AOS 3 final study material
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
This occurs when a mountain range forces air to rise.
orographic lifting
The most common mechanism of cloud formation is
lowering the air temperature to the dew point by adiabatic cooling of rising air.
You would most likely expect a rain shadow on the
east side of the Cascade Mountains in the Pacific Northwest.
This type of air will keep rising after an initial upward push.
statically unstable air
When the environmental lapse rate exceeds both the dry adiabatic lapse rate and the wet adiabatic lapse rate of a parcel of air, that air parcel contains
absolutely unstable air
The lower atmosphere is most likely to have the steepest environmental lapse rate at this time.
mid-day
This is the most important mechanism for stopping the rise of unstable air parcels.
encountering a layer of stable air
Clouds that are high and are always composed entirely of ice crystals are
cirrus
Cumuliform clouds
typically have higher water content than stratiform clouds.
Collision-coalescence is the predominant cause of precipitation in this region.
the Tropics.
The process by which supercooled water droplets freeze onto falling ice crystals is called
riming.
The collision-coalescence process
is dependent upon the different downward velocities of different-sized droplets.
Aggregation
is facilitated by a thin coating of water on ice crystals.
Which of the following cloud constituents would have the highest terminal velocity?
hailstones
The most important principle underlying the Bergeron process is this.
For a given temperature, the saturation vapor pressure of ice is less than that for supercooled water.
Lake-effect snowfall
requires that the lake be relatively warm.
In middle latitudes, rain
usually begins as snow.
Snow results from all of the following processes, except
coalscence
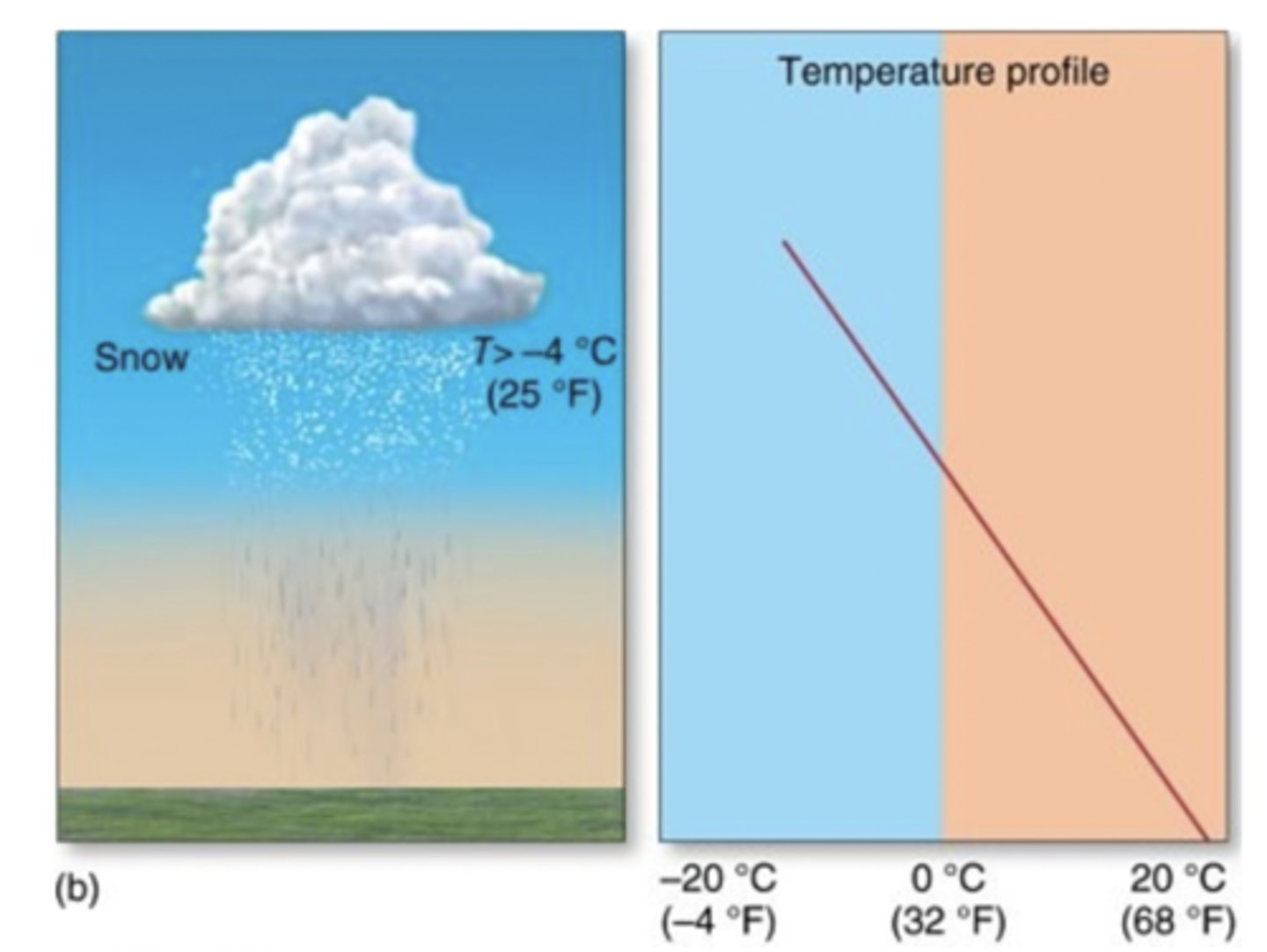
Precipitation falling through this temperature profile will arrive to the surface as
rain
Which of the following best describes the scale at which cyclones, anticyclones, troughs, and ridges, covering hundreds or thousands of square kilometers, occur?
Hint 1.
The types of scale are global, mesoscale, synoptic scale, and mircoscale.
Synoptic scale.
Features such as cyclones, anticyclones, troughs, and ridges exist at what is called the synoptic scale, meaning that they cover hundreds or thousands of square kilometers. Synoptic scale features persist from periods of days to as much as a couple of weeks.
Meridional flow is characterized by flow that is ________; while zonal flow is characterized by flow that is ________.
north/south; west/east
The four scales of atmospheric motion from largest to smallest are
planetary, synoptic, meso, and micro.
According to the Hadley cell model,
air rises at the equator and sinks at the poles.
