Ecology Exam 1
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from lecture slides, some definitions supplemented through google.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
Ecology is the scientific study of the biotic & abiotic factors that determine the ____ and ___ of organisms.
distribution and abundance
Why should we learn about ecology?
Improve our economy (agriculture, fisheries & wildlife, forestry), environmental concerns (salt marsh dieback, sewage runoff, forest fires)
Organismal: ___ ____ and ___ ways an individual deals with environment.
behavioral, physiological, morphological
___ is a group of individuals of a single species at a particular space & time.
Population.
__is a group of species in a particular place & time & the interactions that bind them.
community
___is a set of interacting species plus the physical space they occupy.
Ecosystem
What drives species diversity?
Competition (competitive exclusion), other stuff he hasnt gotten to yet
___is the whole earth ecosystem
biosphere
Explaining how different features of organisms suit them for life in particular environments is called ecology of ____.
individuals
Understanding population change and interactions among species is called ___and___ ecology.
population & community
To understand natural cycles of matter and energy at scales of ecosystem and biosphere is called ecology of ___.
ecosystems
To understand the role of ecological factors in the diversification of life is called ____ ecology.
Evolutionary
Earth’s surface releases __ energy than it receives.
more
Review Image
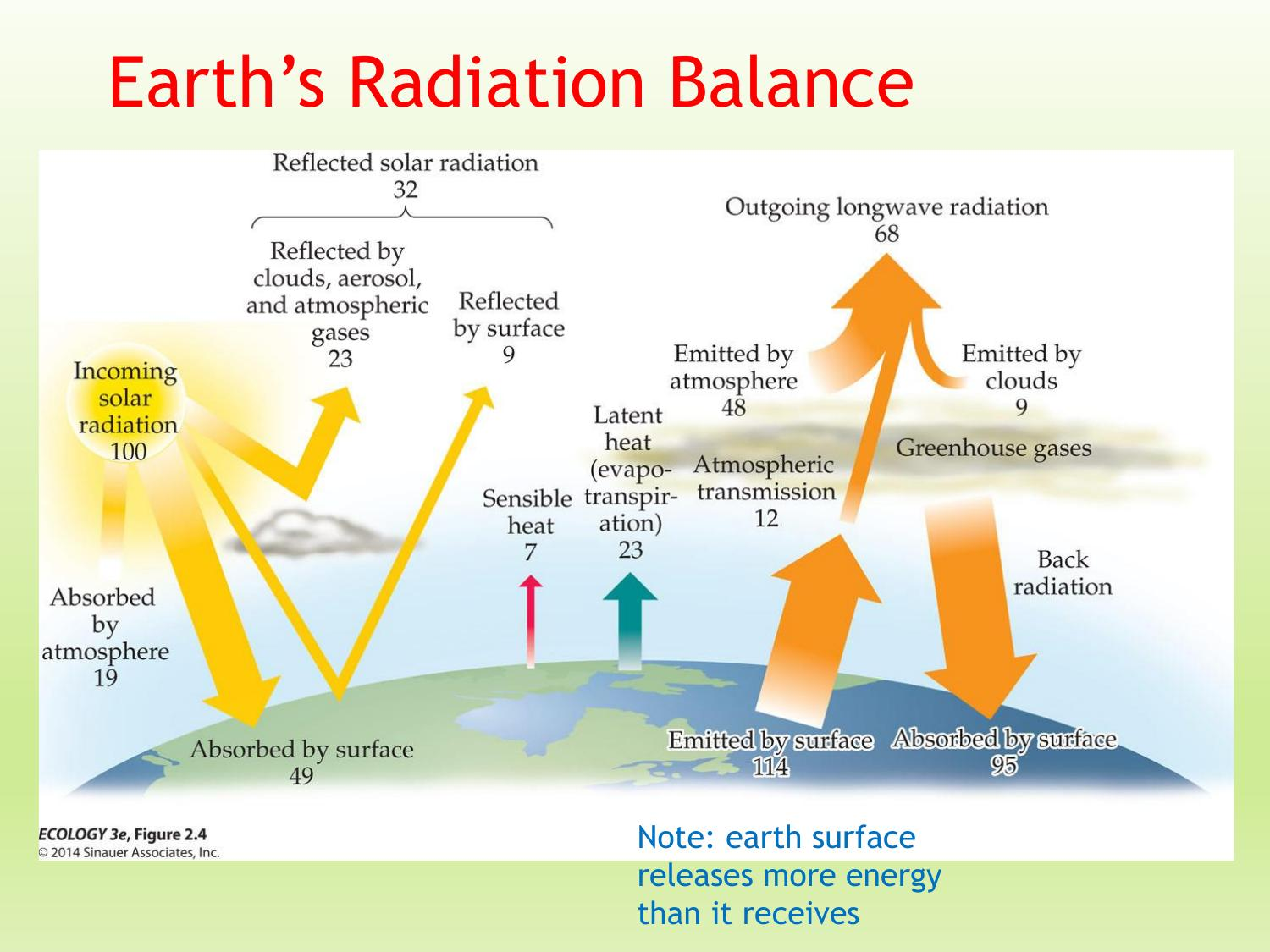
____refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface (open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation) into the atmosphere.[2] It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpiration (evaporation that occurs through the stomata, or openings, in plant leaves)
Evapotranspiration
___= (solar energy/area) decreases towards poles bc. of greater depth of atmosphere, greater angle of incidence. Determines why it is cooler towards the poles.
