Dreaming & Sleep
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Consciousnesses
Awareness of oneself and their environment
Electroencephalogram(EEG)
Neural imaging using electrodes on the scalp to record the brain’s electrical activity
FMRI:
a neuroimaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow
Active brain areas use more oxygen, increasing blood flow to those areas

Circular Rhythm
change in blood pressure,internal temp,hormones( can be dirupted by jet lag and night shift work) This can shift depending on your age
Brain waves Beta waves
13-30 Hz (During most activities while awake)
Alpha Waves
8-12. 99 ( While relaxed or sleepy)
Theta Waves
4- 7.99Hz ( During stage 1 and 2 light sleep)
Delta Waves
1-3.99Hz During stage 3 (deep) sleep)
NREM Stage N1
heartbeat and breathing slow down
muscles begin to relax
Last a few min
alpha -theta waves
Hypnagogic Sensations
Sensations you image are real (ex: feeling of falling)
Happens during NREM 1
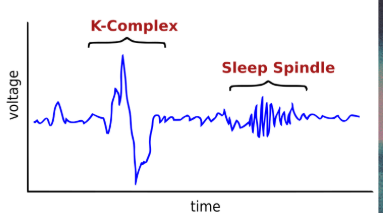
NREM Stage N2 (Light Sleep)
Heartbeat and breathing slow down further
no eye movements
body temp drops
brain produces “sleep spindles
Last about 25 min
NREM Stage N3
Deepest sleep state
heartbeat and breathing are at their slowest rate
no eye movements
body is fully relaxed
Delta Waves are present
tissues repair and growth and cell regeneration
immune system strengthen
REM Stage R
primary dreaming stage
eye movement becomes rapid
breathing and heart rate increases
limb muscles become temporarily paralyzed
brain activity is markedly increased
No REM sleep
memory loss
Muscle Atonia
During REM, noradrenaline serotonin, and histamine blocked = no muscle movement
You wake up but still be paralyzed
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
Loss of muscle Atonia( sleep paralysis), causing a person to act out their dream. Not Sleepwalking
REM
REM deprivation over a night/nights causes REM rebound
This means entering REM sleep more often/more easily the following night/s
Fatal Familial Insomnia
Rare genetic disease of that causes all patients to gradually lose the ability to sleep over span of a mere few months. untimely leading to death
Consolidation Theory
a primary function theory
proposes that dreams may help sift,sort, and fix the day’s experiences in our memory
Activation Synthesis Theory
REM sleep triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories, which our sleeping brain weaves into stories
Restoration Theory
sleep allows the body to repair and replenish cellular components that are depleted during the day. Sleep helps organism be healthy and productive by restoring energy lost during the day.
Narcolepsy
chronic neurological disorder that makes it difficult for the brain to regulate sleep-wake cycles
Sleep Apnea
A sleep disorder that causes people to stop breathing or breath shallowly while they sleep
Sommanbulism
Sleep walking and sleep talking occur during stage nREM3 of sleep