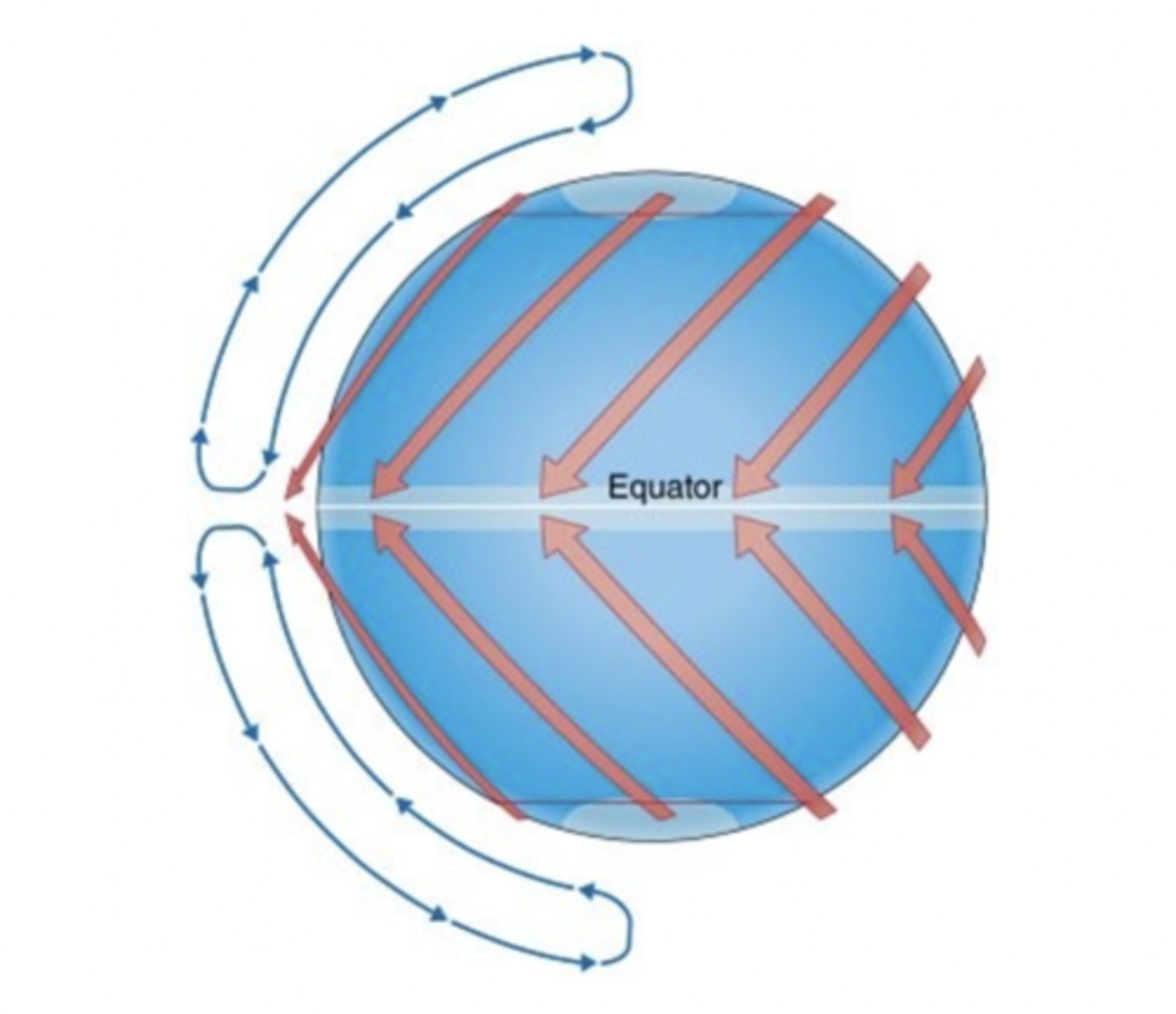
The Hadley Cell was originally envisaged to cover most, if not all of each hemisphere, North and South. What area does it actually cover?
just areas near the equator
Areas close to the ITCZ
receive abundant precipitation.
Examine Figure 8-15 in the textbook, which is a sequence of Rossby Waves.
What are the southward bulges in the patterns called?
Hint 1. What are Rossby Waves?
Rossby Waves have a tremendous impact on day-to-day weather. They are very long waves that cover the entire world.
Troughs.
The dips in the wavelike patterns are troughs (low pressure), while northward bulges are ridges (high pressure).
The polar front
is a region marked by a sharp change in horizontal temperature.
Winds in the upper atmosphere are
westerly in both the northern and southern hemisphere.
Westerly winds in the upper atmosphere at mid-latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere
are the reason most mid-latitude storms move from west to east.
The Ferrel Cell is associated with the
mid latitudes
In which direction do jet streams generally travel?
west to east
What are jet streams ?
Bands of high-speed wind found at elevations of 9-15 km
What are Rossby waves?
major undulations in the path of a jet stream
How can the jet stream return to normal zonal flow after Rossby waves build?
through separation of a mass of cold air from the jet stream
The Hadley model of atmospheric circulation assumes
a planet covered entirely by water.
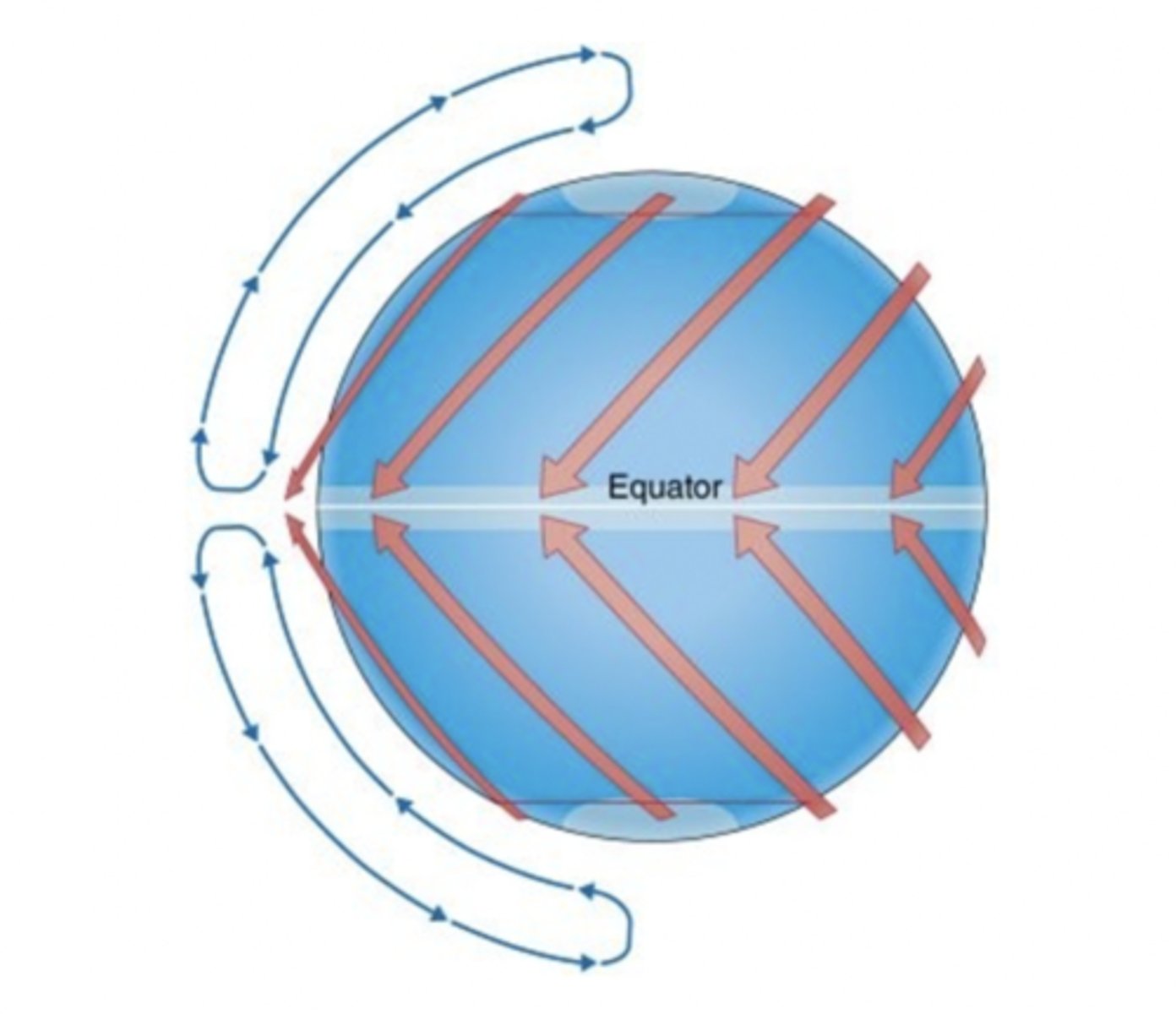
The Hadley cell
originates with strong solar heating at the equator.
