BIOCHEMISTRY - LIPIDS
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
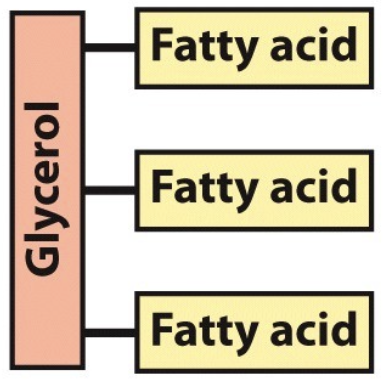
What is the name of this molecule and what category of lipids does it fit into?
triacylglycerol
storage lipids
storage lipids
2
New cards
What is the main function of structural lipids?
support of biological membranes
3
New cards
What is the name, category, and net charge of this lipid?
phosphatidylglycerol
glycerophospholipid
net -1
glycerophospholipid
net -1
4
New cards
What does the following carbon skeleton tell you about the structure of the fatty acid?
18:2 (9,12)
18:2 (9,12)
common name: linoleic acid
there are 18 carbons with 2 double bonds between carbons 9-10 and 12-13
there are 18 carbons with 2 double bonds between carbons 9-10 and 12-13
5
New cards
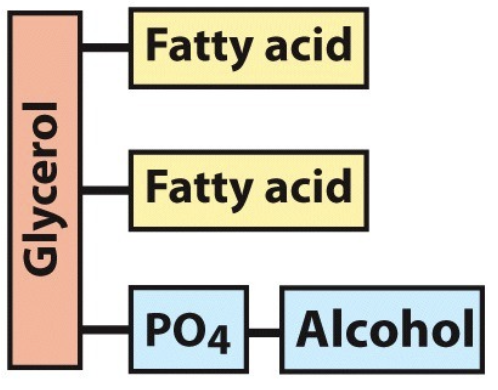
What is the name of this molecule and what category of lipids does it fit into?
glycerophosolipid
phospholipids (structural lipids)
phospholipids (structural lipids)
6
New cards
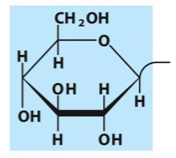
What is the name and category of this lipid?
glucosylcerebroside
sphingolipid (glycolipid)
sphingolipid (glycolipid)
7
New cards
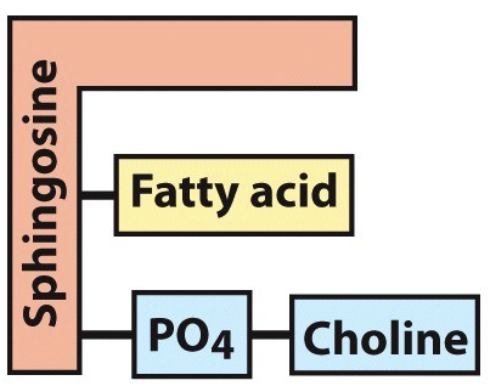
What is the name of this molecule and what category of lipids does it fit into?
sphingolipid
phospholipids (structural lipids)
phospholipids (structural lipids)
8
New cards
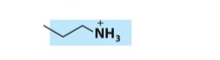
What is the name, category, and net charge of this lipid?
phosphatidylethanolamine
glycerophospholipid
net 0
glycerophospholipid
net 0
9
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
20:0
20:0
arachidic acid
10
New cards
What type of bond attaches fatty acids in sphingolipids?
amide bond
11
New cards
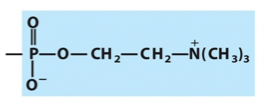
What is the name and category of this lipid?
sphingomyelin
sphingolipids (glycolipids)
sphingolipids (glycolipids)
12
New cards
What is the most decorated biomolecule of all time?
cholesterol
13
New cards
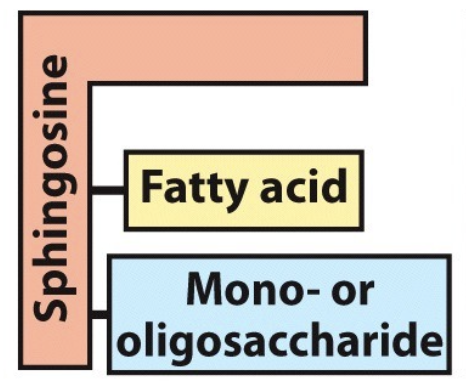
What is the name of this molecule and what category of lipids does it fit into?
sphingolipid
glycolipids (structural lipids)
glycolipids (structural lipids)
14
New cards
What is cholesterol a precursor of?
