Biology 108 Quiz 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/205
Earn XP
Last updated 3:23 PM on 2/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
1
New cards
isotopes
atoms of an element can differ in number of neutrons
2
New cards
How many bonds does hydrogen have?
1
3
New cards
How many bonds does oxygen have?
2
4
New cards
How many bonds does sulfur have?
2
5
New cards
How many bonds does nitrogen have?
3
6
New cards
How many bonds does carbon have?
4
7
New cards
How many bonds does phosphorus have?
5
8
New cards
carbon atoms are
tetrahedral
9
New cards
Three ways to draw organic molecules
all atoms, all bonds except for hydrogens, all carbons missing (implied) + no hydrogens attached to carbon
10
New cards
How to determine the # of hydrogens attached to a carbon
Count # of lines (= bonds) at each vertex and the # of hydrogens is 4- bonds to carbon
11
New cards
Functional Groups
Hydroxyl, Aldehyde, Keto, Carboxylate, Amino, Phosphate,
sulfhydryl
sulfhydryl
12
New cards
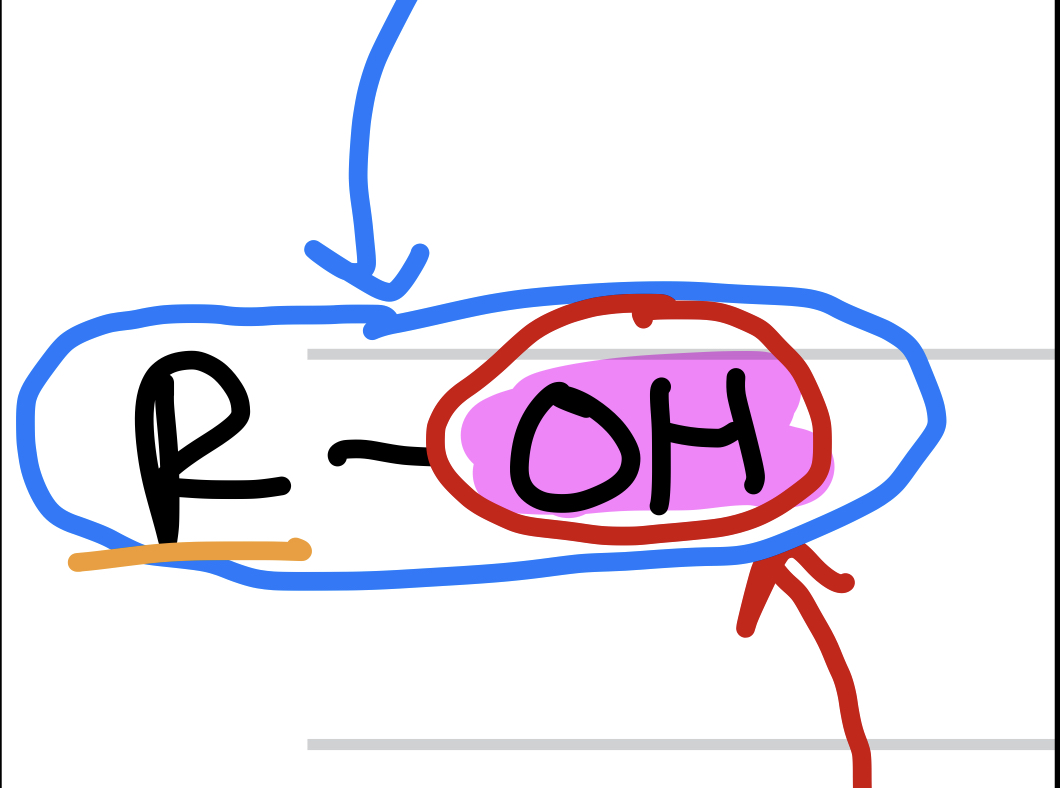
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Alcohols, Hydroxyl
13
New cards
