02. Hypothalamus & Pituitary Hormones
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
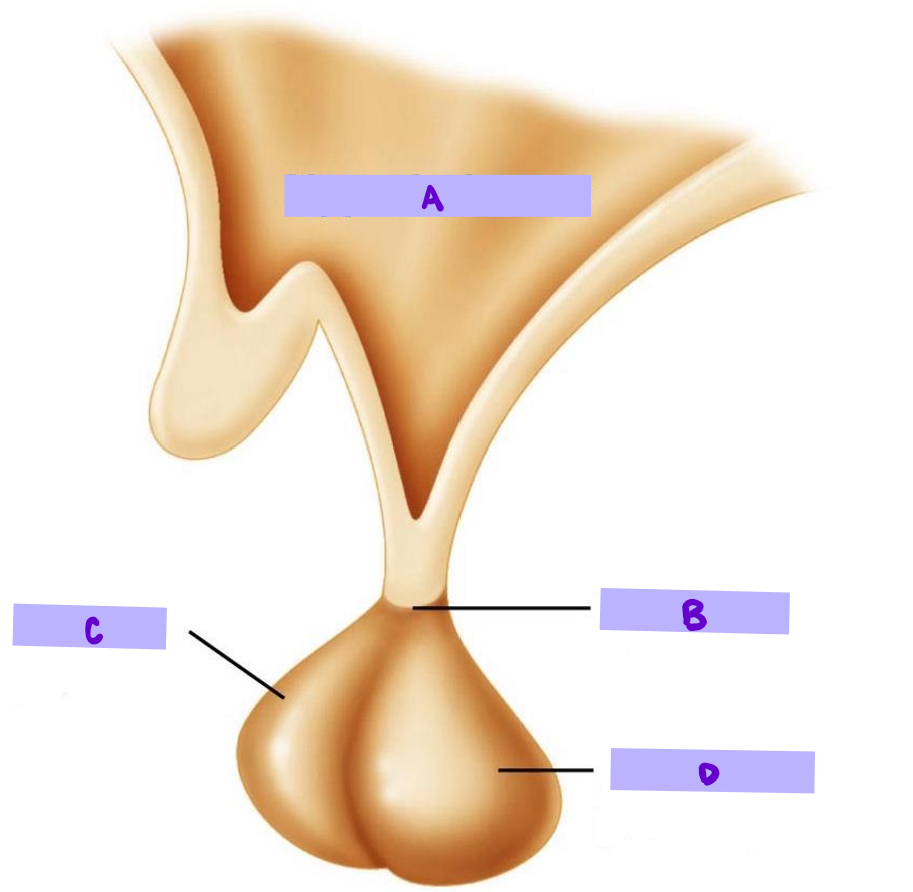
Label:
A: hypothalamus
B: infundibulum
C: anterior pituitary
D: posterior pituitary
Define: Hypophysiotropic Hormones
hypothalamic hormones that regulate anterior pituitary fxn
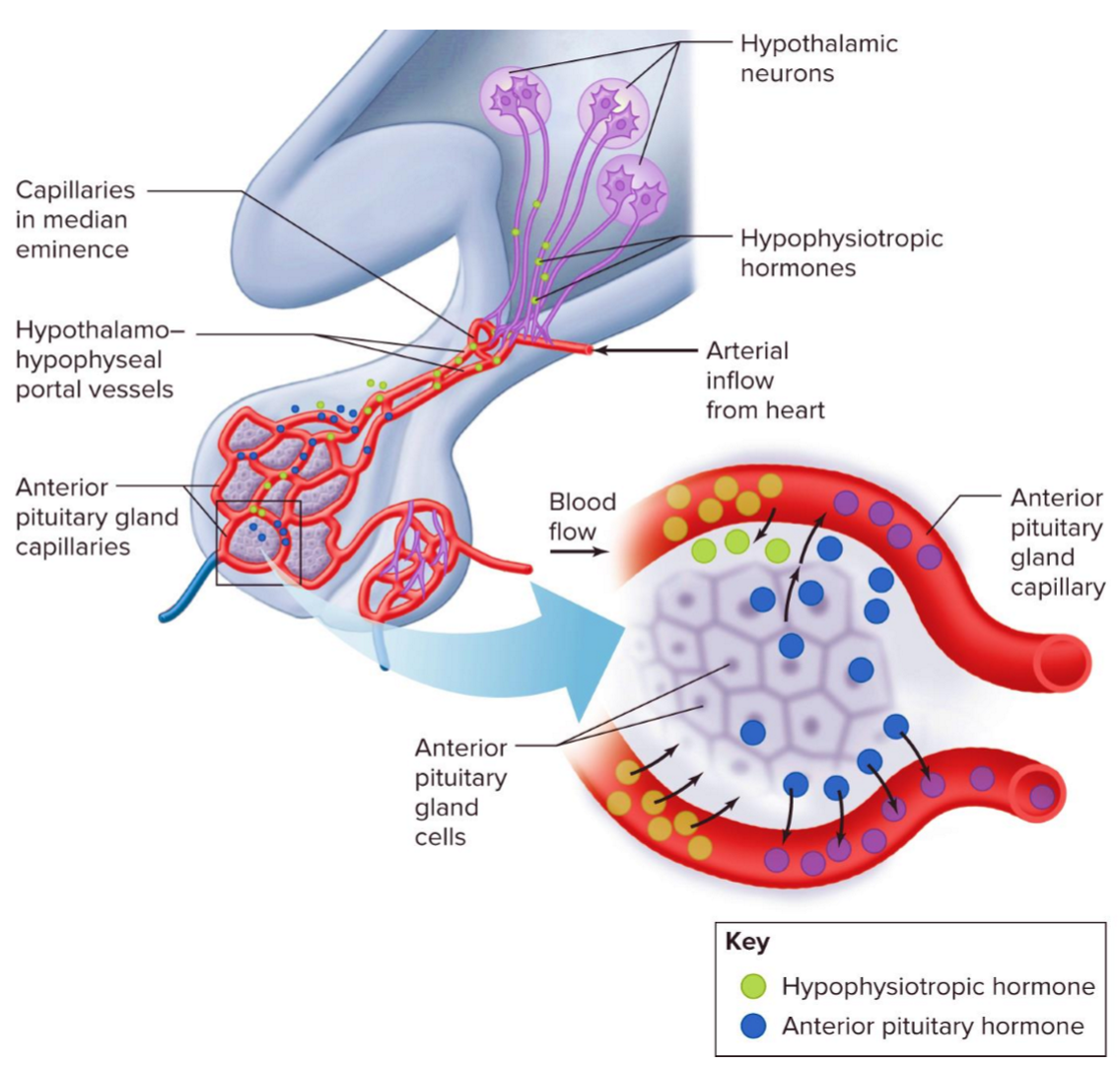
