IAPS - unit one
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
social science
The study of human society, thought, culture and behaviour
2
New cards
What do social scientists do?
field work, research published in journals, lots of time on computers, differing work environments
3
New cards
anthropology
The study of the lives and cultures of human beings
4
New cards
psychology
the scientific study of behaviour and the mind
5
New cards
sociology
the systematic study of human relationships within social organizations
6
New cards
what is the basis for social sciences
scientific observation
7
New cards
current issues in anthro
gangs, religion, biology/genetics/evolution, primate behaviour, cults, human cultures (ex: teenage culture), ethic groups in Canada, social organization
8
New cards
current issues in psychology
suicide and depression, mental illness, the self/self-image, eating disorders, violence, child development, learning, reasoning, dreams/fantasies, thoughts/feelings/emotions, stress
9
New cards
current issues in sociology
poverty, racism, abuse, criminology/deviance, role of new tech, marriage/family, multiculturalism, prisons, unemployment
10
New cards
origins of the social sciences
created as a response to the age of enlightenment, wanted to shine a light on the world
11
New cards
social science venn diagram
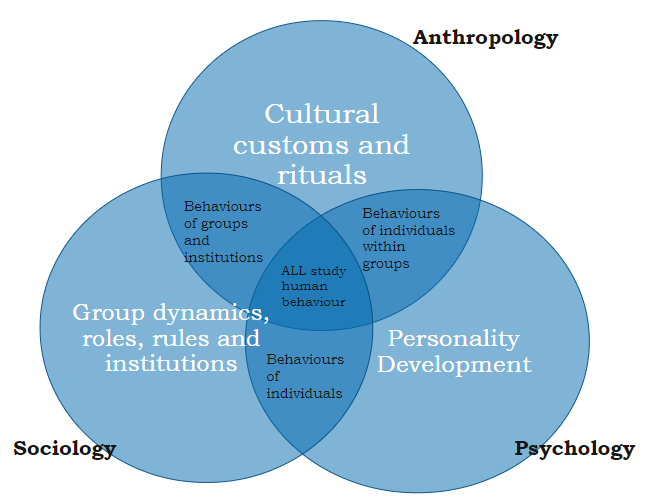
12
New cards
what is anthro
the broad study of humankind around the world and throughout time
13
New cards
what are the two aspects of humans that anthro is concerned with?
biological and cultural
14
New cards
main subdivisions of anthro
physical, cultural, archaeology and linguistic
15
New cards
physical anthro
bio evolution, genetic inheritance, human adaptability/variation, primatology, fossil records, and forensic anthro
16
New cards
cultural anthro
culture, ethnocentrism, cultural aspects of lang and comm, subsistence and other economic patters, kinship, sex, marriage, socialization, social control, political organization, class, ethnicity, gender, religion, and culture change
17
New cards
linguistic anthro
human comm process focusing on the importance of socio-cultural infulences, nonverbal comm; and the structure, function and history of languages/dialects
18
New cards
what is the best way to get to know another society and its culture?
Participant observation - live in it as an active participant
19
New cards
how to get accepted as a member of a society you don’t belong to
By physically and emotionally participating in the social interaction of the host society
20
New cards
four classifications of culture
physical environment, level of technology, social organization, system of symbols
21
New cards
physical environment explanation
physical geography, weather, etc ➡️length of winter may effects popular sports or fashion
22
New cards
level of technology
the degree of tech determines how receptive a culture will be to change/how well they will adapt
23
New cards
social organization
how is culture organzied? kinship system? how is labour divided?
24
New cards
system of symbols
physical objects, gestures, dance trends, hairstyles, etc
25
New cards
what is sociology?
study of social life, social change, social causes and consequences of human behaviour
26
New cards
What does sociology look at?
development and structure of human societ (institutions) and how it works, the structure of groups, orgs, and societies, and how people interact in these contexts
27
New cards
status
term used to decribe our position within an institution
28
New cards
values
each role/status has values that the practitioner of that role is expected to accept and internalize
29
New cards
norms
rules set of for a particular role that are considered standard behaviour (priests being celibate)
30
New cards
rules
developed by a culture based on their system of values (can be formal laws or things that are just accepted ex: snitches get stiches)
31
New cards
structural functionalism
each society should provide its members with the fundamental requirements for functioning; systems fufill material needs, socializing/educating the young, regulating human reproduction, etc
32
New cards
what do structural-functionalists believe their role is?
to try to explain the role of sciety’s systems in enabling human society to function
33
New cards
what do structural functionsits concern themselves with instead of change?
how society works to meet their needs
34
New cards
what do sybolic interactionalists believe about instinct?
humans have complex brains and little instinctive behaviour
35
New cards
what does symbolic interactionism say about meanining?
we give meaning to things based on our social interactions and this meaning is not permanent; we base interactions on our interpetation of symbols which can change
36
New cards
what did karl marx see as the driving force of history
material concerns (relationship between the classes)
37
New cards
what did marx think social change came from?
competiton/conflicts between social classes battling for power and economic resources
38
New cards
conflict/marxist theory
conflict propels change to the economic system and/or to society as a whole
39
New cards
what do conflict theorists study?
