5: Reabsorption of Salt & Water: Loop of Henle
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Loop of Henle reabsorbs ≈..% of salt and water from the tubular fluid?
20%
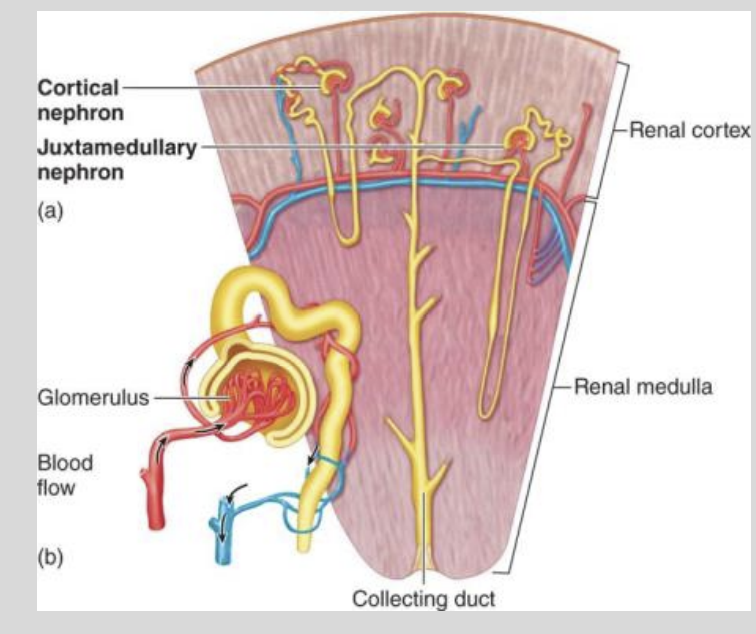
The descending limb of the loop of Henle extends down into the?
Medullary Tissue of the Kidney
Descending Limb is also called ?
Nephron Loop
ascending loop comes back up into the renal cortex of the kidney and forms?
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Water cannot be transported across the plasma membrane if the tubular filtrate?
Surrounding Interstitial Fluid
Is Isotonic
For water to be absorbed by osmosis the surrounding interstitial fluid must be?
Hypertonic
The osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid in the renal medulla is?
4x that of Blood Plasma
Interstitial fluid is the fluid that?
Baths the cell bodies.
it is one component of the extracellular fluid.
The descending and ascending limbs of the nephron loop are close enough..?
To Interact
the movement of water and salt is not?
Coupled
The interaction between the descending and ascending limbs creates a system known as the?
Counter Current Multiplier System
Ascending Nephron Limb Diagram
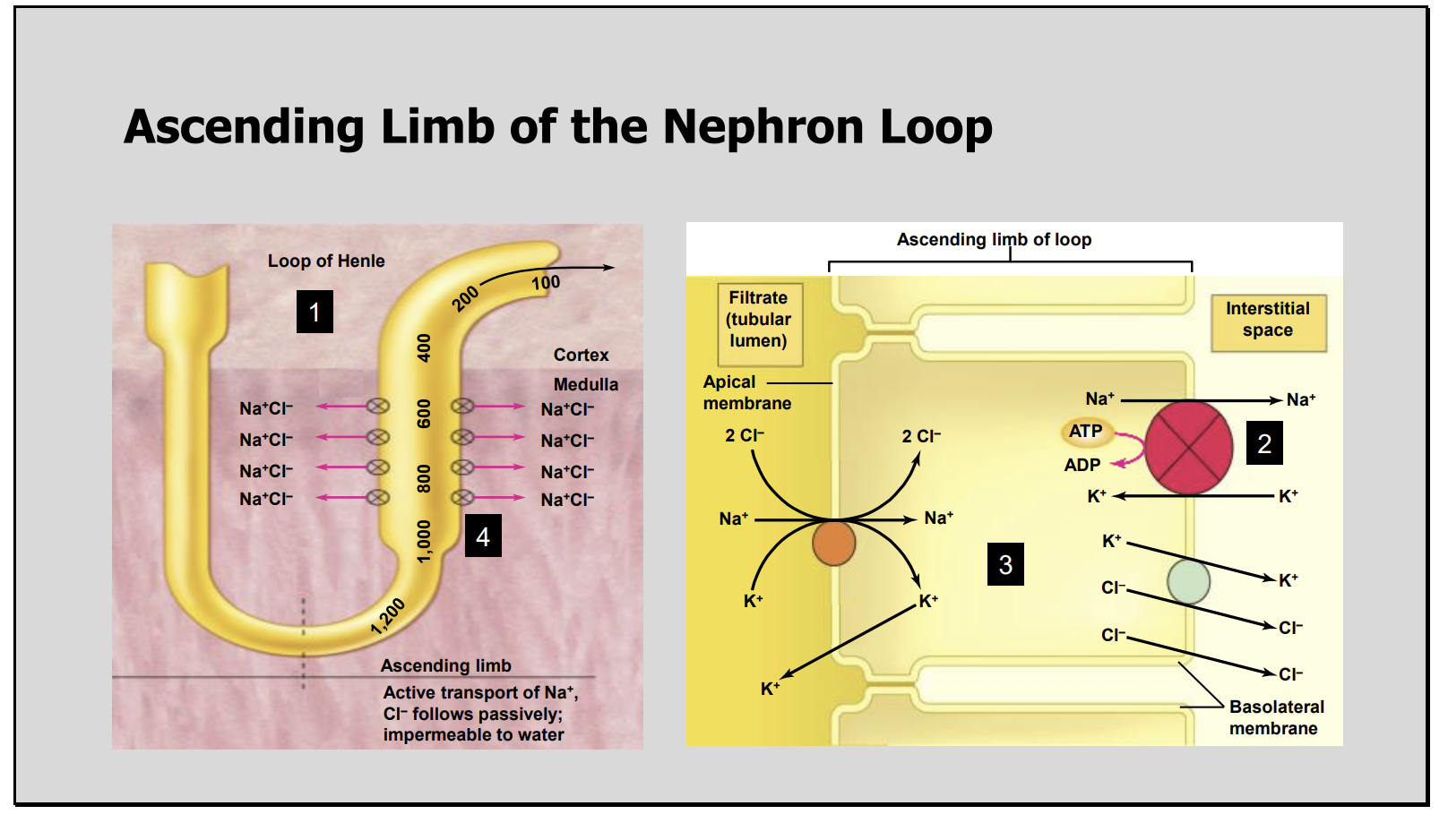
The ascending limb of the nephron loop is composed of?
2 Segments
What are the 2 Segments of the Ascending Limb?
Thin ascending limb which is nearest to the tip of the loop
Thick ascending limb which brings filtrate to the distal convoluted tubule
NaCl is pumped out of the filtrate by the?