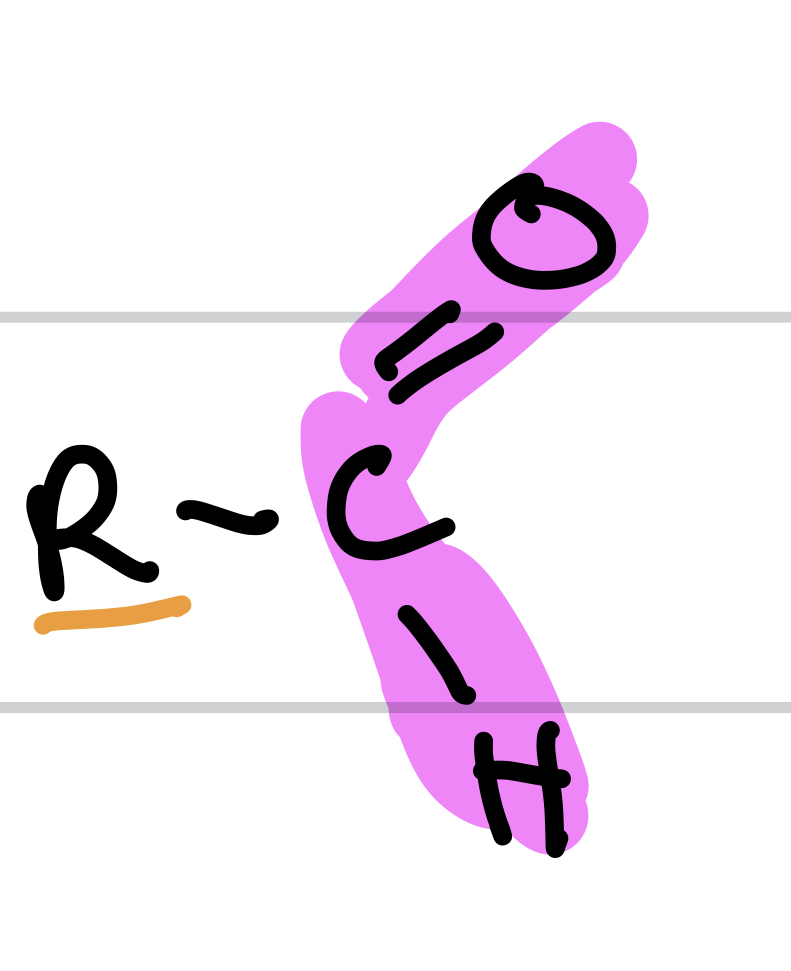
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Aldehydes, Aldehyde
14
New cards
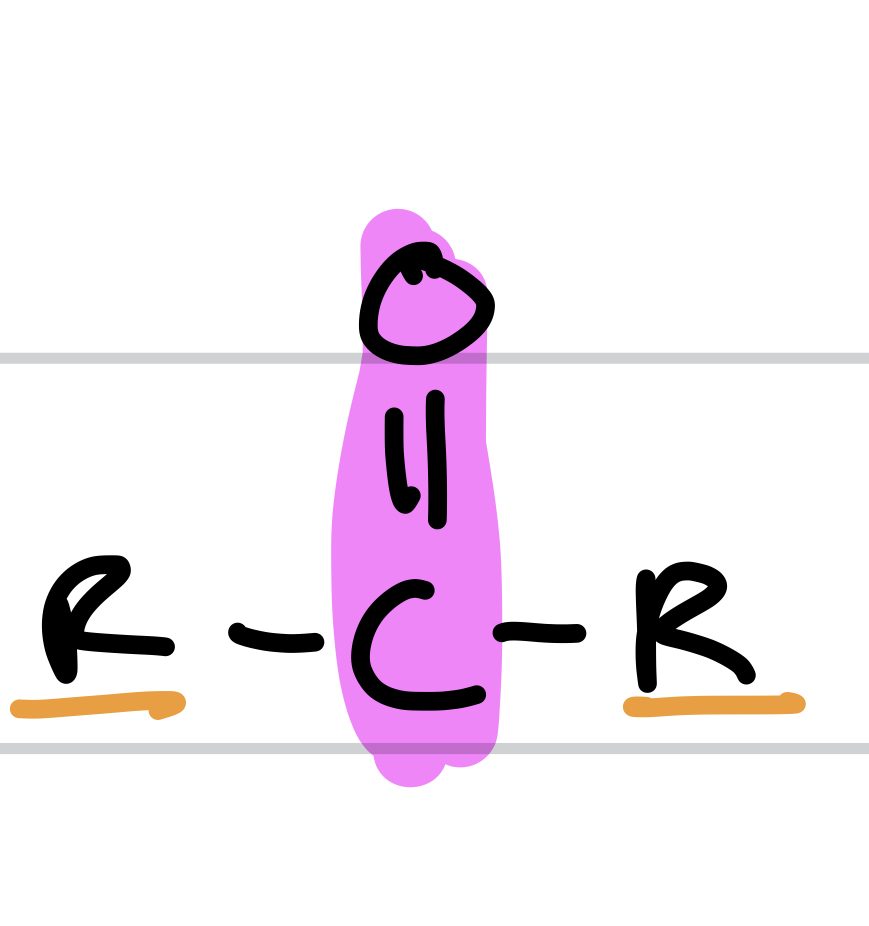
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Ketones, Keto
15
New cards
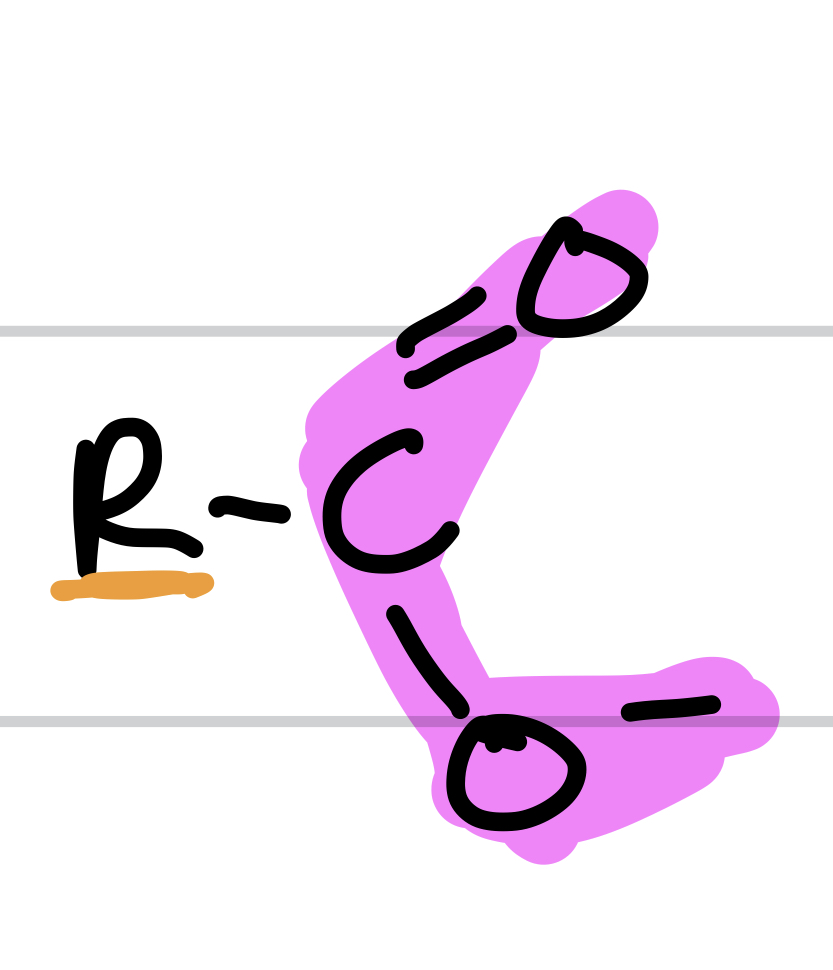
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Carboxylate, Carboxylate
16
New cards
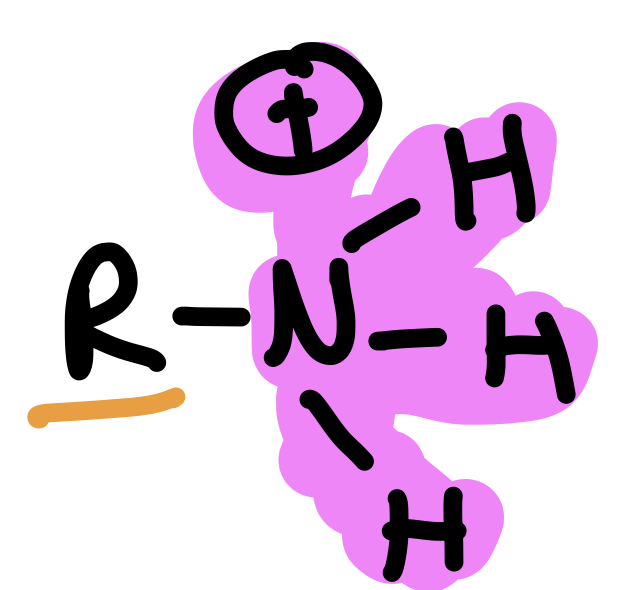
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Amine, Amino
17
New cards
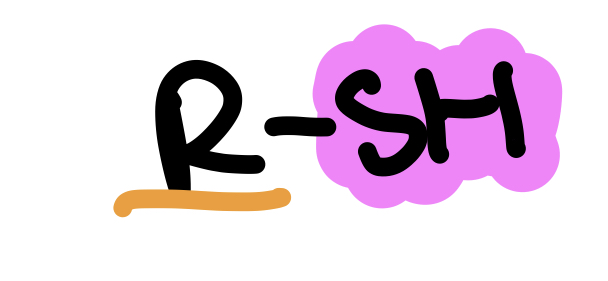
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Thiol, Sulfhydryl
18
New cards
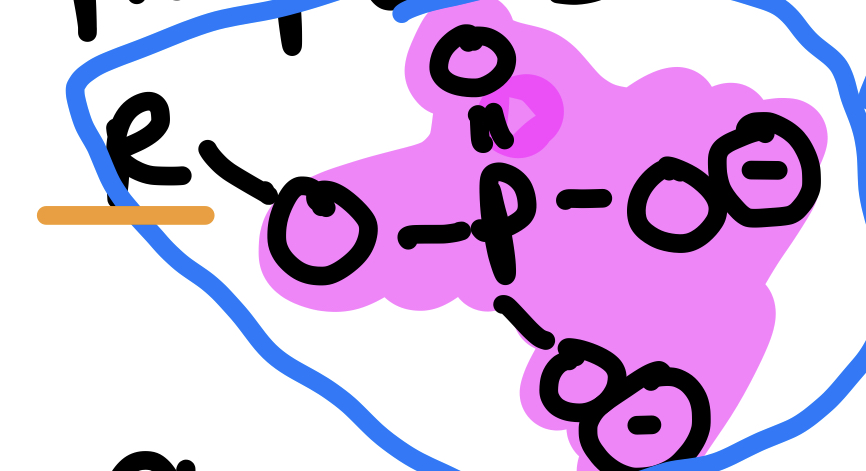
Type of Compound + Functional Group
Organic Phosphates, Phosphate
19
New cards
Electronegativity
attractive force that the nucleus exerts on its electrons
20
New cards
Negative Charge tendency
O, N, CL
21
New cards
Neutral Charge Tendency
H, C, P, S
22
New cards
Positive Charge Tendency
Na, K
23
New cards
With Polar Bonds: O or N are usually bonded to
H, S, C, P
24
New cards
Coulomic is a
non-covalent interaction
25
New cards
cations
positive ion
26
New cards
anions
negative ion
27
