Time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is mass spectrometry used to do? (2)
Find the mass and abundance of each isotope in an element
Find the relative molecular mass of substances made of molecules
What is relative atomic mass?
The average weighted mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
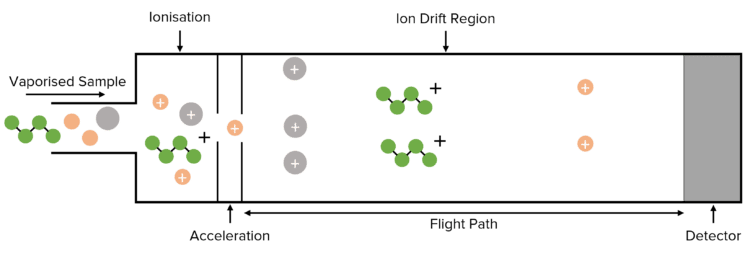
What are the four stages of the mass spectrometer?
Ionisation, acceleration, ion drift and detection
Why is the sample vaporised?
So it can travel through the TOF mass spectrometer
Why is the whole mass spectrometer kept under a high vacuum?
To prevent air particles from ionising which would also register on the detector
What is the first stage of a mass spectrometer?
Ionisation
What are the two ways that a sample can be ionised in a mass spectrometer?
By electron impact or electrospray ionisation
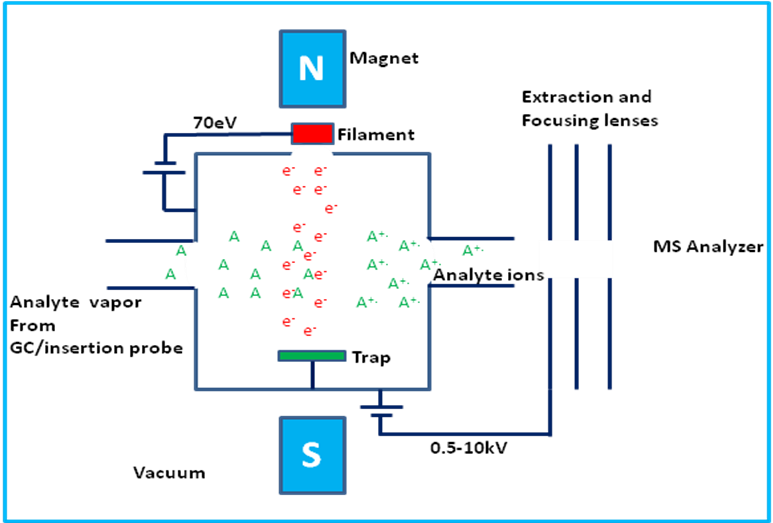
What is used in electron impact?
An ‘electron gun’
What is an electron gun?
A hot wire filament with a current running through it that emits electrons
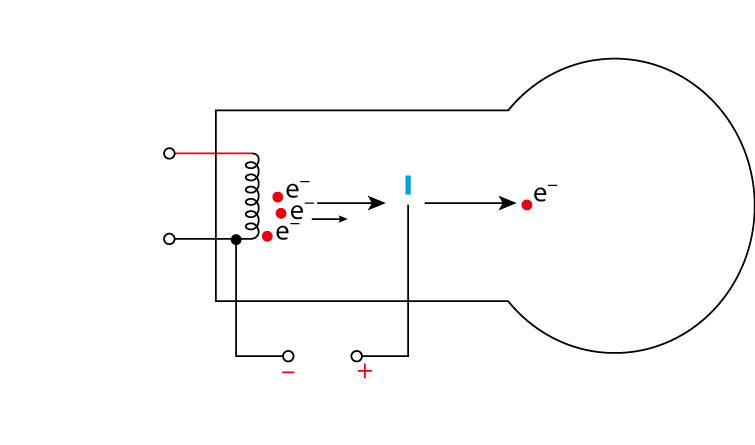
What does an electron gun do? What type of ions are created?