The northeast trade winds
are the result of air flowing from the subtropical high to the ITCZ.
Usually, the pressure gradient force would be strongest at the
700 mb level.
Considering Coriolis, what is the direction of wind predicted for the upper branch of the Ferrel cell? Does this prediction make sense to you ? Why?
east
The polar front is
cold air from the pole meets warmer air from the subtropical high at the polar front.
The Polar Jet stream
this creates much stronger PGFs at the polar front, which also increase significantly with height
In which direction does the air in the polar jet stream flow in the Northern Hemisphere?
From west to east.
Fronts
are boundaries between different air masses
To observers at the ground, the weather for a cold-type looks like a ___ front when it approaches, and a ___front after it passes.
warm; cold
[Discussion] At the same temperature and pressure, dry air is heavier than moist air. Is this statement true or false ?
True.
= moist air is lifter -potential for severe storms
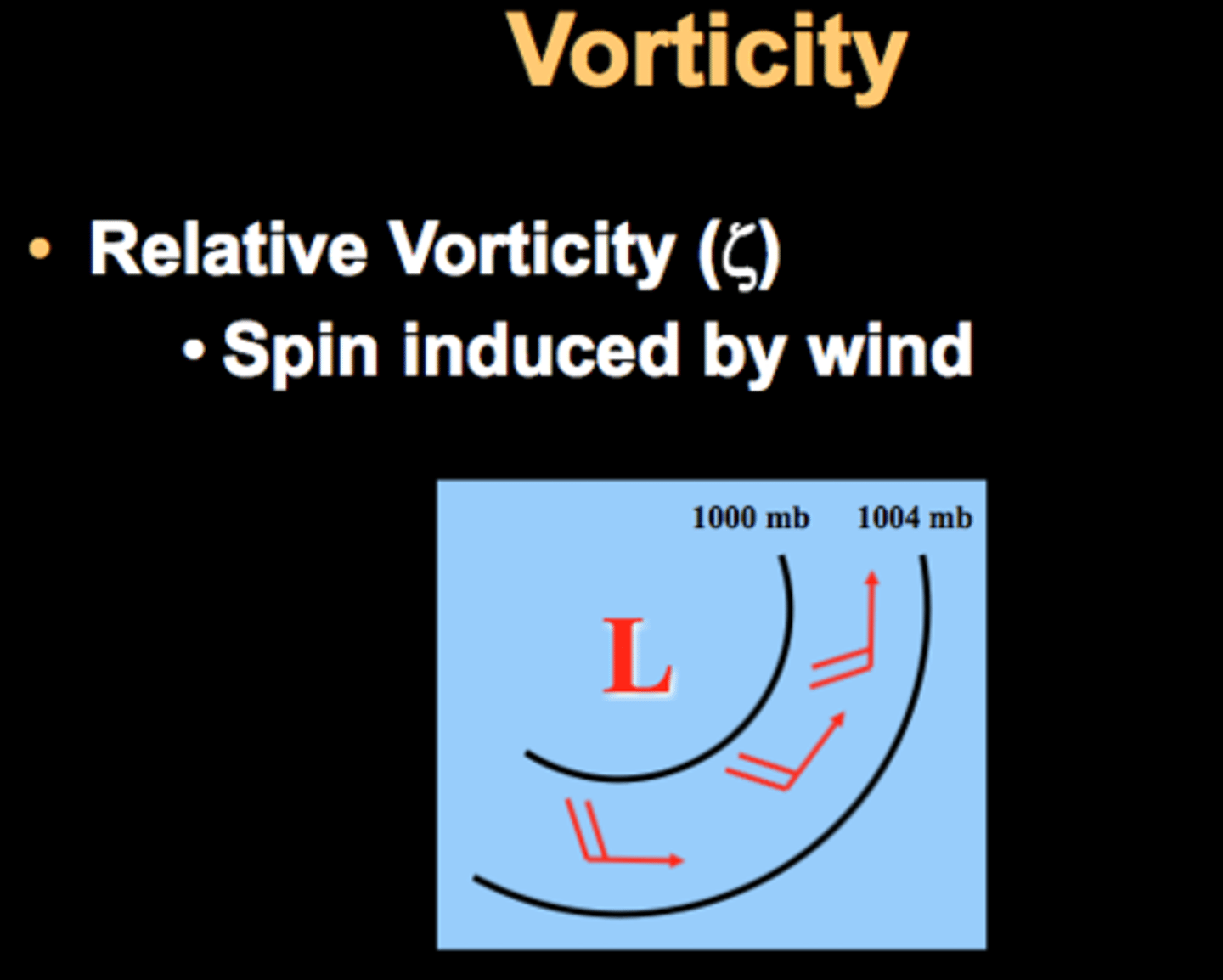
vorticity
is the spinning motion of air parcels, and it is useful to describe the amount of rotation in the wind
- the important question here is where air parcels are rotating around their own center or not.
