Enthalpy and Entropy RECALL
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Enthalpy Change
The change in the heat content of a system during a reaction (kJ mol^-1)
Lattice enthalpy
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions
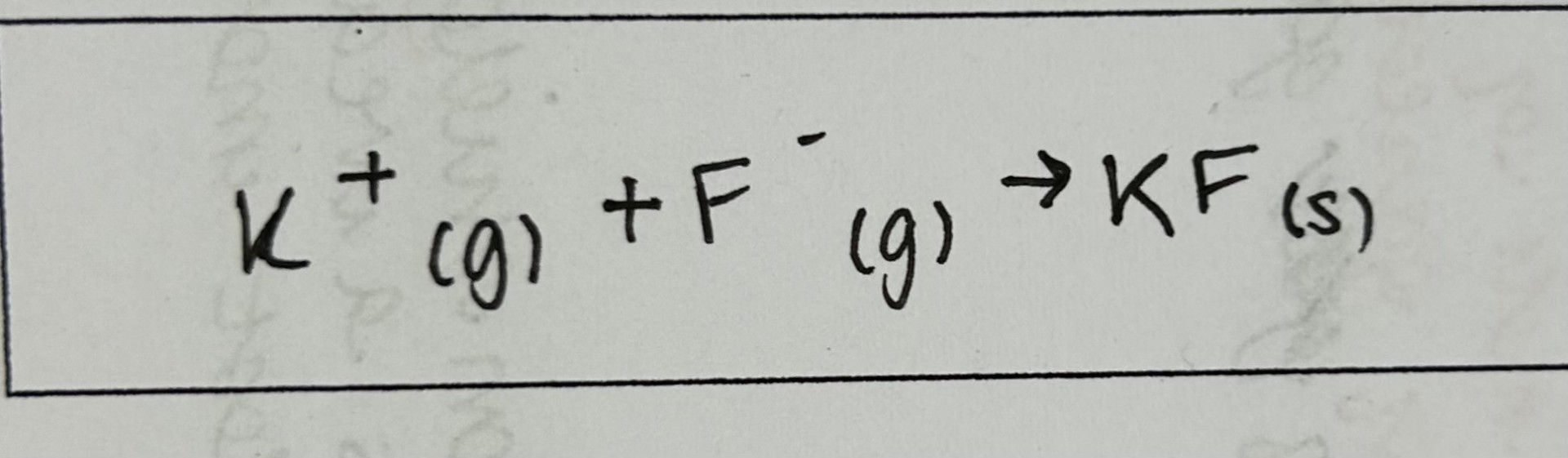
Enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states
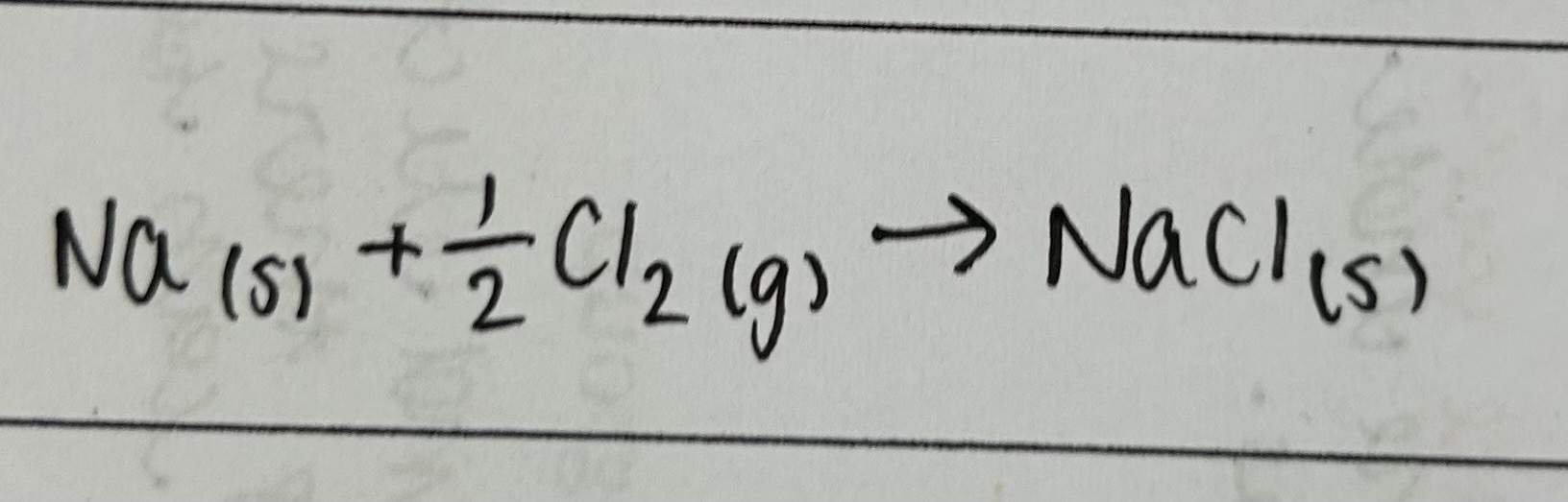
Enthalpy change of atomisation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms forms from the element in its standard state
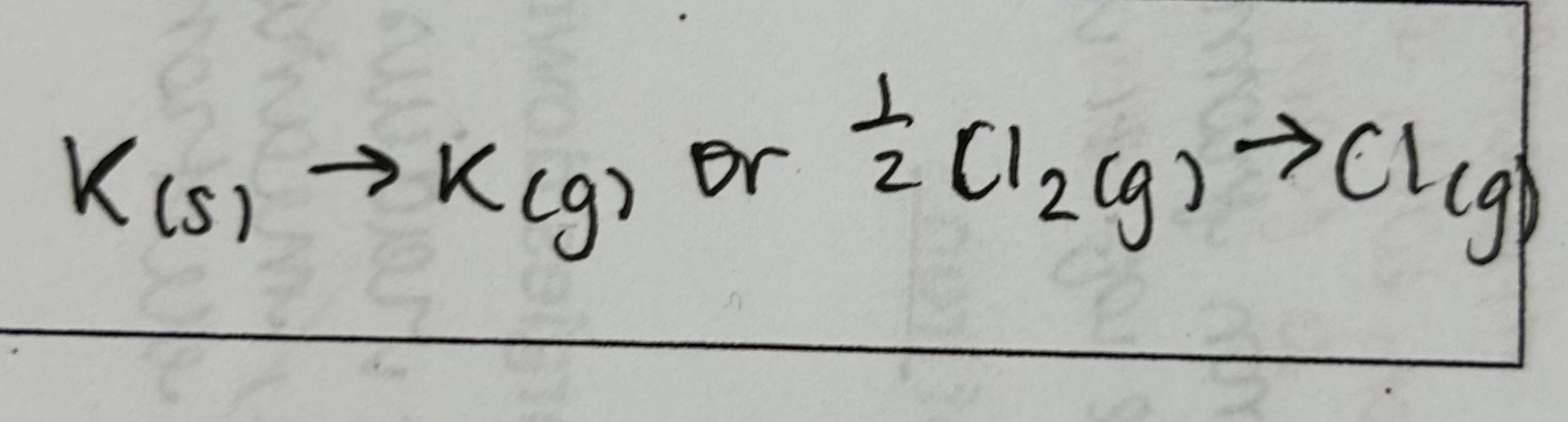
First ionisation energy