It bombards the sample with high-energy electrons that hits the sample and knocks an electron off the relevant atoms or molecules, creating 1+ ions
X (g) + e- → X+ (g) + 2e-
What type of elements and substances is electron impact used for?
Those with low formula mass
What is the 1+ ion formed called?
A molecular ion
What do molecular ions often do during electron impact?
They break down into smaller fragments, some of which are also detected in the mass spectrum
How is the sample X prepared for electrospray ionisation?
It is dissolved in a volatile solvent - eg. water or ethanol
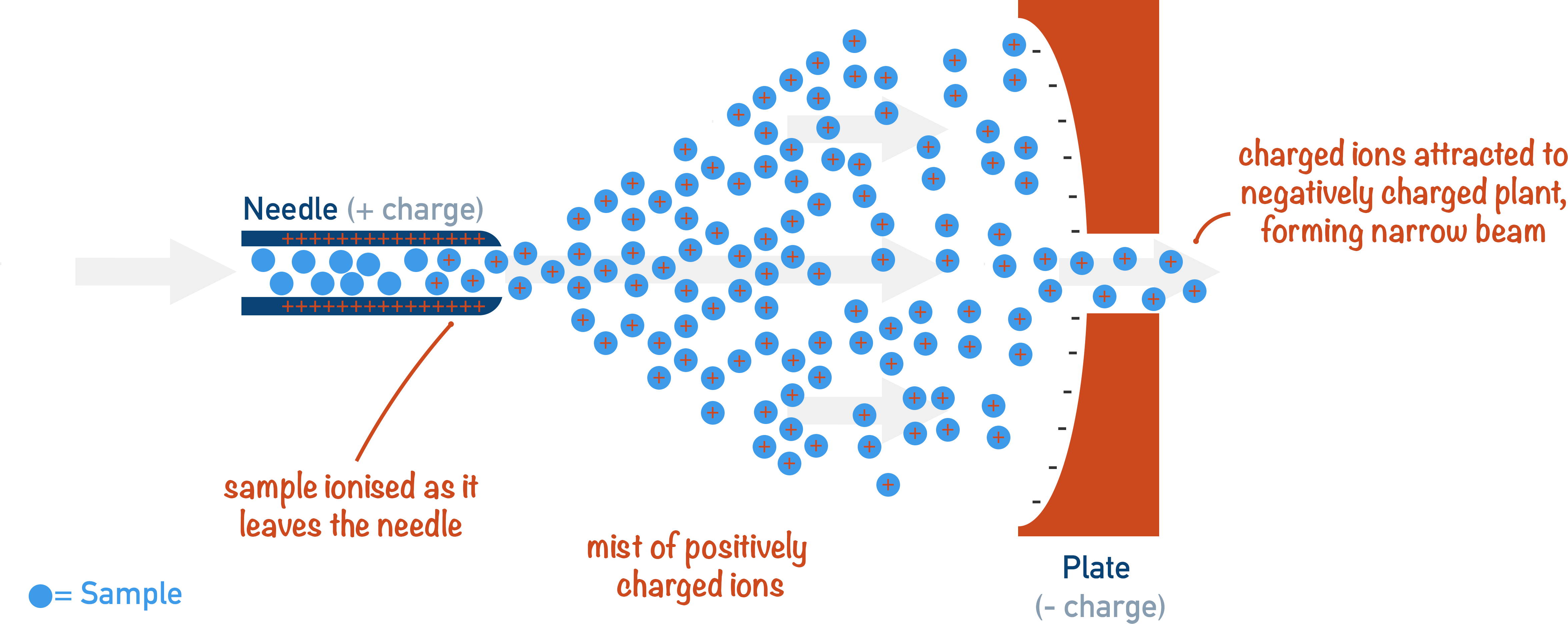
What happens to the sample in electrospray ionisation?
It is injected through a fine hypodermic needle to give a fine mist
What is the tip of the fine hypodermic needle attached to?
A positive terminal of a high-voltage power supply.
How are the particles ionised in electrospray ionisation?