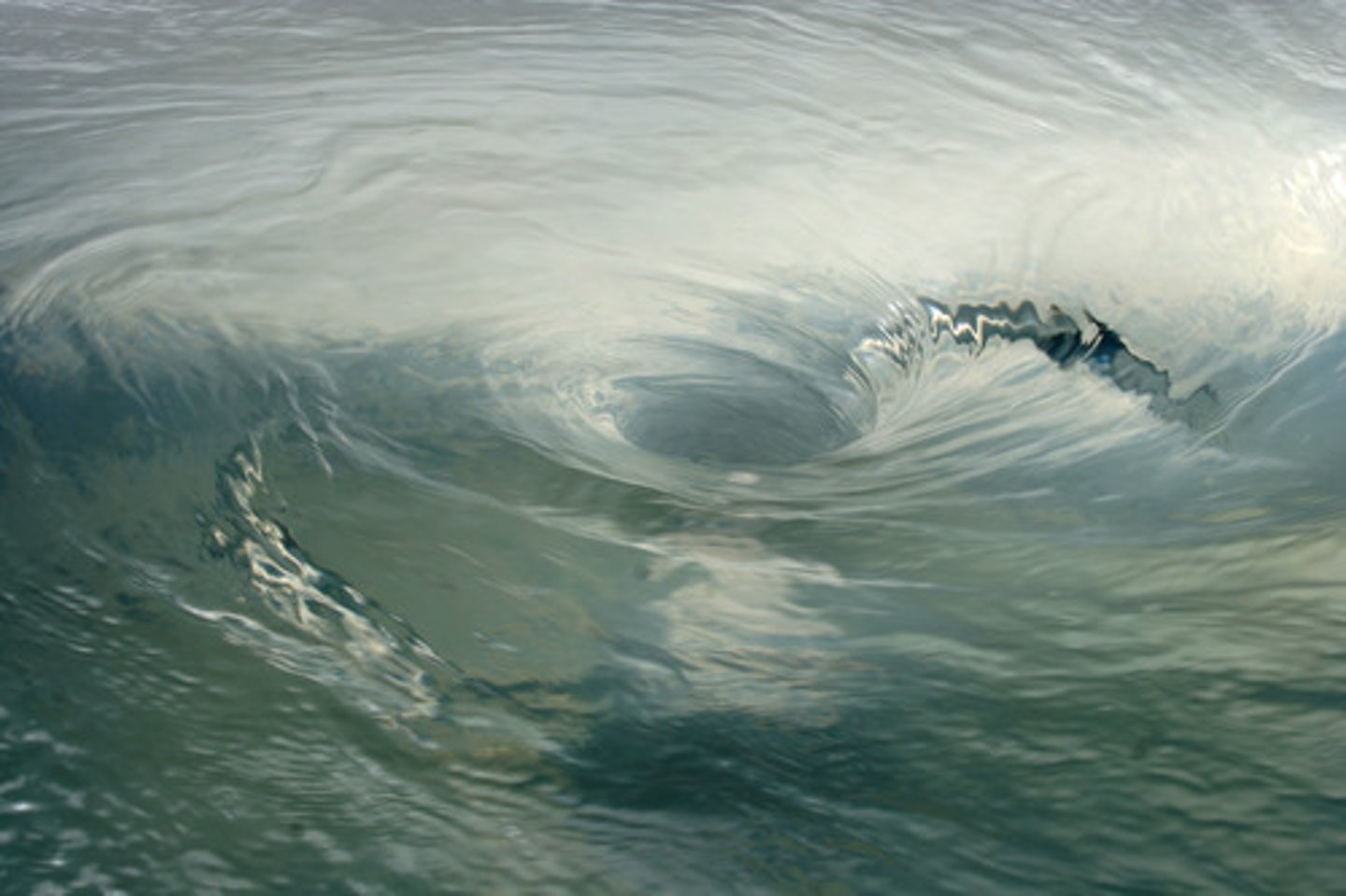

[Quiz] Regarding the vorticity of the "smiley face" in the two cases below, we can state that:
Vorticity is non-zero only in the second case
planetary vorticity
any object (including air parcels) that are just sitting on top of the planet have vertical vorticity, since they are rotating together with the planet
- the only exception is for objects (and air parcels) at the equator
- the vorticity, due to the rotation of the planet, is called planetary vorticity.
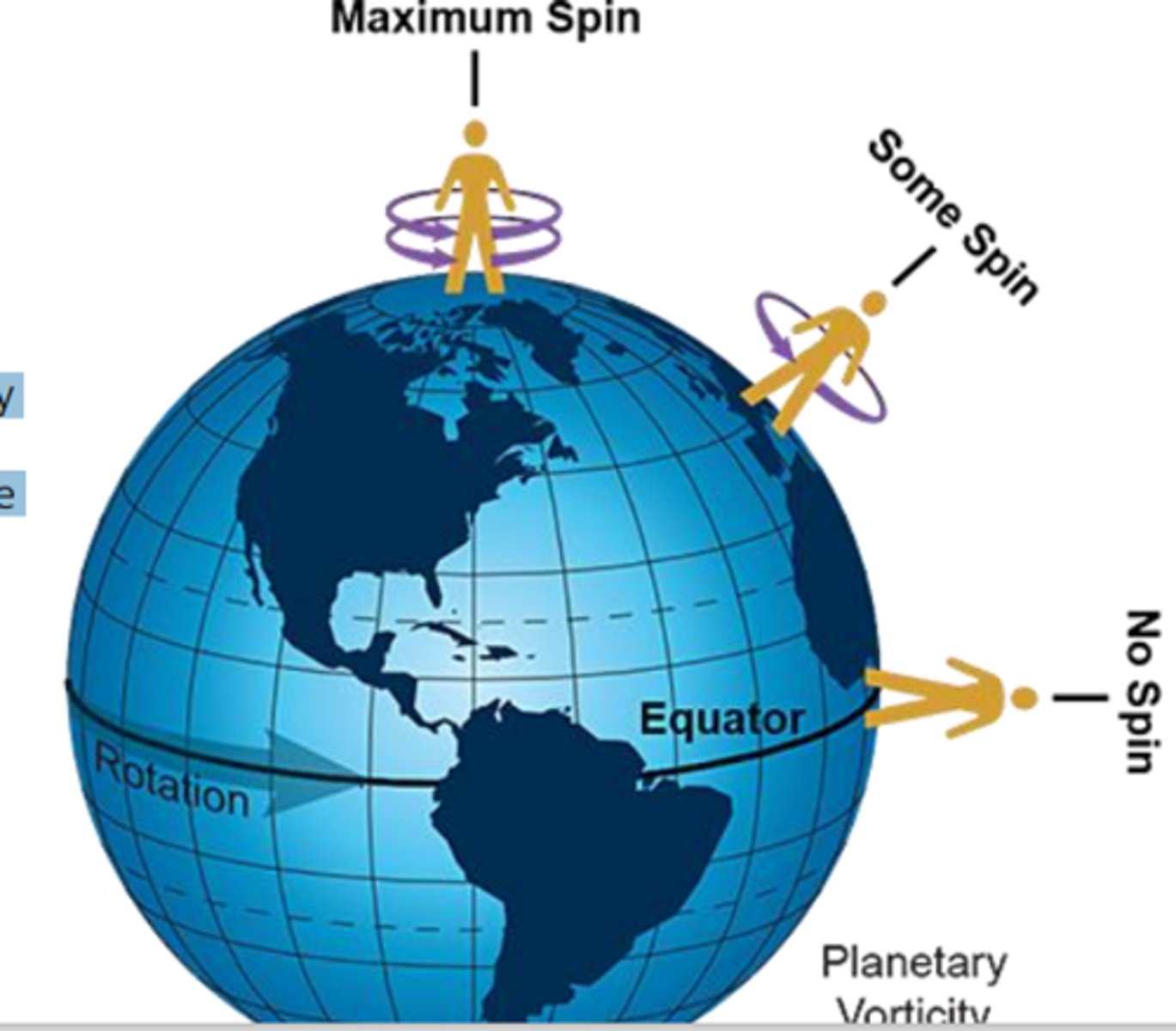
relative vorticity
this is the vorticity associated with the wind motions
- if the wind is such that is causes air parcels to rotate, this rotation is called relative vorticity
- relative vorticity is positive when the direction of rotation is the same as the planet's
Which of the following best defines an air mass?