New cards
Hydrogens that do not form hydrogen bonds example
amino acids
28
New cards
Coulombic charge to charge interactions
ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds are qualitatively similar ionic positive charge with negative charge
29
New cards
polar is synonyms with
hydrophilic
30
New cards
hydrophilic
water-loving
31
New cards
polar
H-bonds with water
32
New cards
non-polar is synonyms with
hydrophobic
33
New cards
hydrophobic
water-hating
34
New cards
non-polar
not forming h-bonds with water
35
New cards
non-polar substances tend to __ in water
coalesce
36
New cards
coalesce
cluster
37
New cards
hydraphobic effect
when non-polar substances cluster in water
38
New cards
example of hydraphobic effect
oil and water/dressing
39
New cards
Why do the hydrophobic molecules coalesce in water
to maximize strong water-water interactions. To minimize weak water-oil interactions
40
New cards
hydrophobic molecules are a more ___ when coalesce in water
energetically favorable structure
41
New cards
hydrophobic interactions are driven by
maximizing strong water-water interactions
42
New cards
van de Waals interactions
induced dipoles and are greatest when shapes are complimenting
43
New cards
Synonyms for Sugar
carbohydrate and saccharide
44
New cards
sugar is a
macromolecule
45
New cards
monomer form of sugar
Cn(H2O)n, n needs to be greater than 3 total carbons to be considered a sugar
46
New cards
purposes for sugar
energy, metabolic intermediates, structural, other
47
New cards
6 carbon sugar vs 5 carbon sugar
6 carbon is a hexose like glucose while 5 carbon is a pentose like ribose
48
New cards
Most sugar named molecules end in
“ose”
49
New cards
Glucose has multiple forms
straight chain, then a beta-D-glucose or a alpha-D-glucose
50
New cards
straight chain glucose is __ % of forms found in nature
0\.02%
51
New cards
Beta-D-glucose is __% of forms found in nature
66%
52
New cards
Alpha-D-glucose is __% of forms found in nature
34%
53
New cards
straight chain ring closure
In a straight chain carbon 5 hydrogen reactions with carbon 1 oxygen to create a ring
54
New cards
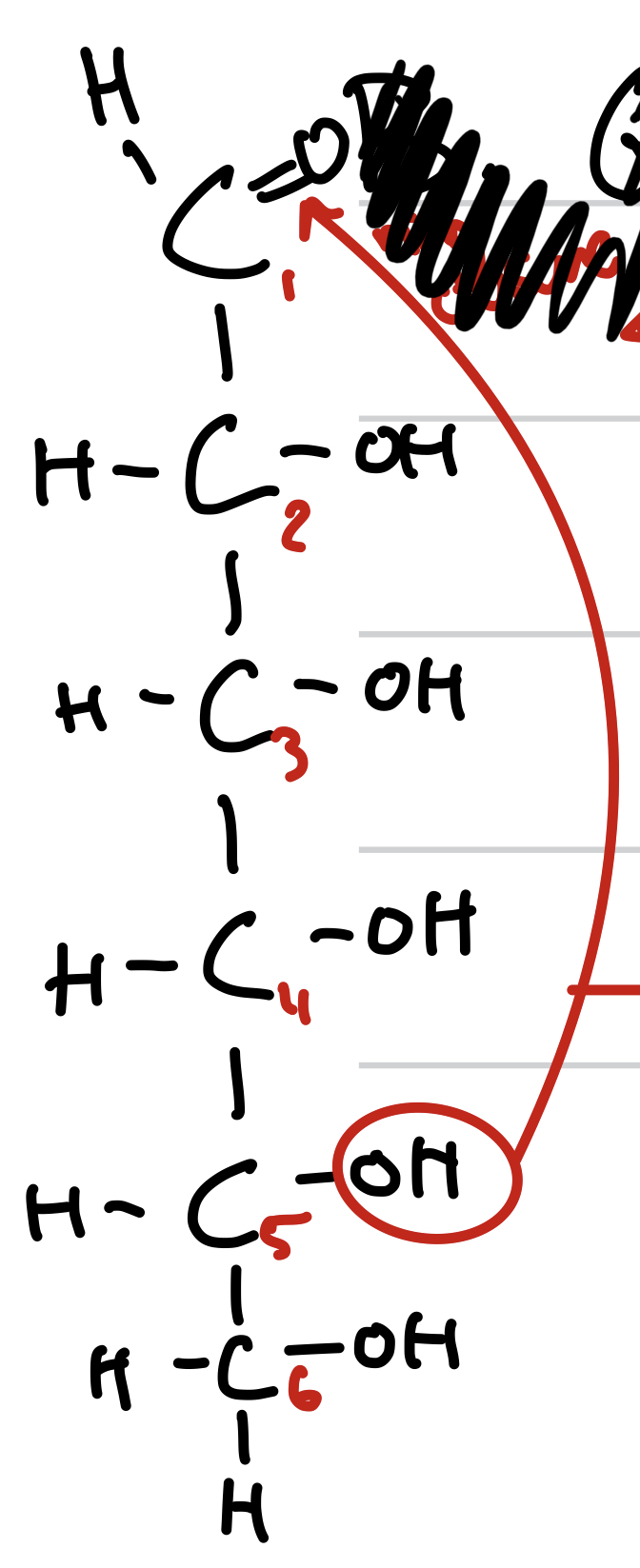
this is
ring closure of straight sugar chain
55
New cards
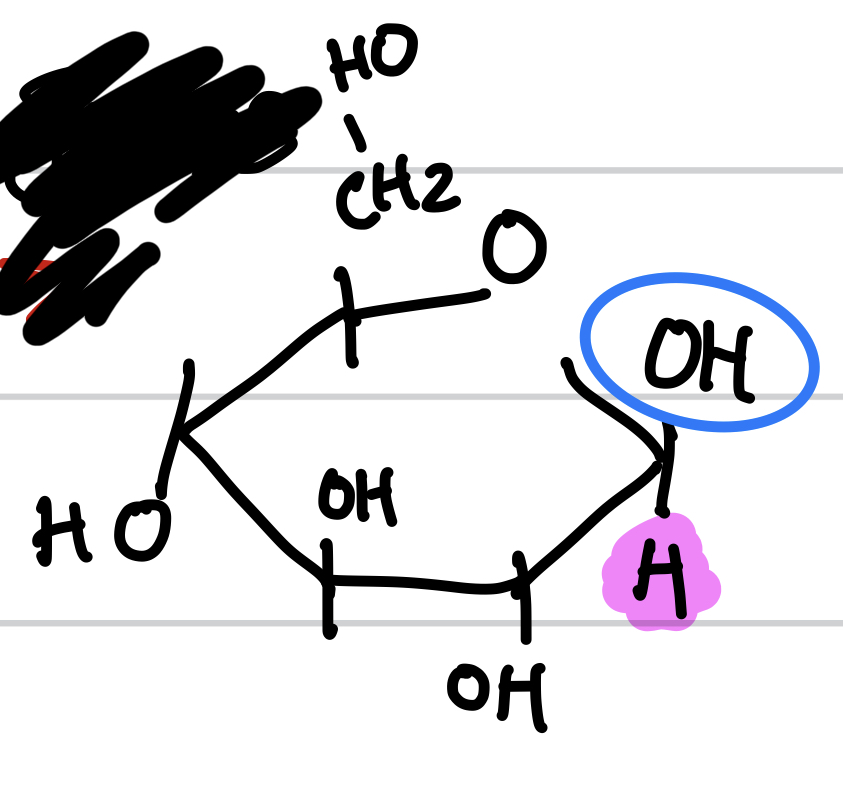
this is
Beta-D-Glucose (ring form)