Thick segment of the Ascending Limb
The basolateral membrane of the thick ascending limb epithelial cells are rich in?
Na+ /K+ pumps.
This ensures that Na+ concentration inside the epithelial cells is very low
Na+ enters the cell through a secondary active transporter that also functions to transport?
k+ and CI- into the cell
The ratio =
2 Cl- ,1 K+ , 1 Na+
The deeper regions of the medulla become extremely?
Hypertonic
concentrations of ≈1,200mOsm
concentrations of ≈1,200mOsm?
Must remain trapped in the Medulla
The capillaries in the medulla are uniquely arranged so?
So a High NaCl concentration can be maintained in the medullary interstitial fluid
The descending limb does not actively transport?
Salt
is impermeable to the passive diffusion of salt
However, the descending limb is permeable to?
Water
due to the presence of aquaporins in the apical membrane
Because the surrounding interstitial fluid of the medulla is very?
Hypertonic
Water is drawn out of the Filtrate Passively.
As more and more water leaves the filtrate, the filtrate itself becomes more?
Hypertonic
the filtrate itself becomes more hypertonic the deeper the descending limb advances into the?
Renal Medulla
At the tip of the loop, the hypertonic filtrate then passes into the?
Ascending Limb
Filtrate in the descending limb flows deeper into the?
Medulla
filtrate in the ascending limb flows in the opposite direction towards the?
Cortex
Since the ascending and descending limbs are in such close proximity to each other, it allows?
