Ch. 10 Lymphatic System, H&N, Fall 2025
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Lymphatic system is part of the
immune system
Lymphatic System is a
NETWORK OF TINY CHANNELS AND NODES
Tonsillar tissue in oral cavity & pharynx are
part of the lymphatic system
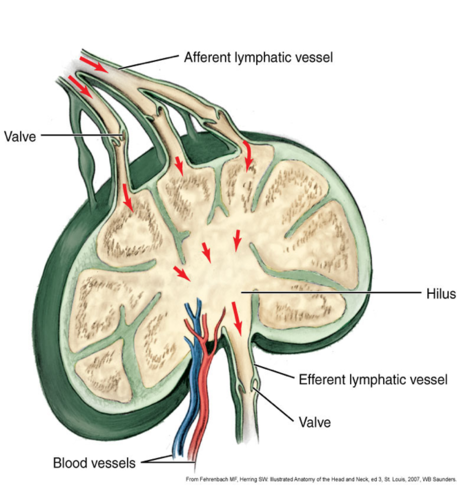
afferent vessels
lymph flows IN
efferent vessels
lymph flows OUT
Lymph vessels are found in
pulp tissue in a tooth
Lymph vessels have one way
valves
tonsils are helpful in
immune process
in clinic we palpate the whole
chain of lymph nodes
shape of lymph nodes
Bean shaped and clustered
lymph nodes filter
toxins
_______ and _______ in lymph nodes can indicate an infection
swelling and tenderness
lymph nodes contain lymphocytes/ they are derived from
stem cells in bone marrow
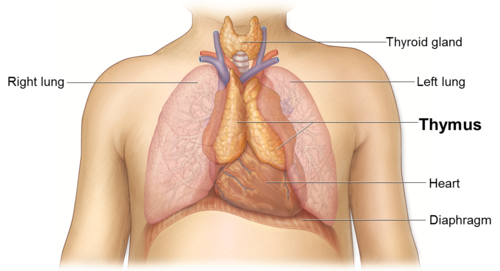
T-cells mature in the
thymus gland
--Respond to foreign antigens in tissue fluids
2 types of nodes
• Superficial
• Deep
lymph nodes components
-afferent vessel
-efferent vessel
-hilus
-types of nodes
hilus
depression on one side where the lymph flows out/ material settles there before it goes out
types of nodes
-Primary (regional) "master nodes"—drain into secondary nodes (heavy hitters)
-Secondary (central)
-tertiary
tonsillar tissue
Masses of tissue in the oral cavity and pharynx that remove toxic products
tonsillar tissue located
near airway and food passages
lymphatic ducts size
large
where do lymph ducts drain
drain into the venous system of the blood of the chest area
-Drainage depends of the side of the body involved
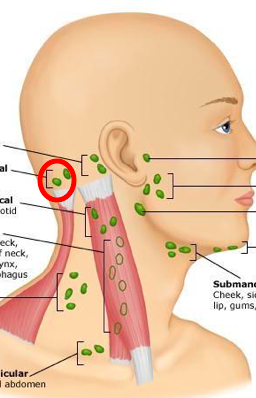
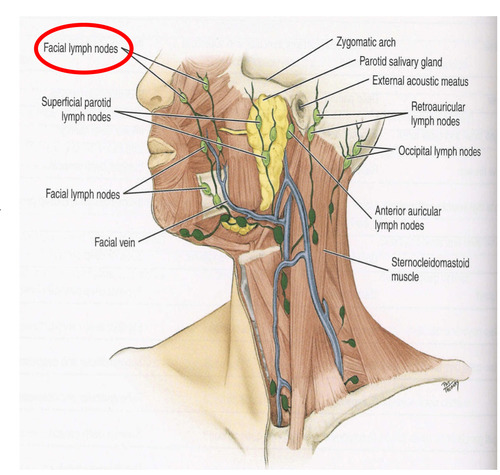
5 groups of superficial lymph nodes in the head
occipital
-retroauricular/ posterioauricular
-anterior auricular
-superficial parotid
-facial nodes
occipital lymph nodes/ how many and where do they empty into
-1-3 bilaterally on the posterior base of the head /back of skull
• Empty into the deep cervical nodes of the neck
occipital nodes drain the
scalp
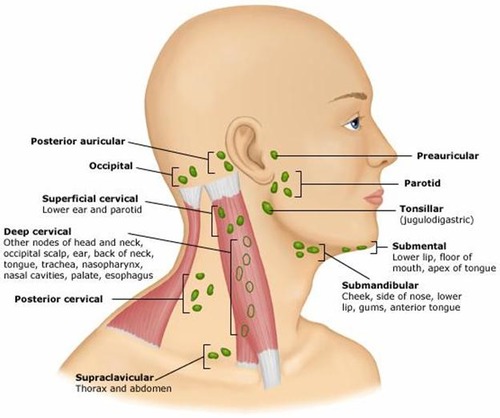
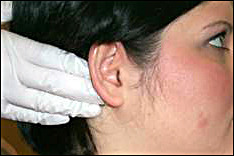
where are postauricular or retro auricular lymph nodes
posterior to each ear
the retro auricular nodes and the anterior auricular nodes drain the
scalp
external ear
lacrimal gland
where is the anterior auricular node or the preauricular node?