Hint 1.
Air masses are important because they help bring various types of weather patterns all over the world.
Correct!
A large body of air with similar temperature and moisture characteristics.
- An air mass is a large body of air having more-or-less uniform temperature and moisture characteristics.
1. - air masses originate over water.
2. - and polar (p) air masses are cold.
3. - and - air masses are warm and humid.
4. - and - air masses are warm and dry.
5. - and - air masses originate at high latitudes.
6. Continental (c) is a term referring to dry air masses.
1. Maritime
2. Arctic & Polar
3. Maritime and Tropical
4. Contintental and Tropical
5. Arctic and Polar
6. continental
As the name implies, maritime air masses originate over water. Polar and Arctic air masses originate at high latitudes and are cold. Maritime and Tropical air masses are warm and humid. Continental tropical air masses are warm and dry while continental polar air masses are cold and dry.
Hint 1. Moving air and changing seasons
As air masses move over Earth, they change. Keeping in mind that land changes temperatures much more dramatically than does water, think about how the temperature of air masses might be different depending on the season and whether they originate over land or water. For example, wintertime cP is colder than mP air masses yet summertime cP is warmer than mP.
The source region and time of year impact the overall temperature of an air mass. In summary, polar air masses are cooler than tropical air masses, and continental air masses compared to maritime air masses at similar latitudes are more extreme (e.g. warmer in summer, colder in winter). Therefore, the order from coldest to warmest of the following air masses is: a wintertime cP air mass, a wintertime mP air mass, a wintertime mT air mass, a summertime cT air mass.
When a cold air front moves rapidly toward a warm air front, there isn’t time to predict the light and longer-lasting rains that result from the warm air dissipating.
false.
When warm air collides with a cold air front, its slow journey up the slope of the cold air front causes longer rains. Because it moves slowly, its rain is long foretold and long to last.
true.
Rainstorms are generally shorter when a cold air front comes in quickly and collides with a warm air front.
true
Heavier, intense, long-lasting rainstorms occur when a warm air front encounters a receding cold air front.
false
It’s hard to apply this proverb to most storm conditions, because storms typically result when fronts are moving at the same speed and in the same direction.
false.
Air-mass source regions are least likely to be found here.
middle latitudes
Which of the following air mass types generally has the highest dew point?
Hint 1.
Air masses are important because they help bring various types of weather patterns to all parts of the world.
Maritime Tropical (mT) air masses develop over warm tropical waters. They are warm, moist (high dew points), and unstable near the surface, which is ideal for the development of clouds and precipitation.
Most of the air masses in the central part of the United States are either
continental polar ot maritime tropical.
Which of the following best defines a front?
Hint 1.
Fronts are important because, in conjunction with air masses, they help bring various types of weather patterns to all parts of the world.
A narrow boundary separating different air masses
- All fronts are boundaries that separate air masses with differing temperature and other characteristics.
If you observe short, intense, scattered rainfall as a front passes, which of the following are you most likely to be experiencing?
Hint 1.
Fronts are important because, in conjunction with air masses, they help bring various types of weather patterns to all parts of the world.
a cold front.
- The air ahead of a cold front tends to be unstable and therefore easily lifted. This promotes development of cumuliform clouds along these boundaries. With their large vertical extent, cumuliform clouds can often produce intense precipitation. However, because of the limited horizontal extent and rapid movement of the frontal wedge, such precipitation is often of short duration.
Between a cold front and a warm front, we find
a warm, moist, and unstable air mass.
This type of front has a mass of warm air cut off from the surface.
occluded front
The sources of air masses occur only in low and high latitudes because
middle-latitude weather is too variable.
Northeasters
often bring heavy snowfall
Which air mass is responsible for bringing virtually all of the moisture that impacts the United States east of the Rocky Mountains?
Maritime Tropical
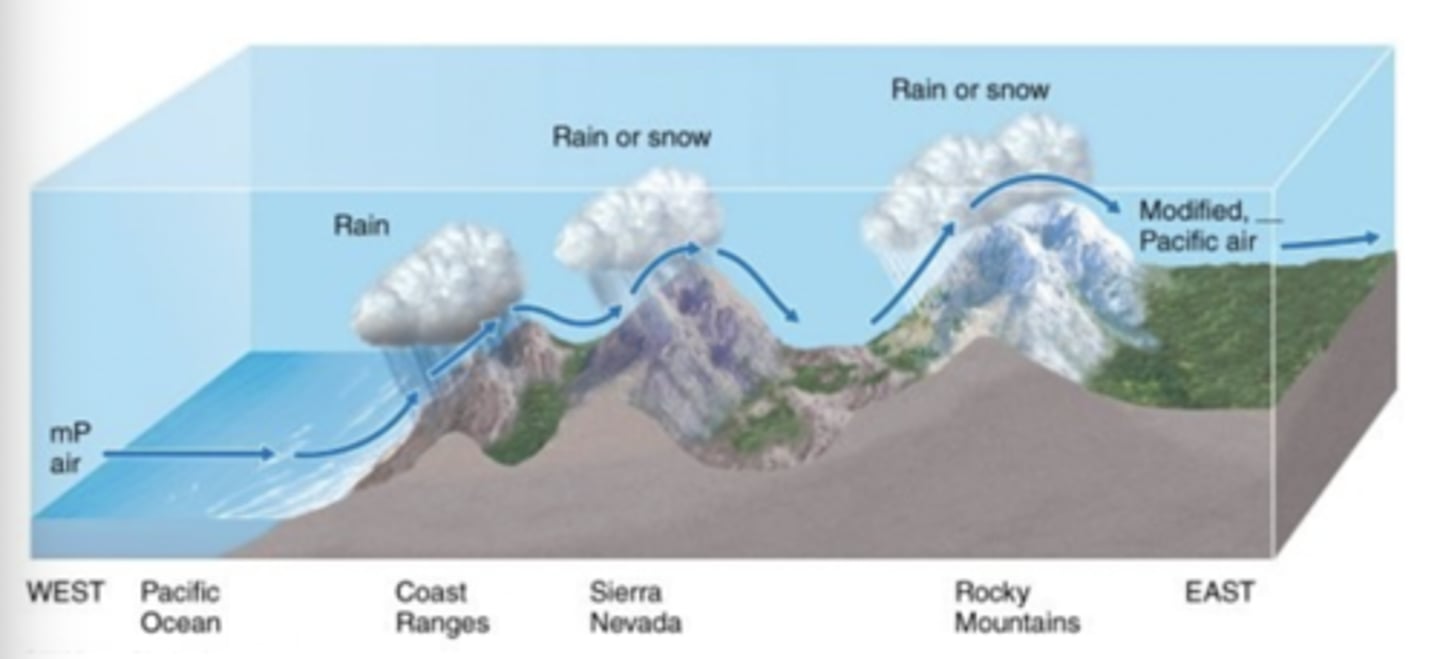
After passing over a series of mountain ranges, maritime polar air becomes
drier
Which of the following best describes midlatitude cyclones that move along the U.S. East Coast and bring moist maritime air towards New England, often producing cold winds and heavy snowfall in winter?
