Dopaminergic Neurotransmission
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
How is dopamine synthesised in humans?
Dopamine is synthesized in humans from the amino acid L-tyrosine, which is first converted to L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (substrate specific) by catalysing the addition of an OH. L-DOPA is then decarboxylated by DOPA decarboxylase to form dopamine.
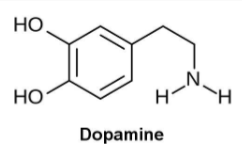
Describe the structure of Dopamine
Benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups
One substituted amine group (catecholamine).
What is the rate limiting step of dopamine synthesis?
Tyrosine hydroxylase converts L-tyrosine to L-DOPA.
L-DOPA to dopamine is faster because it is catalysed by a non-specific enzyme.
What is DAT?
An active transporter protein for dopamine
It is presynaptic and transmembrane.
It facilitates the reuptake of dopamine from the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic neuron, thereby regulating dopamine levels in the brain.
Has a high affinity for dopamine reuptake.
How does cocaine, amphetamine etc affect DAT?
Inhibit DAT by binding and deactivating it, leading to increased synaptic dopamine levels by preventing its reuptake. This enhances dopaminergic signaling and can lead to euphoria in humans and hyperactivity in rats.
What is VMAT?
Vesicular Monoamine Transporter
Responsible for packaging dopamine into vesicles for storage and release in presynaptic neurons.
Blocking the action of VMAT leads to Parkinson’s phenotype.
What is 6-OHDA?
6-Hydroxydopamine, a neurotoxin with a similar structure to dopamine.
It is taken up by DAT but induces oxidative stress, leading to a buildup of reactive oxygen species.
Produces hydrogen peroxide and ultimately causes neuronal damage and apoptosis.
What can happen to mice that are introduced to 6-hydroxydopamine?
Neurodegenerative symptoms
Behavioural changes and changes in memory.
If they produce an antioxidant, they may recover.
How is dopamine metabolised and what is funny about it?
It is metabolised by Monoamine oxidase (MAO) on the inner mitochondrial membrane and COMT in the cytosol. The enzymes can work in either order to produce HVA, an inactive metabolite that is secreted normally.
What is the difference between dopaminergic, noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons?
Dopaminergic neurons lack dopamine-b-hydroxylase and PNMT.
Noradrenergic neurones just lack PNMT.
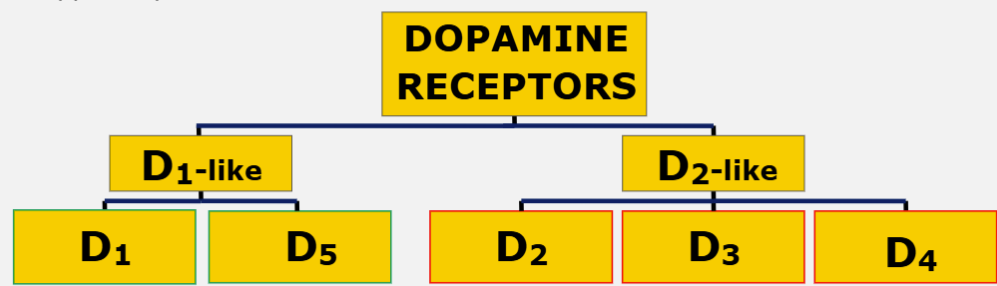
What are the different types of DA receptors?
DA receptors - all G-coupled protein receptors (GPCR)
D1-like - D1 and D5
D2-like - D2, D3 and D4
Describe D1-type receptors
Upregulate cAMP (signal transduction)
Increase PIP hydrolysis
Activate PKC (protein kinase C).
Describe D2-type receptors
Decrease cAMP levels.
Regulate ion channels by increasing K+ currents and have less Ca2+ channels.
Where are all the D-type receptors most active?
D1 - striatum, neocortex
D5 - hippocampus, hypothalamus
D2 - striatum, pituitary
D3 - olfactory tubercle
D4 - frontal cortex
How can you visualise dopaminergic neurones in the brain?
Antibodies are used to detect tyrosine hydroxylase and then visualised using labelling.
What are the 4 dopamine pathways in the brain?
Nigrostriatal
Mesolimbic
Mesocortical
Tuberoinfundibular
Describe the Nigrostriatal Dopamine Pathway
From the substantia nigra to the basal ganglia.
Controls the execution of voluntary muscle movement
Degeneration occurs in Parkinson’s.
Describe the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway
From tegmental area to nucleus accumbens.
Limbic system - controls emotion and pleasure/reward.
Over-activity in the pathway contributes to the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Describe the Mesocortical Dopamine Pathway
From tegmental area to the frontal cortex.
Associated with motivation and emotion.
Under-activity contributes to negative schizophrenia symptoms.
Describe the Tuberoindundibular Dopamine Pathway
From the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
TIDA neurones release DA that inhibits prolactin secretion, so in maternal behaviour, DA synthesis is downregulated.
What role do D2-type receptors play in addiction?
D2-type receptors are involved in the reward system; their decreased function is associated with addiction vulnerability.
What is the significance of HVA in dopamine metabolism?
HVA (homovanillic acid) is an inactive metabolite of dopamine, commonly used as a biomarker for dopamine activity in the body.
Describe the differences in dopamine synthesis in the brain vs. the periphery.
In the brain, dopamine is synthesized primarily in dopaminergic neurons, while in the periphery, it is produced in areas like the adrenal glands and is involved in different functions, such as cardiovascular regulation.
What are dopamine antagonists and their therapeutic uses?
Dopamine antagonists are drugs that block dopamine receptors, used clinically to treat conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and emesis (nausea and vomiting).
How does the body regulate dopamine levels?
Dopamine levels are regulated by synthesis (tyrosine hydroxylase activity), reuptake (via DAT), and metabolism (via MAO and COMT).