Neurotransmission Quiz Study Guide
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters GABA?
Inhibitory, effects: relaxation, calming, anti-anxiety, sleep
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Dopamine?
Excitatory, effects: pleasure, reward-centers, addiction, “feel good NT”
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Serotonin?
Excitatory, effects: sleep, mood, appetite, pain, body temperature; low serotonin linked to depression
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Acetylcholine?
Excitatory, effects: alertness, memory, muscle contraction
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Glutamate?
Excitatory, effects: stimulates learning and memory formation, most abundant NT
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Endorphins?
Excitatory and Inhibitory, effects: alertness, blocks pain, often released after physical activity
What are the effects of the following neurotransmitters Norepinephrine?
Excitatory, effects: alertness, energy, stress
Excitatory NTs ______________ in the next neurons
cause impulses
Inhibitory NTs __________ from being sent in the next neuron
stop an impulse
What kind of charge does the inside of the cell have?
Net negative charge
What kind of charge does the outside of the cell have?
Net positive charge
1st step of neurotransmission
A neuron is stimulated by another neuron or the environment
2nd step of neurotransmission
Gates in the sodium channels open allowing positively charged sodium ions to flow into the cell causing an action potential.
3rd step of neurotransmission
As the action potential passes, gates in the potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to flow out of the cell. This restores the negative potential inside the neuron.
4th step of neurotransmission
The action potential jumps from node to node along the axon until it reaches the axon terminal.
5th step of neurotransmission
Neurotransmitters are released from the vesicles into the synapse.
6th step of neurotransmission
After the neurotransmitter has done its job, it is taken back into the axon terminal to be used again or broken down.
1st way drugs can interfere with neurotransmission?
Increase number of impulses
2nd way drugs can interfere with neurotransmission?
Release NT from vesicles with or without an impulse
3rd way drugs can interfere with neurotransmission?
Block reuptake or block receptors
4th way drugs can interfere with neurotransmission?
Produce more or less NT
5th way drugs can interfere with neurotransmission?
Prevent vesicles from releasing neurotransmitter
The junction between two communicating neurons is called the:
synapse
Gaps in the myelin sheath are called:
nodes of navier
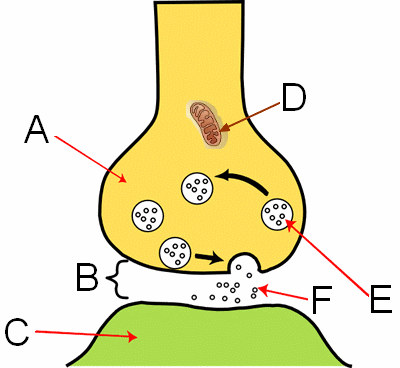
What are the circles (labeled F) in the image?
neurotransmitters
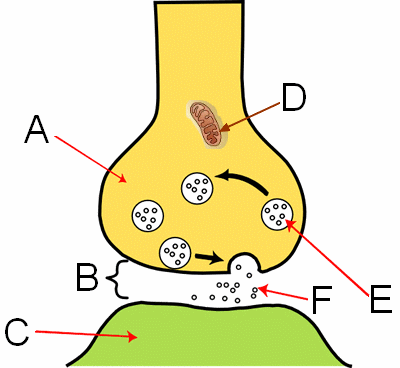
What is the structure labeled "B" in the image?
synapse
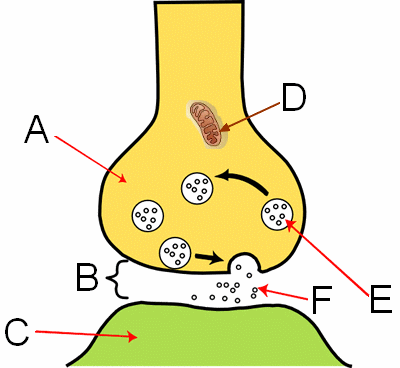
What is the structure labeled "A" in the image?
axon on the nerve cell
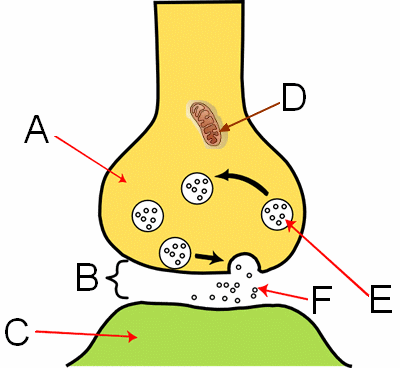
What is the structure labeled "E" in the image?
vesicles
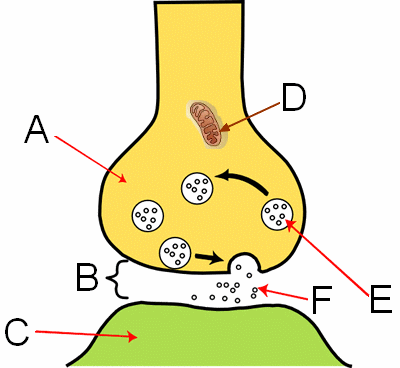
What is the structure labeled "C" in the image?
dendrite
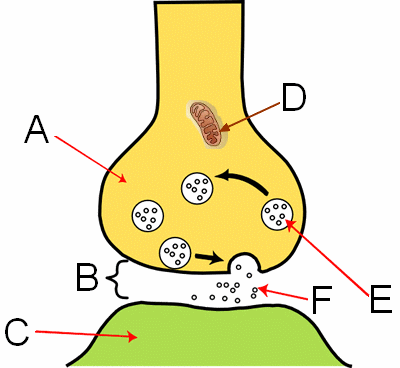
What is the structure labeled "D" in the image?
mitochondria
Which of the following will cause an impulse to move faster?
myelin sheath
These neurotransmitters are associated with mood and sleep:
seratonin
Types of neurotransmitters that increase membrane permeability:
excitatory
Axons that are myelinated will have __ impulses
faster
Which of the following neurotransmitters works with the muscles?
acetylcholine
Cocaine causes pleasureble feeling because it:
blocks reuptake of dopamine
Which neurotransmitter is released in the reward pathway?
dopamine
The most common cause of death from using this drug is overheating
ecstasy
This part of the neuron receives impulses.
dendrite
This part of the neuron conducts info away.
axon
This part of the neuron gaps in insulation
node
This part of the neuron contains the nucleus and other cell organelles.
cell body
This part of the neuron transmits impulse to next cell.
axon terminal
Re-uptake is
after the neurotransmitters have done their jobs they are taken back to the axon terminal so it can be used again or broken down.