How do hypophysiotropic hormones reach the anterior pituitary gland?
hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal vessels
neurons synthesize trophic neurohormones → release into capillaries of portal system → portal veins carry to anterior pituitary → act on endocrine cells → endocrine cells release peptide hormones into second set of capillaries for distribution to body
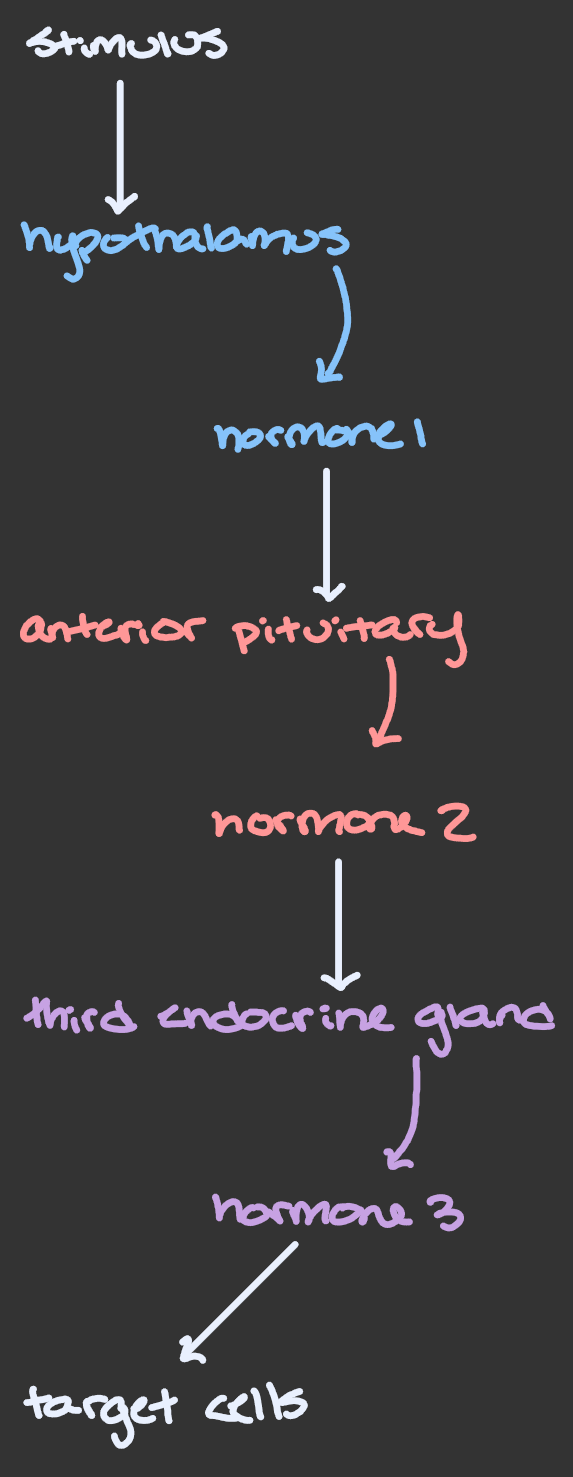
Basic Format of Three-Hormone Sequence
stimulus → hypothalamus → anterior pituitary → third endocrine gland → target
Three-Hormone Sequences
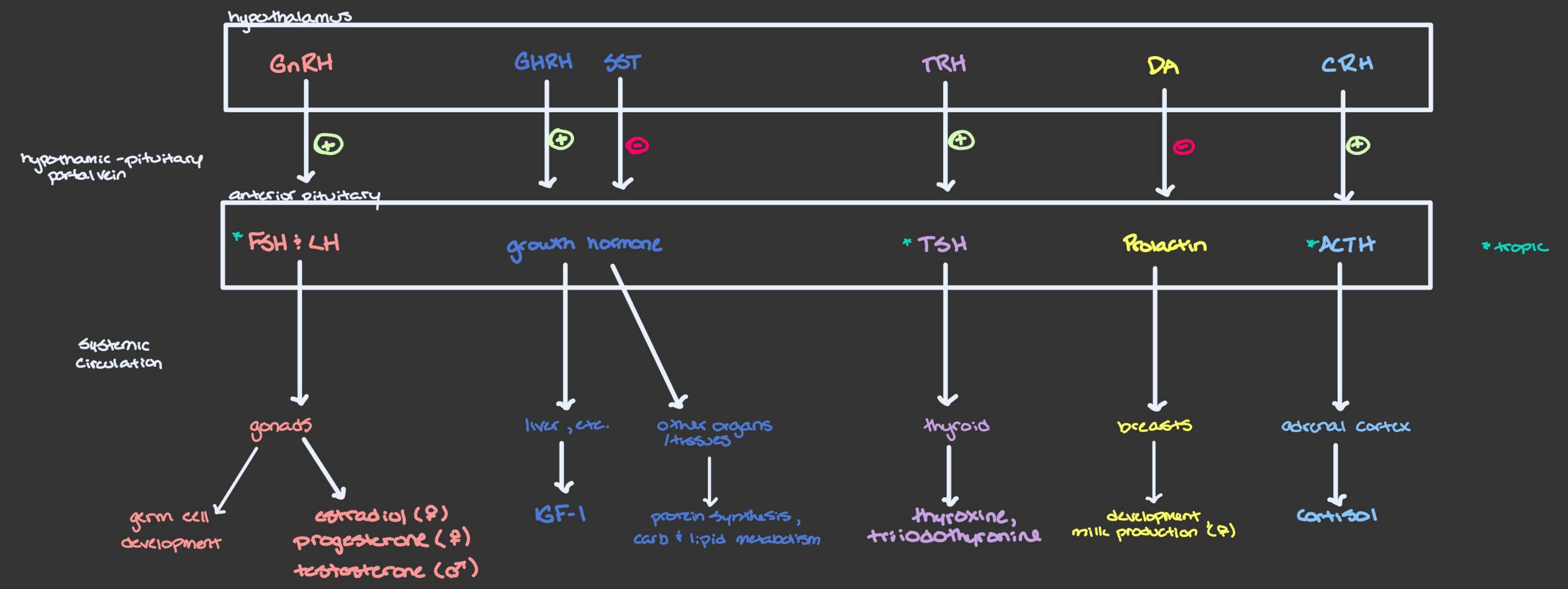
Which anterior pituitary hormones are tropic?
What does this mean?
