Cells and Tissues
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Last updated 1:13 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jelly like substance that suspends the organelles. Cytosol is the liquid part.
2
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Microfilaments (thin threads) and microtubules (hollow tubes) within the cytoplasm, give cell shape, assist in movement of materials, organelles + whole cell.
3
New cards
Nucleus
Controls all activities within the cell. Contains DNA. DNA + nucleolus is suspended in the nucleoplasm.
4
New cards
Nucleolus
Produces cell's ribosomes.
5
New cards
Ribosomes
In cytoplasm
Forms rough endoplasmic reticulum
Joins amino acids together to make proteins
Free ribosomes produce proteins, used by cell. Ribosomes on membrane produce proteins to export for use outside of cell.
Forms rough endoplasmic reticulum
Joins amino acids together to make proteins
Free ribosomes produce proteins, used by cell. Ribosomes on membrane produce proteins to export for use outside of cell.
6
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER)
Ribosomes on surface produce proteins, which are then sent to the Golgi Apparatus.
7
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Pairs of parallel membranes. Provide the surface for chemical reactions, channels to transport molecules and proteins.
8
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (sER)
No ribosomes. Produces lipids and steroids.
9
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Flattened, stacked membranous sacs, cisternae. Modifies and packages proteins in vesicles for exit from cell.
10
New cards
Lysomes
Vesicles produced by the Golgi Apparatus that contain digestive enzymes.
=> break down worn-out organelles.
=> break down materials brought into the cell.
=> break down worn-out organelles.
=> break down materials brought into the cell.
11
New cards
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell. Produces and releases energy (ATP) via aerobic cellular respiration.
12
New cards
Centrioles
Pair of cylindrical structures located near the nucleus. Used in mitosis/ meiosis. Produces spindle fibre.
13
New cards
Cilia (cell projections)
Numerous short projections resembling tiny hairs. Waft back and forth to push mucus out of trachea, bronchi.
14
New cards
Flagella (cell projections)
Long projection(s) from a cell to help it move. E.g. the tail of sperm.
15
New cards
Smallest functioning unit in the human body.
Cells
16
New cards
Hierarchal Organisation
Cells => Tissues => Organs => Systems
17
New cards
Plasma (cell) membrane
A differentially/ semi permeable membrane, allowing certain chemicals to pass through but restricts the movement of others.
18
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer
Phosphide - hydrophilic (water loving)
2 x Fatty Acid Tails - hydrophobic (water repelling)
2 x Fatty Acid Tails - hydrophobic (water repelling)
19
New cards
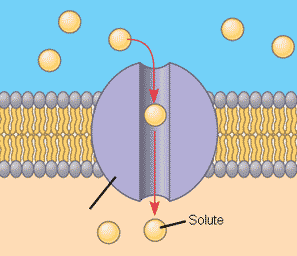
Channel Protein
- transport certain molecules
- allows substance into cell, moves with concentration gradient.
- allows substance into cell, moves with concentration gradient.
20
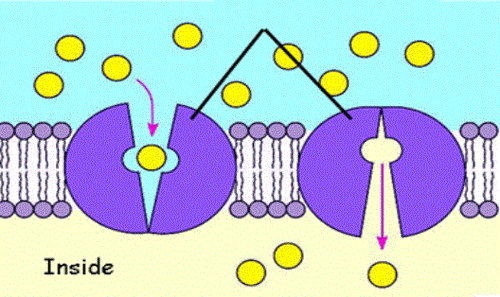
New cards
Carrier Protein
- large + charged molecules, against the concentration gradient.
- form a hydrophilic pore
- requires energy
- form a hydrophilic pore
- requires energy
21
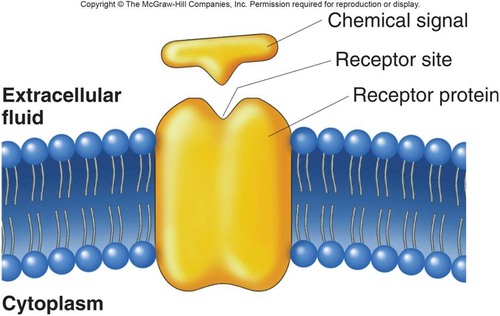
New cards
Receptor Protein
- provide binding sites for substances such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
22
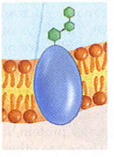
New cards
Recognition Proteins
- important in cell - cell recognition.