Average temperature drops, variation increases towards poles.
Insolation
If earth were a flat disk, where would you expect max insolation?
the whole disk, everywhere would be hit with same amount of sun
Areas with high insolation are expected to have ___ amounts of precipitation.
High
Large-scale tropical atmospheric circulation patterns where warm, moist air rises at the equator, flows poleward in the upper atmosphere, cools, and then descends around 30° latitude, creating subtropical high-pressure zones, before returning toward the equator as surface winds (trade winds).
Hadley Cell
The apparent deflection of moving objects (like air, water, or planes) on a rotating Earth, making them curve right in the Northern Hemisphere and left in the Southern Hemisphere, due to the planet's spin beneath them. It's not a true force but an inertial effect, strongest at the poles and zero at the equator, significantly influencing large-scale systems like weather patterns, wind currents, and ocean currents.
Coriolis Effect
Air circulation is deflected by Earth’s rotation. From NE up to __N, from SW between 30-60 N.
30
Major __ at 30 N, rainforests at equator and 60 N.
deserts
Ocean currents rotate ___ in northern hemisphere, so winds coming in off cool waters create deserts on western side of continents. This also affects the distribution of marine organisms.
clockwise
Does water or air have a higher specific heat capacity?
water
Mountains block clouds, cause leeward rain shadows. This is the ___-___ effect.
Rain-shadow
____ climates are more moderate than continental.
maritime
____ cause a cooler, wetter climate.
Forests.
Rain forests in__ . Precipitation occurs in winter (warm ocean air dumps moisture), few deciduous trees.
NW
Deserts in __ (ocean air picks up moisture)
SW
___-___ east of Rockies creates temperate grasslands (short to tall grass prairie as it move eastwards).
Rain-shadow
Eastern seaboard has ___ climate.
maritime
___ of ______ changes seasonally. 23 N in summer and 23 S in winter.
Axis of inclination
Sun passes over equator __ a year. Creates 2 rainy seasons.
twice
Temperate continents heat up and rain in ____.
Summer
__ ___ is a pattern with a longer term (9 months every 2-7 years) East-West oscillation, creating wet climate in the western Americas and drought in Asia.
Causes changes in climate in certain areas.
El Nino
This phenomenon when there is a lot causes more radiation. Maunder minimum.
Are temporary, dark, planet-sized patches on the Sun's surface caused by intense magnetic fields that inhibit convection, making them cooler than the surrounding photosphere
11 year cycle.
Sunspots
Earth’s temperature varies over longer time intervals due to changes in ___ and inclination of axis.
