**MCAT need to knows**
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Glycolysis goal
Take 1 Glucose + 2 ATP ---> 2 Pyruvic Acid
What inhibits Glycolysis?
ATP
Does glycolysis require oxygen?
No, it is anaerobic
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
list the glycolysis enzymes
"Honey, I'm Pretty Accurately Gonna Punch My Eager PI"
HPi PxAT G3PPK PmEP
Hexokinase
Phosphoglucose Isomerase
Phosphofructose Kinase
Aldolase
Triose phosphate Isomerase
Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
Enolase
Pyruvate Kinase
Hexokinase
Glucose + ATP -> Glucose 6 Phosphate + ADP
(one way reaction)
Phosphoglucose Isomerase
Glucose 6 Phosphate -> Fructose 6 Phosphate
(reversible)
Phosphofructose Kinase
rate limiting step!!
one way reaction
Fructose 6 Phosphate + ATP -> Fructose 1 6 Bisphosphate + ADP
Aldolase
Fructose 1 6 Bisphosphate -> Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP) + Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate
(reversible)
Triose Phosphate Isomerase
Dihydroxyacetone (DHAP) -> Glucose 3 Phosphate
(reversible)
Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate dehydrogenase
Glucose 3 phosphate dehydrogenase + NAD+ + Pi -> 1 3 bisphosphoglycerate (13 BPG)
Phosphoglycerate kinase
13 BPG + ADP + H+ -> 3 phosphoglycerate
substrate level phosphorylation
Phosphoglycerate mutase
3 phosphoglycerate -> 2 phosphoglycerate
Enolase
2 phosphoglycerate -> phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) + H2O
pyruvate kinase
phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) + ADP + H+ -> pyruvate + ATP
aerobic decarboxylation
converts pyruvate (3 C) -> acetyl CoA
aerobic decarboxylation location
mitochondrial matrix
pyruvate dehydrogenase
pyruvate + NAD+ + coenzyme A -> Acetyl CoA + NADH + CO2
purpose of fermentation
to regenerate NAD+ to be used in glycolysis
fermentation
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of O2
fermentation process
pyruvate + NADH -> lactase dehydrogenase -> lactate + NAD+
pyruvate is reduced to produce lactate
Gluconeogenesis
formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources
What are the "new enzymes" in gluconeogenesis?
- pyruvate carboxylase
- PEP carboxykinase
- fructose 1 6 bisphosphatase
- glucose 6 phosphatase
Gluconeogesis steps
1. pyruvate -> pyruvate carboxylase -> oxaloacetate
2. oxaloacetate -> PEP carboxykinase -> PEP
3. PEP -> enolase -> 2 phosphoglycerate
3. 2 phosphoglycerate -> mutase -> 3 phosphoenolglycerate
4. 3 phosphoenolglycerate -> kinase -> 13BPG
5. 13BPG -> G3P dehydrogenase -> G3P
6. G3P -> Triose Phosphate Isomerase -> DHAP
7. DHAP + G3P -> aldolase -> F16BP
F16BP -> fructose 1 6 bisphosphate -> F6P
F6P -> Phosphoglucose Isomerase -> G6P
G6P -> Glucose 6 Phosphatase -> Glucose
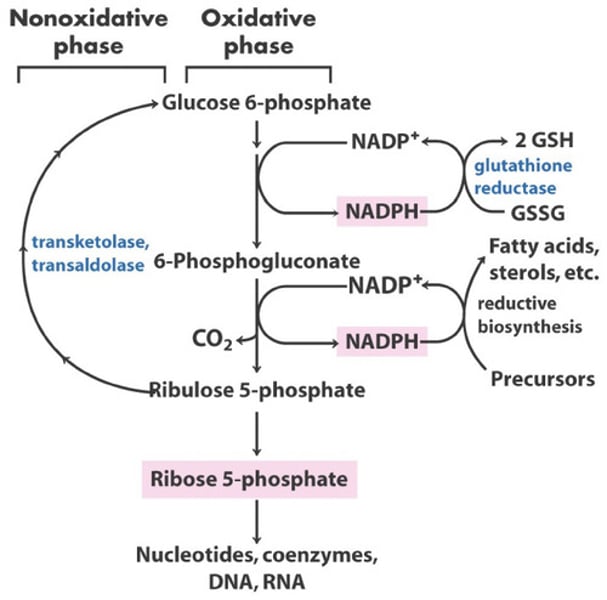
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
A metabolic process that produces NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis.
When does the pentose phosphate pathway occur?
when the cell is dividing
What step does pentose phosphate intervene in glycolysis?
glucose -> hexokinase -> G6P -> glucose 6 phosphatase dehydrogenase
pentose phosphate pathway location
cytosol
Pentose Phosphate Enzyme
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase
Purpose of Pentose Phosphate Pathway
forms ribose 5 phosphate (for sugar to make DNA & RNA)
forms NADPH to help build other molecules
Pentose Phosphate Pathway Steps
1. Glucose 6 Phosphate + NAD+ -> Glucose 6 Phosphate dehydrogenase -> 6 phosphogluconate + NADH
2. 6 phosphogluconate + NAD+ -> ribulose 5 phosphate +NADPH
3. ribulose 5 phosphate -> ribose 5 phosphate
4. ribose 5 phosphate -> nucleotides, coenzymes, DNA, RNA
How many ATP does glycolysis produce?
2 ATP per glucose molecule
2 NADH
How many ATP produced in pyruvate oxidation?
2 NADH
How many ATP produced in TCA?
2 ATP
6 NADH
2 FADPH2
What hormones are used to regulate blood glucose levels?
insulin: decreasing glucose levels by promoting glycolysis
glucagon: increasing glucose levels by promoting gluconeogensis
if blood glucose level rises
stimulate insulin (which promotes glycolysis)
if blood glucose decreases
stimulate glucagon (which promotes gluconeogenesis)
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen into glucose
glycogenolysis rate limiting step
glycogen phosphorylase
glycogen phoshorylase
glucose 1 phosphate -> glucose 6 phosphate
found in gluconeolysis (converts glycogen -> glucose)
glycogenesis
synthesis of glycogen granules
glycogenesis rate limiting step
glycogen synthase
glycogen synthase
forms alpha 1 4 glycosidic bond in the granule
stimulated by glucose 6 phosphate and insulin.
inhibited by epinephrine and glucagon
oxidative phosphorylation is driven by
proton gradient
H+ high in the intermembrane space than the matrix
TCA cycle
a series of metabolic reactions that break down molecules of acetyl CoA to carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms
rate limiting step of TCA
isocitrate dehydrogenase
TCA location
mitochondrial matrix
Citrate
acetyl coa -> isocitrate
isocitrate dehydrogenase
isocitrate -> alpha ketoglutarate
alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
alpha ketoglutrate -> succinyl CoA
succinyl CoA synthetase
succinyl CoA -> succinate
succinate dehydrogenase
succinate -> fumarate
fumarase
fumarate -> malate
malate dehydrogenase
malate -> oxaloacetate