To Interact
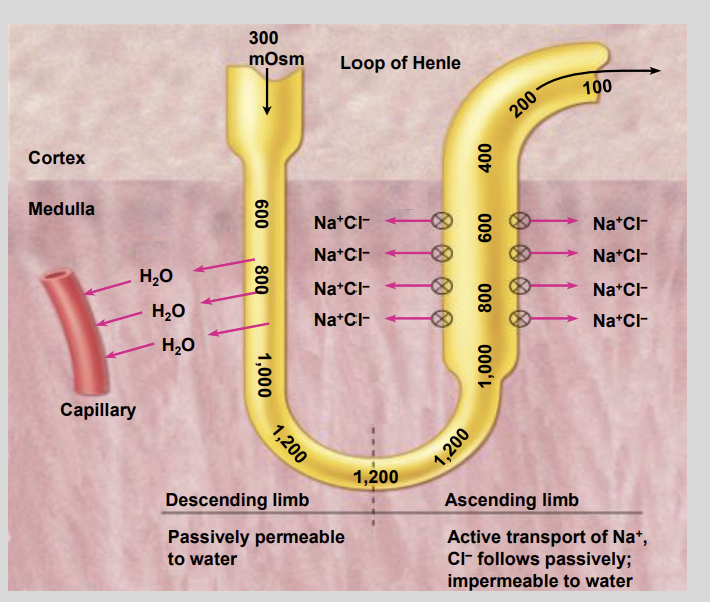
The concentration of the filtrate in the descending limb is reflective of that of the surrounding?
Interstitial Fluid
The concentration of this interstitial fluid is raised by the active?
Active Extrusion of Salt
from the ascending limb which receives it’s filtrate from the descending limb
The pumping of salt into the interstitium creates a
Hypertonic Environment
in the medulla that draws water out of the descending limb filtrate creating a hypertonic filtrate
This hypertonic filtrate advances through into the ascending?
Ascending Limb
providing the ascending limb with a salt rich solution
The ascending limb beings to pump the salt from the hypertonic filtrate into the?
Interstitium
Making it even more Hypertonic
The vasa recta are long blood?
Vessels that form the Efferent Arteriole
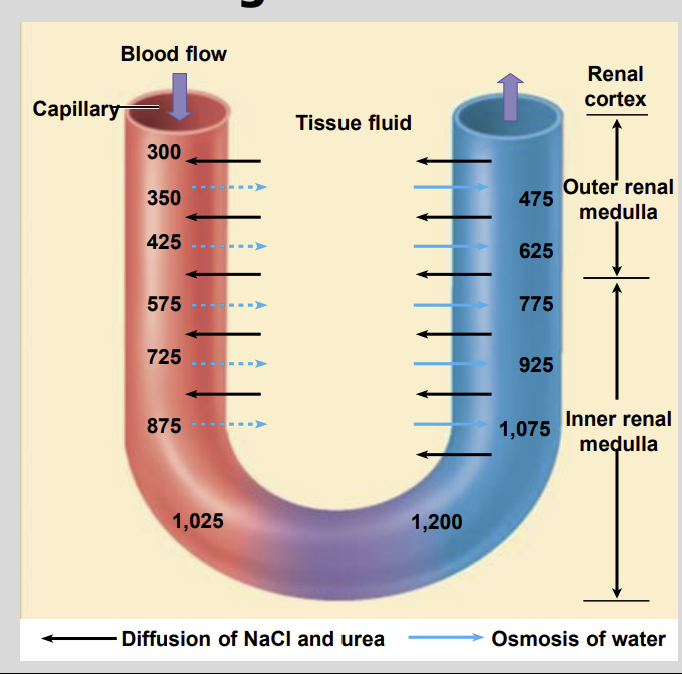
The Vasa Receta blood vessels run in parallel with the?
Loop of Henle
Serving as major blood vessels to the Renal Medulla
Vasa recta contain what making them water permeable?
These blood vessels have aquaporins
This progression of the countercurrent multiplier system continues until the maximum concentration is reached in the?
Inner Medulla
The vasa recta maintains hypertonicity within?
Renal Medulla
As the vasa recta descend into the hypertonic medulla salt and urea moves into the?
The blood whilst Water Moves out.
as the vasa recta ascend back towards the cortex the blood plasma is?
Concentrated than the surrounding Interstitial Fluid
blood plasma is more concentrated than the surrounding interstitial fluid. As a result, the ascending vasa recta?
Loose Salt and Urea
Gaining Water
The active extrusion of NaCl into by the thick ascending limb of the nephron loop contributes the most to the?
Hypertonic Solution of the Renal Medulla
The terminal portion of the collecting ducts contain?
Urea Channels
. Urea can leave the collecting ducts deep in the inner medulla adding to the?
Hypertonicity of Inner Medulla Interstitial Fluid