Hint 1.
Think about the various types of midlatitude cyclones that can bring strong storms. A midlatitude cyclone forms when a cold front approaches a warm front.
Northeasters
- When midlatitude cyclones move along the East Coast of the United States, surface winds sweep around the low-pressure system and approach the New England coast from the northeast. The resultant winds are the famous northeasters (or nor'easters) that can bring cold winds and heavy snowfall.
Which of the following fronts do not separate tropical from polar air masses?
occluded
________ fronts usually have showery precipitation while ________ fronts usually have continuous precipitation.
Correct!
cold; warm
This is the first type of cloud an observer will see when a warm front is approaching
cirrus.
Which of the following frontal systems often move with greatest forward velocity?
cold front
Drylines in the United States
typically have continental air to the west.
According to the polar front theory,
midlatitude cyclones form along a boundary separating polar air and warmer air to the south.
Within a Rossby wave, which of the following locations generally has the largest absolute vorticity?
Hint 1.
A Rossby wave is a huge river-like undulation that has a profound effect on the weather.
At the trough axis
- The areas of greatest vorticity occur along the trough axis. Downwind of this zone, vorticity decreases very rapidly. Thus, as air flows away from the vorticity maxima, upper-level divergence occurs, which in turn promotes low pressure at the surface. The region of lowest absolute vorticity occurs near the ridge axis.
Which of the following are associated with the formation and intensification of surface mid-latitude cyclones?
upper-level divergence and lower-level convergence
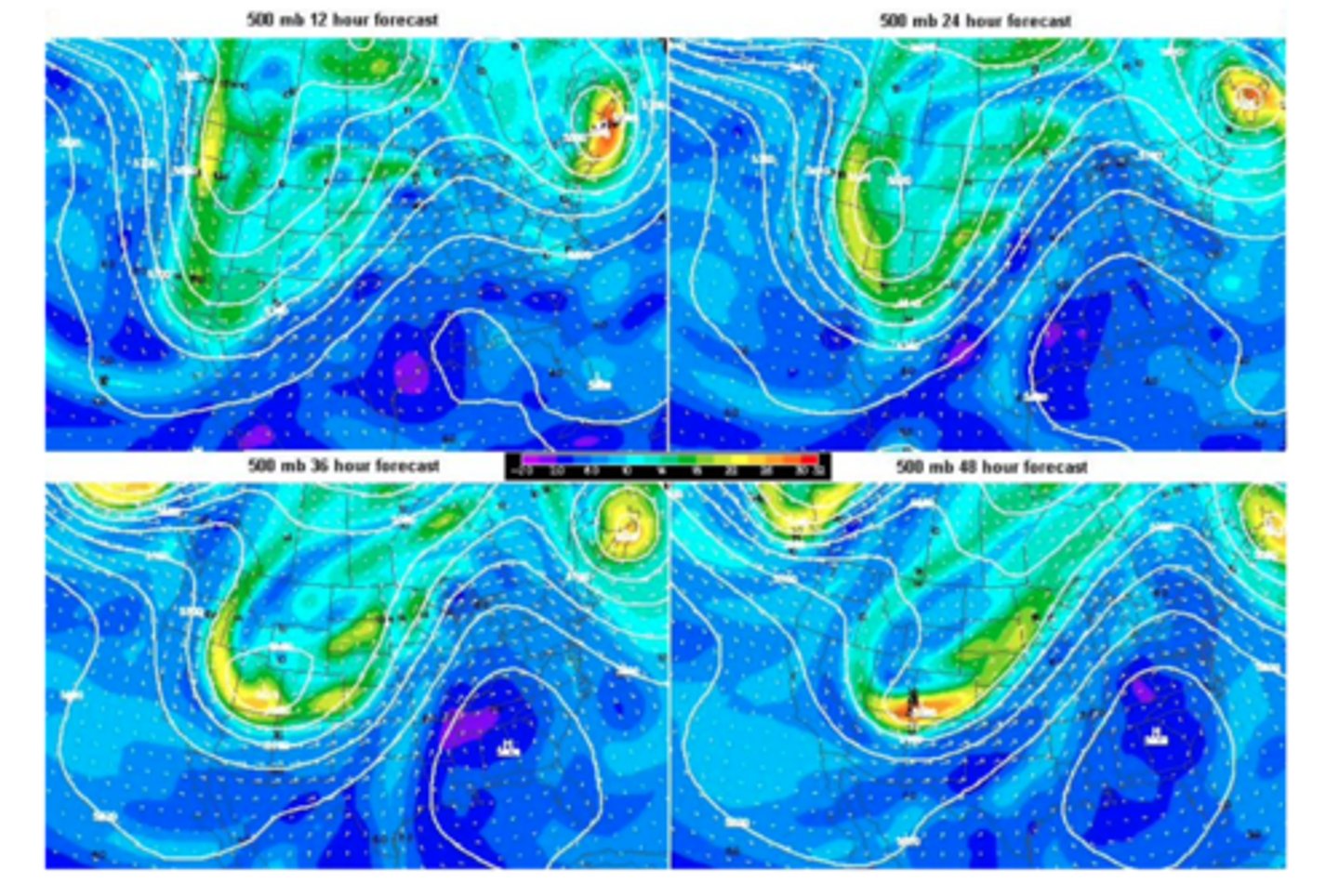
By the end of the forecast period, where should the maximum divergence at 500 mb take place?
Hint 1. What is absolute vorticity?
Absolute voracity is the overall rotation of air, which is made up of relative vorticity and Earth, or planetary, vorticity. Think about where these maxima of absolute vorticity are located, with this in mind
Downstream of the trough axis, from Minnesota to Colorado.
- Downwind of the trough axis, vorticity decreases very rapidly. Thus, as air flows away from the vorticity maxima, upper-level divergence occurs, which in turn promotes low pressure at the surface.