orbit
_____ Cycles: Earth’s orbit varies. As does the tilt of it’s angles.
Milankovitch
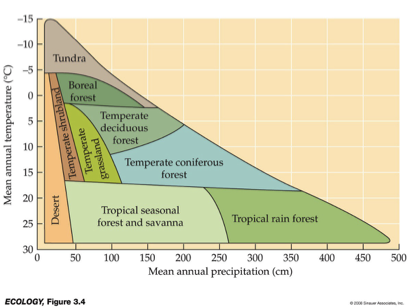
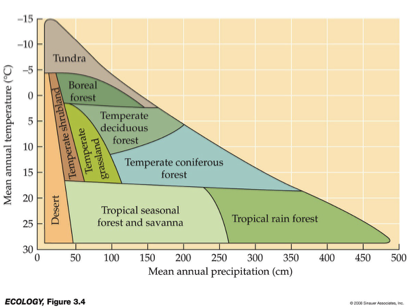
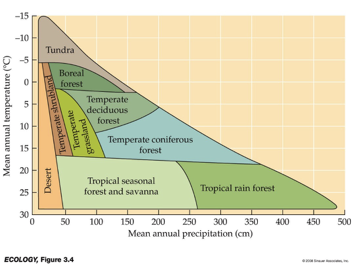
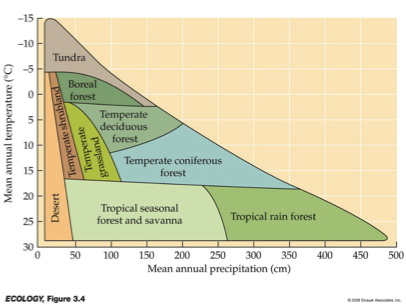
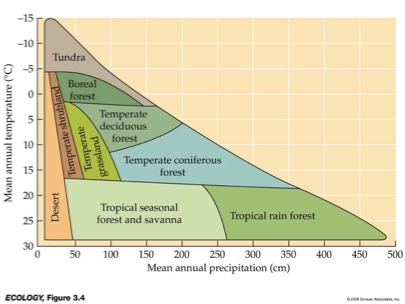
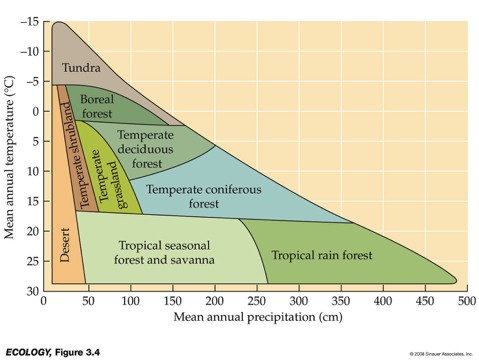
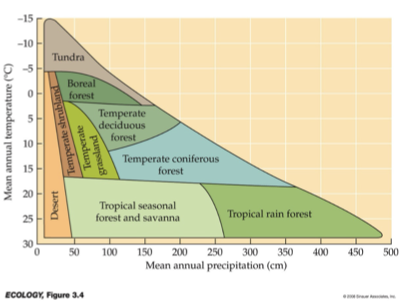
__ are distinguished primarily by predominant plants & are associated with particular climates.
Biomes
___ and __ variation in temperature and precipitation are fundamental components of terrestrial biomes.
Geographic & seasonal
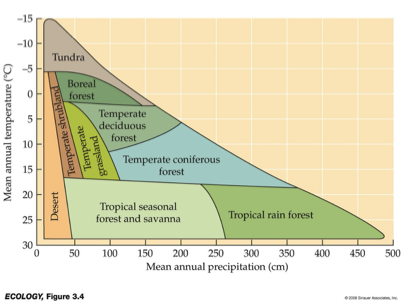
Be familiar with diagram
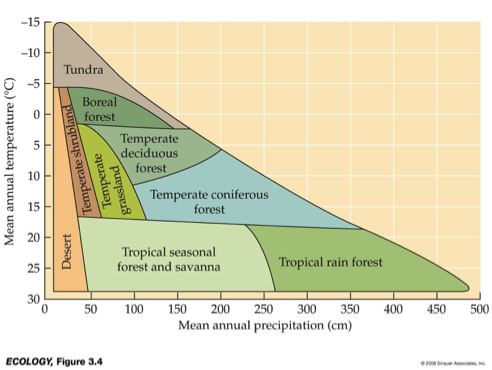
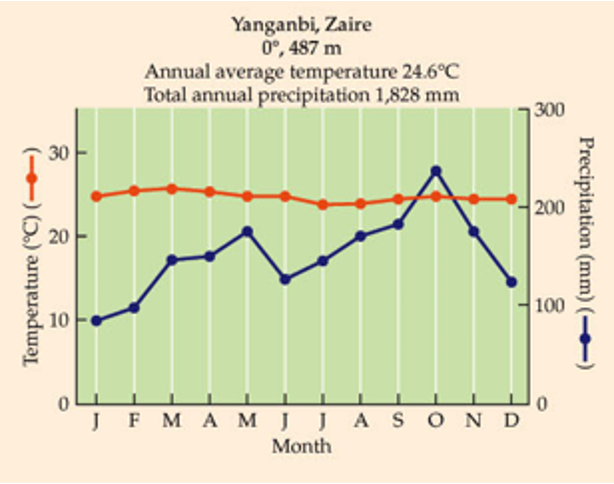
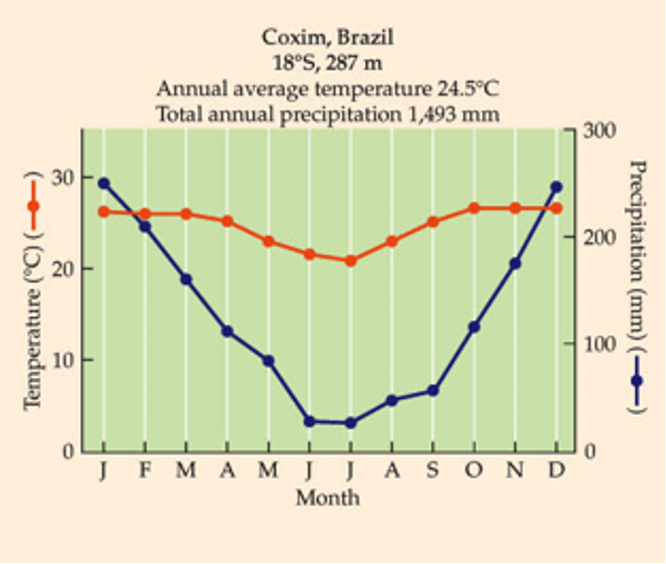
What biome is this?
Little temp. variation between months.
May contain half the world’s species, despite 11% of terrestrial vegetative cover.
Annual rainfall of 2,000-4,000 mm relatively evenly distributed throughout the year. Quickly leaches nutrients. (As things die, broken down quick bc hot and wet, bacteria, etc break it down, lots of competition for the nutrients and get sucked out quickly).
Tropical Rainforest
uNotice the stability of temperature in the top figure.
uAlso, notice the actual temperature.
uAt what latitudes do you see such temperatures?
uAlso notice the total amount of rainfall. For reference, Baton Rouge receives 1,411 mm annually
Farming in _____ ____, they burn the soil periodically. Have to relocate and deforestation occurs.
tropical rainforests
How many vegetative layers in a tropical rain forest?
How does water get all the way up?
Up to 5 (canopy trees light adapted, understory layers shade adapted).
