to less coverage and shock absorption for the articular cartilage
What percentage of ACL injuries occur through non-contact mechanisms?
About 70%
Non-contact ACL injuries happen without a direct hit
They occur during:
sudden stops
sharp turns
awkward landing (from a jump)
twisting or bending beyond normal

What are common non-contact mechanisms of ACL injury?
Injuries that happen without a direct hit or collision to the body part involved
Ex:
Landing from a jump
Quickly decelerating
Quick pivoting over a single planted foot
What biomechanical factors contribute to ACL injury?
Strong quad activation over a slightly flexed knee
Valgus collapse
Excessive ER + planted foot
Femur IR on fixed tibia
Knee IR + Ext + Valgus
Excessive Hyperextension + Planted foot
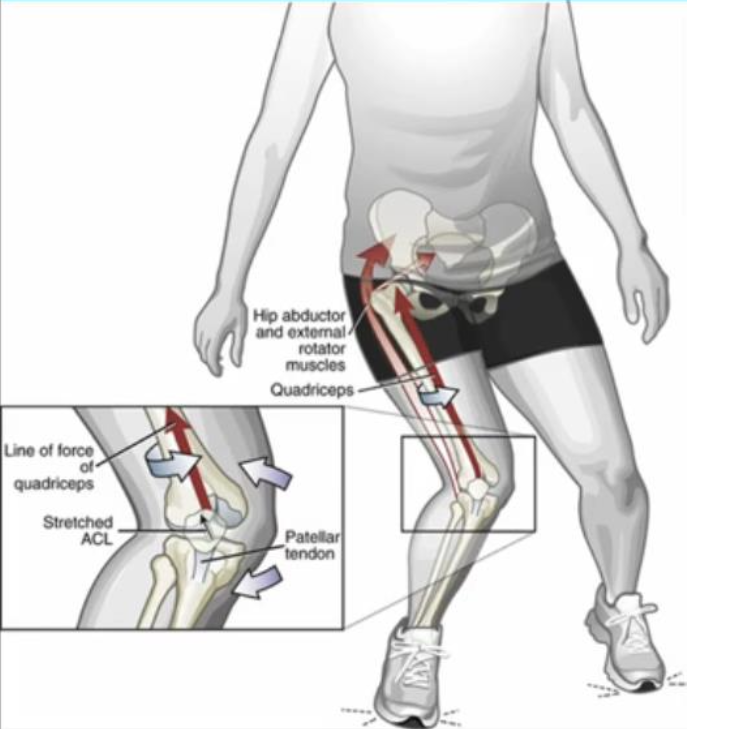
What other injuries commonly occur with ACL tears?
Bone
cartilage
menisci
MCL injuries
What is the "Terrible Triad" (Unhappy Triad) of the knee?
ACL tear
MCL tear
medial meniscus tear
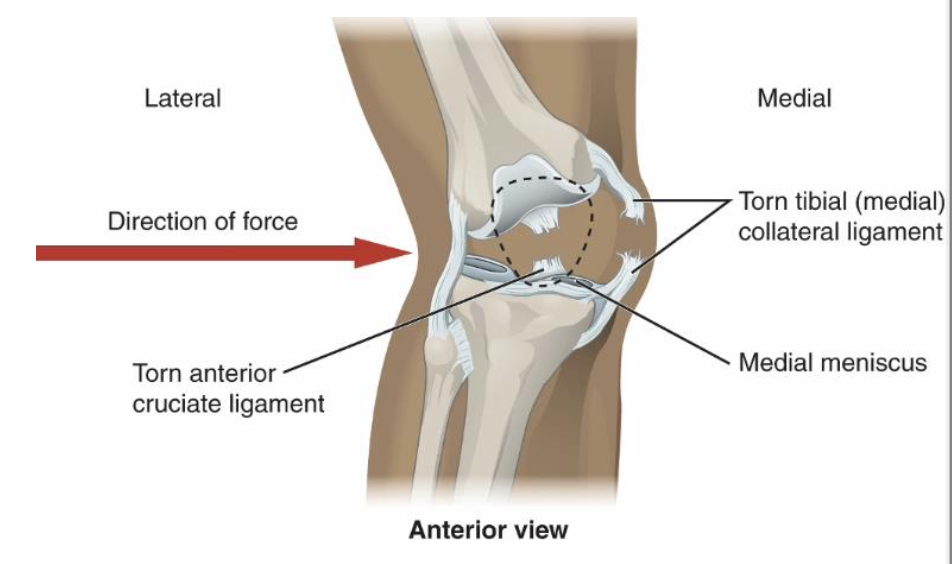
Why is the MCL often not surgically repaired after an ACL injury?