competition for power between different groups (constant struggle between those who have power and those who do not)
40
New cards
those who have ____ seek to keep it away from those who do not
power
41
New cards
what do conflict theorists believe about social institutions
created to perpetuate the division between that powerful and the powerless
42
New cards
what did feminist theorists conclude?
women were marginalized, deprived of power and without equal membership in society
43
New cards
what do feminsit theorists focus on?
gender inequality, the role of women, discrimination agaisnt women, sex and gender issues
44
New cards
what is the goal of feminist theory?
raise issues of inequalities and bring about change
45
New cards
bystander effect
Diminished sense of personal responsibility to act when in a big group
46
New cards
what is psychology?
study of how and why humand act as they do
47
New cards
what do psychologists focus on?
the idividuals, personal and unique experiences that influence how the individual acts and thinks
48
New cards
what do psychologists do?
work to describe explain predict anf control behaviour and mental processes.
Work to help people overcome fear, cope with illness, understans senses and makes their lives happier and safer
Work to help people overcome fear, cope with illness, understans senses and makes their lives happier and safer
49
New cards
types of psychology
biological, psychoanalytical, behavioral, cognitive, humanistic, evolutionary, sociocultural
50
New cards
biological psych
the roles of bio process and heredity in explaining behaviour
51
New cards
behavioural psych
the role of environment in shaping and controlling behaviour
52
New cards
humanistic psch
the importance of the indiv’s subjective experience as a key to understanding behaviour
53
New cards
evolutionary psych
the role of interited tendencies that have proven adaptive in humans
54
New cards
sociocultural psych
the effect of society on culture and behaviour
55
New cards
cognitive psych
the importance of mental processes that underlie behaviour
56
New cards
psychoanalytic psych
role of unconcious motivation and early childhood experiences in determining behaviour and thought
57
New cards
what are the two parts of our mind
the concious and unconsious
58
New cards
psychoanalytic theory
our unconsicous mind has more influence than our consicous mind on our personalities and behaviour
59
New cards
three parts of the unconscious mind
id, superego, ego
60
New cards
what does the id do?
encourages us to seek physical satisfaction, can be self-destructive
61
New cards
what does the superego do?
encourges us to do the moral thing, no the one that feels best
62
New cards
what does the ego do?
acts as a referee between the other two, and deals with external reality
63
New cards
freuds psychosexual theory of development
belief that personality was developed based on how we deal with toilet and sexual functions (if we deal with them with acceptance and openness we are happy, confident, etc; if we deal with them with shame and guilt we are nervous, insecure, etc)
64
New cards
five stanges of psychosexual theory of development
oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital
65
New cards
oral stage (birth - 18 months) - id’s pleasure focus
on oral gratification (sucking on bottle, placing things in mouth)
66
New cards
oral stage - signs the id won
overeating, smoking, nail-biting
67
New cards
anal stage (18 months - 3 yrs) - id’s pleasure focus
on bowel pleasure, resisting toilet training (coming to terms with society’s control relating to toilet training
68
New cards
anal stage - signs the id won
meanness, resentment of authority, obsessive neatness
69
New cards
phallic stage (3-6 yrs) - id’s pleasure focus
awarness of sex organs, love/hate relationship with same sex parent (oedipus complex)
70
New cards
phallic stage - signs the id won
selfishness, manipulativeness, poor opposite sex relationships
71
New cards
latency phase (6 yrs - puberty) - id’s pleasure focus
on same-sex friends, few friends of opposite sex (sexual concerns are unimportant)
72
New cards
latancy phase - signs the id won
lack of close friends
73
New cards
genital phase (adolenscence to adulthood) - id’s pleasure focus
dating and marriage, sexual energy (mature sexual relationships)
74
New cards
genital phase - signs the id won
guilt about sexuality, feelings of inadequacy, poor sexual relationships
75
New cards
what do learning theorists say about instinct?
humans are born with very little instinct, but much learning potential
76
New cards
what do learning theorists belive about human behaviour?
it is learned, especially in children and youth
77
New cards
how can society influence individual’s personalities?
contolling the way they learn beahviours (ex: brought up in a loving family = become secure/loving adults, if parents provided clear expectations for good behaviour and swift but fair consequences for bad behaviour
78
New cards
what do behaviourists belive?
psuchologists can predict, and control/modify human behaviours by identifying the factors that motivate it
79
New cards
what do behavioursists believe about the rules/practices parents used to raise their children?
they have a huge infulence of an individual’s character (even into adulthood)
80
New cards
what did alfred adler beleive
if people don’t overcome their difficulties in gaining self-esteen and recognition, it could lead conpensatory behaviour and an inferiority complex
81
New cards
what did Carl Jung identify?
the terms extrovert (outwards looking and rely on others for well-being) and introvert (inwards looking and wellbeing comes from within)
82
New cards
what did pavlov pioneer
classical conditioning
83
New cards
classical conditioning
a type of learning where a once neutral stimulus comes to produce a particular response after pairings with a conditioned stimulus
84
New cards
what did bf skinner pioneer?
operant conditioning
85
New cards
operant conditioning
a type of learning that uses rewards and punishment to achieve a desired behaviour