56
New cards
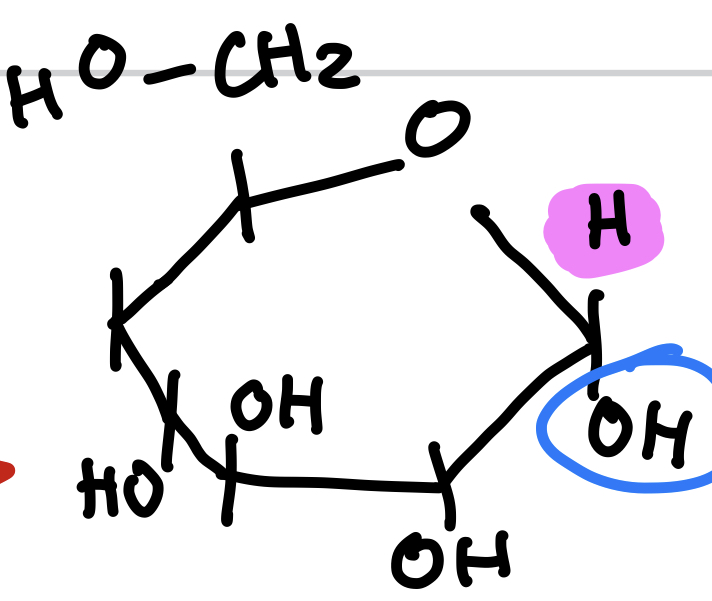
this is
Alpha-D-Glucose (ring form)
57
New cards
types of sugar polymers
disaccharides, oligosaccharide, polysaccharide
58
New cards
Disaccharides example is
glucose + fructose → sucrose
59
New cards
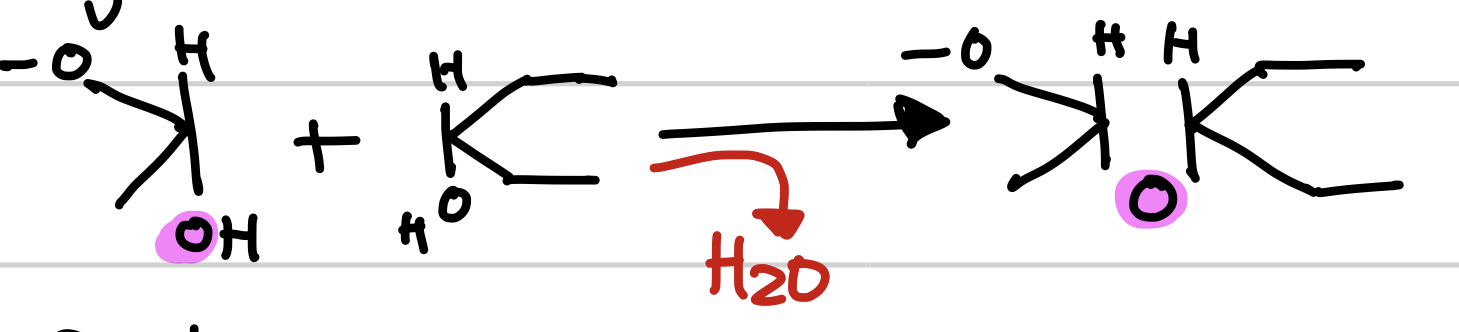
this is an example of _ and a _ reaction
disaccharides, dehydration
60
New cards
oligosaccharide can have
3-20 monomers
61
New cards
polysaccharide can have
from 3-thousands of monomers
62
New cards
examples of polysaccharides
cellulose: plants linear structural, starch: plants branched sugar storage, glycogen: animals highly branched sugar storage
63
New cards
Types of Lipids
fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids
64
New cards
Types of fatty lipids
saturated, unsaturated
65
New cards
Saturated fatty lipids
solid at room temperature found in animals, example is lard
66
New cards
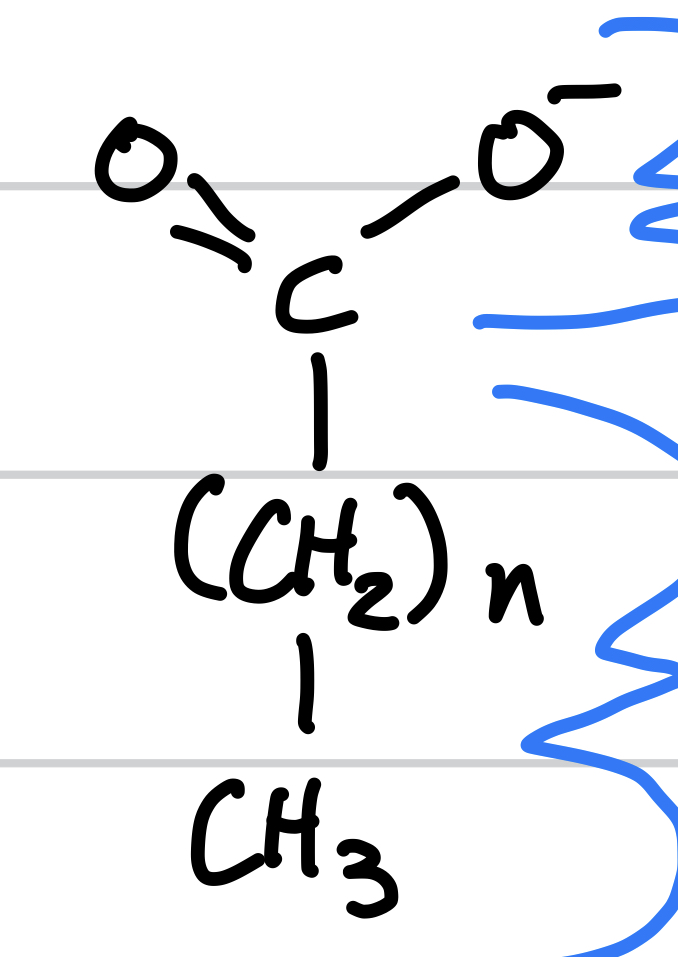
this is
saturated fatty lipid
67
New cards
the saturated fatty lipid is not _ , the tail/head of the saturated fatty lipid is _ while the rest of the chain is _
kinked, polar/hydrophilic, non-polar/hydrophobic
