Experiment 1 - Common Laboratory Operations
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
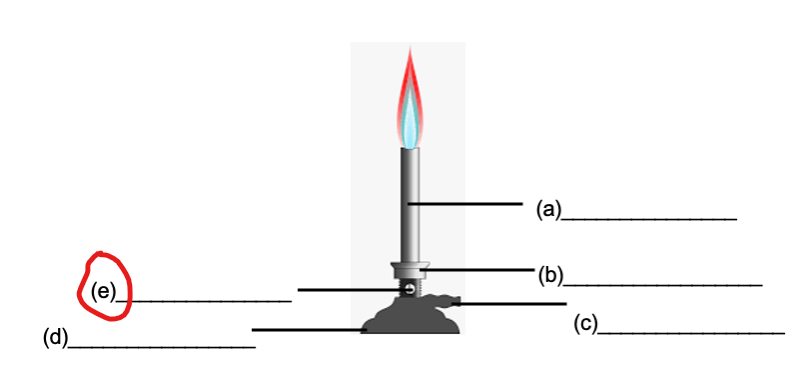
BARREL
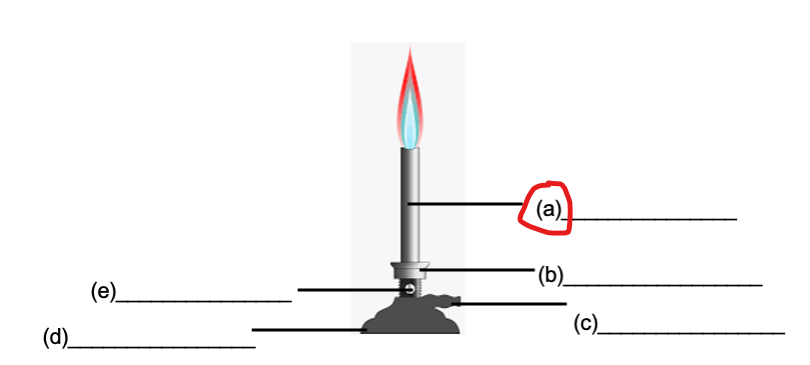
COLLAR
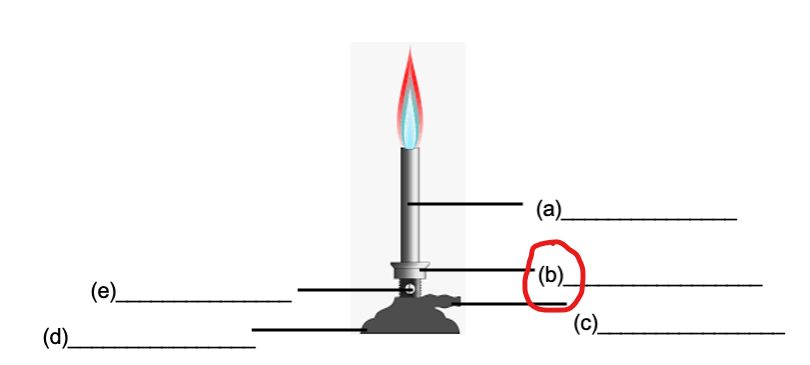
GAS INLET

BASE
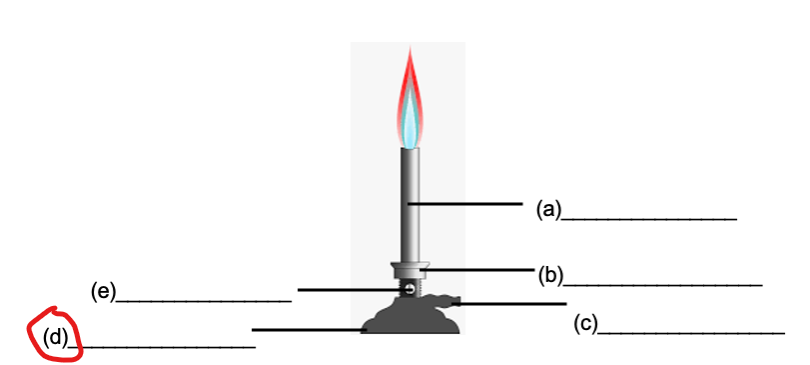
AIR HOLE
PLACE
________ the Bunsen burner away from any overhead shelving, equipment, or light fixtures
REMOVE
________ all papers, combustible materials, and chemicals from the area
TIE-BACK
________ any long hair, dangling jewelry, or loose clothing
INSPECT
________ hose for cracks, holes, pinched points, or any other defect and ensure that the hose fits securely on the gas valve and the Bunsen burner
NOTIFY
________ others in the laboratory the burner will be in use
ADJUST
________ the flame by turning the collar to regulate air flow and produce an appropriate flame for the experiment
DO NOT
________ leave open flames unattended
SHUT OFF
________ gas when its use is complete
ALLOW
________ the burner to cool before handling
ENSURE
________ that the main gas valve is off before leaving the laboratory
Luminous flame
Non-luminous flame
Types of Bunsen Burner Flame:
Luminous flame
also known as safety flame
Luminous flame
It can be obtained when the air hole is fully closed
Luminous flame
This is the coolest flame characterized by bright yellow color producing black soot on top of the flame
Luminous flame
never used in heating. It is just used when starting a burner
Production of soot
indicates that combustion of the fuel in this type of flame is incomplete
Non-luminous flame
This is the flame used for heating. It can be obtained when the air hole is fully opened
Non-luminous flame
This is characterized by a faint blue color that is difficult to see in a well-lit room
Non-luminous flame
There is no soot production when using this flame indicating that the combustion of fuel is complete
Reagent bottles
Solid chemicals are generally kept in ________
Spatula or Paper
Removal of solid chemicals from the reagent bottle should be done by _________, not by bare hands
Designated waste disposal bin
Any excess chemical that is already taken out from the bottle should not be returned but should be disposed in _________
Weighing
very crucial process in the chemistry laboratory to obtain accurate results
Clean and Dry
Before transferring any solid chemicals into the test tube, it must be first noted that all the apparatuses to be used should be ________ to avoid contamination
Indentation
the cleft in the mouth of glassware like the one in beakers
Non-luminous flame
The flame during heating, as discussed previously, should be a ________ of a Bunsen burner
Filtration
process of separating solid from liquid solution using a filtration membrane, in most cases a filter paper
Filter paper
Filtration is a process of separating solid from liquid solution using a filtration membrane, in most cases a ________
to remove solid impurities from a liquid
to collect a desired solid from the solution from which it was precipitated
Two Main Purposes of Filtration:
Residue
The solid that is left on the filter paper after filtration is called
Filtrate
The liquid that comes out from the filter paper is called
Evaporation
a process of separating soluble solids from a solution
Evaporation
This is carried out by evaporating the solvent to dryness leaving the solute residue behind
Solubility of a solute
a dissolved substance
Solvent
the dissolving medium
Solubility of solute in a solvent
the most important chemical principle underlying some of the basic techniques in the organic chemistry laboratory
Soluble
dissolved
Insoluble
not dissolved
grams of solute per liter (g/L)
milligrams of solute per milliliter (mg/mL)
Solubility may be expressed in terms of:
Miscible and Immiscible
When the solubility of a liquid solute in a solvent is described, it is sometimes helpful to use the terms
Miscible
mix homogeneously
Immiscible
do not mix homogeneously
Precipitate
The solid that is formed is called
Loading Balance
Weighing Solid Chemicals Using to
Test Tube
Transferring Solid Chemicals in a
Graduated Cylinder
Measuring the Volume of Liquid Chemicals Using
Dropper
Transferring Liquid Using