in front of the ear
superficial parotid nodes location
Superficial to Parotid gland/ in the cheeks
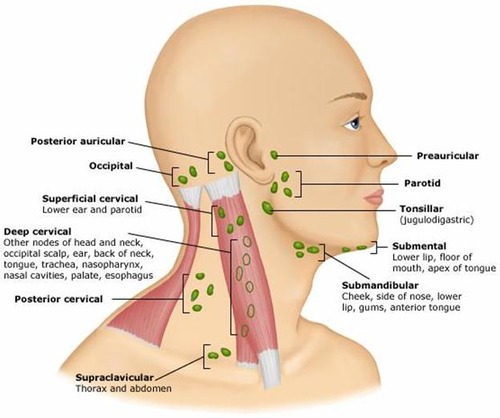
superficial parotid nodes drain the
scalp
external ear
lacrimal gland
facial nodes location
superficial to the facial vein
close to the nose, upper lip area, and toward the angle of the mandible
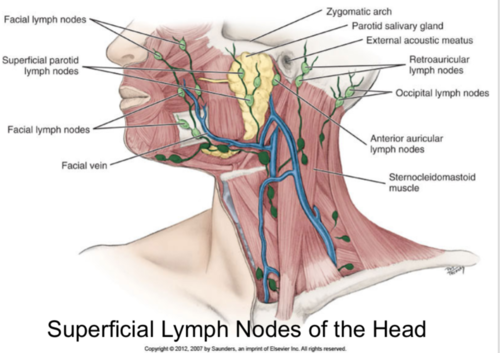
facial lymph nodes drain the
lateral eyelid
nose
cheek
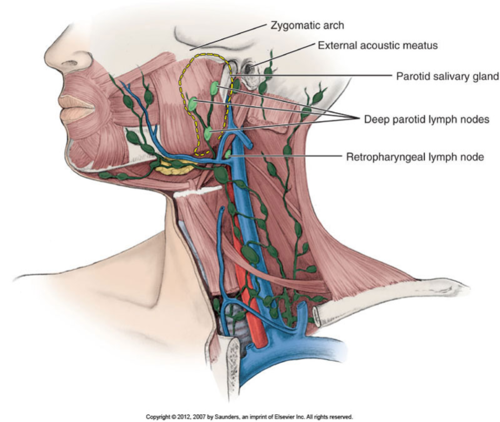
Deep lymph nodes of the head cannot be
Cannot be palpated due to depth!!!
Deep Parotid Nodes- how many and what do they drain
10 drains the middle ear, auditory tube, and parotid salivary gland
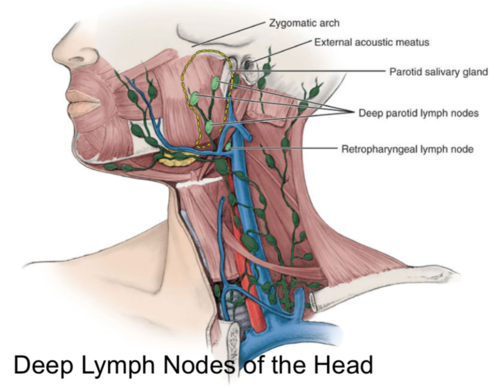
Retropharyngeal Nodes
- Drains the pharynx, palate, paranasal sinuses, and nasal cavity/ behind the pharynx
cervical nodes
They drain either the right or left sides Categorized as: Upper/Middle/Lower Anterior or Lateral/Posterior Superficial or deep
the 3 deep lymph nodes of the head
deep parotid glands
Retropharyngeal Nodes
cervical nodes
superficial cervical lymph nodes
submental
submandibular
external jugular
anterior jugular
deep cervical lymph nodes
submental nodes are located
under the chin
2-3 nodes inferior to chin (between bellies of the digastric muscle)
submental nodes drains fluid from the
-mandibular incisors/ anterior teeth
-tip or apex of tongue
-chin
-lower lip
- floor of mouth
- with associated periodontium and gingiva
submental nodes Empty into
submandibular nodes and then deep cervical nodes.
submandibular (more on the angle of the mandible) nodes drain
-submental nodes
-cheeks, upper lip, body of tongue
• anterior hard palate
• most of teeth with associated periodontium and gingiva EXCEPT MAND. INCISORS AND MAX 3rd MOLARS.