68
New cards
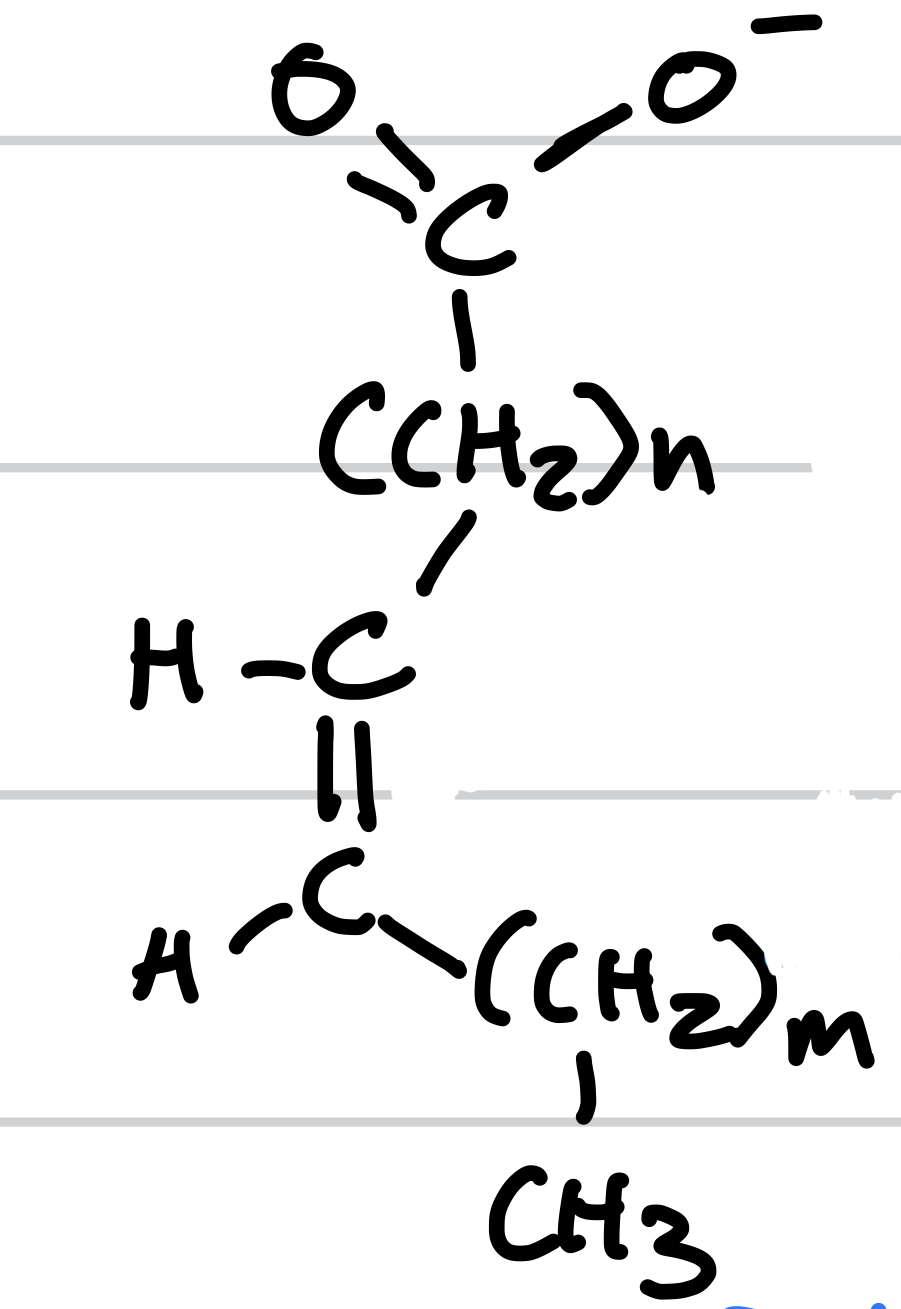
this is
unsaturated fatty lipid
69
New cards
the unsaturated fatty lipid is _, it requires to have _ , and it is not __
kinked, one or more double bonds with carbon, packed tightly
70
New cards
example of unsaturated fatty acid in nature
at room temp appears as oils (in plants) like palm oil
71
New cards
Triglycerides are
a lipid
72
New cards
ester bond is a
functional group
73
New cards
ester bond
a bond between (acid + alcohol) called fats and oils
74
New cards
triglycerides are a set of
three fatty acids lined up like spoons put on top of each other
75
New cards
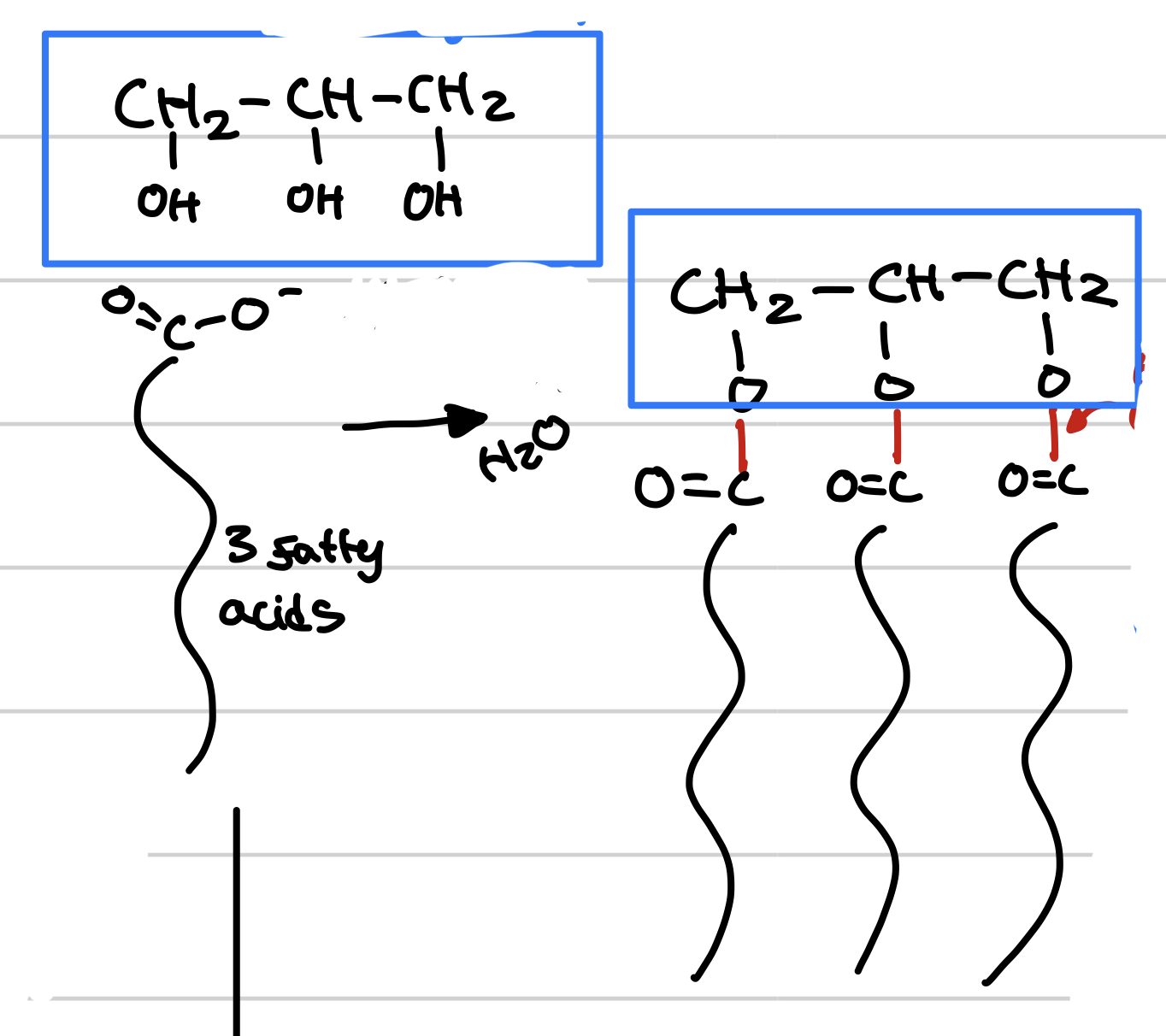
this is a _ reaction with __
dehydrate reaction, H2O
76
New cards
the triglycerides after the dehydration reaction with H2O is
largely hydrophobic
77
New cards
phospholipids
a glycerol molecule with two fatty acids and one nonpolar/hydrophobic attached to a phosphate which is attached to an organic amine. The phosphate and organic amine is polar/hydrophilic
78
New cards
phospholipids form
bilayers
79
New cards
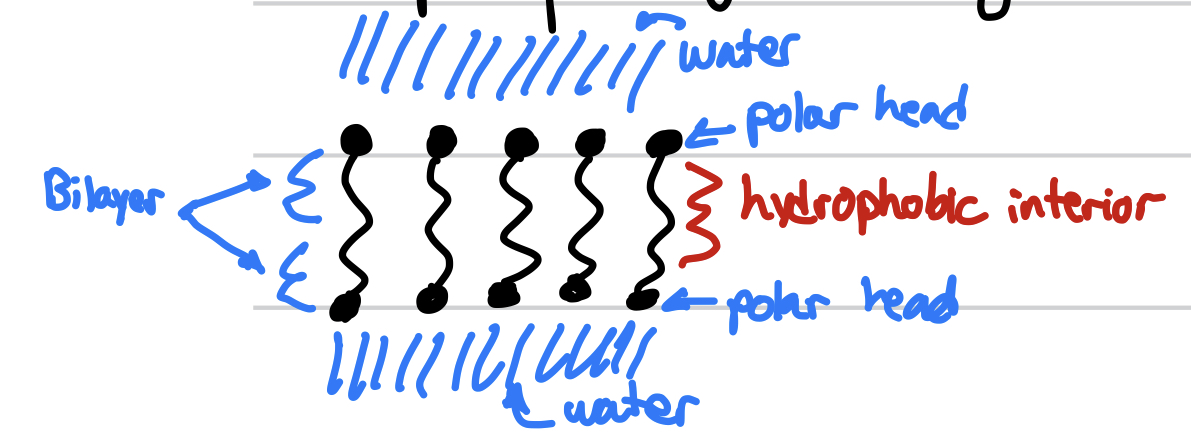