They gain a proton from the solvent as they leave the needle, producing XH+ ions
X (g) + H+ → XH+ (g)
What type of substances is electrospray ionisation used for?
Substances with higher molecular mass, including many biological molecules such as proteins
Why is electrospray ionisation known as a ‘soft’ ionisation technique?
Because fragmentation rarely takes place
What is the second stage of a mass spectrometer?
Acceleration
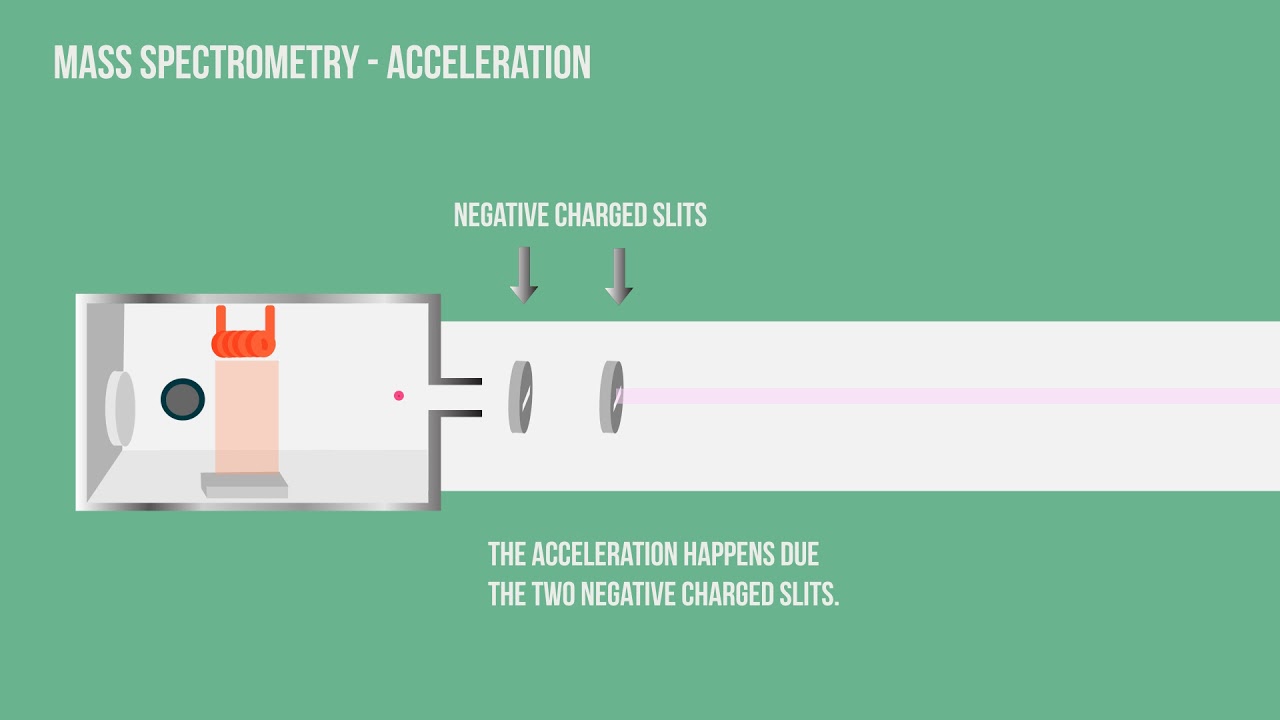
How is the ionised sample accelerated?
With a negatively charged plate that creates an electric field
What happens during the acceleration process?
The positive ions are attracted towards a negatively charged plate and so accelerate towards it
Molecules are accelerated to have the...
same kinetic energy
Whar is the equation for kinetic energy?
KE = ½ m v2
What are the units the kinetic energy, mass and velocity of the particle?
KE in J
Mass in kg
Velocity in ms-1
How would you work out the velocity of each particle?
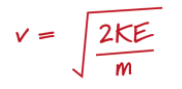
If all of the molecules have the same kinetic energy, what is the speed of the molecules dependent on?