enthalpy change when 1 electron is removed from each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
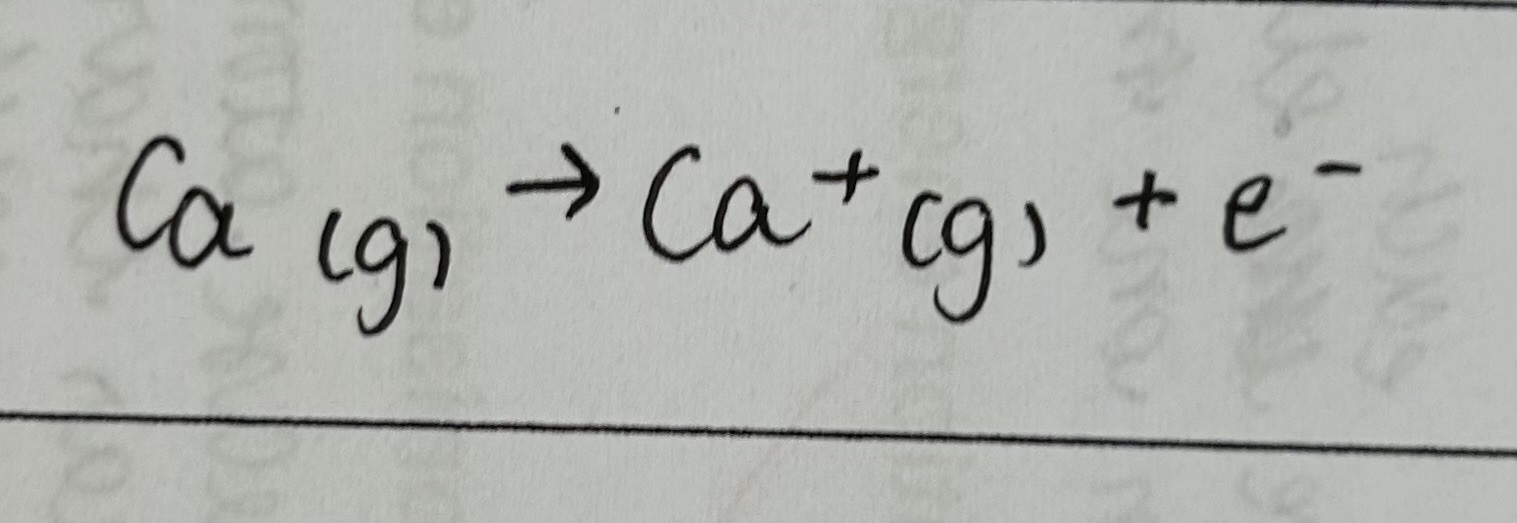
second ionisation energy
the enthalpy change when 1 electron is removed from each ion in 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions to form 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
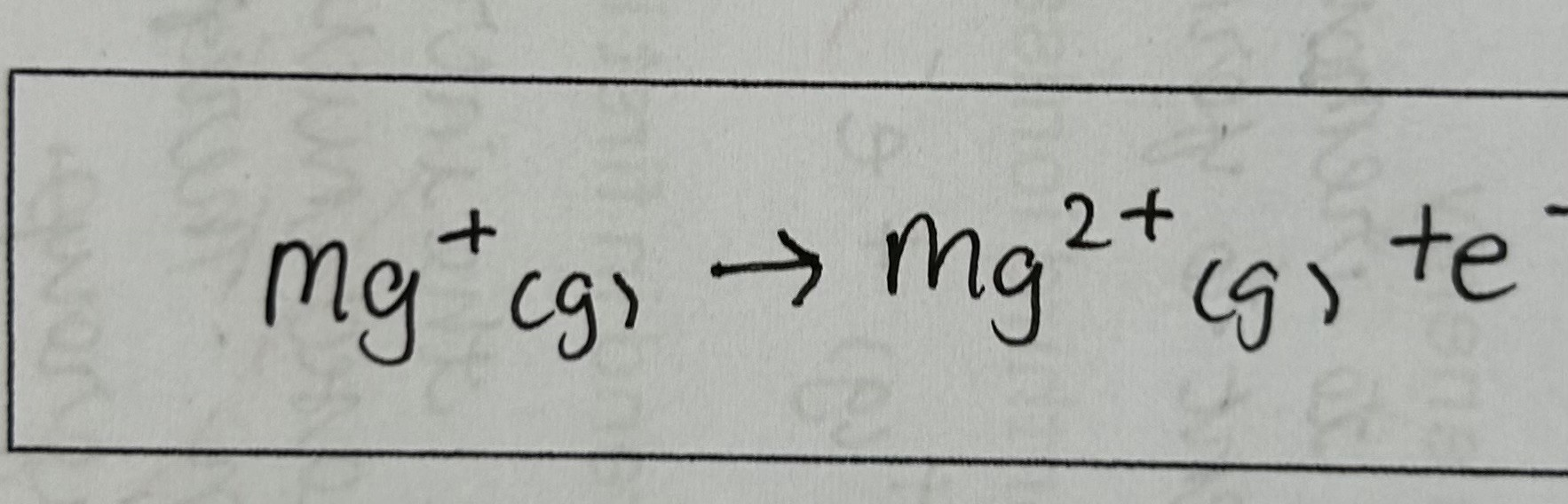
First electron affinity
enthalpy change when 1 electron is added to each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions
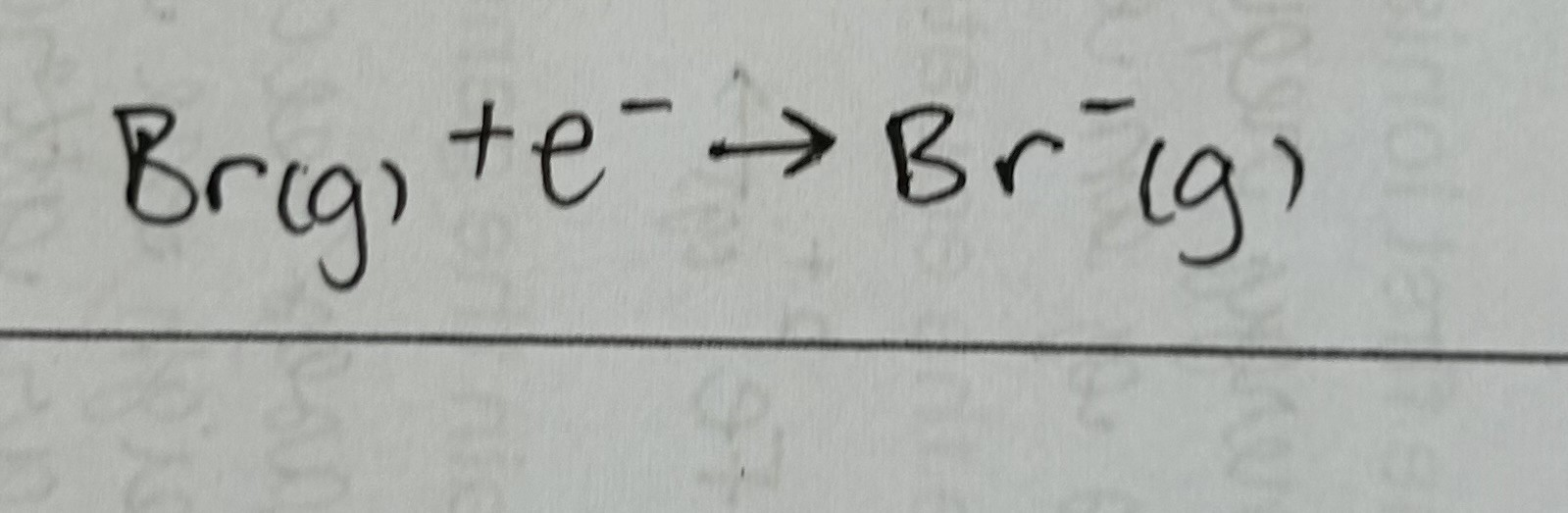
Second electron affinity