External Jugular Nodes aka
Superficial cervical nodes
• These empty into the Deep Cervical Nodes
Anterior Jugular Nodes
AKA Anterior Cervical Nodes
• Drain infrahyoid region of neck
• Empty into Deep Cervical Nodes
Deep Cervical Nodes- number and what they drain
15-30 that drain submandibular nodes
• Drains 3rd molar region
• Structures of the oropharynx are drained by the Superior Deep Cervical Nodes
• Superior Deep Cervical Nodes are drained by Inferior Deep Cervical Nodes
paper- deep cervical nodes drain the
posterior hard palate
soft palate
maxillary third molars
tonsils
base of tongue
thyroid gland
Primary Node, Secondary Node, and Tertiary Node
1st node affected by a disease process is primary___________
• 2nd node affected by a disease process is secondary___________
• 3rd node affected by a disease process is tertiary_________
The superior deep cervial lymph nodes are located deep beneath the
SCM muscle, superior relative to the point where the omohyoid muscle crosses the internal jugular veins/ cervical nodes are in front of and behind the SCM
One node of the superior deep cervical nodes can be prominent and palpable, the
jugulodiagastirc lymph node or the tonsillar lymph node, when the palatine tonsils undergo node enlargement or lymphadenopathy.
The jugulodiagastric node or the tonsilar node is located
inferior to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and posterior to the angle of the mandible
superior deep cervical lymph nodes drainage- The superior deep cervical nodes are primary nodes draining the
posterior nasal cavity, posterior hard palate, soft palate, base of the tongue, maxillary third molars with associated periodontium and gingiva, tmj, esophagus, trachea, and the thyroid gland
Superior deep cervical lymph nodes, may be secondary nodes for all other nodes of the head and neck, except for
inferior deep cervical nodes
-the superior deep cervical nodes empty into the inferior deep cervical nodes or directly into the jugular trunk
The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are a continuation of the
superior deep cervical group
The inferior deep cervical nodes are also located deep to the
scm muscle
-ask permission to palpate this area
inferior deep cervical lymph nodes cancers
thus because of this node communication, the inferior deep cervical nodes are at the greatest risk for the spread of breast cancer or adenocarcinoma
In addition to the deep cervical lymph nodes are the accessory and
supraclavicular node groups in the most inferior part of the neck
Accessory lymph nodes location/ drainage
The accessory lymph nodes are 2 to 6 in number and are located along the eleventh cranial or accessory nerve
-these nodes drain the scalp and neck regions and then drain into the supraclavicular nodes
the supraclavicular lymph nodes are located
Superiorly along the clavicle close to where the sternum joins
-bilateral
Supraclavicular lymph nodes: drainage
these nodes drain the lateral cervical triangles
(the supraclavicular nodes may empty into one of the jugular trunks or directly into the right lymphatic duct or thoracic duct) know that part
supraclavicular nodes pathology
-these nodes are located in the final endpoint of lymphatic drainage from the entire body