this is
phospholipid bilayer
80
New cards
large bilayers form
vesicles
81
New cards
large bilayers forming vesicles explains
how cells are developed by phospholipids. Proteins are found on the surface of cells and can interact with phospholipds
82
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes
membranes are mostly phospholipids, which move transversely in its layer but does not flip between layers
83
New cards
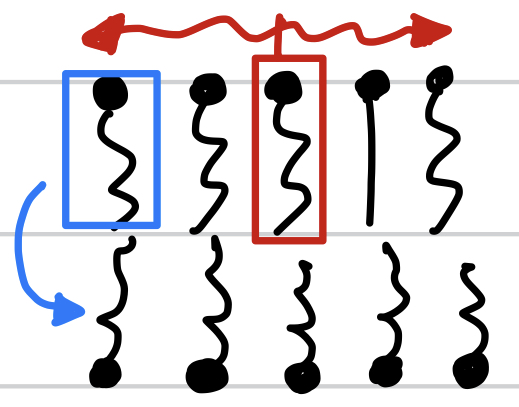
this is the
fluid mosaic model
84
New cards
Lipid rafts
“float” in the membrane and contain special lipids to which proteins bind
85
New cards
example of special lipids in lipid rafts
sphingomyelin and cholesterol
86
New cards
sphingomyelin represents a
phospholipid who’s head sticks out and the non-polar tail embeds in the membrane
87
New cards
cholesterol represents a
smaller molecule who’s head is lower but is within the same polar region as the phospholipid head and embeds in the membrane
88
New cards
3 types of proteins in membranes
integral, anchored, peripheral
89
New cards
intergral membrane protein
fits through the bilayer, which is called transmembrane protein