Capillary action: as the water evaporates it is pulled up through the plants (xylem).
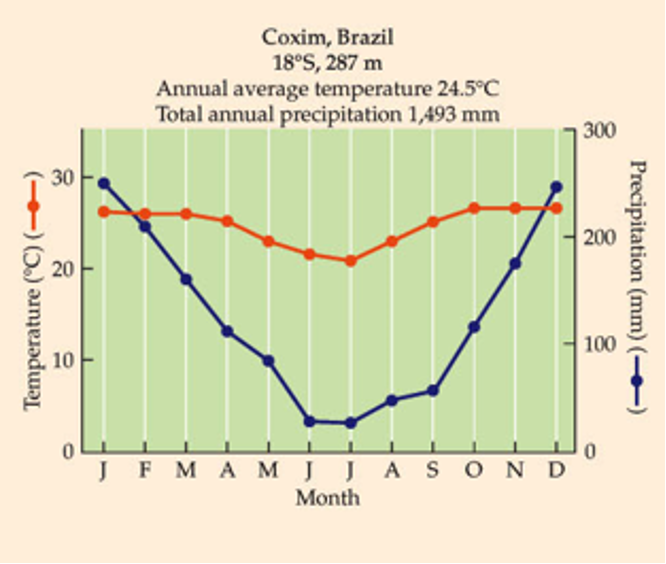
What biome is this?
Rainfall more seasonal than tropical rainforest.
Soils rich in nutrients, but vulnerable to erosion.
Shares many animal & plant species with tropical rainforests.
Heavily settled by humans with extensive clearing for agriculture.
Tropical seasonal forest
What biome?
Climate alternates btw wet/dry seasons. Drought in dry season leads to lightning-caused wildfires. Intense grazing pressures - ecosystem engineers. Bottomland hardwoods don’t establish - disturbance.
Soils have low water permeability - saturated soils keep trees out, especially near Orinoco River in South America.
Supports rich herbivore communities, but increasing pressure to produce livestock.
<50% of biome is intact due to forestry and agriculture.
All these prevent it from turning into a tropical seasonal forest.
Tropical savanna
Which of the following explains the lack of rainfall in desert biomes?
1.High temperature
2.Increased evapotranspiration
3.Hadley cell
4.Low atmospheric pressure
Hadley Cells.
On test “high atmospheric pressure, aka colder, dryer air, could be the best answer.
Examples of ecosystem engineers?
They are organisms that significantly modify, create, or maintain habitats, influencing resource availability for other species
Beavers, elephants, earthworms, oysters
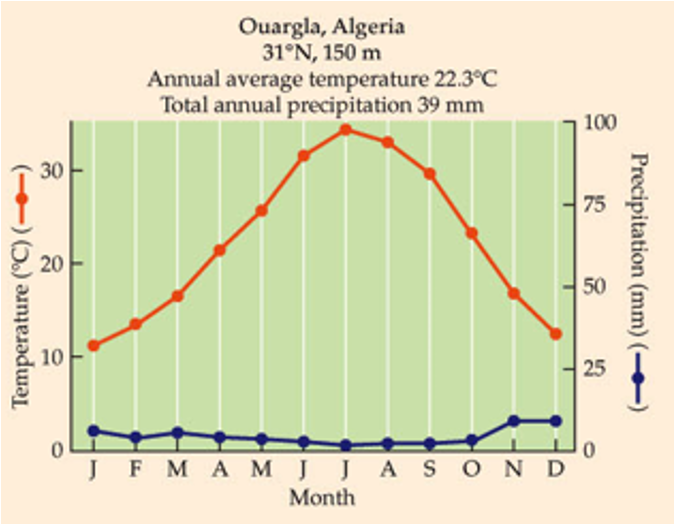
What biome is this?
Desert
Low atmospheric pressure is more __ air.
wet
Examples of animals in deserts?
lizards, camels, snakes like sidewinder, desert iguanas, camel spiders, scorpions, desert tortoise, kit fox
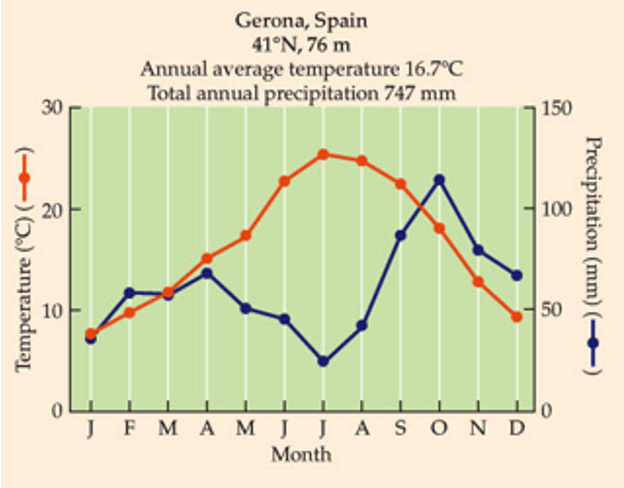
What is this biome?
In all continents except Antarctica.
Cool and moist in fall, winter, spring, but hot and dry in summer - asynchrony between precipitation & growing season.
Fragile soils with moderate fertility.
Evergreen trees and shrubs.
Fire-resistant plants due to fire regime.
Long history of human intrusion - cleared for agriculture.
uThe key here is the disparity between temperature and precipitation
“Mediterranean climate” aka temperate woodland & shrubland.
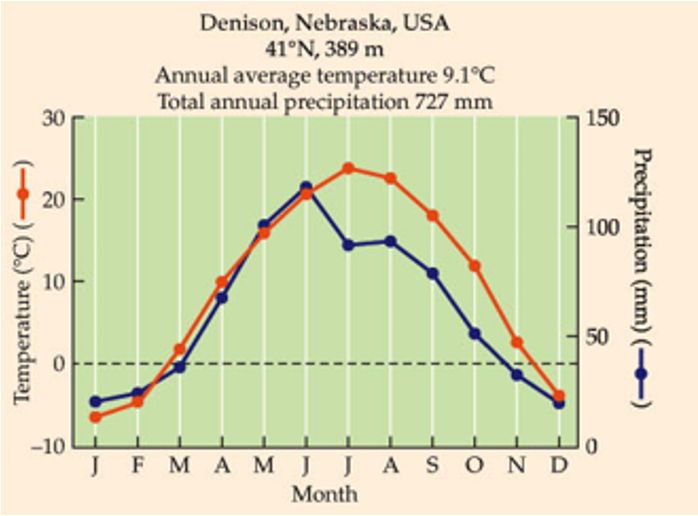
What is this biome?
Extremely widespread.
Annual rainfall 300-1000 mm.
Experience periodic droughts.
Soils extremely nutrient rich and deep.
Dominated by herbaceous vegetation.
Most fertile grasslands in NA and Eurasia converted to agriculture.
Large roaming ungulates - bison vs cattle
Temperate grassland. Dry in the US because of Rocky mountains, wind west to east, very little moisture passes over the mountains.
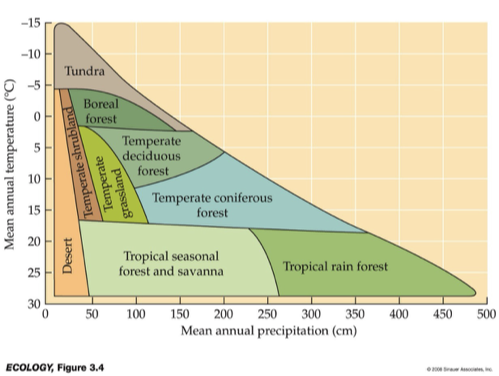
What is this biome?
uRainfall averages 500-2,500mm for deciduous, 500-4000mm for evergreen
uNutrient rich soils
uLong growing seasons dominated by deciduous plants.
uShort growing seasons dominated by conifers.
uBiomass production very high.
uMajor human population centers, little old growth forest remains.
temperate forest
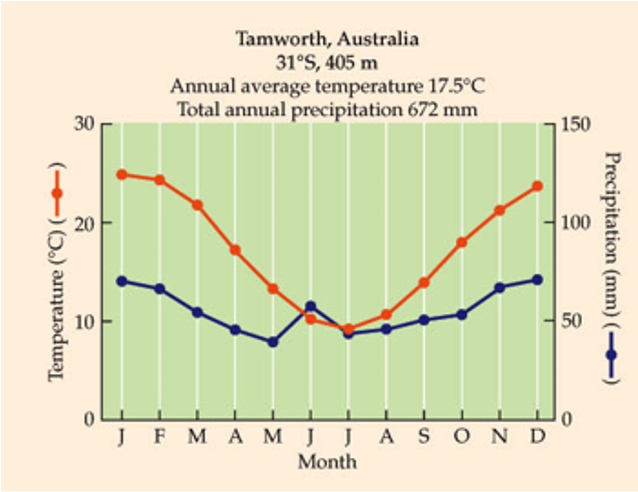
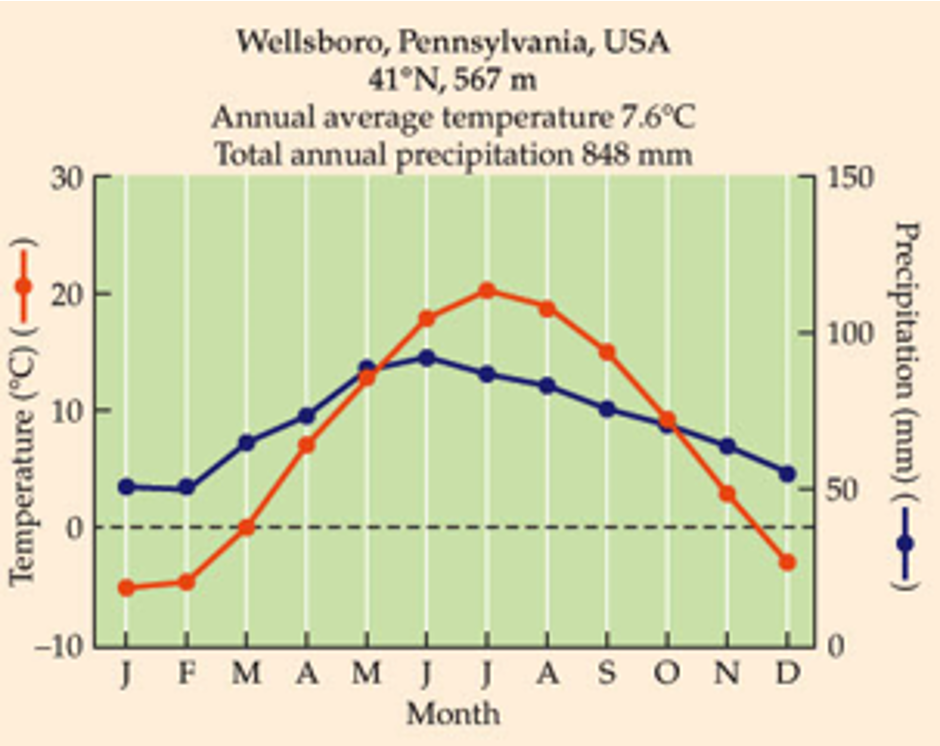
What is this biome?
uDon’t let the fact that these data come from the southern hemisphere trip you up
u1 wet season in Australian summer
uRainfall averages 500-2,500mm for deciduous, 500-4000mm for evergreen
uNutrient rich soils
uLong growing seasons dominated by deciduous plants.
uShort growing seasons dominated by conifers.
uBiomass production very high.
uMajor human population centers, little old growth forest remains.
temperate forest
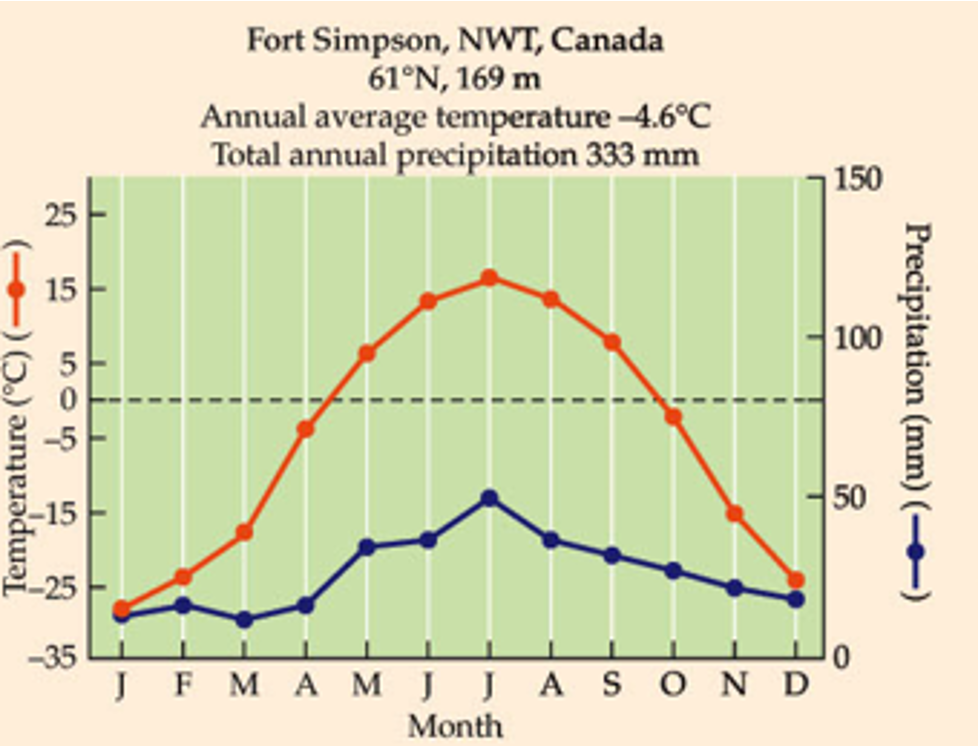
What biome is this?
uConfined to Northern Hemisphere, covers 11% of earth’s land area.
uThin, acidic soils low in fertility (permafrost > 3 years).
uDominated by conifers adapted to frozen soils, short growing season and low precipitation.
uCool temperatures retard decomposition, carbon builds up in soil.
uHistorically, low levels of human intrusion. Changing to meet energy demands (getting natural gas).
Taiga (Boreal forest)
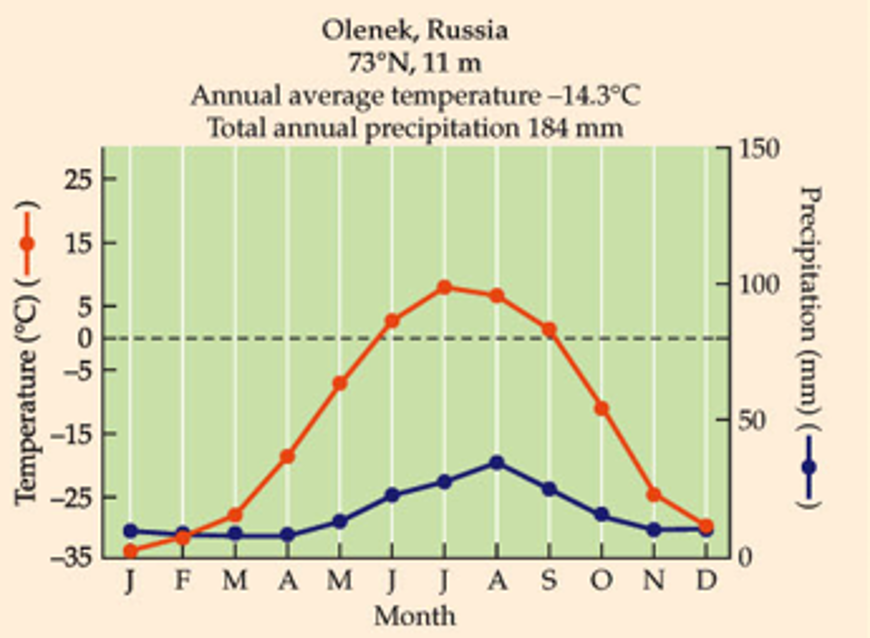
What biome is this?