FSH, LH, TSH, & ACTH → target endocrine glands & stimulate release of other hormones
Two Mechanisms to Regulate Hypophysiotropic Hormones
Neural control → stimulatory/inhibitory input from CNS
Negative feedback control → high levels of final hormone in pathway stops its own production (inhibit secretion from hypothalamus & anterior pituitary) → hormone three not in excess
Negative Feedback Control: Short-Loop vs. Long-Loop Feedback
Short: hormone 2 inhibits release of hormone 1
Long: hormone 3 inhibits release of hormones 1 & 2
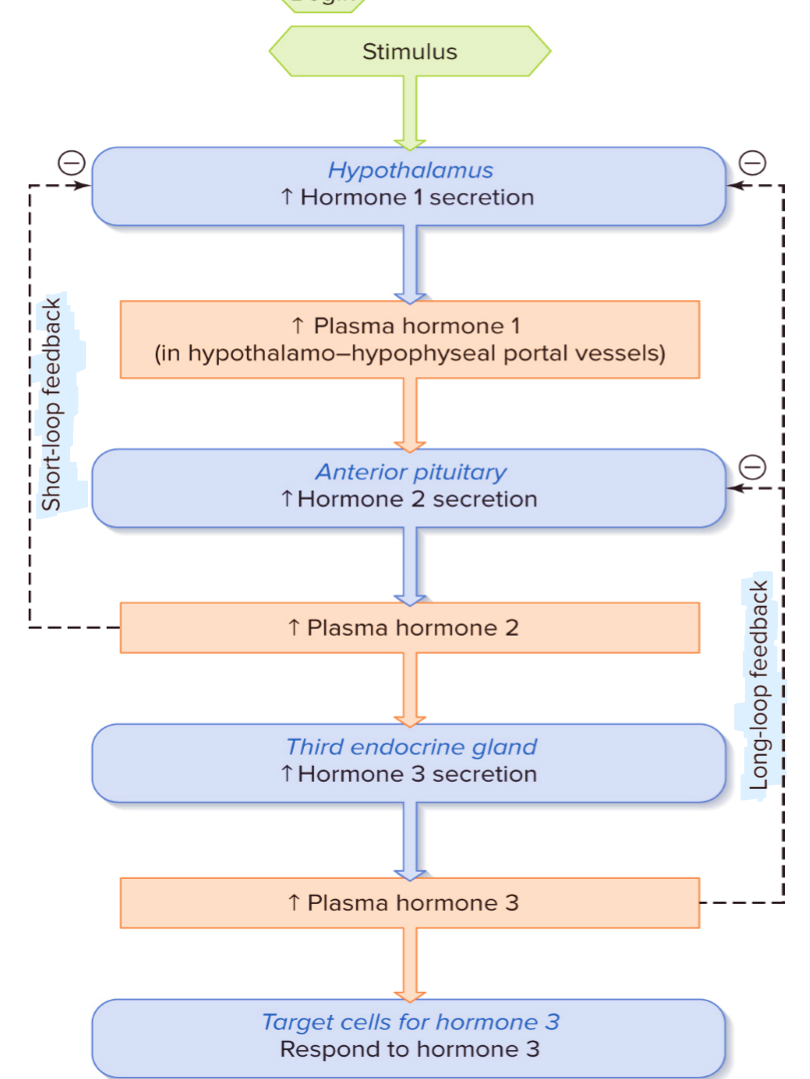
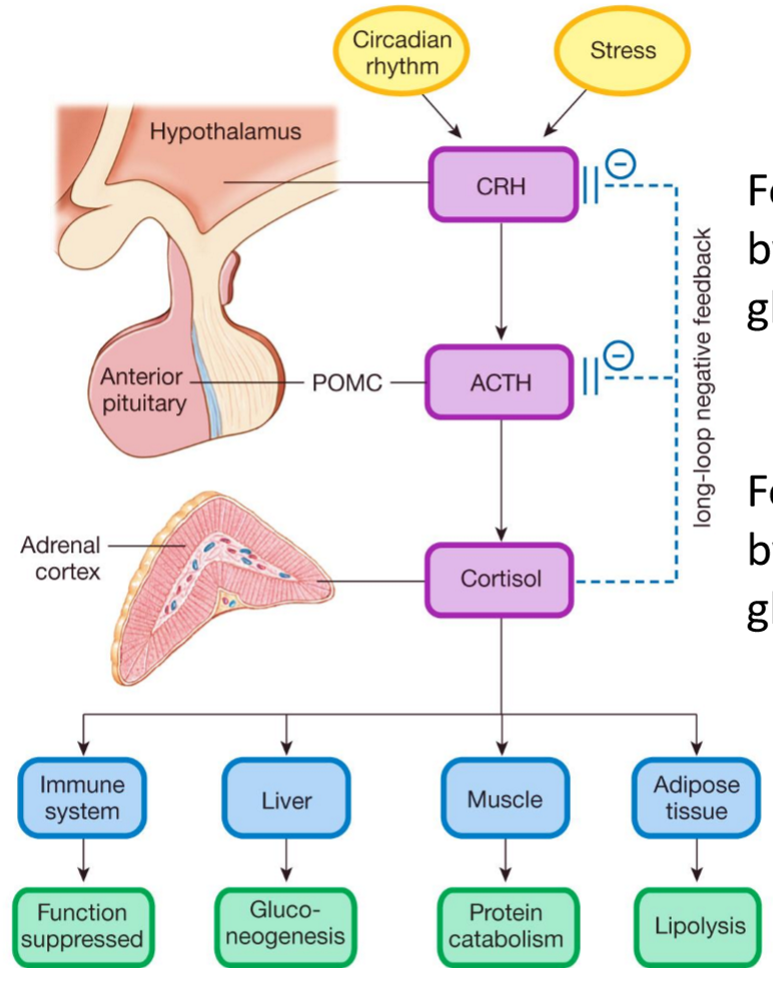
Feedback Loop for CRH
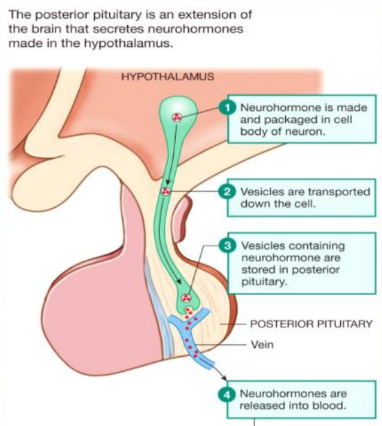
Production of Posterior Pituitary Hormones
produced & packaged in cell body of neuron in hypothalamus
vesicles transported down cell → stored & released into the blood in/from posterior pituitary
What are the two posterior pituitary hormones?
What nucleus is responsible for secreting each?
oxytocin → from supraoptic nucleus
vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) → from paraventricular nucleus
Three Primary Functions of Oxytocin
promotes milk production & ejection reflex of lactation
uterine contractions during childbirth
emotional/social bonding
Three Primary Functions of Vasopressin (ADH)
regulation of blood pressure (via vessel constriction)
regulation of water balance
regulation of osmolarity
Positive Feedback Loops of Oxytocin
Childbirth
oxytocin prompts uterine contractions → pushes head twd cervix → causes cervical stretching (sensed by mechanoreceptors) → stimulates more oxytocin synthesis/release
Breastfeeding
suckling activates nipple mechanoreceptors → triggers oxytocin release → cause milk ducts to contract → milk ejected → stimulate further oxytocin release
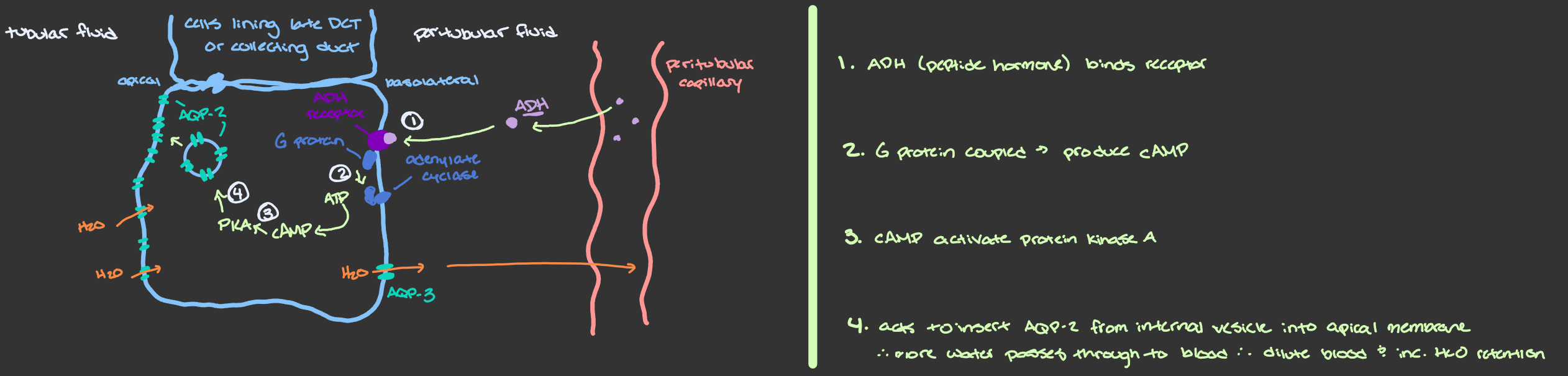
What is the effect of ADH in the kidneys? in the blood vessels?
Kidneys → inc. water reabs. (reduce urine production & conserves water) → helps maintain blood osmolarity
Blood vessels → lead to vasoconstriction → inc. peripheral resistance & inc. BP
Regulation of ADH Release
Neg. feedback
blood osmolarity inc.
inc. ADH secretion
inc. water reabs. in kidneys (helps maintain blood volume/pressure)
blood osmolarity dec. to normal
dec. ADH secretion
inc. BP → detected by stretch receptors → inhibit ADH secretion
dec. BP → reduce inhibition of ADH secretion → promote ADH release
Vasopressin (ADH) Effect at Kidneys
ADH Abnormalities: Alcohol
inhibits ADH release → inc. urine production, dehydration, & hangoverA
ADH Abnormalities: Diabetes Insipidus
(symptoms similar to diabetes but not related to blood sugar)
chronic underproduction of ADH → excessive urination (polyuria) & chronic dehydration
ADH Abnormalities: Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH)
excess ADH release/action, causing…
abnormal water retention
diluted blood Na+ levels (hyponatremia)
blood hypo-osmolality (dilute blood)
high urine osmolality
Four Influences on Normal Growth
growth hormone + other hormones → IGF-1, IGF-2, T3, insulin, sex hormones, cortisol
adequate diet → enough protein, fatty acids, vitamins, minerals
absence of chronic stress
genetics
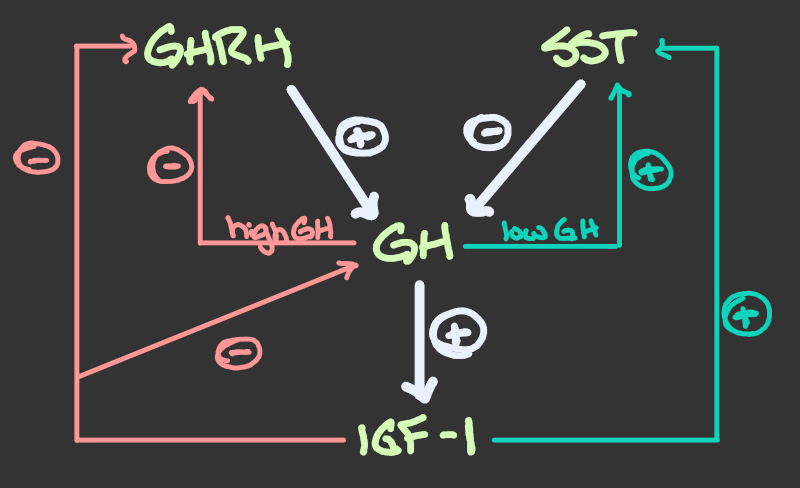
Release & Delivery of Growth Hormone (GH)
release stimulated by growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
release inhibited by growth hormone-inhibiting hormone/somatostatin (GHIH/SST)
GH binds growth hormone-binding protein (GHBP) → very important so bind to ensure proper delivery as peptides have shorter life → stimulate IGF secretion
Function of GH & IGF Together
stimulate protein synthesis
inc. lipolysis (fat breakdown) & gluconeogenesis (new glucose production)
dec. glucose uptake → inc. blood glucose
inc. bone growth
Feedback Control of GH Secretion
Define: Epiphyseal Growth Plate
site of growth in length of bone → composed of hyaline cartilages & located b/w epiphysis & diaphysis (shaft)
Define: Chondrocytes
cartilage cells in the epiphyseal plate → are target cells for GH & IGF-1
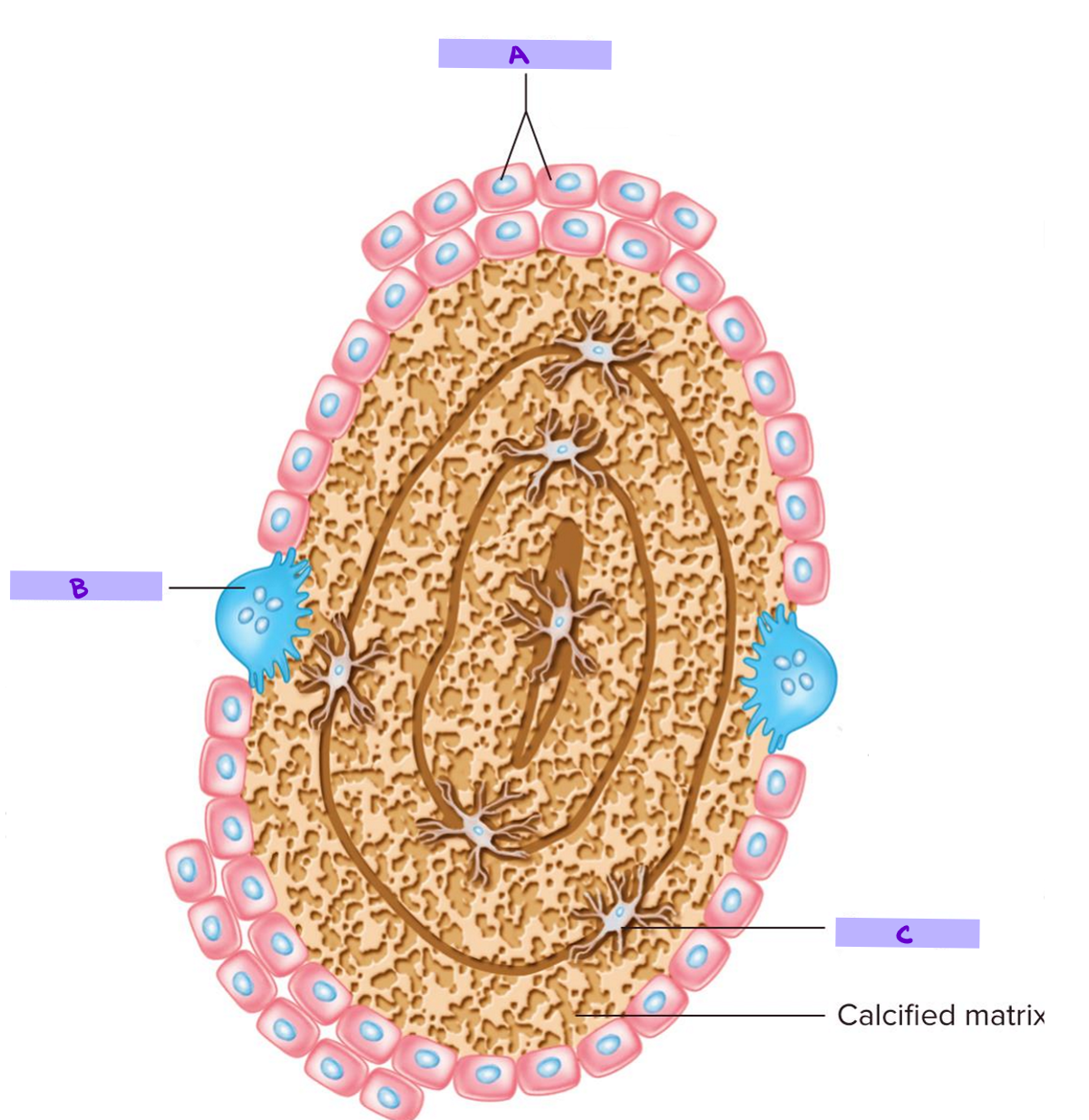
Label: Cross Section of Bone
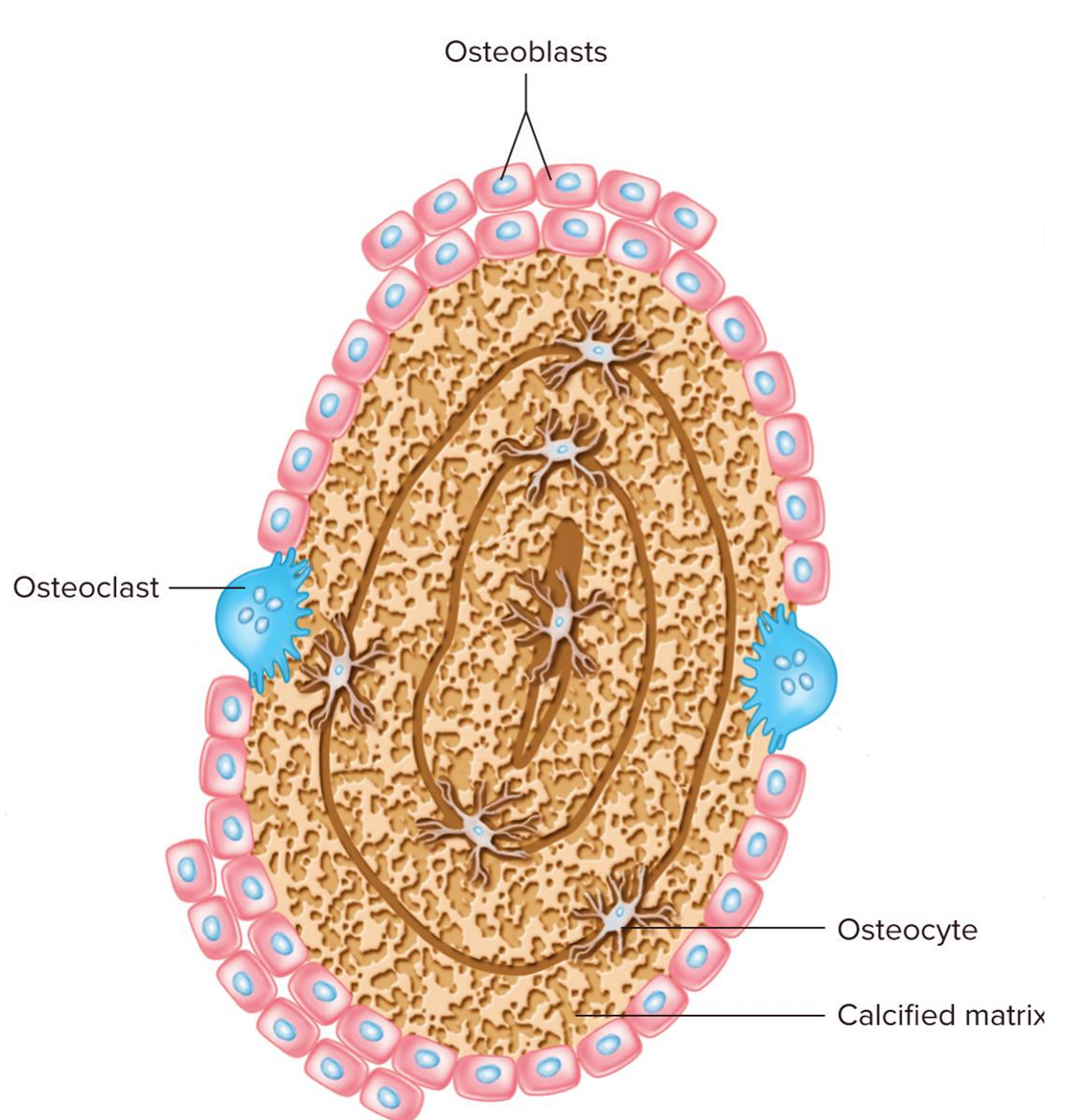
Define: Osteoblasts
bone makers → secrete bone matrix which later mineralize to form bone
opp. of osteoclasts
Define: Osteoclasts
bone breakers → responsible for bone resorption → break down bone & releasing minerals (e.g. Ca2+) into blood
opp. of osteoblasts
Define: Osteocytes
bone maintainers → regulate bone remodeling by directing -blast & -clast activity → maintain mineral content of surrounding matrix
Define: Epiphysis vs. Diaphysis
epiphysis: end of long bone
diaphysis: shaft of long bone
separated by epiphyseal plate → site of growth
Composition of Bone
mostly calcified extracellular matrix
by weight…
~60-65% inorganic material → primarily hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate minerals) → provides hard structure
~30-35% organic material → mainly collagen & other proteins
~5-10% water
Steps of Bone Growth
chondrocytes produce new cartilage (by dividing) in the epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal plate widens → bone lengthens
chondrocytes undergo hypertrophy then die
osteoblasts create calcium phosphate crystals to replace cartilage (chondrocytes) → lay down bone
Epiphyseal Plate Closure / Growth Plate Fusion
senescence of growth plate near end of puberty → chondrocytes die & cartilage replaced by mature bone
end of bone's longitudinal growth
GH Disorders: Gigantism
in children before growth plate fusion
abnormally rapid growth, excessive height, large hands/feet, delayed puberty
caused by benign pituitary tumor (adenoma) → producing excess GH
GH Disorders: Acromegaly
in adults after growth plate fusion
gradual enlargement of bones/soft tissues, enlarged extremities, coarsened facial features, thickened skin
caused by benign pituitary tumor (adenoma) → producing excess GH