90
New cards
anchored membrane protein
has a covalently attached lipid, which inserts into the membrane
91
New cards
peripheral membrane protein
interacts with either membrane surface or integral protein or anchored protein
92
New cards
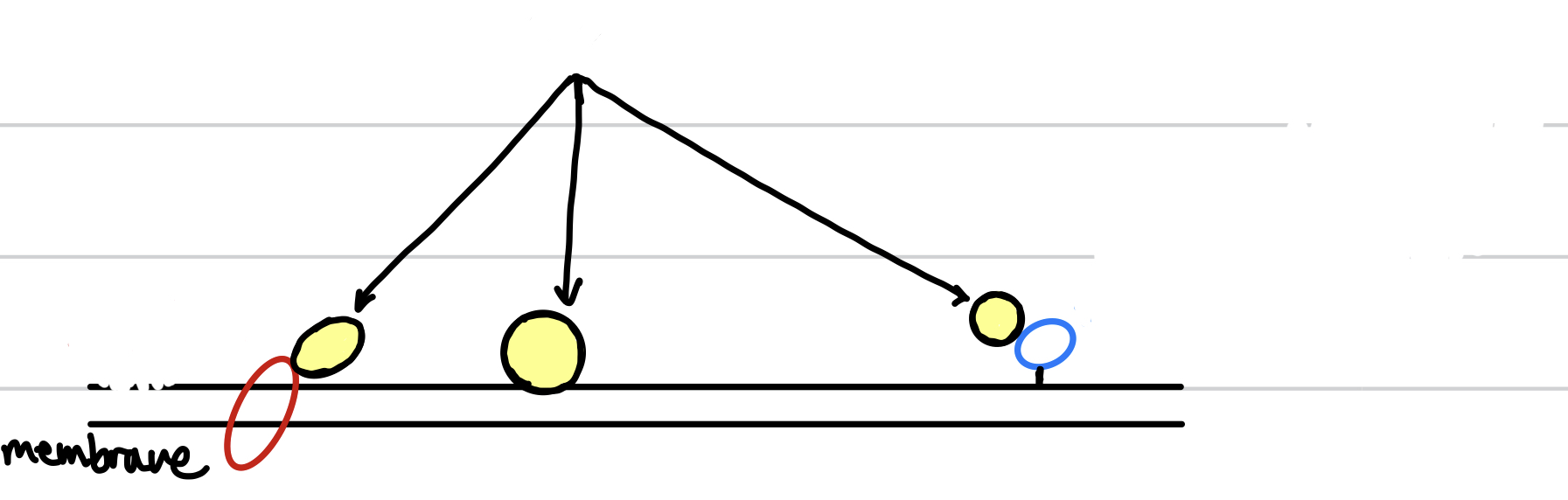
the circles with yellow indicate the
peripheral membrane protein
93
New cards
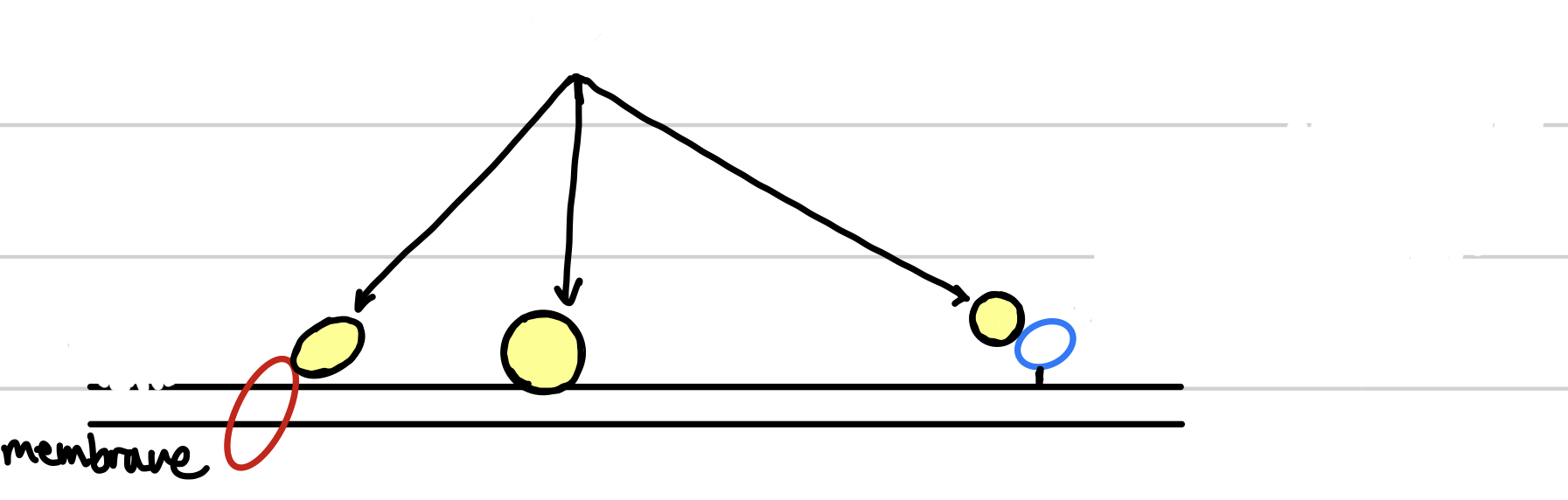
the red circle indicates the
integral membrane protein
94
New cards
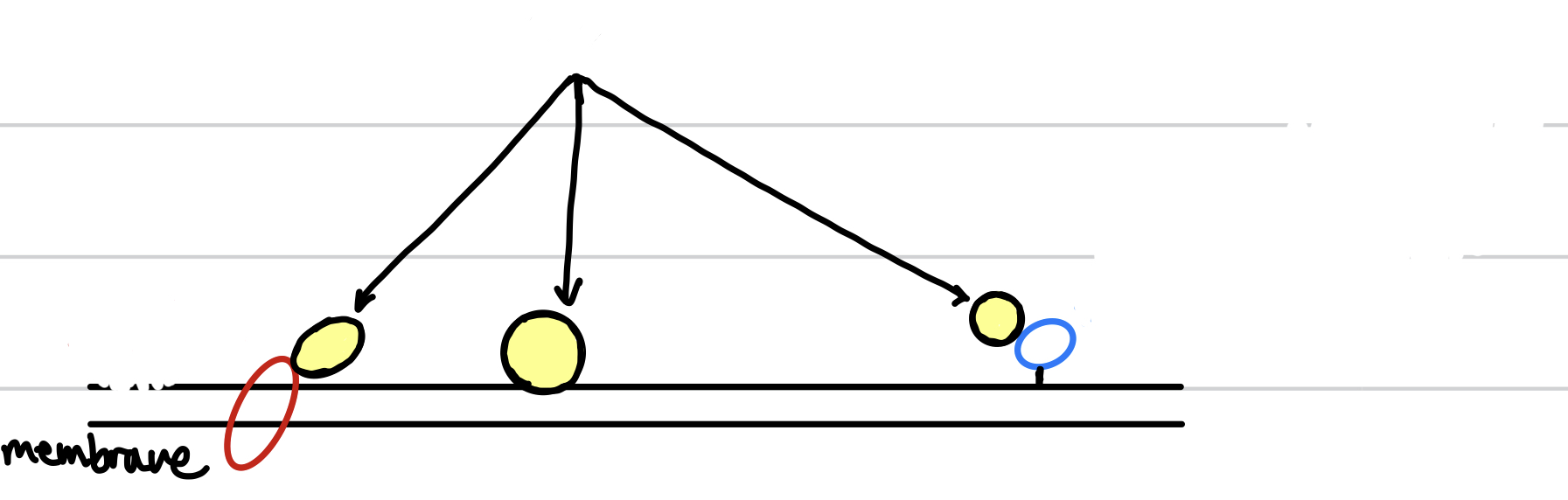
the blue circle indicates the
anchored membrane protein
95
New cards
Cells interact __ requires cell-cell recognition
adhesion
96
New cards
cell uniqueness established by unique cell surface components results in unique cell types like
glycolipids, glycoproteins
97
New cards
glycolipids
carbohydrates covalently linked to lipid
98
New cards
glycoproteins
carbohydrates linked to a membrane
99
New cards
glycolipids and glycoproteins help
cells recognize each other’s individual characteristics such as liver cells versus stomach cells
100
New cards
cell-cell contacts (3 types)
tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions