A&P TEST 1 Flashcards
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
Anatomy
The study of structure & shape of the body & its parts
Physiology
The study of how the body & its parts work/function
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions despite constantly changing external conditions
Levels of Structural Organization
Chemical Level
Cellular Level
Tissue Level
Organ Level
Organ System Level
Organismal Level
Chemical Level
At this level, Atoms combine to form molecules
Cellular Level
At this level, cells are made of molecules
Tissue Level
At this level, tissues consist of similar types of cells
Organ Level
At this level, Organs are made of different types of tissues
Organ System Level
At this level, organ systems consist of different organs that work together
Organismal level
The human organism is made up of many organ systems
Anatomical Position
Body is erect, feet slightly apart
Arms are hanging at sides with palms facing forward
Head and eyes are facing forward
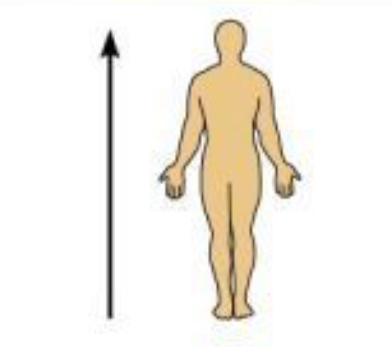
Superior (Cranial)
Above; toward the head
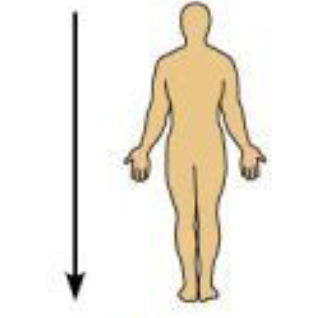
Inferior (Caudal)
Below; away from the head
Anterior (Ventral)
Front of the body
Posterior (Dorsal)
Back of the body
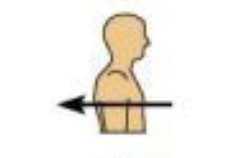
Medial
Toward the midline of the body
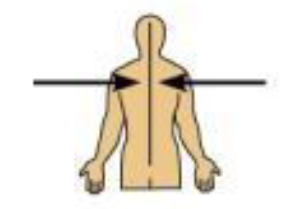
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
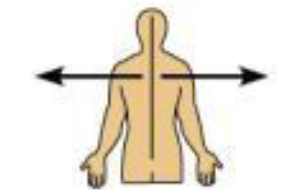
Proximal
Close to the origin of a body part or point of attachment
Distal
Farther away from the origin of a body part or point of attachment
Superficial
Toward or at the body surface
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into left and right parts
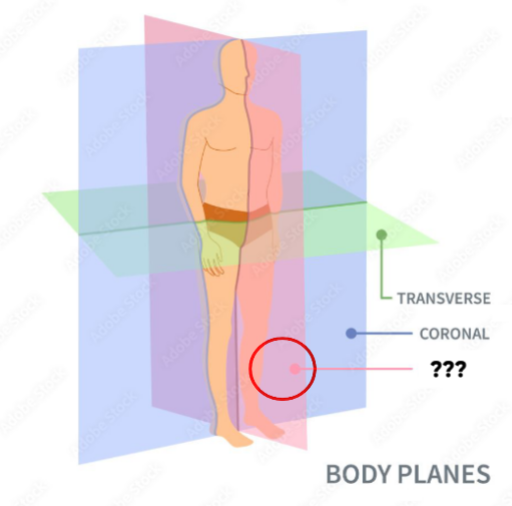
Midsagittal (Median) Plance
Sagittal plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Vertical plane dividing body into anterior & Posterior parts
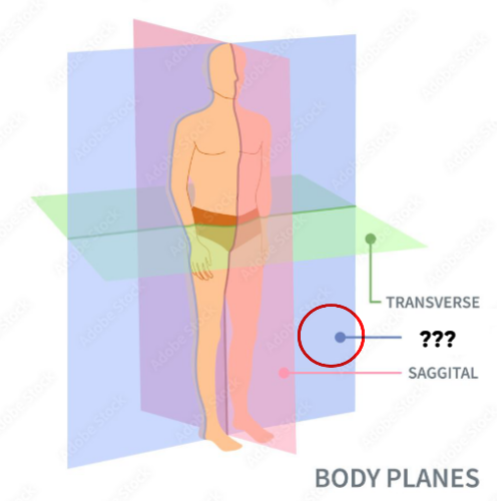
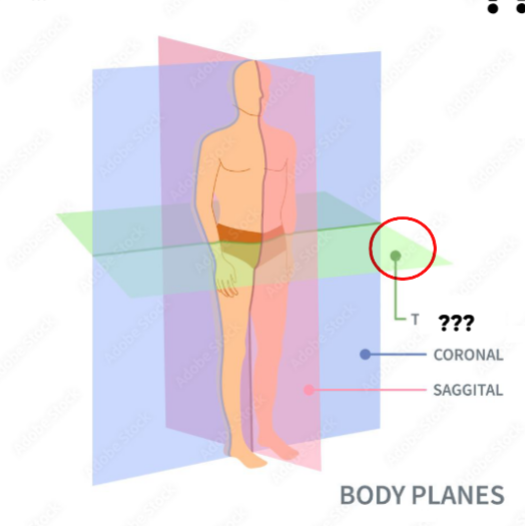
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
horizontal plane dividing the body into superior & inferior parts
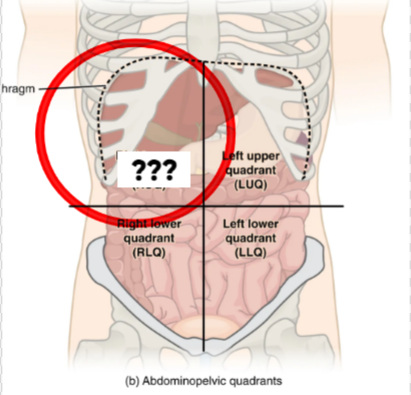
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
This quadrant contains the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, & portions of the stomach & intestines
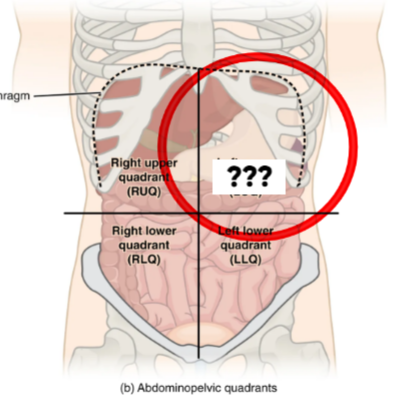
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
This quadrant contains the stomach, spleen, left kidney, portions of the liver & intestines
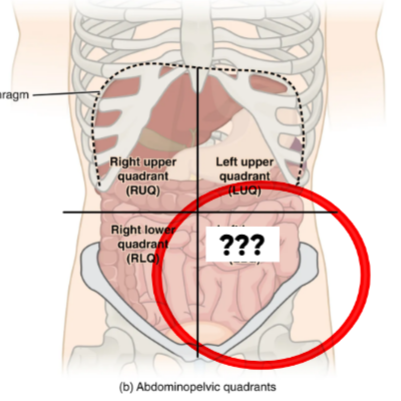
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Contains appendix, portions of intestines, & right reproductive organs
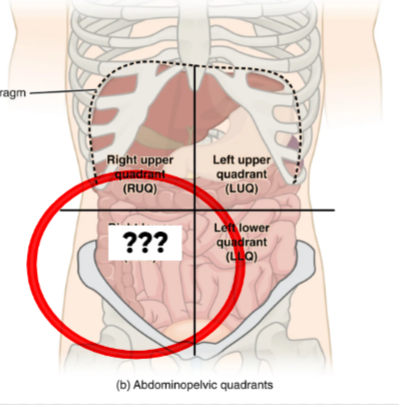
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
This quadrant contains portions of the intestines & left reproductive organs
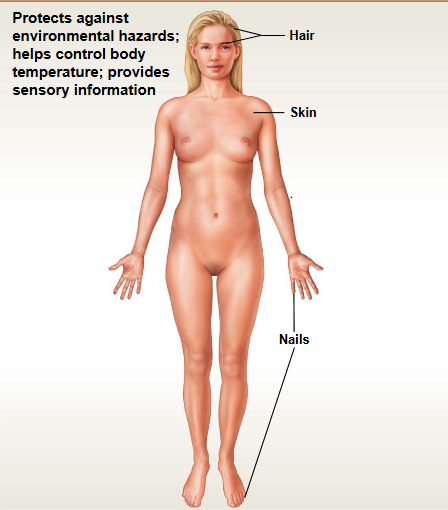
Integumentary System
This system contains: Skin, Hair, & Nails
Functions: protection & temperature regulation
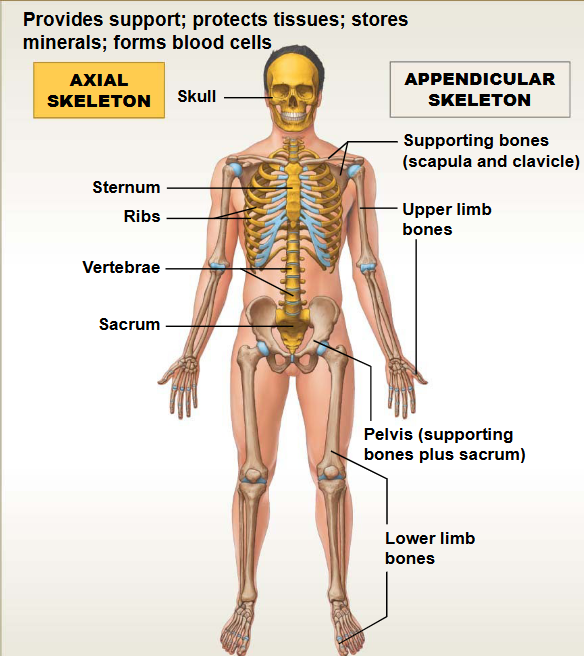
Skeletal System
This system contains: Bones & Joints
Functions: Support & Protection
Muscular System
This system contains: Skeletal Muscles
Functions: Movement
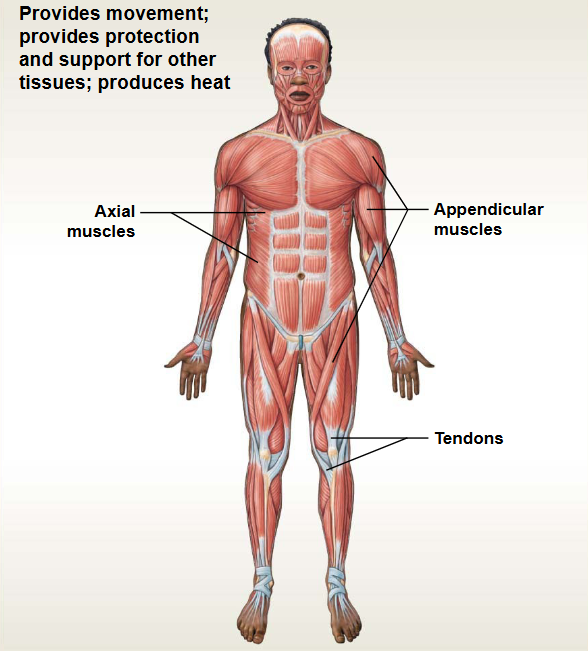
Nervous System
This system contains: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves
Functions: Control & Coordination
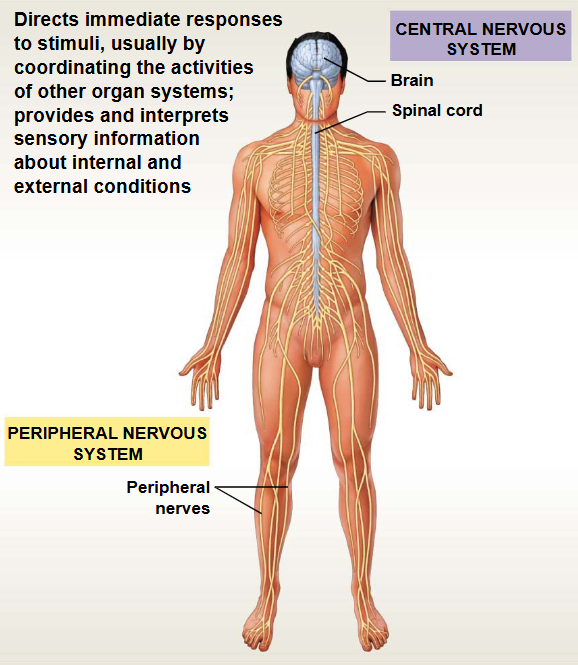
Endocrine System
This system contains: Hormone-producing glands
Functions: Regulation & control
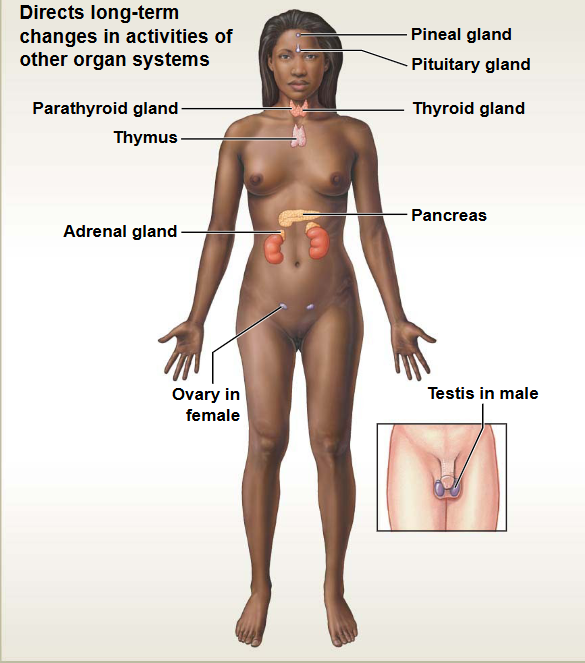
Cardiovascular System
This system contains: Heart & Blood Vessels
Functions: transport
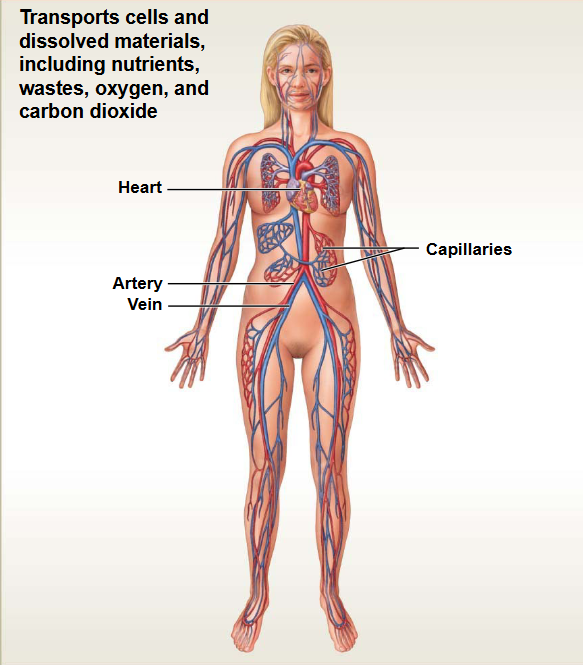
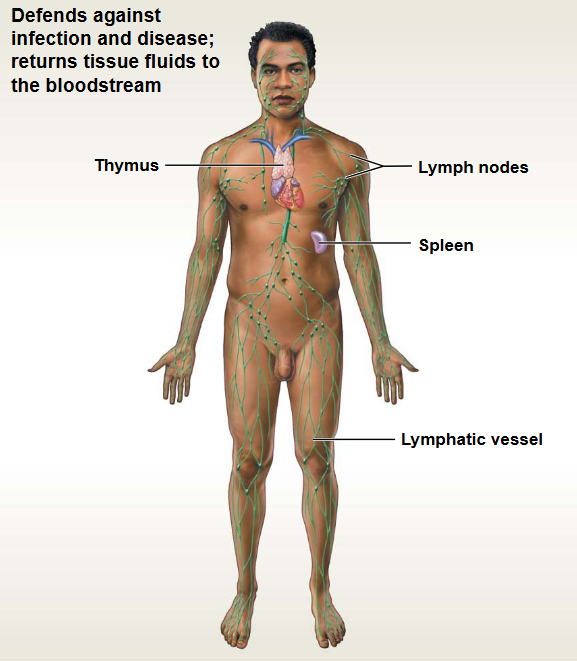
Lymphatic System
This system contains: Lymph nodes, Vessels
Functions: Immunity & fluid balance
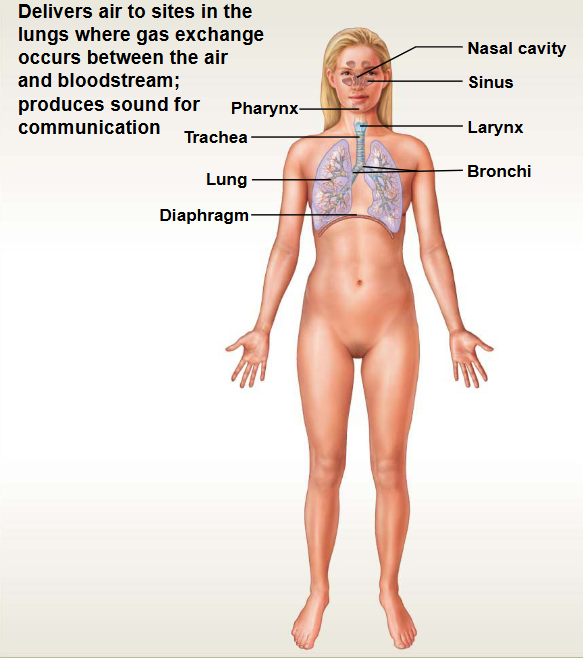
Respiratory System
This system contains: Lungs & Airways
Functions: Gas Exchange
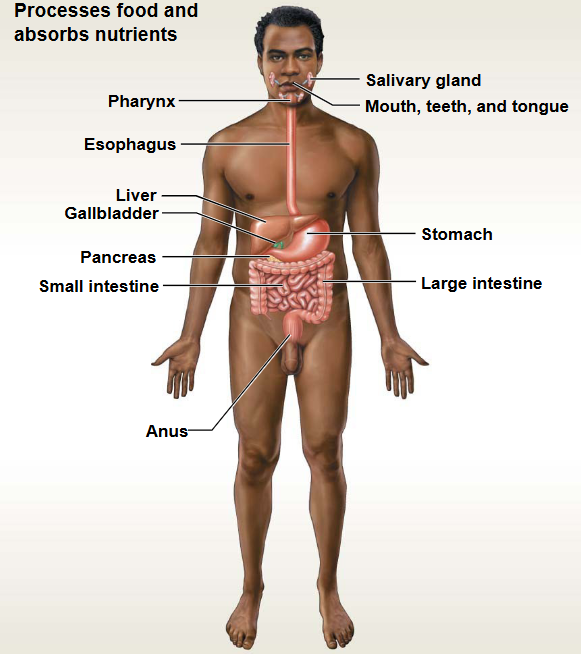
Digestive System
This system contains: Stomach, Intestines, Liver
Functions: Breakdown & absorption of nutrients
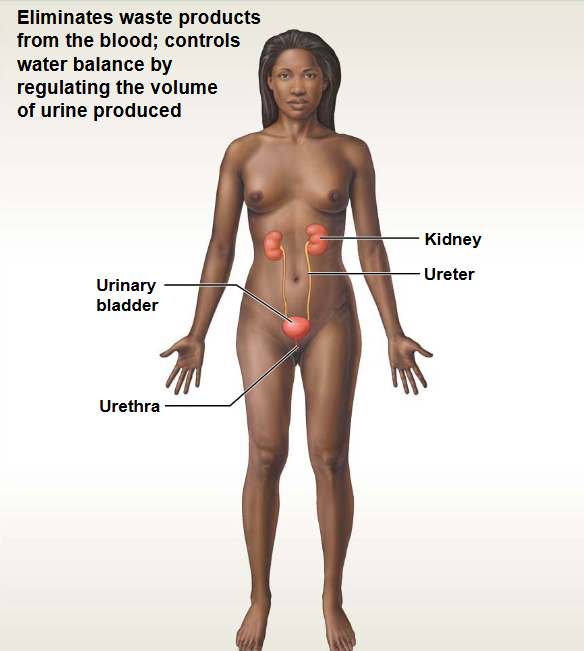
Urinary System
This system contains: Kidneys & Bladder
Functions: Waste elimination & water balance
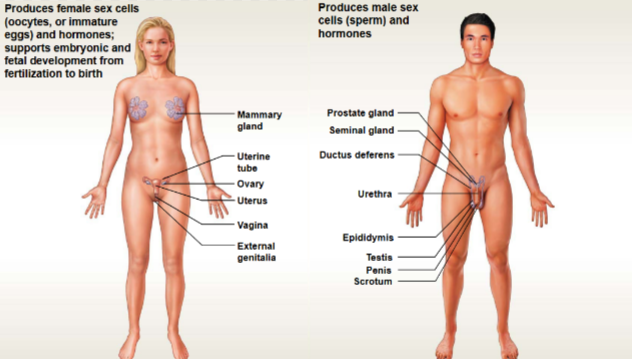
Reproductive System
This system contains: Reproductive organs
Functions: continuation of species
X-Rays
This imaging technique uses electromagnetic radiation
good for dense structures like bones; 2D images
CT Scans (Computed Tomography)
This imaging technique uses x-rays with computer processing
Cross-sectional images; better soft tissue contrast than x-rays
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
This imaging technique uses magnetic fields & radio waves
excellent soft tissue detail; no ionizing radiation
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
This imaging technique uses radioactive tracers\
shows metabolic activity, often combines with CT
Ultrasound
This imaging technique uses sound waves
real-time imaging; safe for pregnancy; good for soft tissues & blood flow
Hydrophobic
“water fearing”
substances that do not dissolve in water (nonpolar)
Hydrophillic
“Water loving”
substances that dissolve in water (Polar)
Atom
Smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze (speed up) biochemical reactions
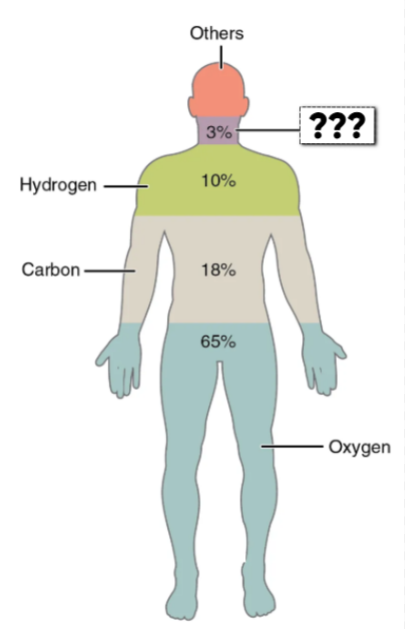
Carbon (C)
this element makes up 18.5% of the body
forms backbone of organic molecules
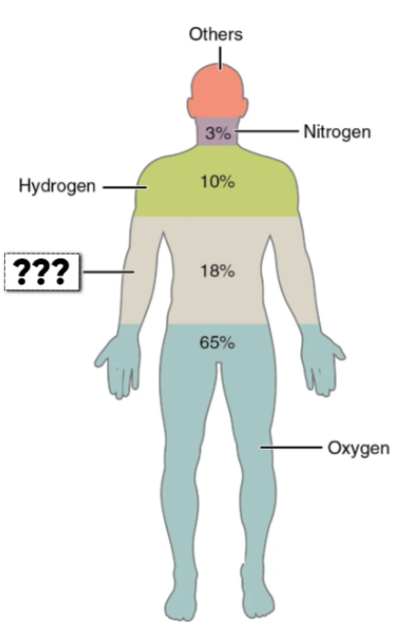
Hydrogen (H)
this element makes up 9.5% of the body
component of water & organic molecules
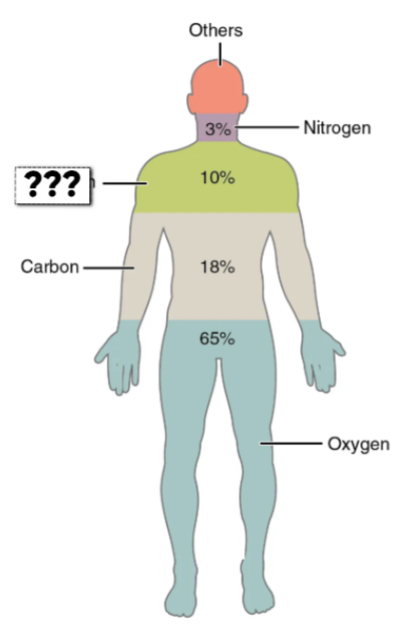
Oxygen (O)
this element makes up 65% of the body
component of water & organic molecules
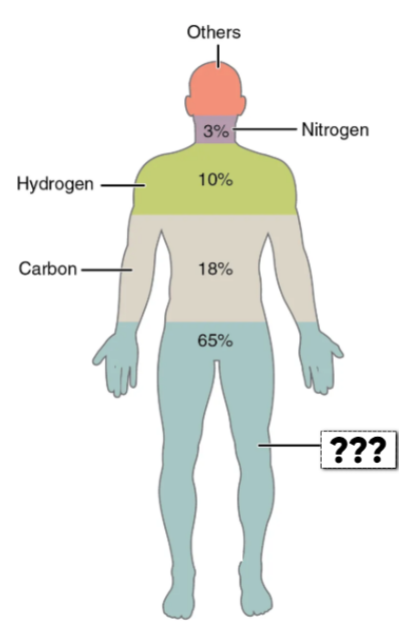
Nitrogen (N)
this element makes up 3.2% of the body
Component of proteins & nucleic acids
Mixture
2+ components physically intermixed
Solution
Homogenous mixture; solute is completely dissolved in solvent
ex: salt water
Colloid
Mixture with particles larger than in solution, but smaller thana in suspension
ex: milk
Suspension
Heterogenous mixture; particles settle out over time
ex: Blood
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds
Give water its unique properties
Important in protein & DNA structure
Enable waters cohesion & adhesion properties
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion
Potential Energy
Stored energy due to position or structure
Chemical Energy
Form of potential energy stored in chemical bonds
Inorganic Compounds
These usually lack carbon
include: water, salts, acids, bases
Organic Compounds
These contain carbon
include: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
Importance of water in the body
makes up 60-80% of body weight
solvent for biological reactions
transport medium
helps with temperature regulation through evaporation
acts as a lubricant for joints
helps maintain cell shape
PH Scale
measures hydrogen ion concentration
ranges from 0-14
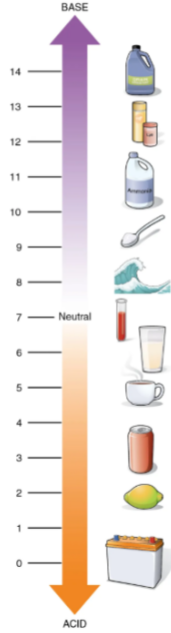
Acid
PH is less than 7
releases hydrogen ions (H+)
Base
PH is greater than 7
releases hydroxide ions (OH-) or accepts H+
Blood
The normal PH of this ranges from 7.35-7.45
is considered slightly basic
Carbohydrates
A molecule composed of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Also referred to as saccharides
3 forms of saccharides: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides
A critical fuel source
Glucose
primary energy source for cells
a type of monosacchride
Fructose
Fruit sugar
a type of monosacchride
Sucrose
Table Sugar
glucose + fructose
a type of disacchride
Lactose
Milk sugar
glucose + galactose
a type of disaccharide
Starch
Storage form of glucose in plants
type of polysacchride
Lipids
class of nonpolar organic compounds built from hydrocarbons and distinguished by the fact that they are not soluble in water
Ex: Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Steroids, Prostaglandins
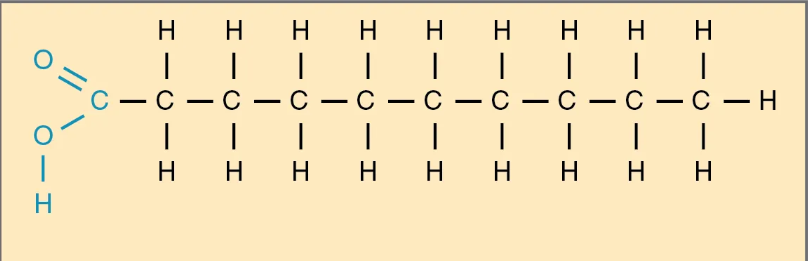
Saturated Triglycerides (Fat)
have no double carbon bonds anywhere along their length and therefore contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms
Solid at room temperature
Diet high in this increases risk of heart disease
Mainly from animals
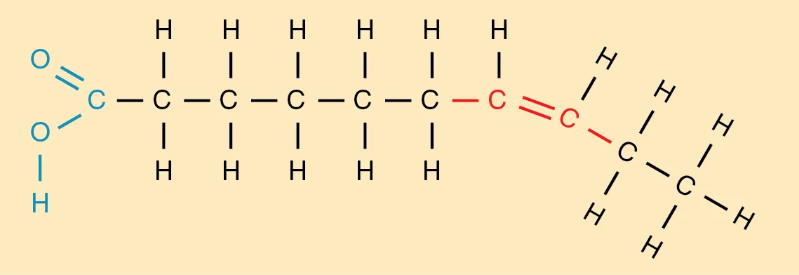
Unsaturated Triglycerides (Fat)
These fatty acids are unable to pack together tightly, have one or more double carbon bonds and are kinked at that bond
Diet high in this lowers risk of heart disease
liquid at room temperature
mainly from plants
Protein
An organic compound composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
functions include: structure, enzymes, transport, defense
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA & RNA
Contain: sugar, phosphate, & a nitrogenous base
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Energy currency of cells
provides energy for cellular processes
Cell
Basic structural & functional unit of life
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration of a substance between two ares
Passive Transport
This form of transport requires no energy
Moves with concentration gradient
Ex: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
Active Transport
This form of transport requires energy (ATP)
moves against concentration gradient
Ex: Sodium-potassium pump, endocytosis, exocytosis
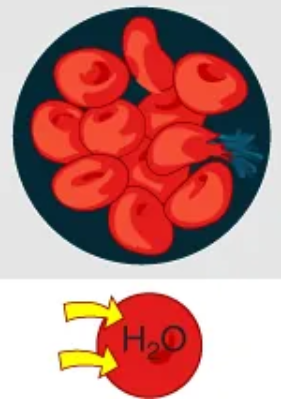
Isotonic
Type of solution in which there is the same concentration of solutes as a cell
there is no net water movement
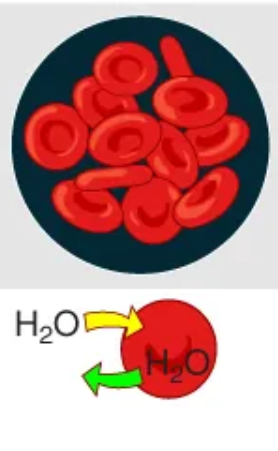
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration than a cell
water enters cell
Cells in this type of solution will swell as a result of taking in too much water (risk of bursting exists)
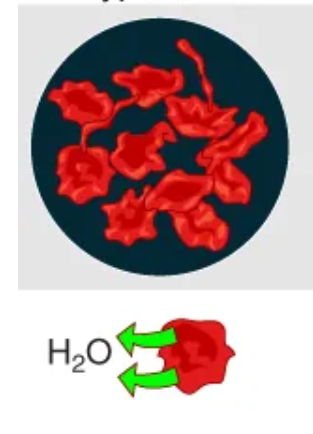
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than a cell
Cells in this type of solution will shrivel as water leaves the cell via osmosis
Cell shrinks
Nucleus
“Control Center”
contains DNA
Controls cell activities
Mitochondria
“Powerhouse”
produces ATP through cellular respiration
Smooth ER
one of the “Manufacturers”
Lipid synthesis & detoxification occurs here
Has no ribosomes
Rough ER
one of the “Manufacturers”
Protein synthesis & modification occurs here
has ribosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, packages & ships proteins from the ER
Ribosomes
Functions in protein synthsis
floats around freely in cytoplasm or attaches to the rough ER
Lysosomes
“Garbage Disposal”
contain digestive enzymes
break down worn-out organelles
Peroxisomes
contain enzymes that neutralize harmful substances (such as alcohol)
many located in the liver
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments
maintains cell shape & organelle position
Centrioles
These organize microtubules during cell division
Cell Membrane
Selectively permeable barrier
controls what enters & leaves cell
Mitosis
process of cell division that produces two identical diploid cells
Selective Permeability
This allows some substances to pass through, while restricting others