uCovers most land north of Arctic Circle.
uCool and dry with short summers.
u200 - 600 mm precipitation.
uLow decomposition rates.
uSupports substantial numbers of native mammals. Lots of aquatic.
uHuman intrusion historically low
Tundra
Pay attention to numbers.
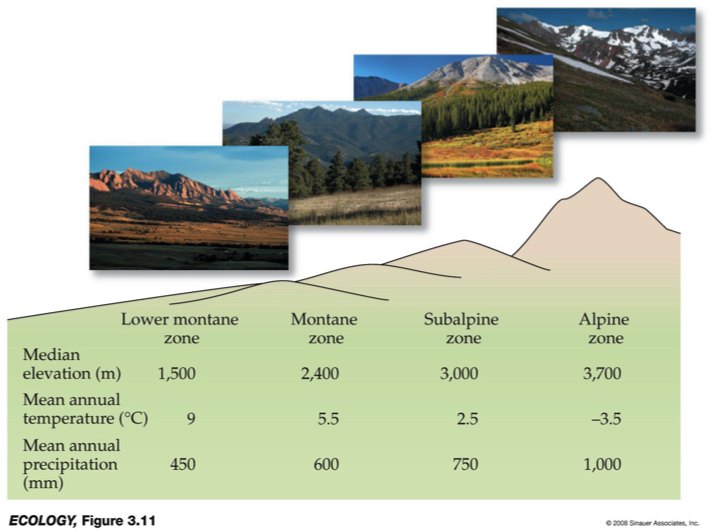
What is this biome?
uBuilt by geological uplift in belts of geological activity.
uClimate changes with elevation and latitude.
uSoils well-drained and thin.
uFlora and fauna change with elevation (from grasses, to deciduous, to evergreens to tundra like alpine zone).
Historical source of raw materials for human settlements.
Mountains (“islands in the sky”)
As you go up, you’ll go from grassland, to temperate forests, to boreal forest, to tundra.
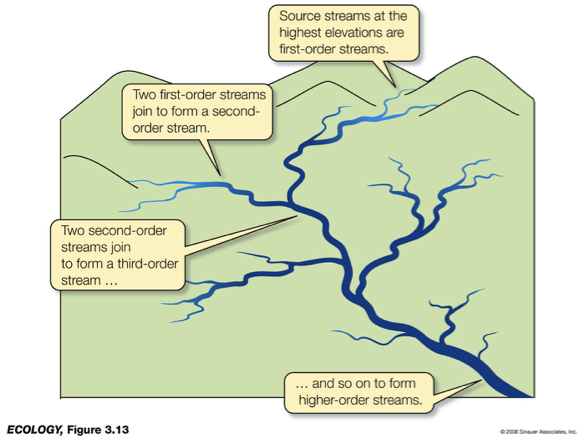
___ & ___ are divided into pools (deeper slower moving), runs (shallower faster moving), and riffles.
Stream order:
First order - headwater.
Second order - joining of two first order.
Third order - joining of two second order, most effected by pollution & impoundments.
And so on, up to 12 (like Amazon river. The Mississippi is a 10 order).
rivers & streams
uGreat Lakes of North America contain 20% of freshwater in the world.
uLakes become thermally stratified as they warm into upper epilimnion (warm lighter water), and lower hypolimnion (cooler heavier water), separated by thermocline.
uLakes vary in productivity:
____: Low biological production, but well oxygenated mountain lakes.
____: High biological production, but hypolimnion depleted of oxygen
Oligotrophic - low
Eutrophic - high
What water structure is this?
u80% of light absorbed in first 10 m
uPhotosynthesis limited to euphotic zone (top 200m).
uSalinity from 34 to 36.5 ppt.
uNew human-induced threats:
uOverharvesting
uPollutants
Deep sea / ocean
Marine shores have a ___ zone. Seperated into:
uUpper Intertidal: Covered during highest tides.
uLower Intertidal: Uncovered during lowest tides.
uSubtidal: Always covered by water.
Most important water movements are waves and tides.
uSemidiurnal tides: Two periods of low and high tides daily.
uDiurnal tides: Single low and high tide each day (as in Gulf of Mexico).
Intertidal
u____ are where rivers meet the sea (5 – 30 ppt), act as nurseries with lowered predation pressure.
u____ _____ and ___ ____ along low-lying coasts.
Driven by tides and river flow.