Vitamin D
bile salts
hormones
bile salts
hormones
15
New cards
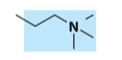
What is the name, category, and net charge of this lipid?
phosphatidylcholine
glycerophospholipid
net 0
glycerophospholipid
net 0
16
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
18:0
18:0
stearic acid
17
New cards
What are the main features of cholesterol?
made of 27 carbons
has a steroid nucleus
amphipathic with polarity at C3 due to an OH group
four ring structures: 3 six ring and 1 five ring
has a steroid nucleus
amphipathic with polarity at C3 due to an OH group
four ring structures: 3 six ring and 1 five ring
18
New cards
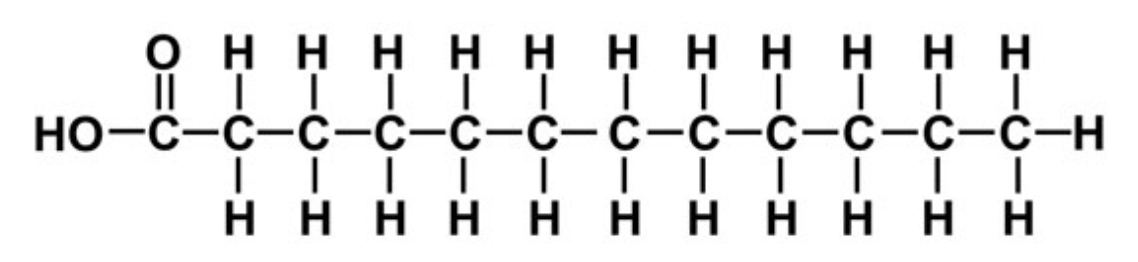
What type of fatty acid is this and why?
saturated
there are no double bonds
there are no double bonds
19
New cards
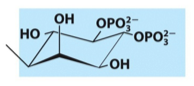
What is the name, category, and net charge of this lipid?
phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate
glycerophospholipid
*don't worry about charge for this lipid*
glycerophospholipid
*don't worry about charge for this lipid*
20
New cards
What are the sterols called in mammals, plants, and fungi?
cholesterol
stigmasterol
ergosterol
stigmasterol
ergosterol
21
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
14:0
14:0
myristic acid
22
New cards
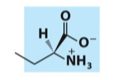
What is the name, category, and net charge of this lipid?
phosphatidylserine
glycerophospholipid
net -1
glycerophospholipid
net -1
23
New cards
What is the general structure of a fatty acid?
polar head group
hydrocarbon chain
hydrocarbon chain
24
New cards
What are the names of the four phospholipases?
phospholipase A1, A2, C, and D
25
New cards
What configuration of double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids has the highest melting point?
trans-configuration
26
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
16:0
16:0
palmitic acid
27
New cards
What is a phosphodiester bond?
2 ester bonds at different sides of the phosphate
28
New cards
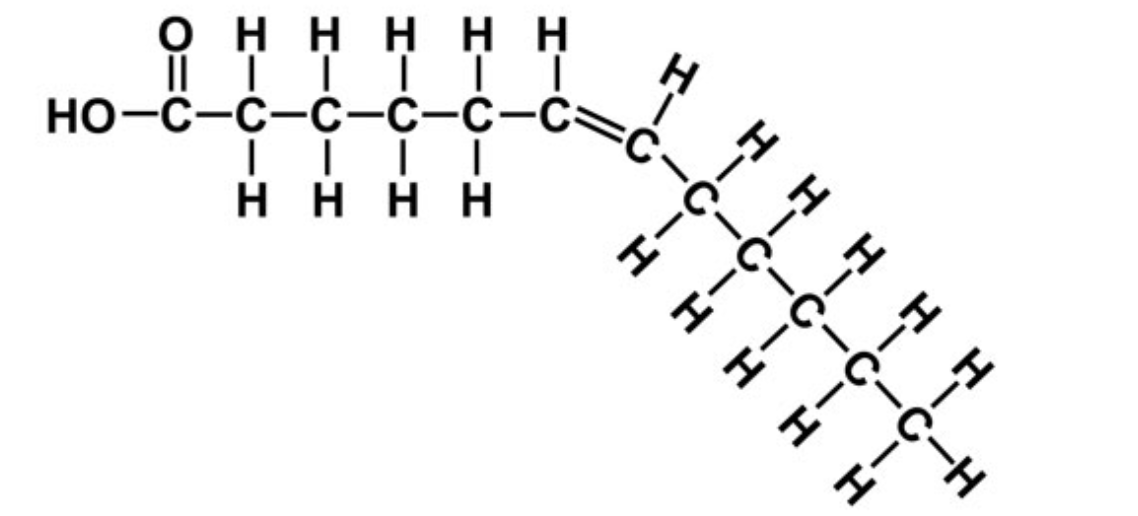
What type of fatty acid is this and why?
