unit 3 anatomy - brain and cranial nerves
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
neural tube
a groove formed in the top layer of differentiated cells in the embryo that eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord
formed by the neuroectoderm
rostral neural tube
"toward the nose" - brain
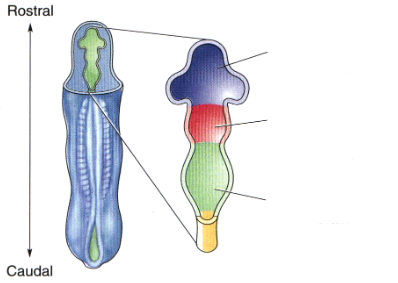
caudal
"toward the tail" - spinal cord, lower
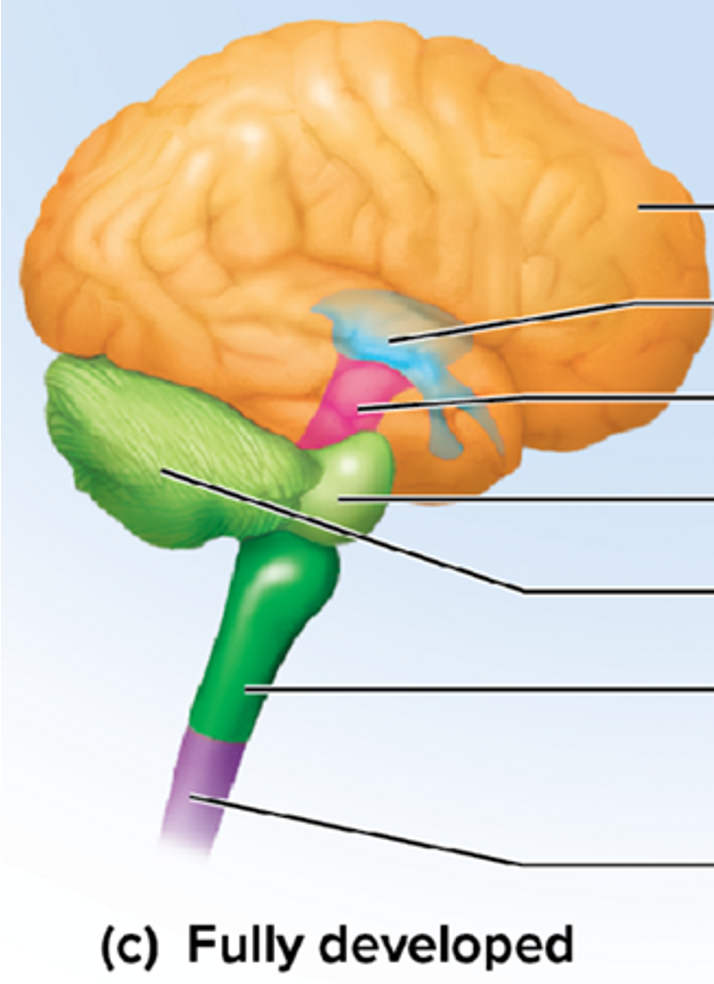
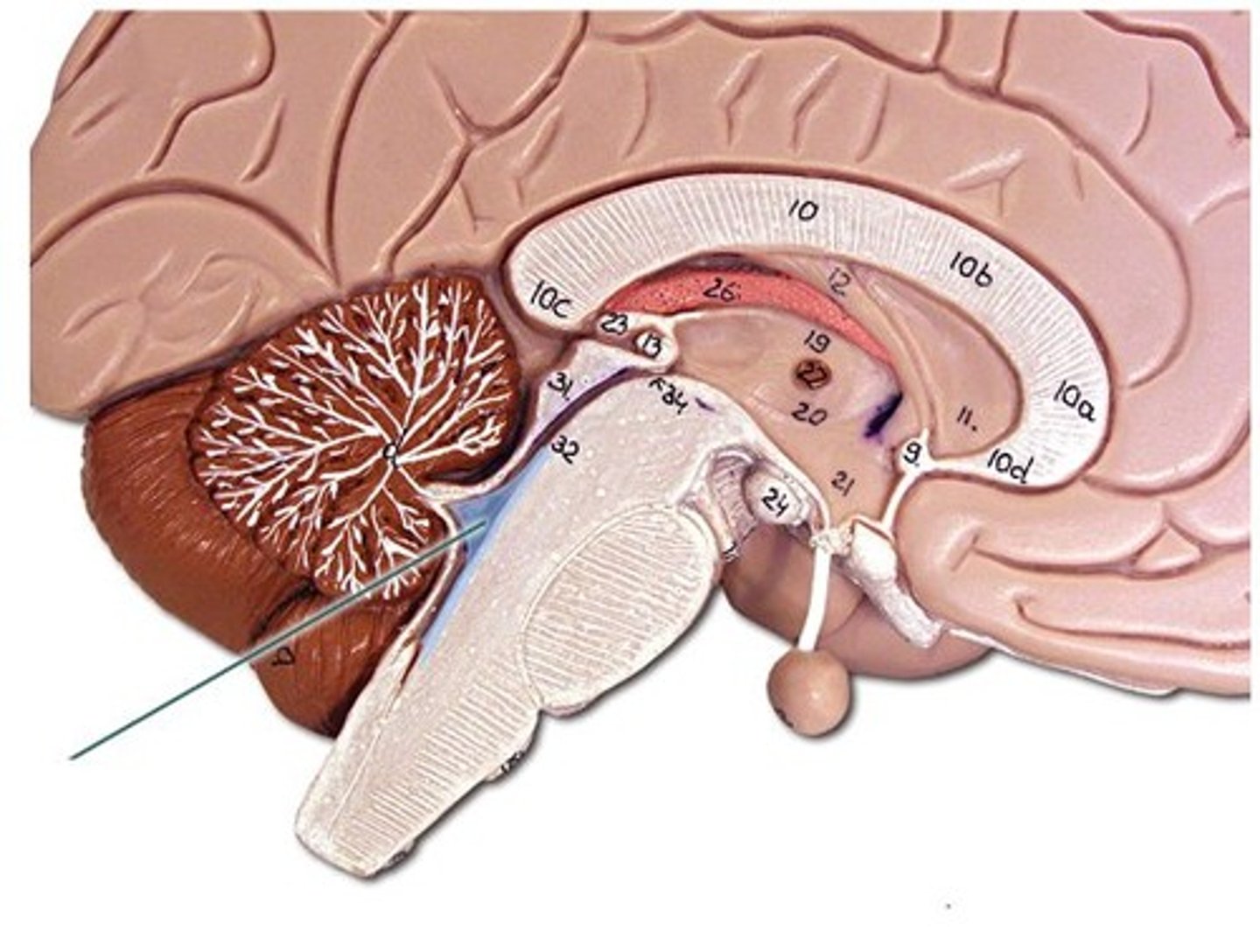
Purple part
the part where the purple and green meet is the foramen magnum
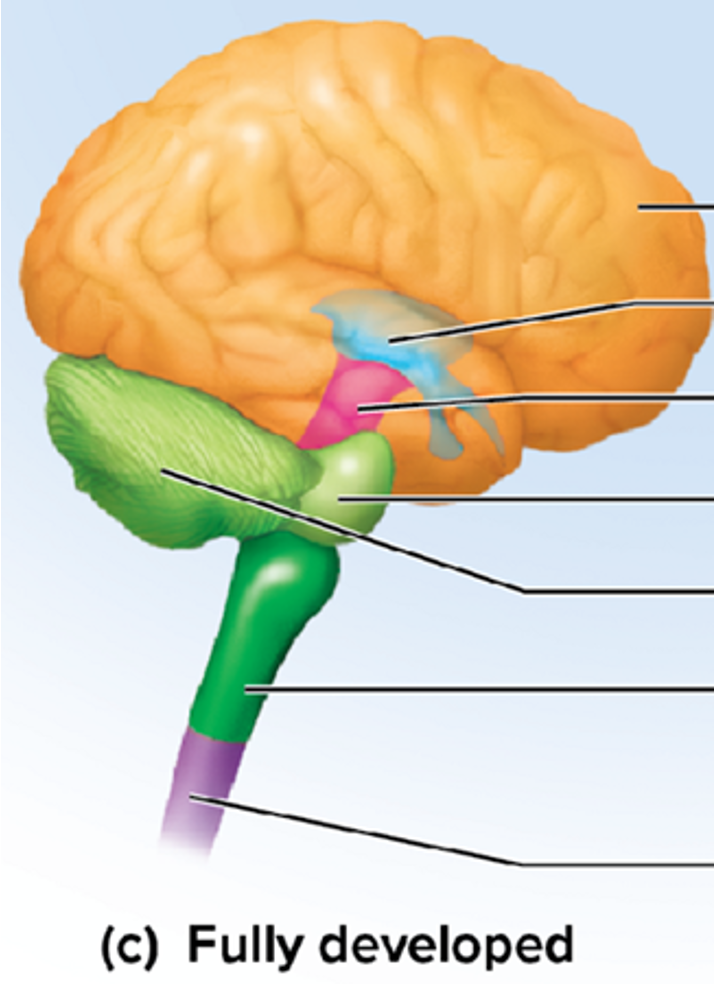
cerebrum
largest and most superior part of the brain, divided into two convoluted cerebral hemispheres separated by a deep longitudinal fissure
cerebellum
s a brain region that coordinates voluntary movements, maintains balance and posture, and fine-tunes motor commands to make movements smooth and precise.
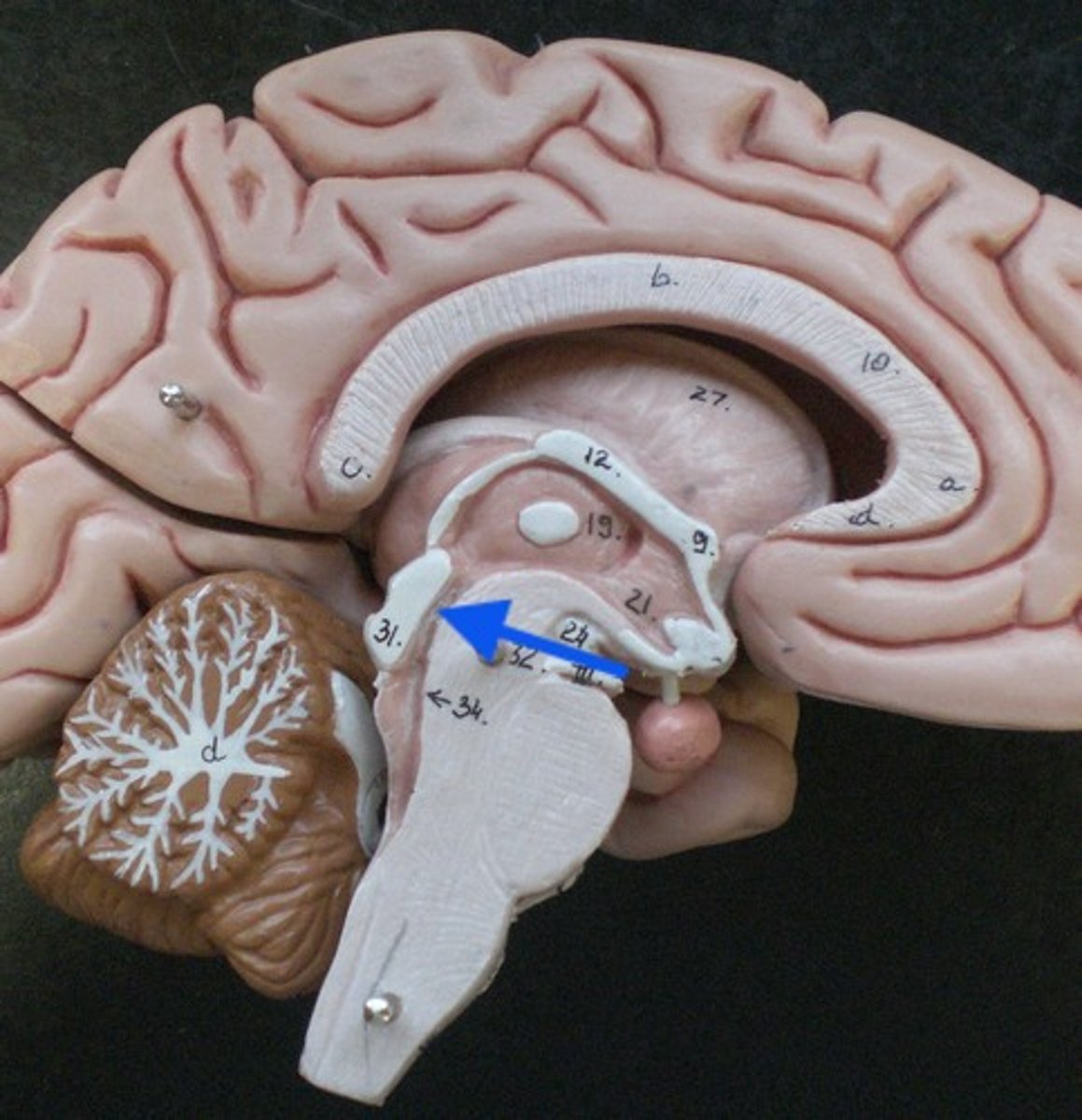
diencephalon
Part of the brain between the midbrain and cerebral hemispheres; includes thalamus and hypothalamus that are important. BLUE part
important in sensory and motor pathways with the ANS
not a part of brain stem
brainstem
stalklike portion, medulla, pons, and midbrain
pia
very thin, delicate membrane that closely follows all the contours of the brain surface
arachnoid
transparent membrane over the brain surface
dura
dense fibrous connective tissue, includes the periosteal and meningeal layer.
function of the dura, pia, and arachnoid
protect the brain and provide structural framework for arteries, veins, and blood sinuses
subarachnoid space
contains CSF
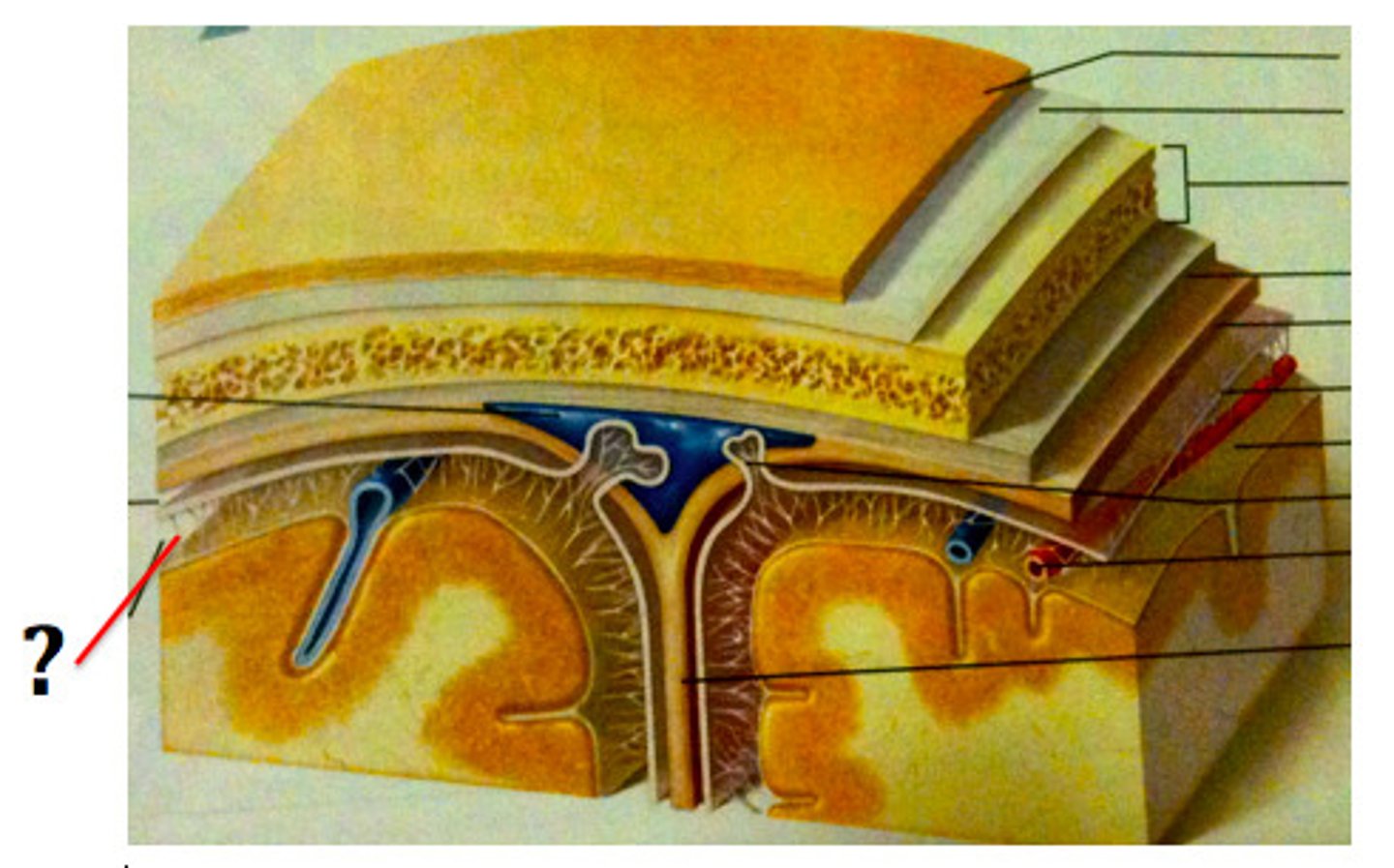
subdural space
between dura mater and arachnoid mater
epidural space
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
choroid plexus
floor or wall of ventricles, spongy mass of blood capillaries
CSF
liquid that fills the ventricles of the brain, central canal of the spinal cord, and space between the CNS and dura mater. secreted into ventricles by the choroid plexus and general ependymal lining
lateral ventricle
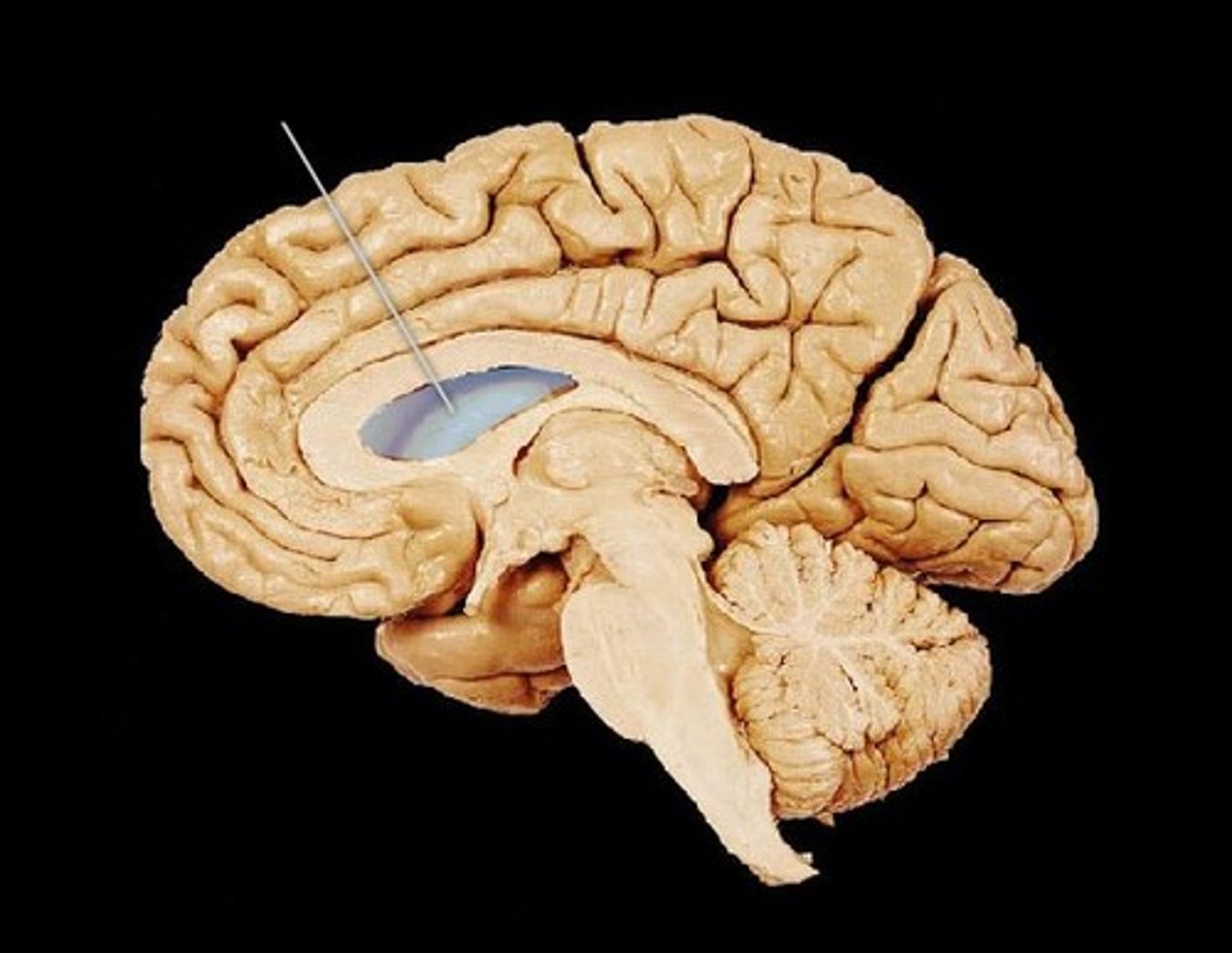
interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle, pore
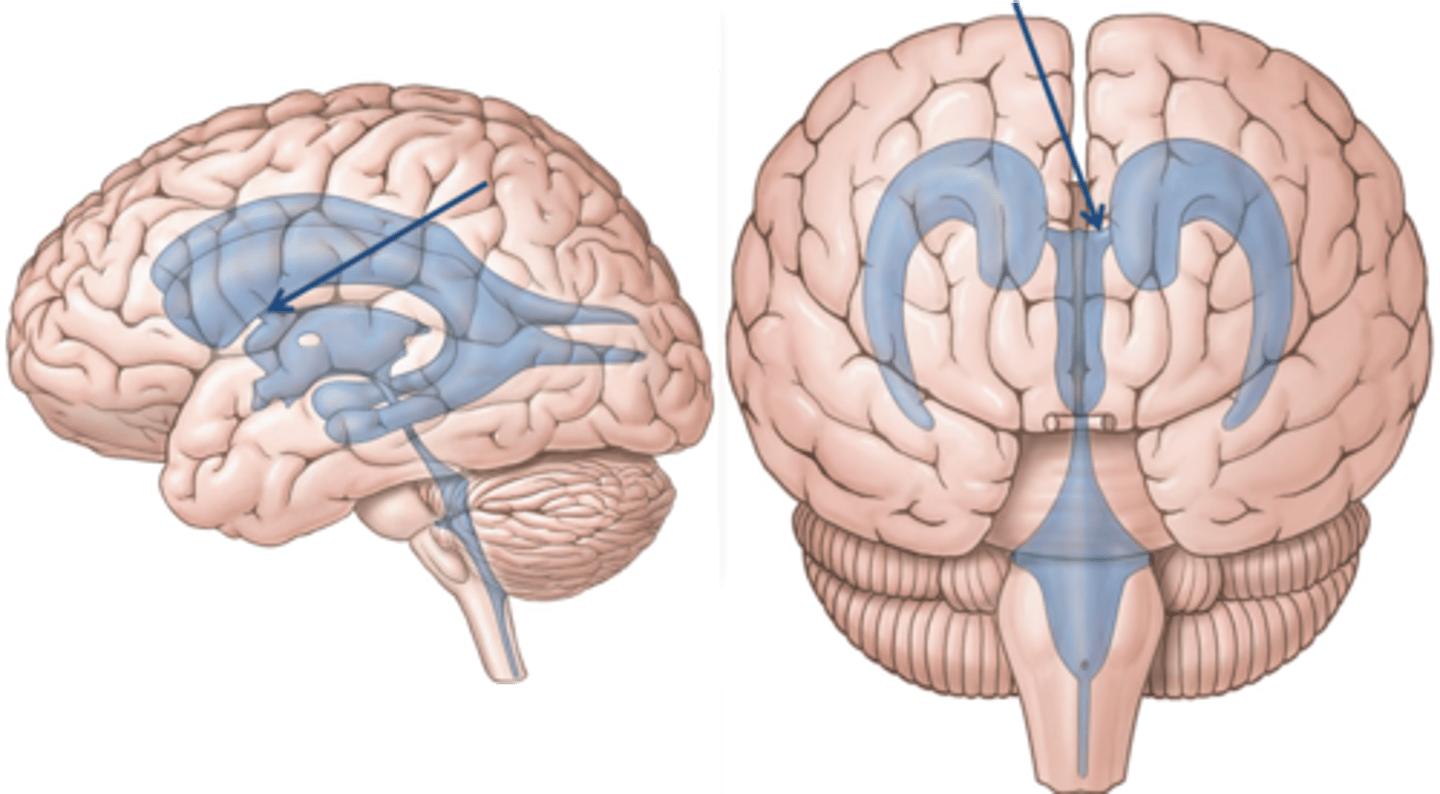
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
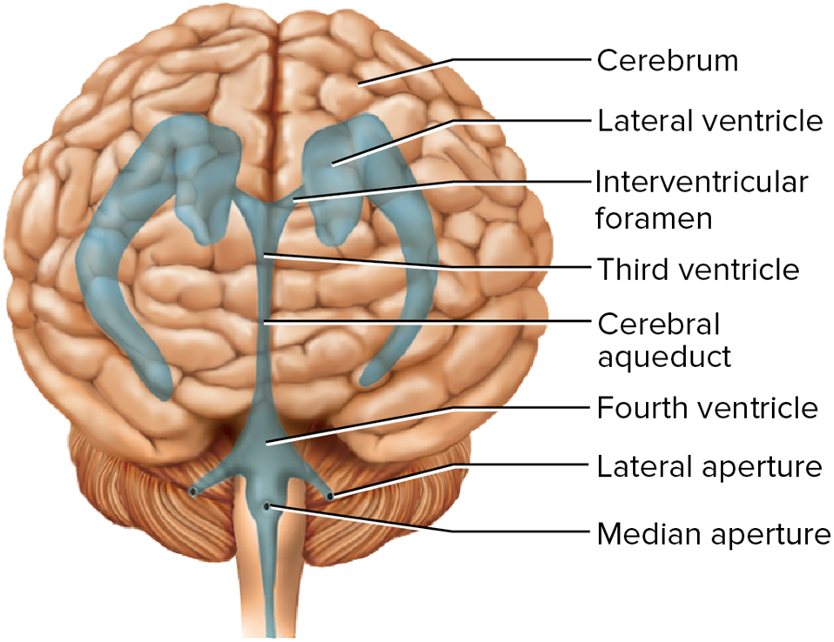
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons, in the center of the metencephalon
arachnoid villi (granulations)
extensions of the arachnoid mater that protrude through the dura mater into the superior sagittal sinus of the brain. reduce pressure on the CNS by draining CSF from the subarachnoid space into the bloodstream
dural venous sinuses
spaces that collect blood that has circulated through the brain
fissures
deep groves in the brain
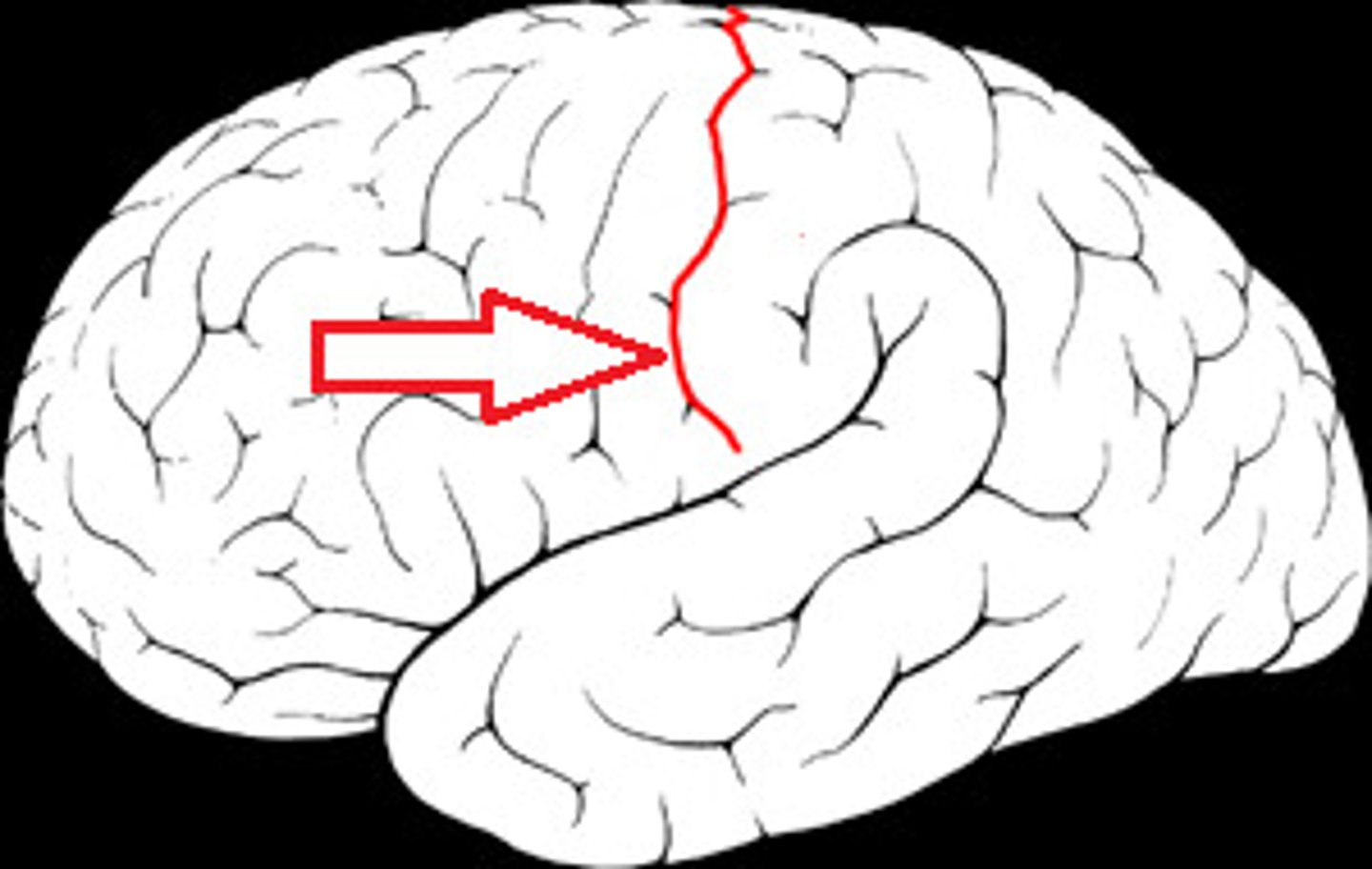
sulcus
groove in the surface of an organ
gyrus
wrinkle or fold in the cortex of the cerebrum or cerebellum
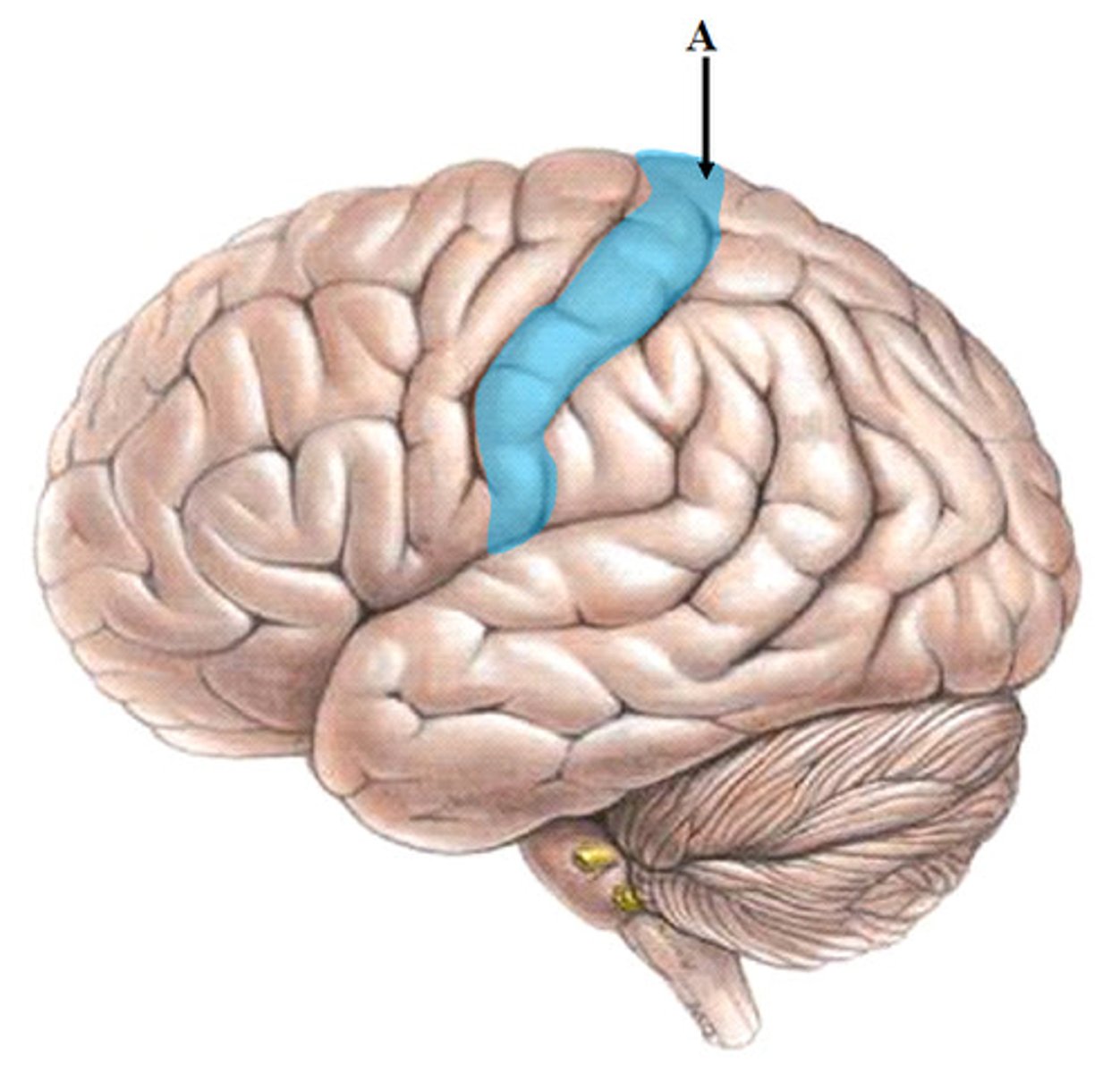
precentral gyrus
upper motor neurons, primary motor cortex, anterior to the central sulcus
postcentral gyrus
sensory homunculus, posterior to the central sulcus, forms border of parietal lobe
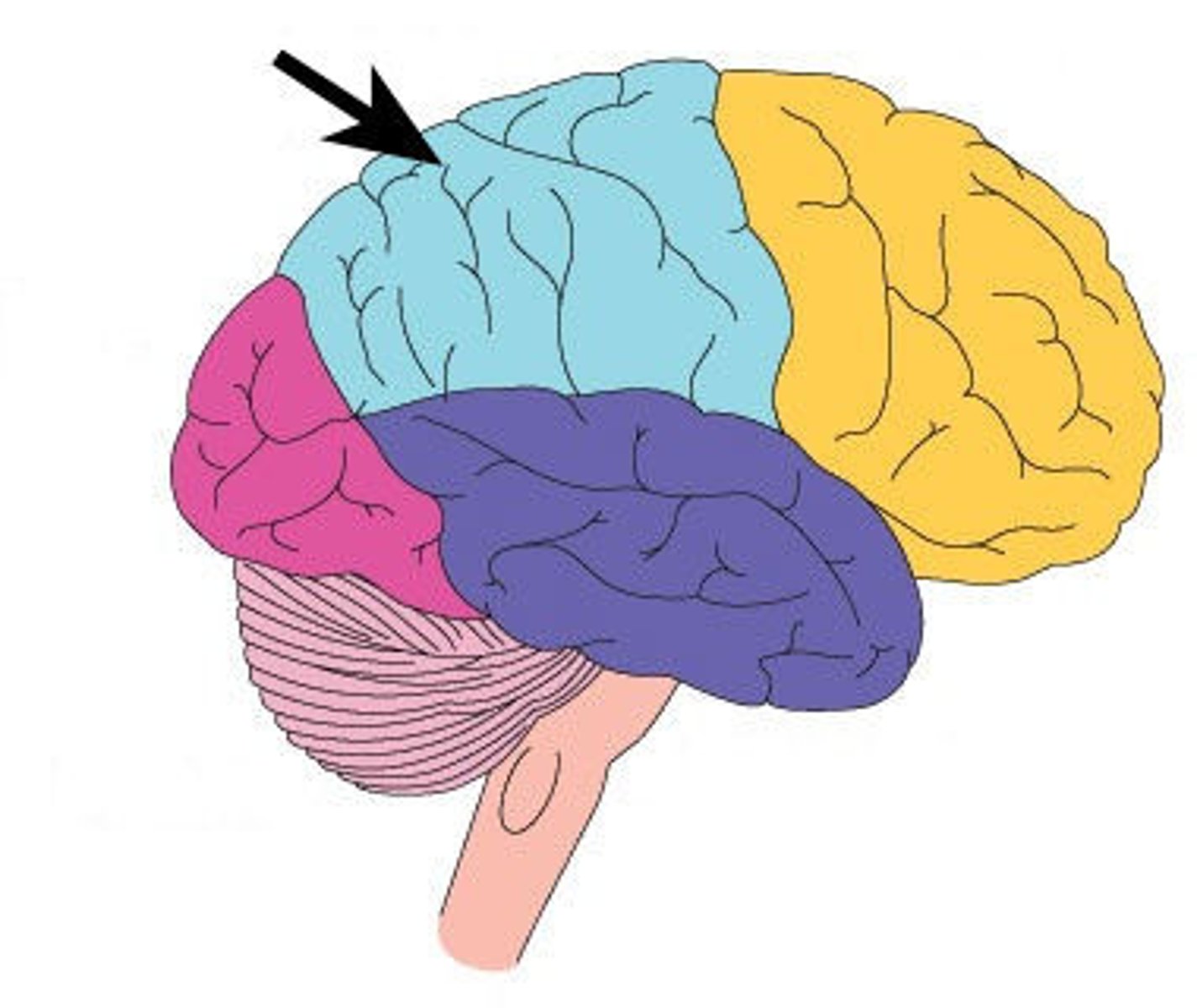
frontal lobe functions
abstract though, explicit memory, mood, motivation, foresight, planning, decision making, emotional control, social judgement, voluntary motor control, speech production
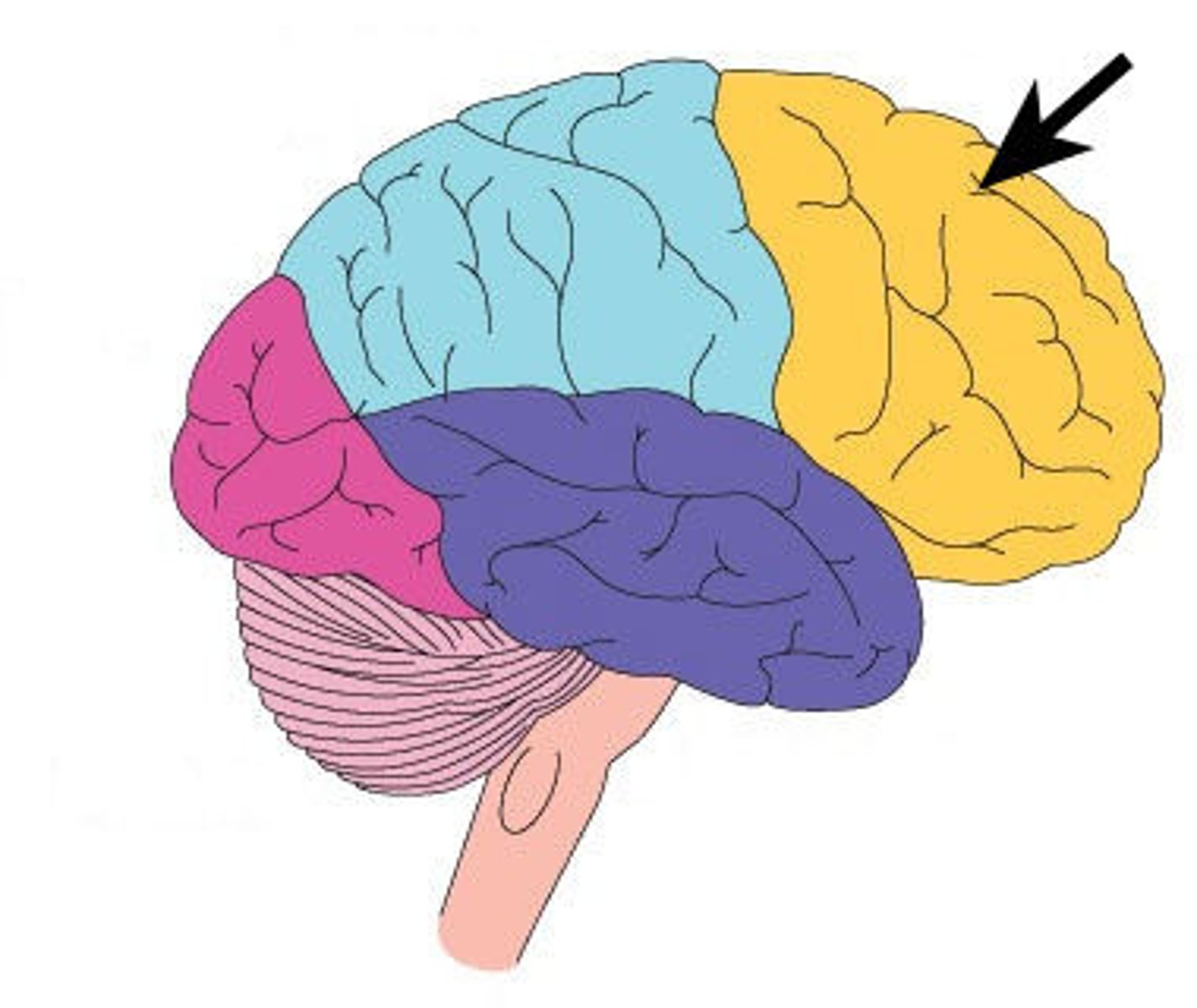
partial lobe functions
taste, somatic sensation, sensory integration, visual processing, spatial perception, language processing, numerical awareness
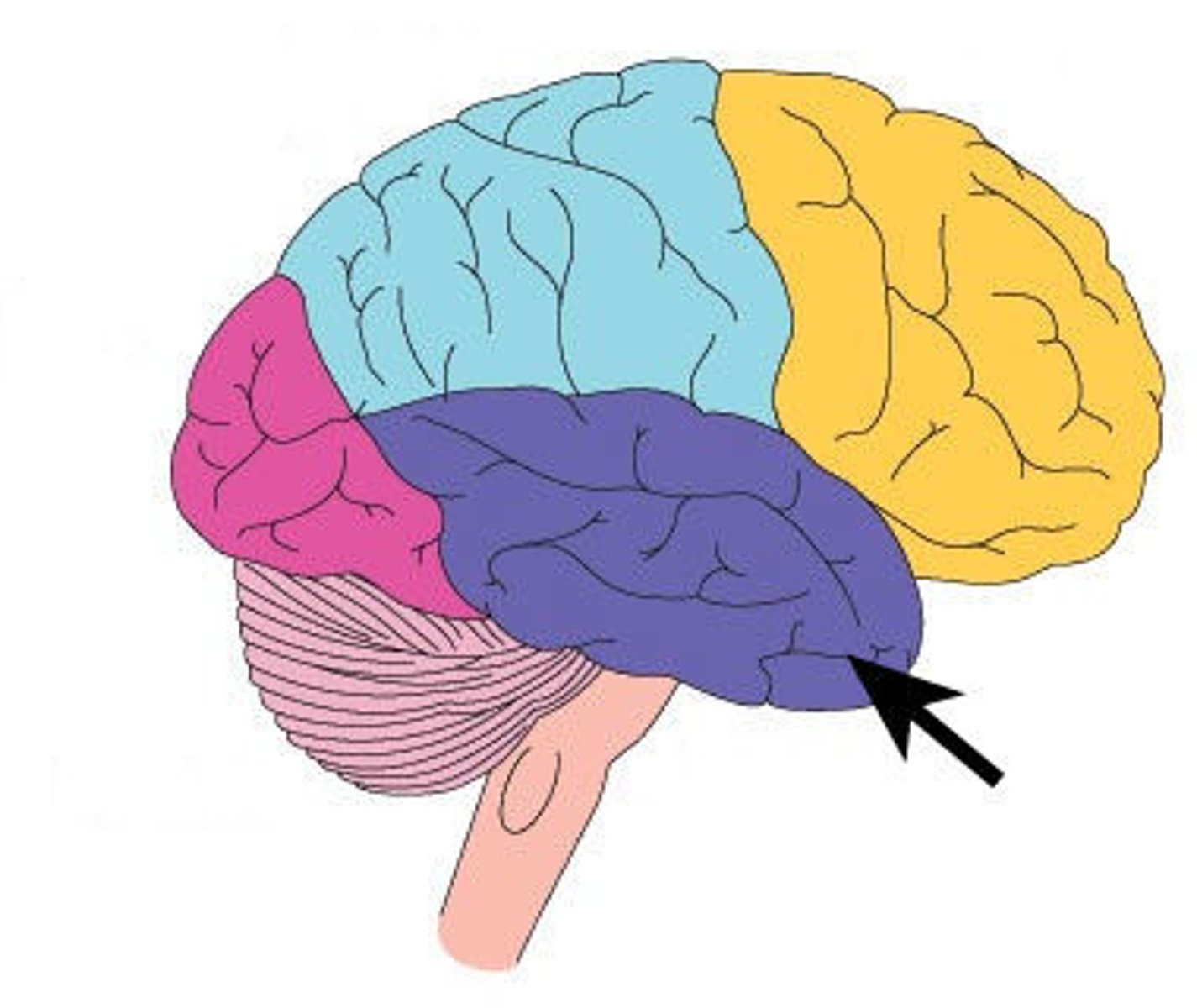
temporal lobe functions
hearing, smell, emotion, learning, language comprehension, memory consolidation, verbal memory, visual and auditory memory
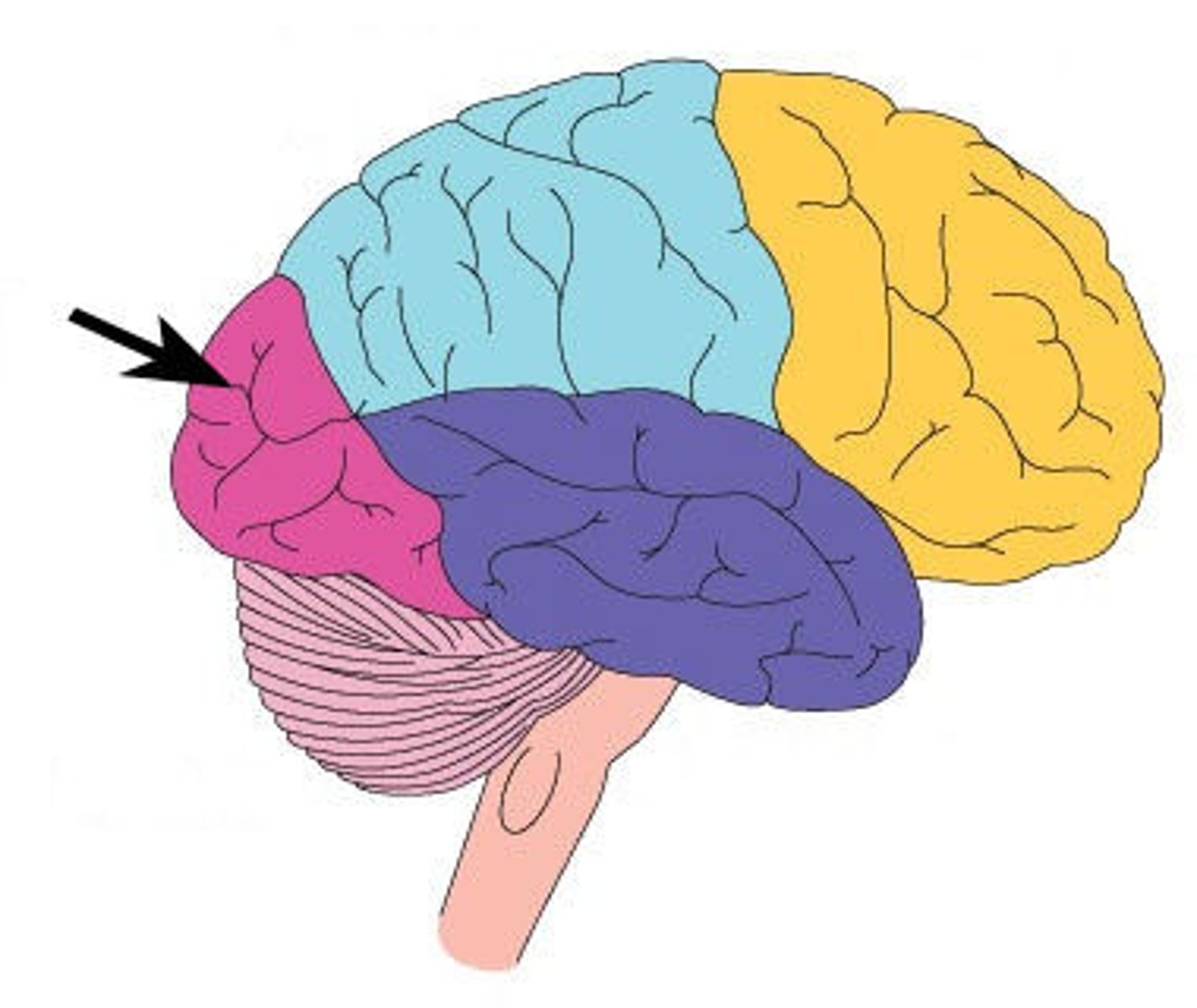
occipital lobe functions
visual awareness and visual processing
primary motor cortex
initiates and plans voluntary movements
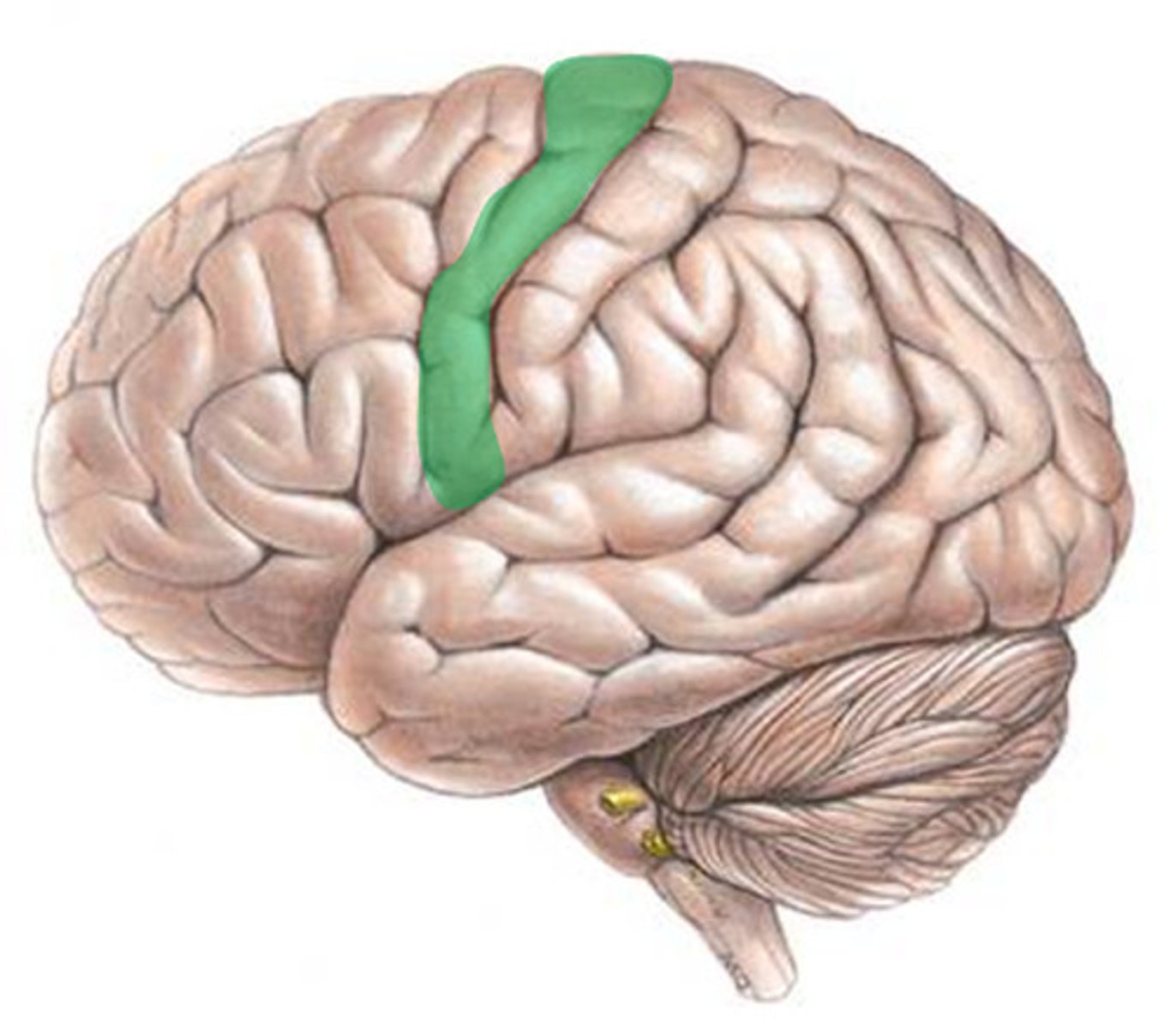
primary somatosensory cortex
receives and processes sensory information from the body ex. touch, temp, pain, texture
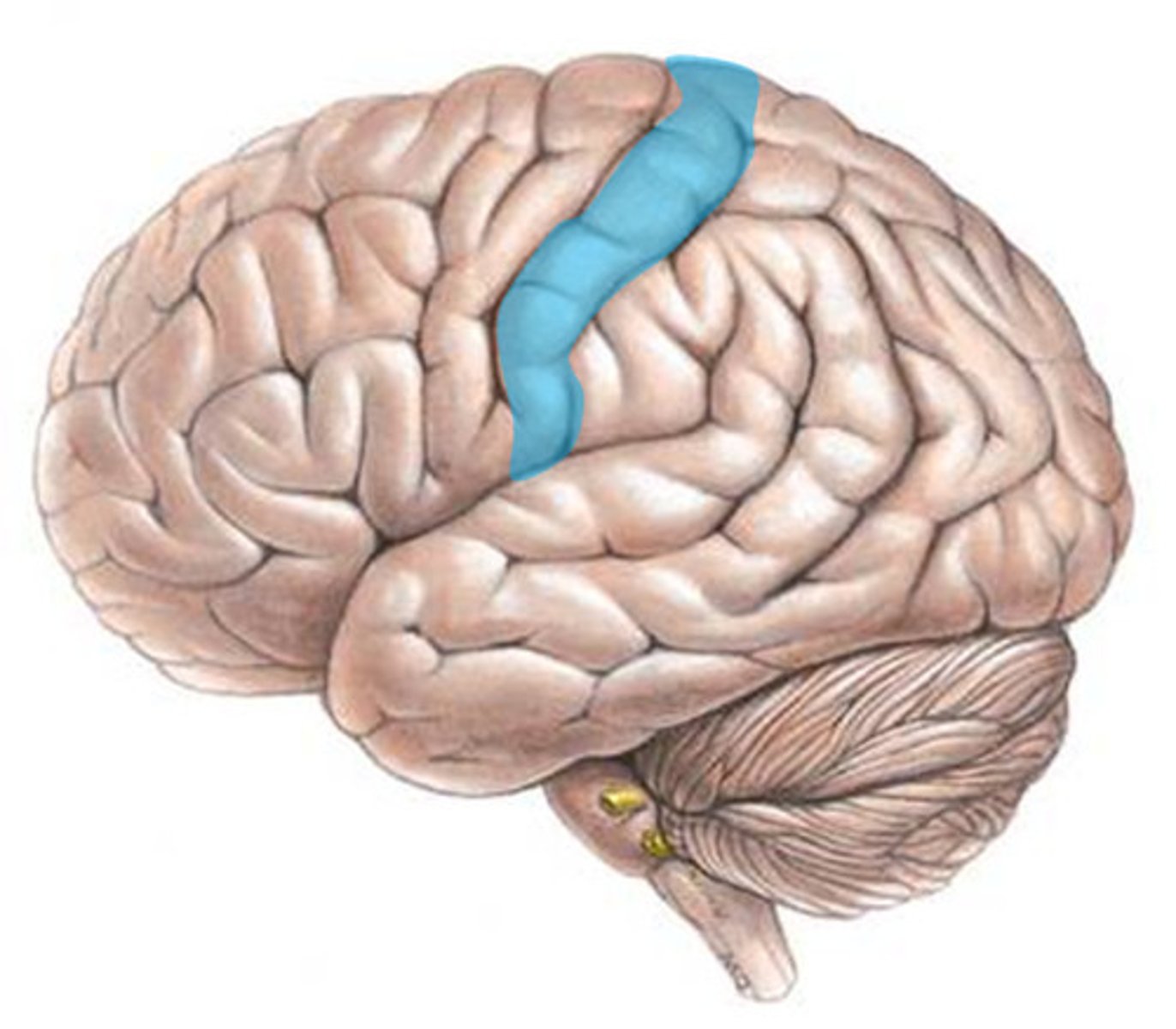
homunculus
map along the cerebral cortex where each part of the body is processed
primary visual cortex
brain receives, processes, and integrates visual informtion
primary auditory cortex
receives and processes auditory information
limbic system
composed of parts of the cerebrum and diencephalon. plays a central role in memory, reproduction, emotion, mood, and nutrition
cingulate gyrus
plays role in expressing emotions via gestures and resolves mental conflict
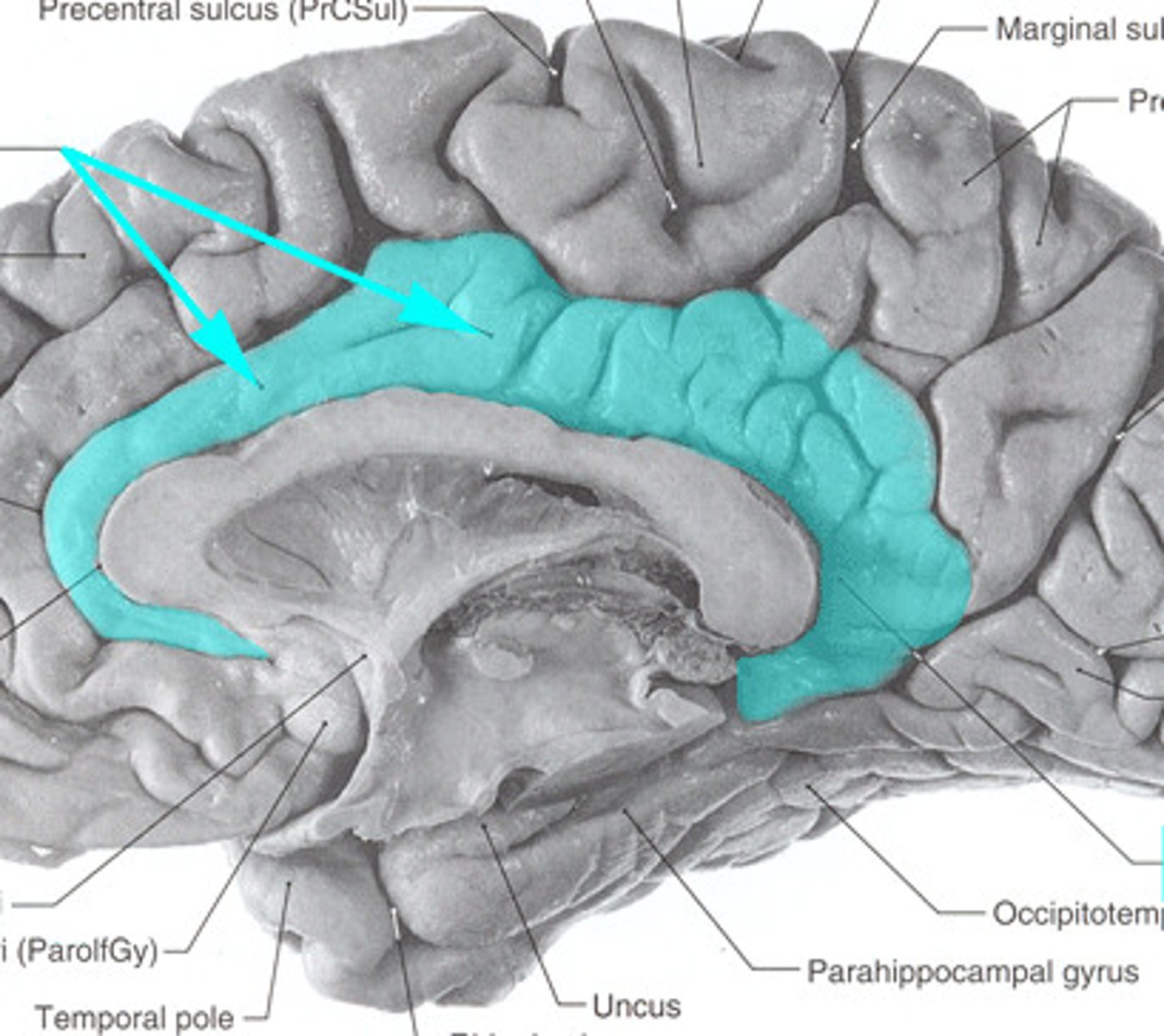
hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
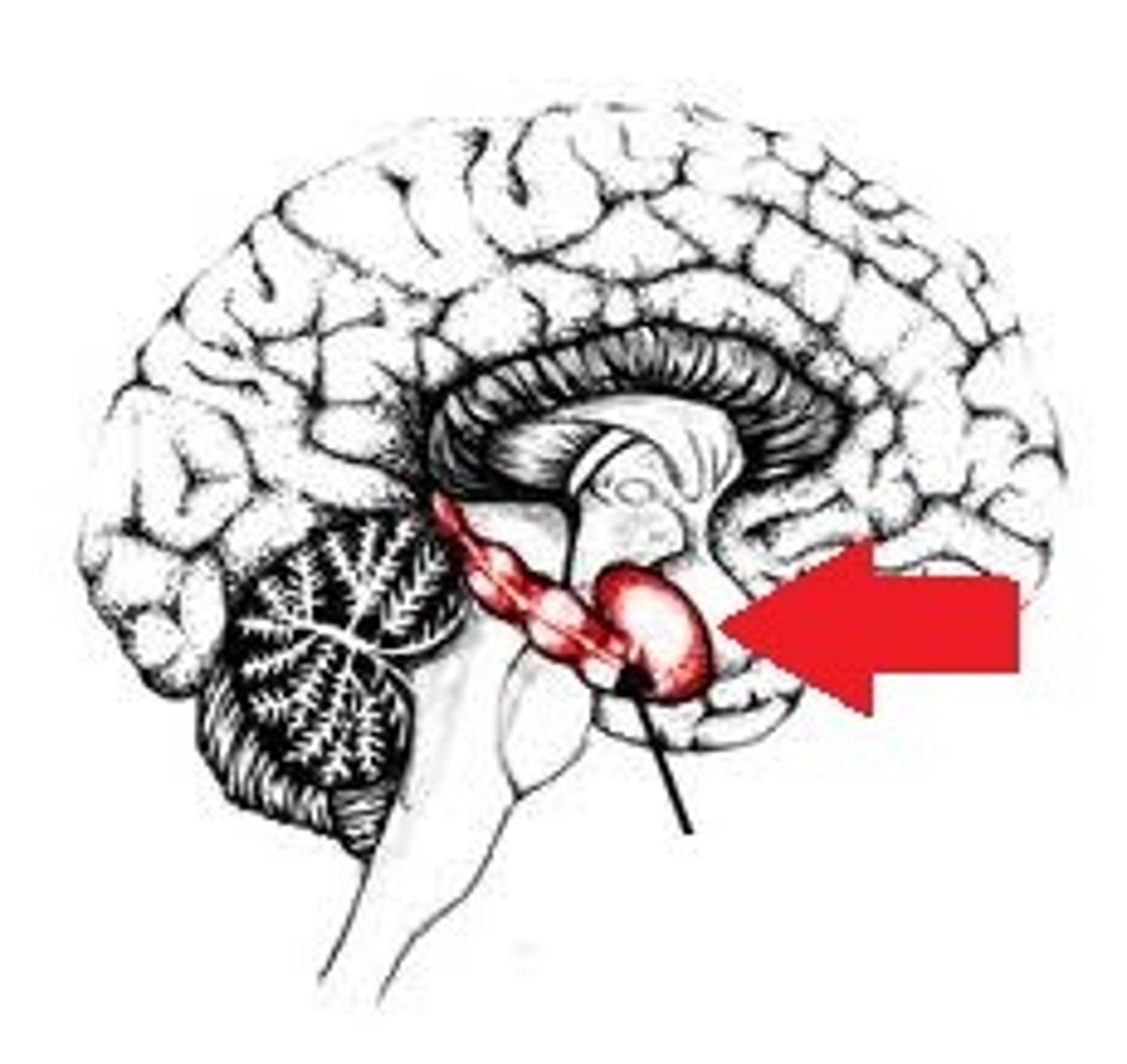
amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
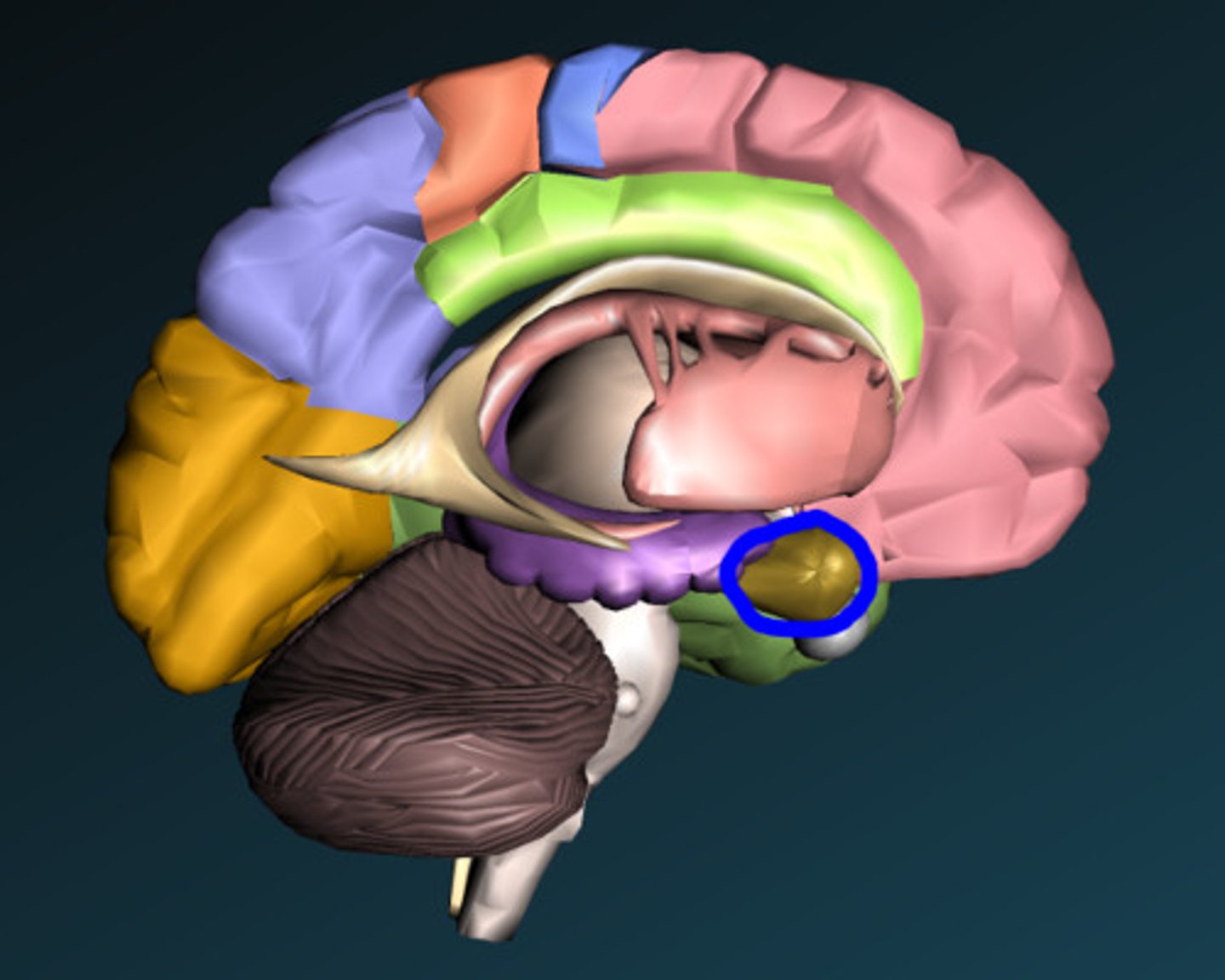
thalamus
largest part, located inferior to the corpus callosum and bulging into each lateral ventricle, point of synaptic relay of nearly all signals passing from lower levels of the CNS to the cerebrum. "gateway to the cerebral cortex". major role in motor control, memory and emotional functions of the limbic system
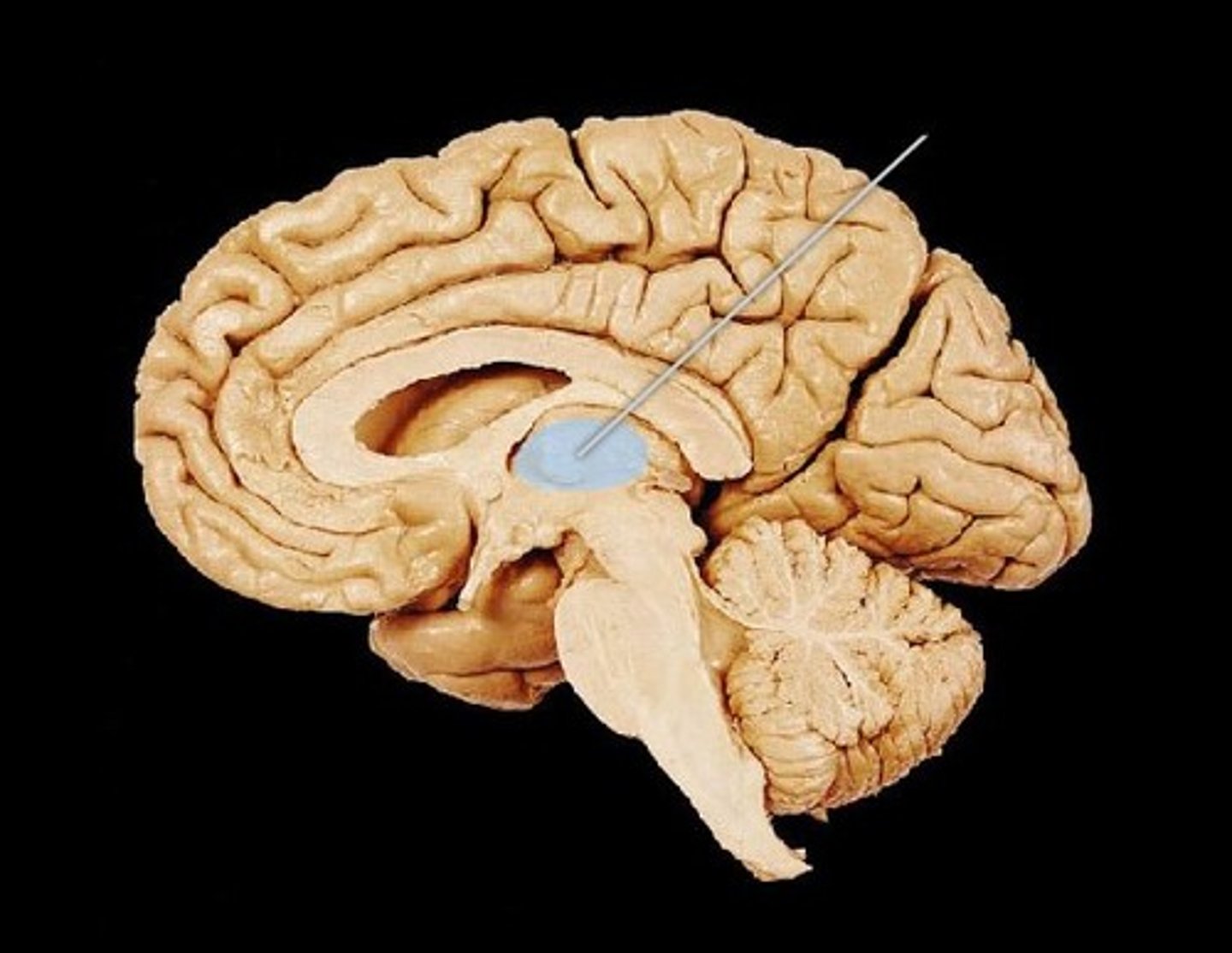
hypothalamus
inferior portion, forming the walls and floor of the 3rd ventricle and giving rise to the posterior pituitary gland, controls many fundamental physiological functions
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
midbrain
short segment of the brainstem, connects hindbrain and forebrain. vision, hearing, sleep, wakefulness, arousal, and temperature regulation
pons
forms a broad anterior bulge in the brainstem just rostral to the medulla. facial sensations and expressions, eye movements, chewing, secretion of saliva and tears
medulla
begins at the foramen magnum of the skill and extends from 3 cm rostrally, ending at a transverse groove. regulates breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, blood circulation, and reflexes
reticular formation
loosely organized web of gray matter that runs vertically through all the levels of the brainstem and has connections with many areas of the cerebrum. functions include: pain modulation, sleep, consciousness, habituation, somatic motor control, cardiovascular control
olfactory nerve, CNI
smell
optic nerve, CNII
sensory
oculomotor nerve, CNIII
eye movements, opening of eyelid, pupillary constriction, focusing
trochlear nerve, CNIV
eye movements
abducens nerve, CNVI
lateral eye movement
facial nerve, CNVII
sensory : taste motor : facial expression, secretion of tears, saliva, nasal and oral mucus
vestibulocochlear nerve, CNVIII
hearing, equilibrium
glossopharyngeal nerve, CNIX
sensory : taste, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature sensations from tongue and outer ear, regulation of blood pressure, respiration. motor : salivation, swallowing, gagging
trigeminal nerve, CNV
V1, ophthalmic - touch, temp, pain sensations from upper face
V2, maxillary - V1, lower face
V3, mandibular - sensory - V1, V2 lower face. motor - mastication
accessory nerve, CNXI
swallowing, head, neck, shoulder movements
hypoglossal nerve, CNXII
tongue movements of speech, food manipulation, and swallowing
vagus nerve, CNX
sensory : taste, sensations of hunger, fullness, gastrointestinal discomfort motor : swallowing, speech, deceleration of heart, broncho-constriction, gastro-intestinal secretion, motility
sensory nerves
CNI-II, carry signals only from outlying sense organs to the brain. begin in receptors located mainly in the head and neck and lead to the brainstem
motor nerves
CN III, IV, VI, XI, XII. carry signals from the brainstem to outlying muscles and glands. begin in the nucleus of the brainstem and lead to glands and muscles
mixed nerves
CN V, VII, VIII, IX, X. carry signals both ways
cranial nerves
12 pairs, arise from the base of the brain, exit the cranium through its foramina, and lead to muscles and sense organs located mainly in the head and neck, labeled CN I - C XII, starting with the most rostal pair