Transport organisms, nutrients, oxygen, and remove wastes.
Extremely vulnerable to human intrusion.
uCoral reefs highly diverse, productive and threatened.
Estuaries
Salt marshes and mangrove forests
What is marine snow?
Detritus falling down from ocean above, like feces, dead material, etc.
A continuous shower of organic particles, like dead plankton, animal waste, and debris, that drifts from the ocean's surface to the deep sea
Distributions often determined by physical factors. At extremes, ____ is lowered, energy acquisition & physiology can be affected even in “optimal” zone. Biotic interactions further restrict distribution.
survival
Low temperatures affect ____ and survival & limit northern distribution.
flowering
Droughts limit ___ distribution.
southern
_____ is short term, physiological response (Increases in concentration of RBC at high altitudes is an example).
Acclimatization
______ is a result of longer term selection for individuals with adaptive phenotypes (over time, Spaniards colonizing the Andes developed higher RBC counts, lung capacity).
Adaptation
____ is loss/gain of temperature by contact (example, warm tongue stuck to cold pole).
conduction
____ is loss/gain of temperature from surrounding air flow.
convection
____is loss of heat when water vaporizes (sweat evaporating cools us off).
evaporation
Fluxes in plants. Inputs = sunlight and infrared radiation, losses are ______ & _____.
evapotranspiration & radiation
Plants close____ to limit evapotranspiration & heat loss (also can’t photosynthesize or make new tissue). They also lose leaves in dry season, or leaf hairs reflect more radiation.
stomata
___ plants have low growth form that minimizes convective heat loss.
Arctic
The SA/V ratio decreases as the object gets larger. True or False?
True.
Smaller objects gain or lose heat more quickly.
_____behaviorally thermoregulate - reptiles
Ectotherms
__sweat in hot environments, shiver in the cold.
Endotherms
Tuna is an example of an ___, it uses swimming muscles to warm body core.
endotherm
____ zone - ambient temperature range where metabolic changes not necessary to maintain constant core temp. Basal metabolic rate (no need to shiver or sweat to maintain constant core temp).
Thermoneutral zone
____ _____ ____= lower bound controlled by acclimatization, insulation, etc. This is lower for arctic animals.
lower critical limit
Endothermy is costly. Small animals enter __ ( a brief drop in metabolic rate, body temp) and larger animals with energy reserves hibernate.
torpor
Water balance in plants: evapotranspiration increases with temperature. So, stomata close at night. Turgor___ at night. Stomata close if soil moisture becomes limiting.
turgor increases
Number of stomata or _____ ratios change with soil moisture.
root/shoot
shoots are the green parts aboveground
Plants growing where water is limiting allocate a greater proportion of their biomass to their ___ than plants growing where precipitation is higher.
roots.
A high root/shoot ratio means more roots. A low root/shoot ratio means they use more green parts/shoots.
Terrestrial animals face water loss, freshwater animals lose salts & gain water osmotically. Reverse for marine animals. True or false?
true
Sharks are ____ (secrete urea into blood)
osmoconformers (water is same inside the creature and outside)
Marine bony fish are ___-_____.
hypo - osmoregulators
(Hypo-osmoregulation involves organisms in salty (hyperosmotic) environments actively losing water and gaining salts. Like marine fish drinking seawater & excreting salt)
Freshwater fish are ___-______
hyper-osmoregulators
(hyper-osmoregulation is for organisms in fresh (hypoosmotic) water, actively taking in salts and excreting dilute urine to avoid swelling).
__must remain near water to reproduce.
amphibians
Amphibians have impermeable epidermis, powerful kidneys reduce water loss.
Frogs adapted to dry environments lose less weight (water).
Most terrestrial arthropods have ____ _____ (waxes) to limit water loss.
cuticular hydrocarbons
What animal is this? Large SA/V ratio, lives in burrows during day. Relies on met. water (doesn’t need to drink). Powerful kidneys produce concentrated urine. Loses much less water than lab rats.
Kangaroo rat
Adaptations to extreme environments include…
Compounds like ___ act as antifreeze.
glycerol
Adaptations to extreme environments include…
Small animals in extreme environments live in burrows. Some animals enter ___ ____ to withstand dry environments like lungfish.
Small size has some advantages in extreme environments, but may be a trade off with competitive ability.
suspended animation
An ___ is an organism that can convert abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms.
autotrophs
An organism deriving its nutritional requirements from complex organic substances is called ____. Cannot produce it’s own food.
heterotroph
What purposes does oxygen serve in metabolism?
terminal electron acceptor in electron transport chain
Air is ___% oxygen?
Oxygen is more soluble in colder water. More oxygen near surface and in fast moving water.
20
How do organisms get oxygen?
Oxygen flows down concentration gradient.
If you’re small, you can get all the oxygen you need from passive diffusion. Larger animals need to create a favorable concentration gradient. Large insects control O2 amount in trachea by opening/closing spiracles. Closed, O2 decreases CO2 increase. Opening spiracles causes O2 and CO2 to move down concentration gradient (also helps with water loss).
Highly folded structures to maximize surface area & gas exchange.
Fish gills use __________ exchange (so do birds). The concentration of O2 in water is always greater than in fish blood.
countercurrent