mono unsaturated
there is only one double bond
there is only one double bond
29
New cards
What type of fatty acids are on carbons 1 and 2 of a glycerophospholipid?
carbon 1: saturated
carbon 2: unsaturated
carbon 2: unsaturated
30
New cards
What are the two products of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis? What do they do?
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)
diacylglycerol (DAG)
IP3 triggers the release of intracellular calcium and also aids DAG in the activation of protein kinase C which leads to the regulation of other enzymes through protein phosphorylation
diacylglycerol (DAG)
IP3 triggers the release of intracellular calcium and also aids DAG in the activation of protein kinase C which leads to the regulation of other enzymes through protein phosphorylation
31
New cards
What is a nonessential fatty acid?
our bodies can produce these fatty acids
32
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
20:4 (5,8,11,14)
20:4 (5,8,11,14)
arachidonic acid
33
New cards
What three molecules does the metabolism of arachidonic acid produce and what do each of them regulate?
prostaglandin: regulates pain
thromboxane: regulates platelet aggregation
leukotriene: regulates smooth muscles (lungs)
thromboxane: regulates platelet aggregation
leukotriene: regulates smooth muscles (lungs)
34
New cards
List the following types of fatty acids in order from highest melting point to lowest.
mono unsaturated
saturated
poly unsaturated
mono unsaturated
saturated
poly unsaturated
saturated > mono unsaturated > poly unsaturated
35
New cards
What is the general structure of a wax?
a long chain fatty acids attached via ester bond to a long chain alcohol
36
New cards
Describe the relationship between solubility and carbon amount in fatty acids.
As the carbon chain increases, the solubility decreases.
37
New cards
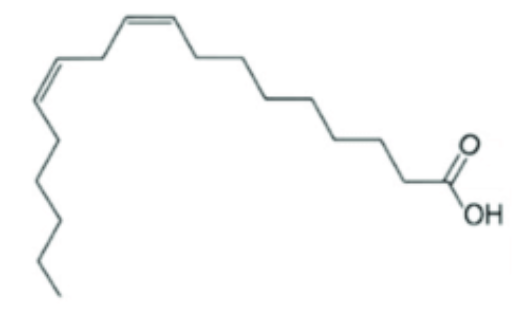
What type of fatty acid is this and why?
poly unsaturated
there is more than one double bond
there is more than one double bond
38
New cards
What is an essential fatty acid? (give an example)
our bodies cannot produce these fatty acids
ex: omega-3 (linolenic acid) 18:3 (9, 12, 15)
ex: omega-3 (linolenic acid) 18:3 (9, 12, 15)
39
New cards
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
12:0
12:0
lauric acid
40
New cards
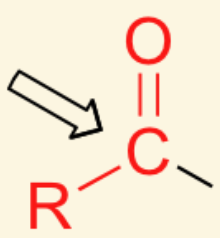
What functional group is this?
acyl
41
New cards
What is the main biological function of triacylglycerol? What is another function?
fuel storage
insulation
insulation
42
New cards
How do aspirin and ibuprofen work?
they work by inhibiting the enzyme COX which then decreases the production of thromboxane and prostaglandins
43
New cards
Describe saponification.
triacylglycerol reacted with a base (NaOH or 2KOH) and heated to form glycerol and soap (K+ salts of fatty acids)
44
New cards
Describe the 4 fat-soluble vitamins and their functions.
Vitamin A: aids in increasing vision
Vitamin D: needed for bone formation
Vitamin E: "antioxidants"
Vitamin K: aids in the blood coagulation process
Vitamin D: needed for bone formation
Vitamin E: "antioxidants"
Vitamin K: aids in the blood coagulation process