At which of the following levels does the wind direction most closely approximate the path that a midlatitude cyclone tends to take?
Hint 1.
Upper-level divergence must occur in order for a midlatitude cyclone to form.
the 500 mb level.
- Although the optimal place for midlatitude cyclones to develop is just beneath the zone of decreasing vorticity aloft, they do not usually remain in a fixed position relative to the upper-level trough. Instead, they are usually pushed along so that they migrate in the same direction (and at about half the speed) as the winds at the 500 mb level.
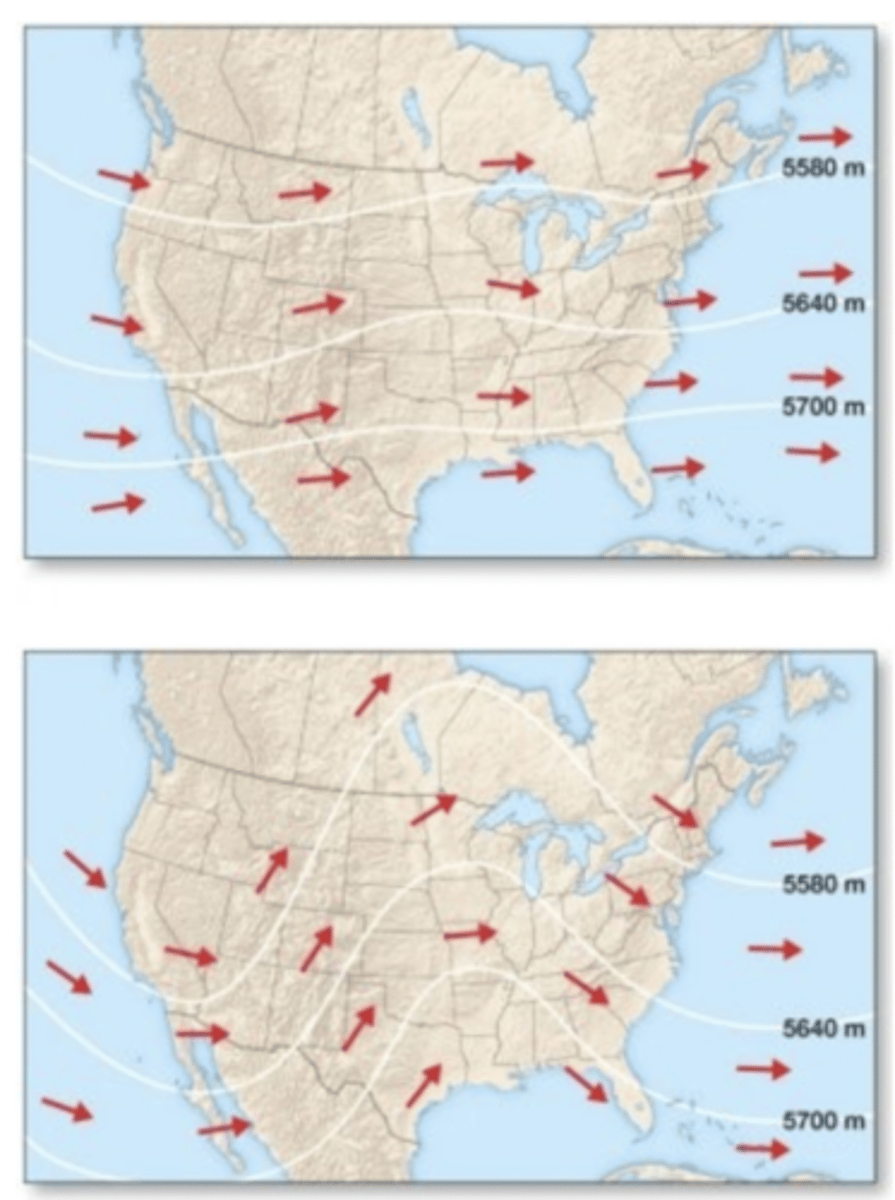
Which of the following is true of the upper-level flow patterns shown in the figure?
The bottom pattern is associated with a middle-latitude cyclone due to its areas of convergence, divergence and temperature advection.
In the conveyor belt model, this belt enters the storm flowing westward toward the surface cyclone.
cold conveyor belt
According to the polar front theory, cyclogenesis begins when
cold air begins to advance southward and warm air begins to advance northward.
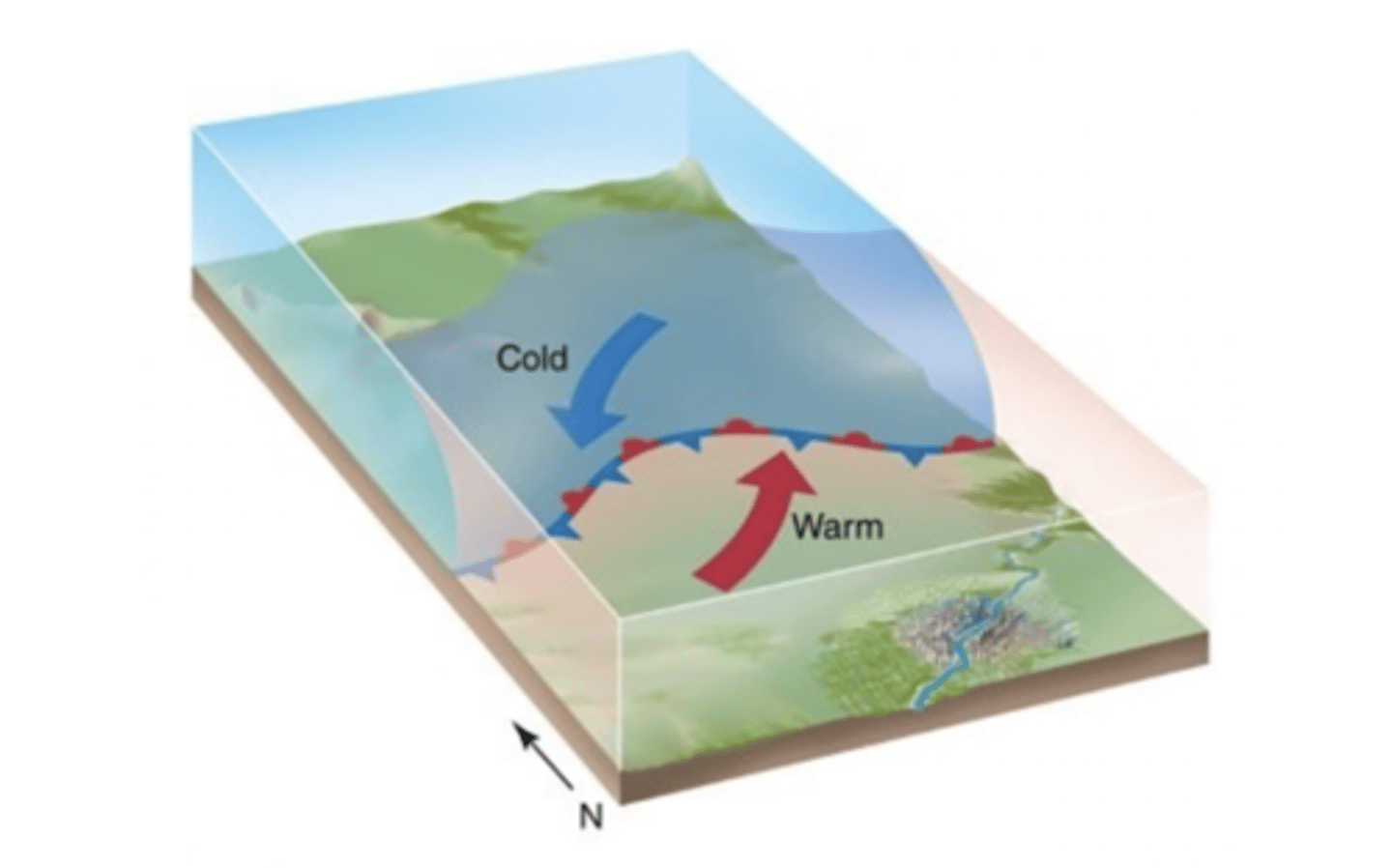
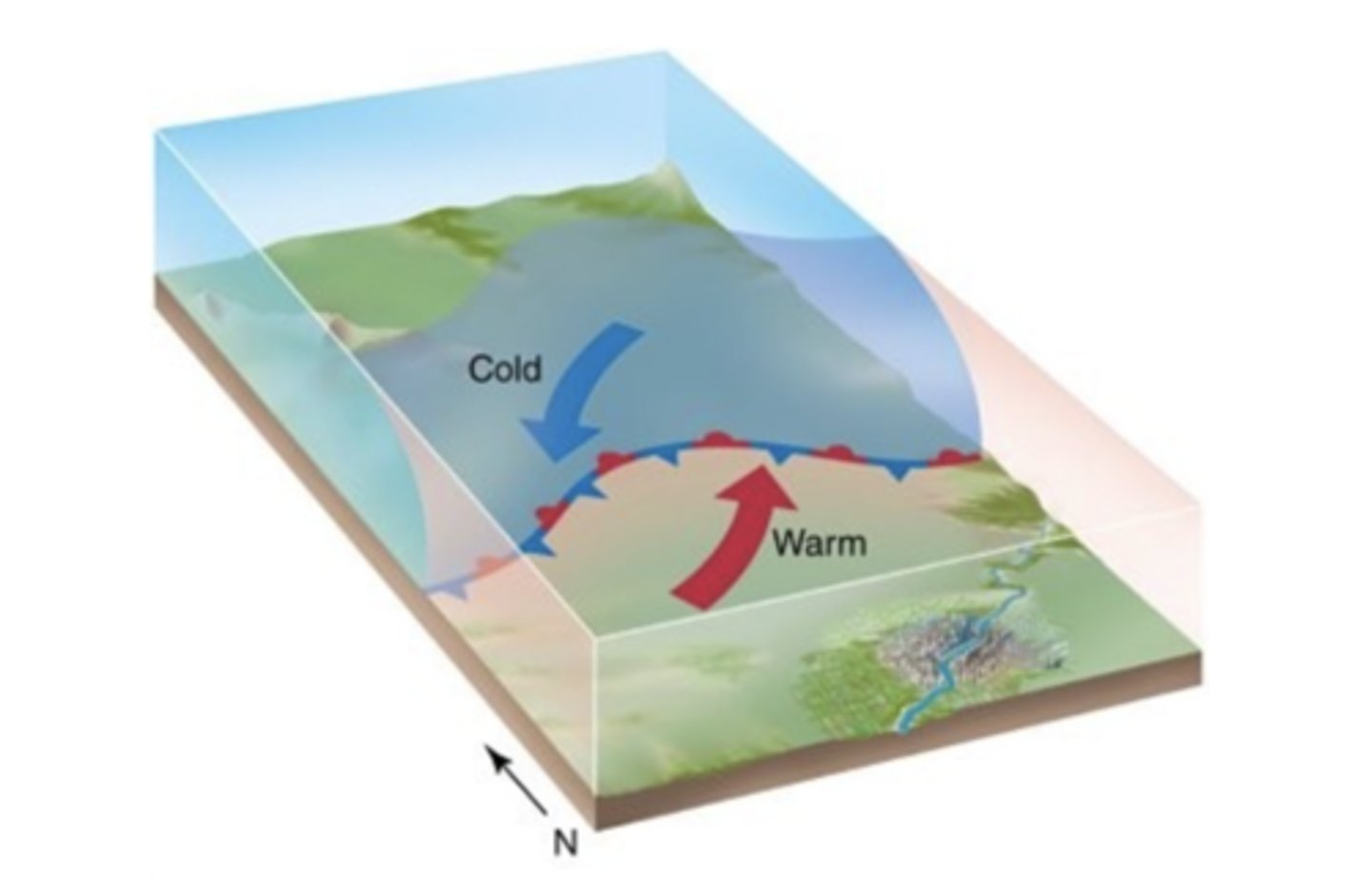
In which of the following areas is cyclogenesis most likely to occur?
Hint 1.
Take apart the word into two separate pieces.
in regions of strong temperature contrasts
- Cyclogenesis commonly occurs near zones of thermal contrasts (such as along coastal regions or at the boundaries between warm and cold ocean currents) or where topographic features (such as major mountain chains) disrupt the normal airflow.
