Conservation of biodiversity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 3 strands of biodiversity
Ecosystem diversity: Variety of ecosystems found in an area or on earth
Species diversity: Number of relative abundance of species found within an ecosystem
Genetic diversity: Variety of genes and alleles present in a species. Species with high genetic biodiversity are more likely to survive change to environment through process of natural selection
What are the two ways of classifying organisms into groups
Lumpers: Focusses on similarities between groups of organisms
Splitters: Focusses on differences between groups of organisms
What is anthropogenic species extinction and what are the causes
Loss of species due to human activities. Human activity causes:
Habitat destruction
Climate change
Pollution
Overexploitation (hunting etc)
invasive species introduction
Disease
Evidence for biodiversity crisis
IPBES (intergovernmental body which provides policy makers with assessments of data collected on biodiversity) concluded that human actions threatens more species with global extinction than ever before. Surveys are done repeatedly to determine if there is a change in biodiversity.
Define richness and evenness of biodiversity
Richness: Number of different species
Evenness: How close the population number are to each other
Biodiverse ecosystems should have wide variety of different species, all with relatively large populations
Simpson’s diversity index
D = Diversity index
N = Total number of organisms
n = Number of organisms in a particular species
High index value suggest stable site with many different niches
Low index value suggests few potential niches where only a few species dominate
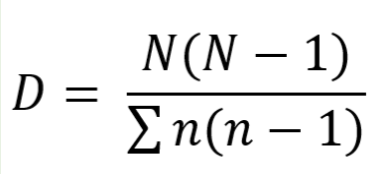
What is citizen scientist
Professional scientists studying biodiversity require as much data as possible
Collect and share data with professional scientists
Benefits of citizen science
Increase quantity of data collected
Cost effective, as citizen scientists are volunteers
Increase public engagement in conservation
Challenges of citizen science
Data quality: Data collected by volunteers may be of varying quality. Quality control measures need to be used
Bias of volunteers: Volunteers may have personal biases on where they collect data
Define Urbanisation
Movement of people to cities and towns.
Negatives of urbanisation
Deforestation: demand for more wood and agricultural land
Agriculture: Displace natural ecosystems, farm waste, fertiliser, pesticied enters natural eco
Define Ex situ conservation
Conservation of species outside of their natural habitat
Zoos
Botanic gardens
Storage of germ plasm in seen or tissue banks
Advantages of ex situ conservation (3)
Protection from predators
Greater control of conditions required for breeding, ensure that offspring survive after birth
Technologies eg ivf can increase number of offspring produced
Disadvantages of ex situ conservation
captive populations have limited genetic diversity
organism are living outside their natural habitats, may not have the required survival strategies when reintroduced to their natural habitats
Does not prevent the destruction of the natural habitat
Define in situ conservation
Protect species within their natural habitat
Restoration of ecosystems
Removal of invasive species
Reintroduce locally extinct species
Legal protection against pollution and development
Controlling access to the ecosystem
Controlling poaching
What is rewilding
Aims to restore degraded ecosystems back to their natural state.
Advantage of in situ conservation
Organism are not held in captivity, so they develop survival strategies
Other species in protected habitat are also protected
Biodiversity in ecosystem is preserved
Disadvantages of in situ conservation
Many endangered species need large areas for population survival
Difficult to prevent poaching of endangered animals
Genetic variety may already be damaged
What is edge program
evolutionarily distinct, and globally endangered program highlights and protects the most unique endangered species
Evolutionarily distinct: Species that are unique in the way that they look and behave. Species should have few or no close relatives
Globally endangered: IUCN red list endangered species.