- knows your cell belongs to you
- bacteria is attacked + starts an immune response.
hexagon line going off = carbohydrates
- knows your cell belongs to you
- bacteria is attacked + starts an immune response.
hexagon line going off = carbohydrates
23
New cards
Cholesterol
Also found within lipid centre of plasma membrane. It disturbs close packing of phospholipid molecules, keeping membrane fluid.
24
New cards
Aquaporin
Movement of water
25
New cards
Proteins
Embedded in phospholipid bilayer. They regulate the processes inside the cell.
26
New cards
with the concentration gradient/ down concentration gradient
from high to low concentration
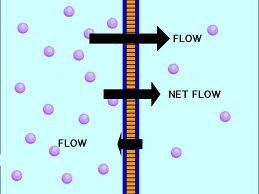
27
New cards
against the concentration gradient/ up concentration gradient
from low to high concentration
28
New cards
What can also travel through the membrane?
Some small uncharged molecules can travel through the membrane
E.g. O2
E.g. O2
29
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid - as the molecules that compose it are constantly changing position.
Mosaic - as it is composed of various different kinds of molecules.
Mosaic - as it is composed of various different kinds of molecules.
30
New cards
Function of Plasma Membrane 1
Regulates passage of materials
= controls what moves in and out of cell
= controls what moves in and out of cell
31
New cards
Function of Plasma Membrane 2
Physical Barrier
= membrane separates cell cytoplasm from extracellular fluid.
= membrane separates cell cytoplasm from extracellular fluid.
32
New cards
Function of Plasma Membrane 3
Sensitivity
= it has receptors that are sensitive to particular molecules in its immediate environment.
= it has receptors that are sensitive to particular molecules in its immediate environment.
33
New cards
Function of Plasma Membrane 4
Support
= the internal part of the membrane is attached to the microfilaments of cells cytoskeleton, thus giving support to whole cell.
= the internal part of the membrane is attached to the microfilaments of cells cytoskeleton, thus giving support to whole cell.
34
New cards
Passive Processes
No energy is required. Down a concentration gradient.
e.g. simple/ facilitated diffusion & osmosis.
e.g. simple/ facilitated diffusion & osmosis.
35
New cards
Active Processes
Requires energy (ATP) for transfer to occur. Up a concentration gradient.
or
Moving large molecules into the cell.
e.g. active & vesicular transport
or
Moving large molecules into the cell.
e.g. active & vesicular transport
36
New cards
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
37
New cards
Simple Diffusion (passive transport)
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down a concentration gradient)
Equilibrium is reached when concentration of particles on either side of membrane are equal. (net movement stops)
e.g Alcohol
Equilibrium is reached when concentration of particles on either side of membrane are equal. (net movement stops)
e.g Alcohol
38
New cards
Factor affecting rate of diffusion across membrane: Steepness of concentration gradient
The diffusion rate will be higher when there is a greater difference in concentration between the two regions
39
New cards
Factor affecting rate of diffusion across membrane: Temperature
Molecules with a higher temperature will have more kinetic energy.
40
New cards
Factor affecting rate of diffusion across membrane: Surface Area
Larger surface where diffusion can occur
41
New cards
Factor affecting rate of diffusion across membrane: Particle Mass
Light particles move faster than heavier particles (at a given temperature).
42
New cards
Factor affecting rate of diffusion across membrane: Physical Barriers
Barries, such as membranes, slow the rate of diffusion. Pores in a barrier may enhance diffusion. Thicker barriers reduce rate.
43
New cards
What is another passive process of diffusion that uses a protein in the plasma membrane?
Channel Protein
Transport molecules that cannot move through the phospholipid bilayer/ across the membrane.
Transport molecules that cannot move through the phospholipid bilayer/ across the membrane.
44
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion (passive transport)
Carrier Mediated Diffusion (Carrier Protein)
Transfers large, hydrophilic molecules (e.g. amino acids) that cannot pass through the hydrophobic centre.
It doesn't require energy (particles are still moving down concentration gradient)
Transfers large, hydrophilic molecules (e.g. amino acids) that cannot pass through the hydrophobic centre.