Mid-latitude cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere typically travel primarily in this direction.
east
The warm sector between the warm and cold fronts is generally characterized by
clear conditions.
A mid-latitude cyclone reaches its most intense stage when
the storm system undergoes occlusion.
This midlatitude cyclone
is beginning the process of cyclogenesis.
Earth vorticity
is a function of latitude
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
Upper level divergence causes high pressure at the surface
Zonal patterns
show little north-south displacement between contour lines on a 500 mb map.
________ motions within anticyclones generally bring ________ skies.
sinking; clear
The stepped-leader
creates the pathway for the flow of electrons.

Thunder
results from the explosive expansion of air.
Which of these can be characteristics of severe thunderstorms?
all of these
- wind speeds in excess of 58 pmh
-hailstones one inch or larger in diameter
-tornadoes
The formation of a mesocyclone requires
vertical wind shear.
Waterspouts tend to form in areas with ________ water and ________ atmospheric conditions.
warm; unstable
A typical cloud-to-ground lightning event consists of
several distinct steps that look to the human eye like a single lightning strike.
Which portion of the lightning process is the most visible?
return stroke.
Supercell storms
account for a majority of tornadoes
An outflow boundary is
all of the above
- the leading edge of cold air from a thunderstorm downdraft.
- can be clearly seen on radar images.
- a favorable place for future severe storm development, especially if two intersect.