Their mass
What type of particles move faster and are detected first?
Lighter particles
What happens after acceleration?
Ion drift
What happens during ion drift?
The ions pass through a hole in the negatively charged plate into a flight tube to then reach a detector
Under what two constant conditions do particles travel under during ion drift?
Constant speed and kinetic energy
What does the time of flight of each particle within the flight tube depend on?
Its velocity, and therefore its mass
What is the unit for time of flight?
Seconds
How would you calculate the time of flight along the flight tube?
time = distance / velocity
t = d / v
d represents the length of the flight tube. What is the units for d?
Metres
Using the equation for velocity, what is the equation for time of flight?

What ions arrive at the detector first and why?
Lighter ions as they have higher velocities
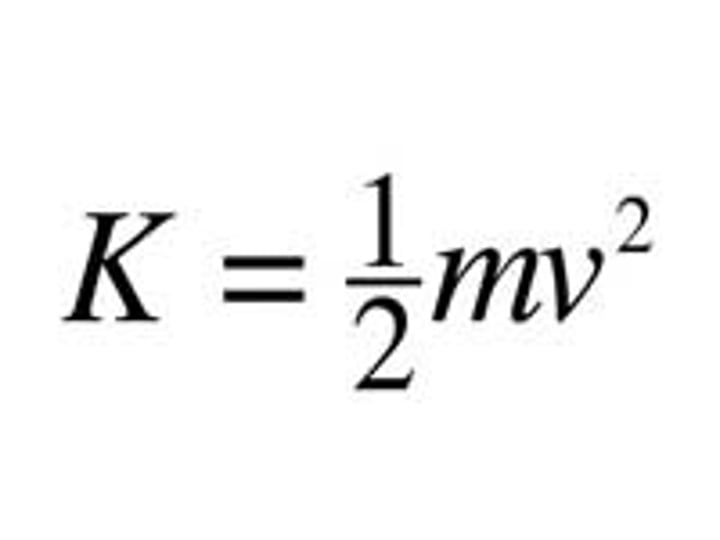
What happens during detection?
When the positive ions hit the negatively charged detection plate, they gain an electron which produces a current that is measured. The greater the number of ions, the greater the current produced
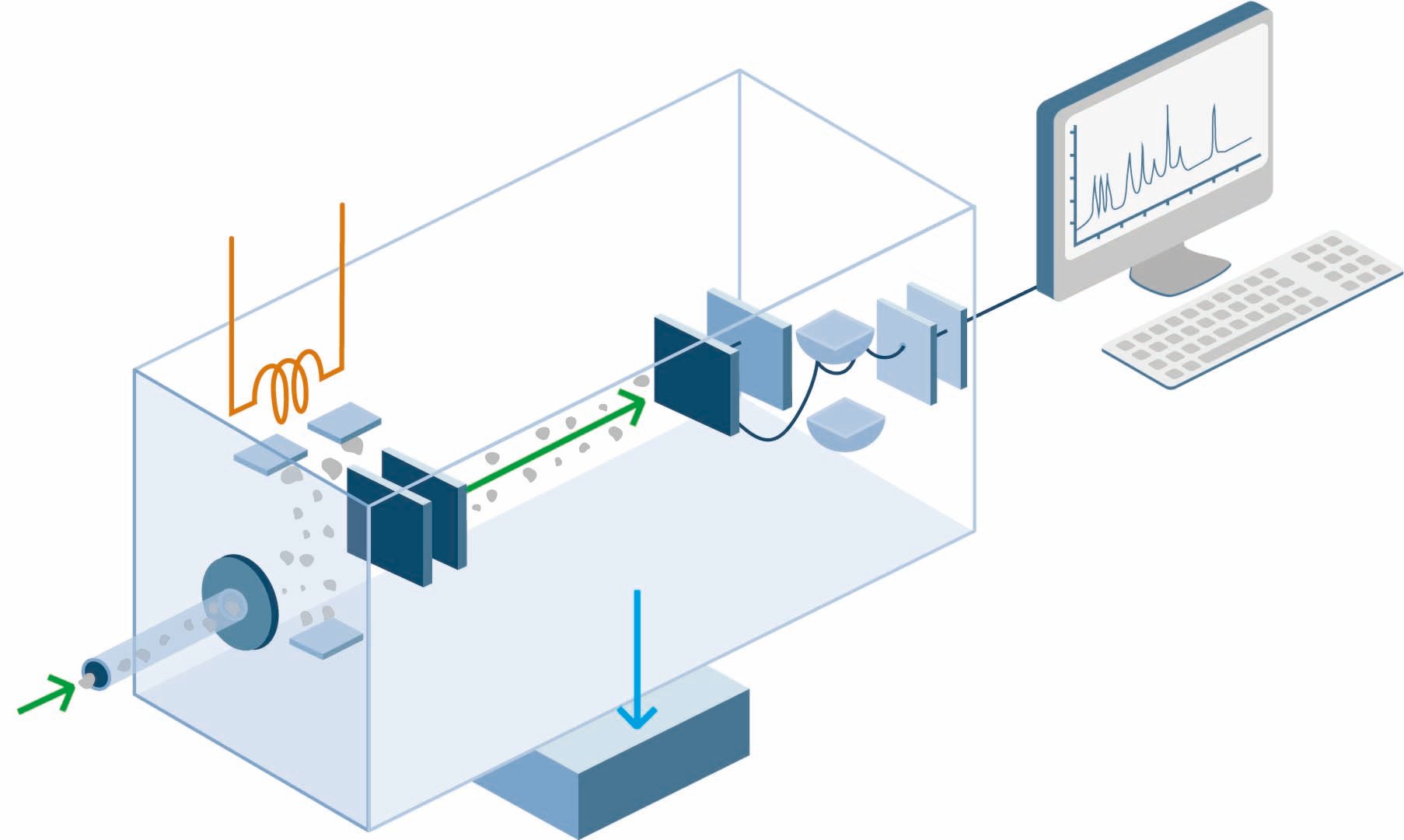
What is recorded at detection?
The flight times
How is the data analysed?
The signal from the detector is passed to a computer which generates a mass spectrum
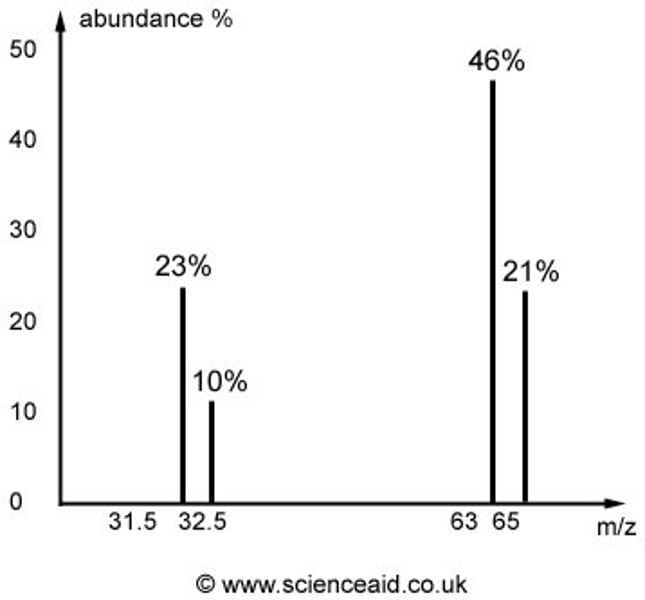
What does the graph show?
The mass to charge (m/z) ratio and abundance of each ion that reaches the detector
Why is the m/z effectively just the mass of the ions?
Because all ions produced by electrospray ionisation and most by electron impact have a 1+ charge
What is relative isotopic mass (Ar)?
The mass of an atom of an isotope relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
How is relative atomic mass calculated?
combined mass of all isotopes / combined abundance of all isotopes