It doesn't require energy (particles are still moving down concentration gradient)
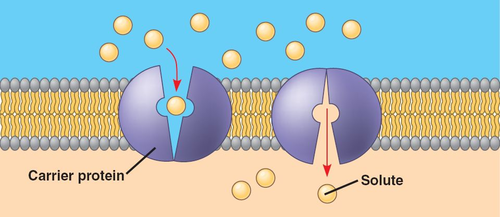
45
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion Process
1. Molecule attaches to binding site on specific carrier protein.
2. Carrier protein changes shape, moving molecule through membrane.
3. Molecule released from carrier protein on other side of membrane.
2. Carrier protein changes shape, moving molecule through membrane.
3. Molecule released from carrier protein on other side of membrane.
46
New cards
Binding Site
(facilitated diffusion - carrier meditated)
(facilitated diffusion - carrier meditated)
shape of a particular molecule they carry
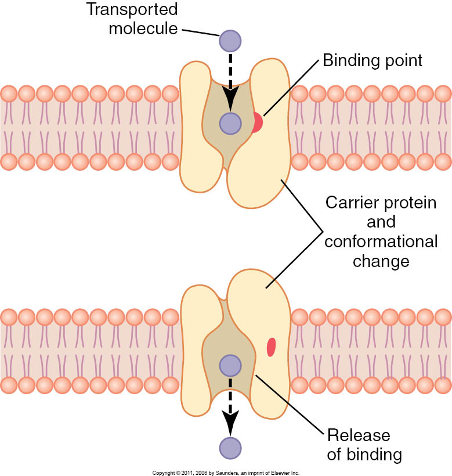
47
New cards
Microtubules
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tubelike structure
48
New cards
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibres that function in the movement and support of the cell
49
New cards
As a cell gets larger what does it require?
It requires more resources to be imported and it produces more waste to be exported.
50
New cards
What does a larger volume require
More exchange of resources and wastes across the membrane.
The exchange processes become less efficient with increasing size.
The exchange processes become less efficient with increasing size.
51
New cards
Smaller Cells
- shorter diffusion pathways
- larger surface area to volume ratio
- larger surface area to volume ratio
52
New cards
What does a larger SA:V ratio mean?
The cell can act more efficiently.
53
New cards
Osmosis (passive transport)
Movement of water molecules from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration) across a partially permeable membrane.
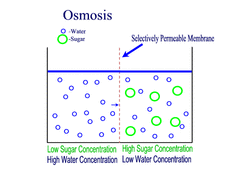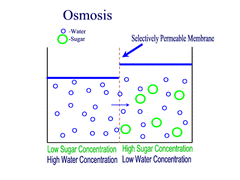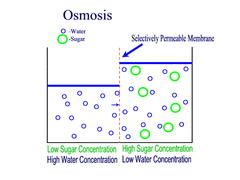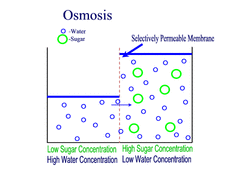
54
New cards
High/ Low Solute Concentration =
= High/ Low Osmotic Pressure
55
New cards
What do water molecules cross the hydrophobic centre of the membrane through?
Aquaporins (channel proteins)
56
New cards
Isotonic
Same osmotic pressure as another solution
57
New cards
Hypotonic
Lower osmotic pressure (lower solute concentration) relative to another solution
58
New cards
Hypertonic
Higher osmotic pressure (higher solute concentration) relative to another solution.
59
New cards
Active Transport
- movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration (up/ against gradient)
- requires energy (ATP)
- requires energy (ATP)
60
New cards
Carrier Meditated Transport
(Active Transport)
(Active Transport)
- harness ATP energy
- low to high concentration
- transfers a phosphate group to the carrier protein
- protein changes shape so that the bound particle can move across membrane.
- low to high concentration
- transfers a phosphate group to the carrier protein
- protein changes shape so that the bound particle can move across membrane.