enthalpy change when 1 electron is added to each ion in 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions to form 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions
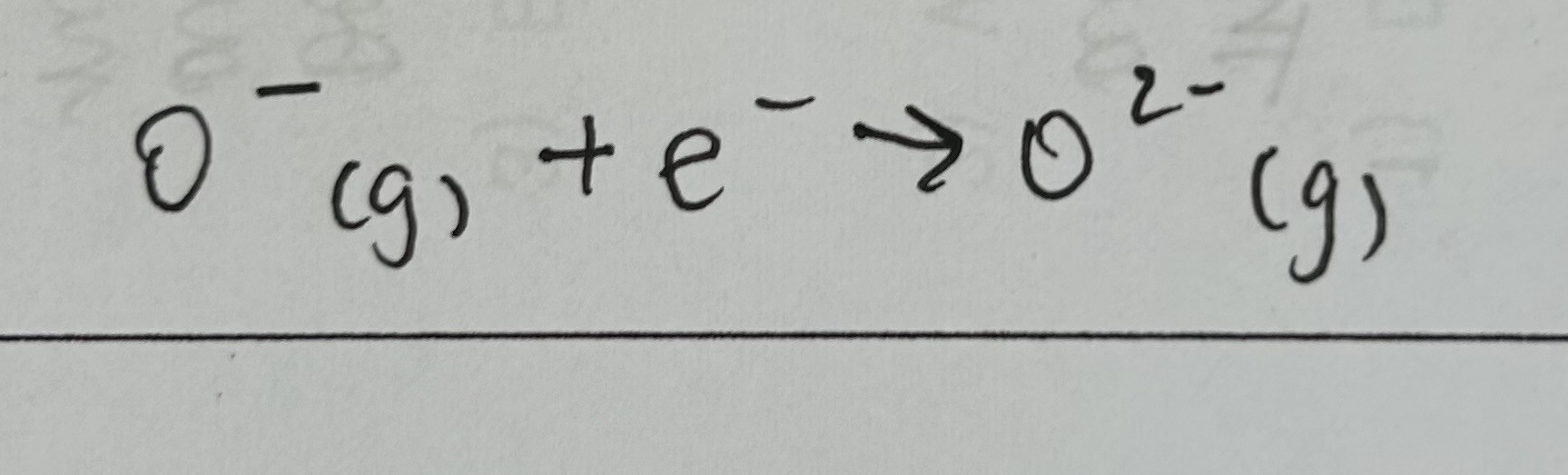
Enthalpy change of solution
when one mole of a compound dissolves in water under standard conditions
Enthalpy change of hydration
when one mole of aqueous ions are formed from their gaseous ions under standard conditions
Entropy
a measure of disorder within a system
What factors affect lattice enthalpy?
the charge on the ions
the radius of the ions
Stronger attractions lead to a more negative lattice enthalpy
Is enthalpy change of solution exothermic or endothermic?
can be either endothermic or exothermic
when an ionic compound is dissolved in water, first energy is taken in to break ionic bonds in ionic lattice
new attractions form between ions and water
Enthalpy change of solution is endothermic when more energy is taken in when breaking bonds in ionic lattice than released when forming attractions
Enthalpy change of solution is exothermic when more energy is given out when making new attractions than taken in when breaking ionic bonds
Is enthalpy change of hydration exothermic or endothermic?
Always exothermic because energy is released when attractions towards the molecules are formed
What is meant by a feasible reaction?
if a reaction when no energy, other than activation energy, is required to sustain the reaction
What factors does the feasibility of a reaction depend on?
the temperature (Kelvin)
the entropy change (convert JK-1 mol to kJ K-1 mol-1)
the enthalpy change (kJ mol-1)
What is the equation (and units) for free energy change?
What is the purpose of the equation?
Finding the value for free energy change predicts the feasibility of a reaction
