livestock nutrition
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Classes of nutrients
Water, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, minerals, vitamins.
Water
Most important
Carbohydrates and fats
Energy
Proteins, minerals, vitamins
Can provide some energy
Components of a feed
Protein is energy consuming. Fat stores energy (dense).
Energy partitioning by a cow
Basal metabolism, activity, growth, basic energy reserve, pregnancy, lactation, additional energy reserve, estrous cycle and pregnancy initiation, excess energy reserve
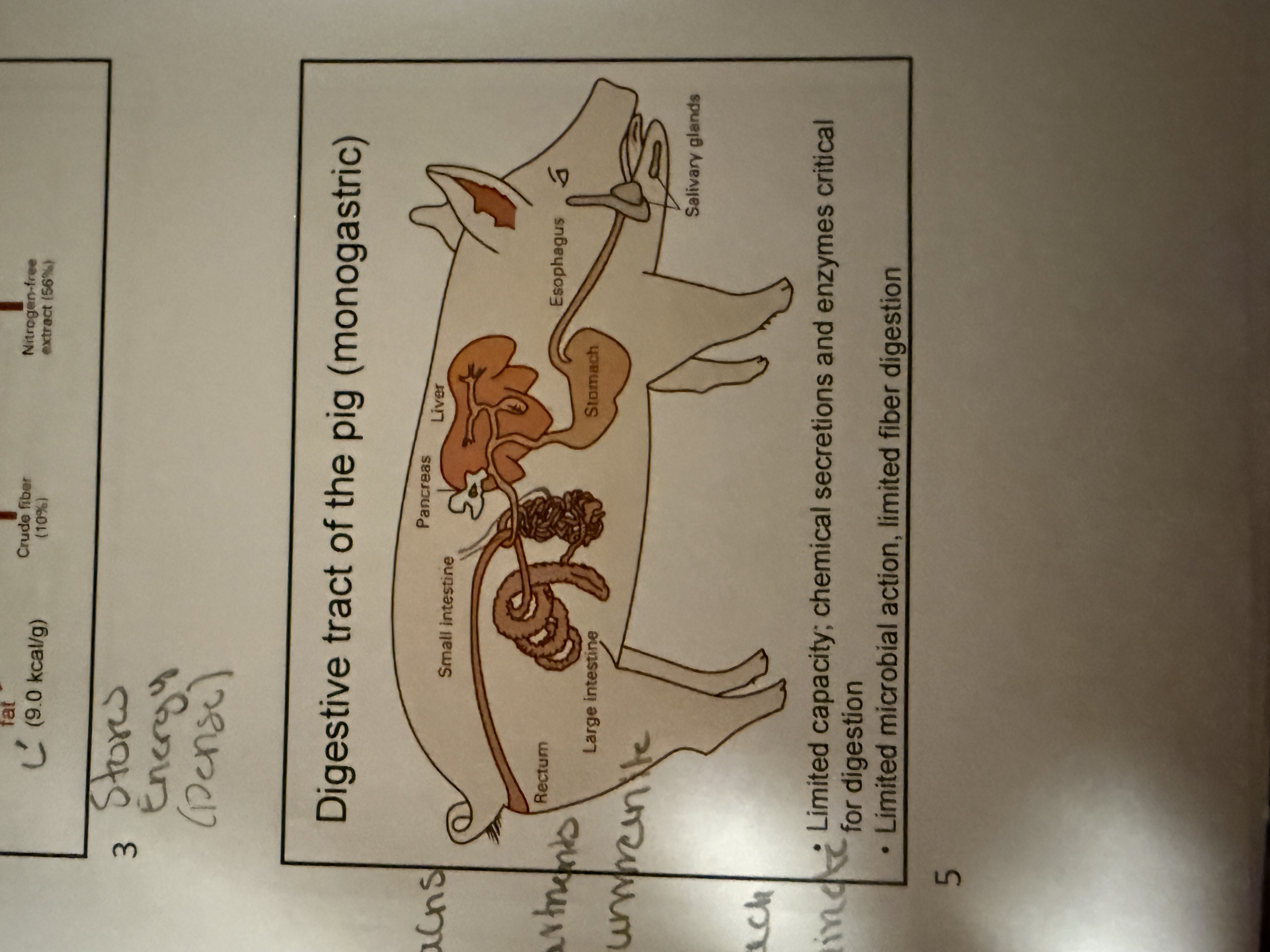
Digestive tracts of a pig
Limited capacity, chemical secretions and enzymes critical for digestion. Limited microbial action, limited fiber digestion