61
New cards
Endocytosis (Vesicular Transport)
- transport of substances to inside the cell
- inside a membrane-bound vesicle/ vacuole
- inside a membrane-bound vesicle/ vacuole
62
New cards
Invagination (endocytosis)
Infolding of plasma membrane
63
New cards
Pinocytosis (endocytosis)
- intake of liquids
- fluid within vesicle transferred to cytosol
- fluid within vesicle transferred to cytosol
64
New cards
Phagocytosis (endocytosis)
- intake of solids
- contained within membrane enclosed sac (vacuole)
- digestion = vacuole fuses with lysomes (enzyme)
- used by white blood cells to clean up bacteria
- contained within membrane enclosed sac (vacuole)
- digestion = vacuole fuses with lysomes (enzyme)
- used by white blood cells to clean up bacteria
65
New cards
Exocytosis
- releases substances out of cell
- fusion of vesicle membrane with plasma membrane
e.g. secretes enzymes and hormones
- fusion of vesicle membrane with plasma membrane
e.g. secretes enzymes and hormones
66
New cards
How many basic tissue types are there?
4 basic tissue types
1. Epithelial
2. Connective Tissue
3. Muscle
4. Nervous
1. Epithelial
2. Connective Tissue
3. Muscle
4. Nervous
67
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
- covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands
e.g. - skin, lining of air passages, blood vessels
(they are named according to their arrangement and shape)
e.g. - skin, lining of air passages, blood vessels
(they are named according to their arrangement and shape)
68
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue
- Single layer of flat cells
- forms capillaries (smallest blood vessels)
- forms alveoli (air sacs in lungs)
- good surface for exchange
- very thin = allows rapid diffusion of substances across the epithelium
- forms capillaries (smallest blood vessels)
- forms alveoli (air sacs in lungs)
- good surface for exchange
- very thin = allows rapid diffusion of substances across the epithelium
69
New cards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- single layer of cube shaped cells
- forms kidney tubules
- forms salivary glands and thyroid glands
- forms kidney tubules
- forms salivary glands and thyroid glands
70
New cards
Simple Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
- single layer of rectangular cells with cilia
- lines the fallopian tubes
- cilia push egg along the fallopian tube
- lines the fallopian tubes
- cilia push egg along the fallopian tube
71
New cards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- many cell layers thick
- cells become progressively thinner as they move up layers (flat up top)
- forms skin, lining of mouth and vagina)
- thickness provides protection from abrasion
- cells become progressively thinner as they move up layers (flat up top)
- forms skin, lining of mouth and vagina)
- thickness provides protection from abrasion
72
New cards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- few layers of cuboidal cells
- forms sweat and mammary glands
- forms sweat and mammary glands
73
New cards
Connective Tissue
- cells rarely touch
- large amount of non-cellular material surrounding them (matrix)
- protect, insulate, connect, support
e.g. cartilage, bone, adipose (fat) or blood
- large amount of non-cellular material surrounding them (matrix)
- protect, insulate, connect, support
e.g. cartilage, bone, adipose (fat) or blood
74
New cards
Matrix
Fibres/ ground substances secreted by connective tissue cells
75
New cards
Cartilage (Collective Tissue)
- cells (chondrocytes) embedded in matrix composed of collagen/ elastin
- repair is slow (no blood vessels/ nerves)
- found covering end of bones, in ear, nose, airway walls and vertebrae
- repair is slow (no blood vessels/ nerves)
- found covering end of bones, in ear, nose, airway walls and vertebrae
76
New cards
Collagen/ Elastin
Support, flexibility and bounce back
77
New cards
Compact Bone (Collective Tissue)
- cells (osteocytes) embedded in concentric rings of matrix
- composed of collagen/ elastin and minerals = e.g. calcium
- forms shaft of long bones
- composed of collagen/ elastin and minerals = e.g. calcium
- forms shaft of long bones
78
New cards
Blood (Collective Tissue)
- liquid matrix plasma
- cells found floating in matrix (erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets)
- forms part of circulatory system
- cells found floating in matrix (erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets)
- forms part of circulatory system
79
New cards
Muscle Tissue
cells that are able to shorten in length (contract)
80
New cards
Smooth Tissue (Muscle)
Location: organs, uterus, digestive system
One nuclei
Not Striated
Involuntary
One nuclei
Not Striated
Involuntary
81
New cards
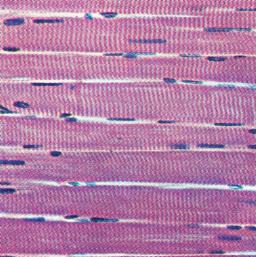
Skeletal Tissue (Muscle)
Location: attached to bones, biceps
many nucleus
Striated
Voluntary
many nucleus
Striated
Voluntary
82
New cards
Cardiac Tissue (muscle)
Location: wall of heart
One nuclei
Striated
Involuntary
One nuclei
Striated
Involuntary
83
New cards
Nerve/ Nervous Tissue
- cells are called neutrons
- carry messages from one part of the body to another - in form of electrical impulses
- carry messages from one part of the body to another - in form of electrical impulses
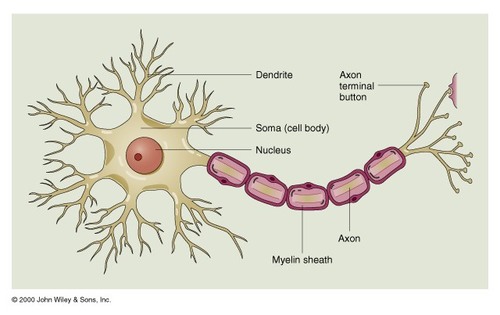
84
New cards
Cancer Definition
An abnormal mass of cells, a tumour that arises from uncontrolled cell division
85
New cards
Mutation of gene (cancer) ~ PROTO - ONCOGENES
Code for proteins which stimulate cell cycle and promote cell growth.
