intro tl biz midterm
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Elastic Demand
when a small price change causes a big demand change.
Inelastic demand
when a price change causes little to no change in demand
Unit elastic demand
when the percentage of the change in price = the change in demand
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
when the demand for a good stays the same no matter the price
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital and Enterprise
Land
All natural resources. including raw materials, minerals, water oil and the physical space for production
Labor
The human effort, skills, and time people contribute to production, both physical and intellectual work.
Capital
Manufactured goods used to make other goods and services such as tools, machinery and infrastructure.
Enterprise or Entrepreneurship
the seeking out of profitable opportunities for production and taking risks in attempting to exploit these
MP =
Marginal product:
L =
labor: the physical and mental efforts of workers
TP
total product
delta (triangle)
change
MP = (triangle)TP / L
marginal product = the change in total output divided by change in number of workers
Economics
Study of how people make choices to satisfy unlimited wants with limited resources
Scarcity
Limited resources force people to make choices
Trade-off
Giving up one thing to get another
Opportunity Cost
The next best alternative you give up when making a choice
Supply
Amount producers are willing and able to sell at each price
Demand
Amount consumers are willing and able to buy at each price
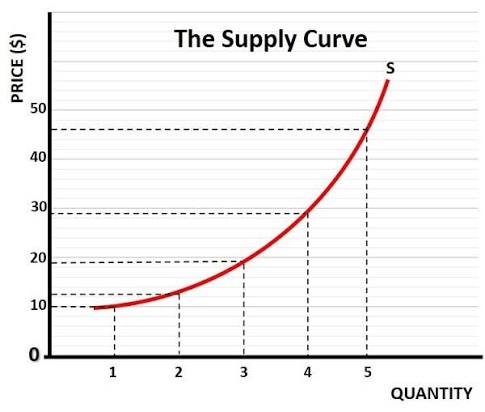
Supply Curve
Shows relationship between price and quantity supplied (upward sloping)
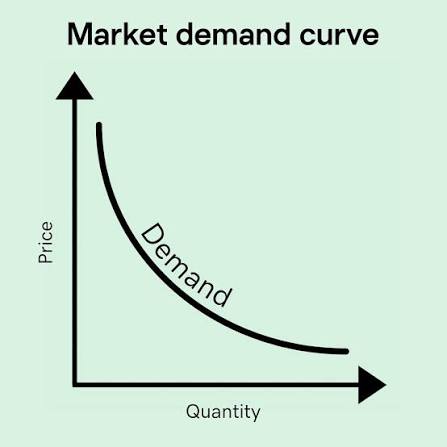
Demand Curve
Shows relationship between price and quantity demanded (downward sloping)
Equilibrium
Where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
Ceteris Paribus
All other things equal
Price Ceiling
Maximum legal price set by government (causes shortages)
Price Floor
Minimum legal price set by government (causes surpluses)
Price Elasticity of Demand
How responsive quantity demanded is to a change in price
Entrepreneurship
Risk-taking ability to start a business
Short Run
Time period where at least one input is fixed
Long Run
Time period where all inputs can change
Marginal Product
Extra output from adding one more worker (MP = ∆TP ÷ ∆L)
Perfect Competition
Many firms selling identical products with no long-run profits
Monopoly
Market with one seller and high barriers to entry
Natural Monopoly
One firm can supply market at lower cost than many firms
Allocative Efficiency
Occurs when price equals marginal cost (P = MC)
Game Theory
Study of decision-making when outcomes depend on others
Prisoner's Dilemma
Self-interest leads to worse outcome for everyone
Comparative Advantage
Ability to produce at lower opportunity cost
Protectionism
Government actions to protect domestic industries
Economic Union
Group of countries that trade freely
Globalization
Increasing economic connection between countries
GDP per Capita
GDP divided by population; measures standard of living
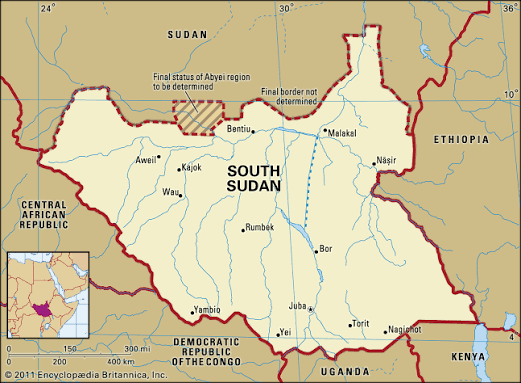
Low-Income Country
Per capita income below $1,025 ex: south sudan
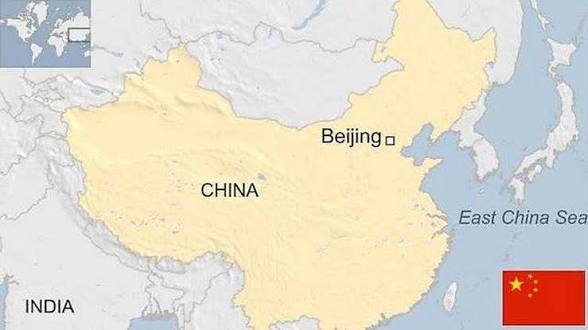
Middle-Income Country
Per capita income between $1,025 and $12,475 ex: china
High-Income Country
Per capita income above $12,475 ex: Japan, United States or UAE
Purchasing Power Parity
Compares what money can buy in different countries
Economic Growth
Increase in ability to produce goods and services
Business Cycle
Prosperity(peak), Recession, Depression, Recovery
Expansion
Period of economic growth
Deficit Spending
Government spends more than it earns to boost economy
Bull Market
Stock prices rising
Downsizing
Reducing workforce to cut costs
Dot-Com Boom
Rapid growth of internet companies in the 1990s
Prosperity in the business cycle
the peak. A period where most people who want to work are working, business produce goods in record numbers and wages are good as GDP increases
Recession in the business cycle
The phase of the business cycle in which demand begins to increase, business lower production, unemployment rises and GDP growth slows
Depression in the business cycle
The phase of the business cycle that is marked by a prolonged period of high unemployment, weak consumer sales and business failures
Recovery in the business cycle
The phase in the business cycle in which employment begins to increase, demand for goods and services increase and GDP begins to rise again
GDP (gross domestic product)
Measures the total value of goods and services produced by that economy during a specific time period