4 stomach
Ruminant animals
4 compartments
ruminant animals
Poultry digestive tract
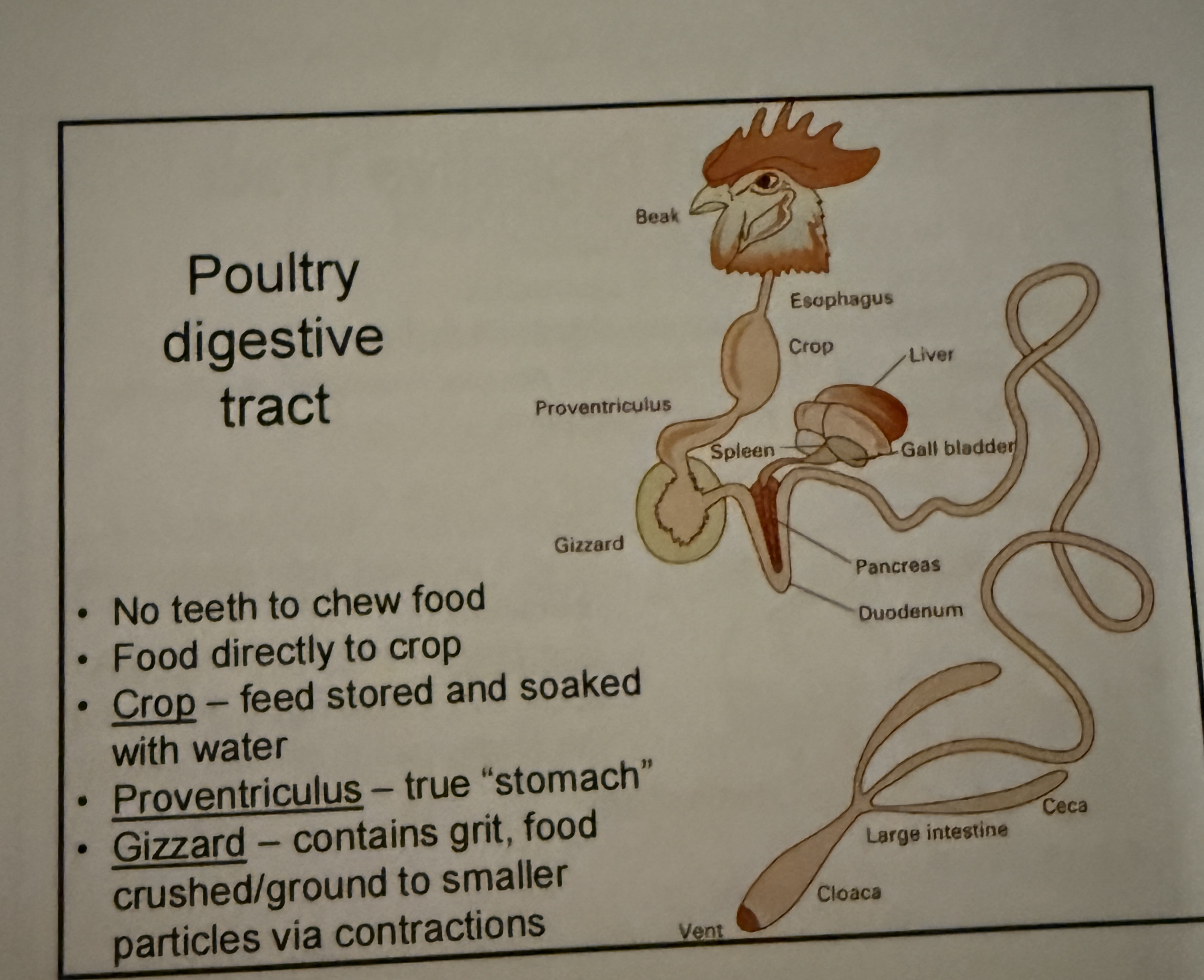
Monogastrics
Eat what? Corn, soybean meal, KEY (easily digested). What does pig feed look like? Ground up, already broken down
Dental
Cattle only have teeth on the bottom
Ruminate digestive tract
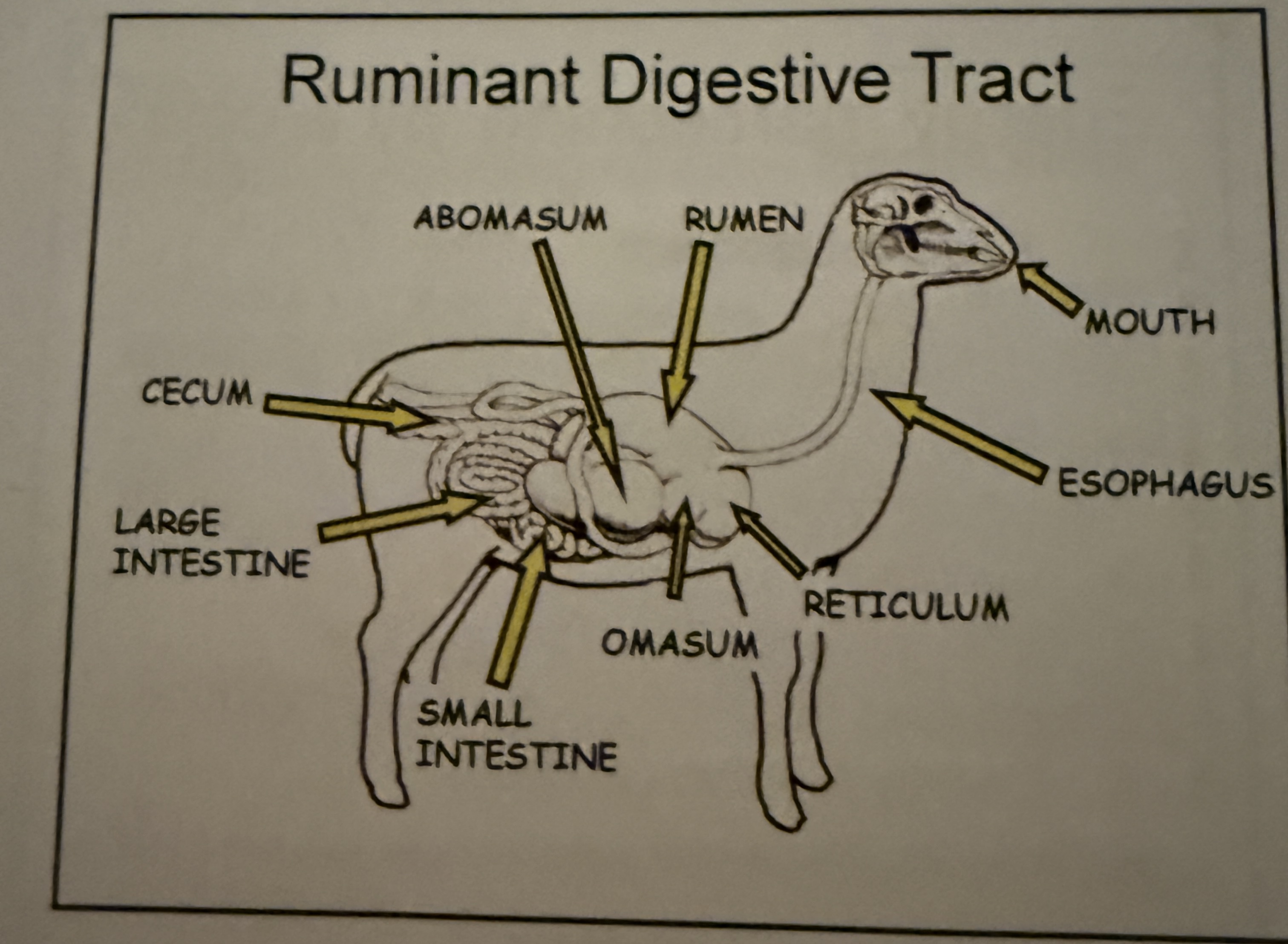

Reverse alphabetical order
Ruminant digestive tract
Fiber digestion focused, not 4 stomachs, fermentation of food by microbes
Volatile fatty acids produced
Acetate, propionate, and butyrate,
Rumination
Regurgitation of forage blouses from rumen and reticulum
Eructation
Belching of gases produced by bloat
1rst Rumen (and rumen papillae)
Very large and filled with wet feeds. Site of fermentation. Release of volatile fatty acids.
4th Abomasum (“true” stomach)
Final compartment that is acidic, and has enzymes to digest feedstuffs and breaks down protein into amino acids that can be absorbed in small intestine
2nd Reticulum ( honeycomb)
Small. Traps large feed particles leaving rumen and allows for regurgitation, re chewing, adding saliva, site where ingest metal pieces are trapped and can cause hardware disease
3rd Omasum (water regulation)
Acts like a filter and a valve, uses its lots of folds to squeeze water out of feed so it stays in the rumen
Ruminates
Are meant to eat grass, partners with microbes, microbes digest “tough stuff” (plant cells), animal digest microbes