Because it has a good blood supply from the capsule, allowing it to heal well without surgery
What are the rehab precautions for meniscus repair vs meniscectomy?
Meniscus repair requires non-weight bearing (NWB), while
Meniscectomy does not have weight bearing precautions
Why are female athletes more likely to tear an ACL than male athletes? And by how much more?
Females tend to land with greater knee valgus alignment and less trunk, hip, and knee flexion
they use a quad-dominant landing that strains the ACL by pulling the tibia anteriorly
3-5x more likely
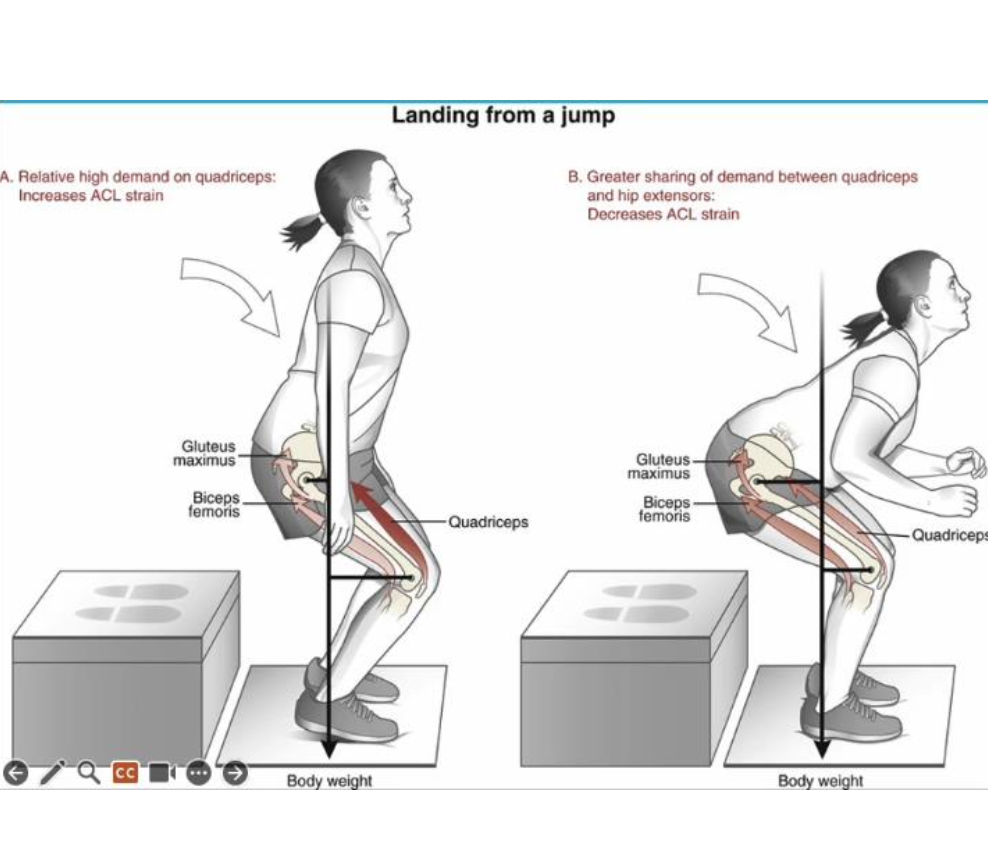
What strategies reduce ACL injury risk in female athletes?
Increasing trunk, hip, and knee flexion during landing
landing with knees behind the toes to shift force from quads to hamstrings and hip extensors;
hamstrings pull posteriorly on tibia, decreasing ACL strain
Why should isolated quad contractions in the last 30-40 degrees of knee extension be avoided early after ACL surgery?
Because the line of pull of the quads on the tibia creates a rotary (anterior translation) force that stresses the ACL
Because they pull the tibia forward, creating high anterior shear force that stresses the healing ACL graft
What type of exercises are preferred early in ACL rehab for strengthening quads?
Closed-chain femoral-on-tibia exercises through moderate degrees of knee flexion that co-activate quads and hamstrings
What degree of knee flexion is recommended early after ACL surgery and why?
>70 degrees
ACL tension from isolated quad contraction is near zero at this angle
aka Quad contraction causes almost no ACL tension here
hamstrings can pull the tibia posteriorly to unload ACL force
What happens to quad force on the tibia at 80 degrees of knee flexion?
The quads line of force is almost parallel to the tibia,
producing less anterior translation force