-because of the location, these nodes are at greatest risk for involving the spread of cancers arising from the lungs, esophagus, and stomach
-therefor inspection of these nodes is important in any patient assesment
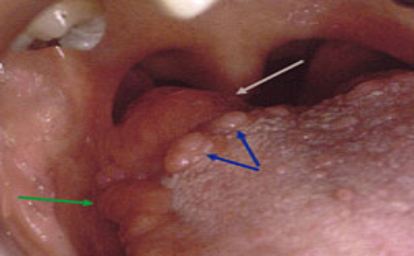
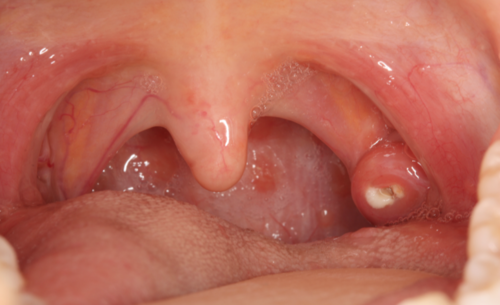
The palatine tonsills, what patients call their tonsills are two rounded masses of variable size located in the
the oral cavity between the anterior and posterior faucial pillars on each side of the fauces
Palatine tonsills
these 2 vertical folds are formed by muscles of the soft palate: the palatoglossus muscle forms the anterior faucial pillar and the palatopharyngeus muscles forms the posterior faucial pillar
-alot of the tissue is linked up as one
Lingual tonsill
the lingual tonsil is an indistinct layer of lymphoid nodules located intraorally on the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue
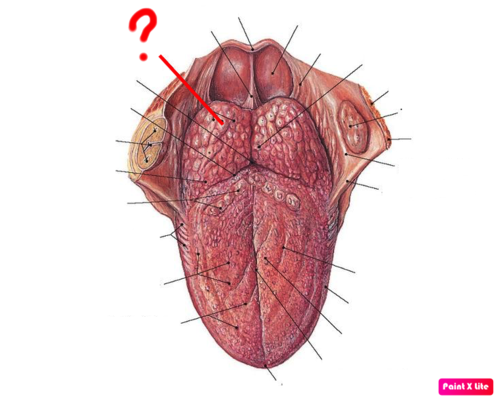
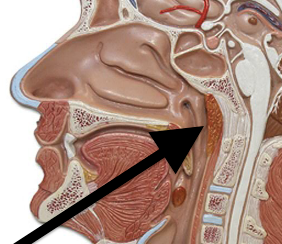
Pharyngeal Tonsils are located
on the posterior wall of the nasopharynx
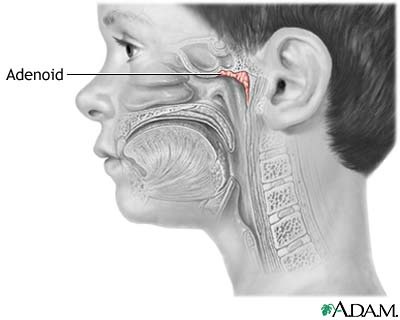
Also called Adenoids
pharyngeal tonsil
-Enlarged in children
What happens when tonsils are removed
When children have tonsils and adenoids removed, usually remove ALL the tonsils except the lingual tonsils in tongue
tonsillar crypts
portion of tonsils that trap and destroy bacteria and particulate matter.
when a patient has a disease process such as cancer or infection active in a region, the regions lymph nodes respond
The resultant increase in size and change consistency of the lymphoid tissue is considered lymphadenopathy
The change in lymph nodes consistancy can range from
firmer to boney hard
Nodes can remain mobile or free from the surrounding tissue during a disease. however these nodes can also become
attached or fixed to the surrounding tissue, such as skin, bone, or muscle, as the disease process progresses to involve the regional tissue
When the nodes are involved with lymphadenopathy
the nodes can also feel tender to the patient when palpated. This tenderness is because of pressure on the area nerves resulting from the node's enlargement.
lymph node inflammation
lymphadenitis
-commonly occurs with microbial infections, such as with S. aureus, and s. pyogenes infections locally with tonsillar or oral abscesses as well as systemically with mononucleosis or HIV infections
Which THREE TONSILS MAKE UP THE WALDEYER RING?
-palatine
-lingual
-pharyngeal (adenoids)
-tubul
What are tonsil stones?
Tonsilloliths, are hard white formations that are located on or within the tonsils.
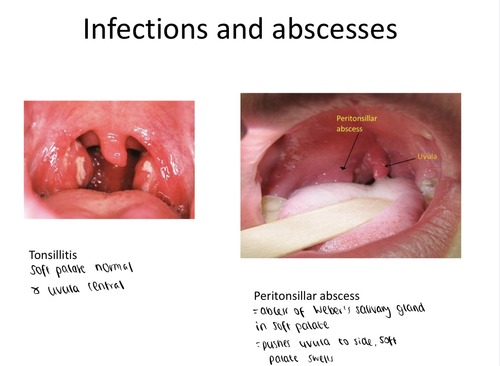
TONSILLITIS & ABSCESS:
Spread of cancer from the primary site of a tumor to a secondary site is called
metastasis
If cancer is not stopped at the primary nodes, it will
spread to secondary nodes, metastasis progresses
If metastasis passes all lymph nodes, the cancer cells enter the
vascular system by way of the lymphatic ducts
Spread of cancer is quicker once it reaches the
blood vessels by way of nodes
Lymph nodes involved with cancer can be
hard, non-mobile and/or fixed
Cancerous nodes are not
tender
Infected nodes are
Mobile and Tender