When mutated it turns into an oncogene, which causes cancer.
When mutated it turns into an oncogene, which causes cancer.
86
New cards
Mutation of gene (cancer) ~ TUMOUR SUPPRESSOR GENES
Code for proteins that stop cell cycle progression and promote cell death.
87
New cards
Cause of Cancer - CARCINOGENS
Cancer causing agent
Environmental factors that cause cancer
e.g. UV radiation, viruses, x-rays, chemicals - alcohol and tobacco
Environmental factors that cause cancer
e.g. UV radiation, viruses, x-rays, chemicals - alcohol and tobacco
88
New cards
Cause of Cancer - RANDOM MUTATIONS
Uncontrolled division of the cell with daughter cells inheriting the mutated gene.
- some mutations can be passed from parent to child
e.g. breast/ colon cancer
- cell must acquire several mutations must occur before they become cancerous
- some mutations can be passed from parent to child
e.g. breast/ colon cancer
- cell must acquire several mutations must occur before they become cancerous
89
New cards
Benign Tumours
Contained within a capital, don't spread to other parts of the body, cells held together by a capsule
90
New cards
Malignant Tumours
Tumour cells that spread to other parts of the body. Known as metastasis
Few cells break off, enter the blood/ lymph vessels and get carried to another place where they can form secondary tumours surrounding them.
Few cells break off, enter the blood/ lymph vessels and get carried to another place where they can form secondary tumours surrounding them.
91
New cards
Metastasis
Process of spreading cancerous cells spreading to other parts of the body
92
New cards
What are Cancers categorised depending on?
Based on the type of cells which they arise, impacting/ infecting
93
New cards
Cancer Category: Carcinomas
Arise from epithelial cells
e.g. skin, lung, bowel cancer
e.g. skin, lung, bowel cancer
94
New cards
Cancer Category: Sarcomas
Arise from non- epithelial tissue
e.g. muscle, cartilage and bone
e.g. muscle, cartilage and bone
95
New cards
Cancer Category: Lymphomas/ Leukemias
Arise from cells of blood/ lymphatic tissues
Leukemias, cancer of white blood cells
Leukemias, cancer of white blood cells
96
New cards
Prevention of Cancer
- education
- legislation
- avoid smoking
- diet adequate in fibre
- wear protective clothing and face masks when handling dangerous chemicals.
- use sunscreens, sunglasses, protective clothing, stay out of direct sunlight e.t.c
- avoid being overweight/ obese
- limit alcohol intake
- legislation
- avoid smoking
- diet adequate in fibre
- wear protective clothing and face masks when handling dangerous chemicals.
- use sunscreens, sunglasses, protective clothing, stay out of direct sunlight e.t.c
- avoid being overweight/ obese
- limit alcohol intake
97
New cards
Early Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Regular Pap smear
98
New cards
Early Prevention of Breast Cancer
Checking for lumps and regular mammograms
99
New cards
Early Prevention of Bowel Cancer
Faecal occult blood test (FOBT)
100
New cards
Early Prevention of Prostate Cancer
Digital rectal exam, prostate specific antigen blood test, biopsy