Module 8 Arthropods, Diseases, and the Military
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are the 3 main topics of why arthropod-borne diseases stand out as major concerns for military deployments?
severely reduced the fighting capacity of armies
caused suspension/cancellation of military operations
wrought havoc on civilian population
Until when were infectious diseases were the main causes of morbidity and mortality among soldiers and civilians?
WWI
Until when were the impacts of vector-borne diseases go from potentially lethal threats to primarily curable illnesses?
WWII
With most recent conflicts involving Western armies that have occurred overseas, what does this risk?
Vector-borne diseases for soldiers and displaced populations
Medical Entomology:
Historically, most casualties are caused by _ in most conflicts.
Arthropods
Medical Entomology:
Western armies worldwide and continually forced to develop new _ for military deployments.
Vector-control strategies
What does Medical entomology focus on?
Insects and arthropods that impact human health
What is Urban entomology?
Study of insects associated with the environments of humans and their companion animals
What does Veterinary entomology focus on?
Insects and arthropods that impact animal health
What does Military entomology include?
Scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors

This image include the Top Forty Infectious Diseases of U.S. Military significance. The ones highlighted in teal (and red) are arthropod-borne diseases.
I don’t think we need to memorize this, however, the ones highlighted in red were directly pointed out in the lecture. Which ones are they?
Malaria
Dengue fever
Chikungunya
Sand fly fever
Leishmaniasis - visceral
Leishmaniasis - cutaneous
Leishmaniasis - cutaneous/mucosal
Tularemia
West Nile fever
Lyme diseases
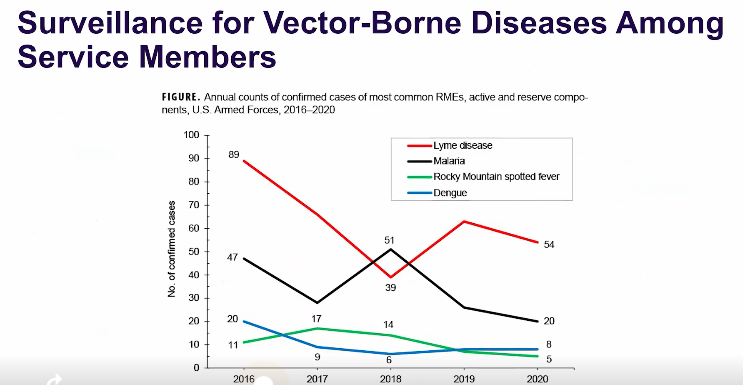
Here is this chart that was shown in the lecture.
In the last decade, the most common vector-borne diseases among US armed forces tended to be?
Lyme disease, Malaria, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Dengue (not added in the chart but also Leishmaniasis)
Malaria was a health threat to US service members located in what kind of areas?
Endemic
During WWI, malaria weakened what armies in Macedonia?
British, French and German
During WWII, malaria emerged as a main cause of illness among troops in what kind of areas? (Think climate)
Tropical
In post-WWII, conflicts in Indochina, Malaysia, and Korea, the impact of malaria was reduced through the introduction of improved..?
Prophylactic drugs and vector-control
During the Vietnam War, what resulted in loss of troops?
Chloroquine resistance
During WWII, nearly _ cases of dengue fever were reported by the US army and morbidity was very high in some areas
90,000
Chikungunya has been a concern in troops in endemic areas in what places?
Asia and Africa
A new variant of the Chikungunya virus formally vectored by the Yellow-fever mosquito is associated with Aedes albopictus (Asian-tiger mosquito) that has adapted to? (Think climate)
Temperate regions
French troops in Gabon and Cameron were affected by chikungunya outbreaks in what years?
2006 and 2007
Leishmaniasis is endemic is what areas? (Think climate)
Tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions
Cutaneous (CL), mucocutaneous (ML), and visceral (VL) leishmaniasis have the potential to cause explosive outbreaks in communities…?
Exposed to the parasite
Estimates of up to 2,500 cases of CL among U.S soldiers in Iraq from what years?
2003-2004
What forces experienced CL outbreaks in Afghanistan?
Dutch, German, and Bristish
How many cases were reported of VL by the US during WWII?
126
The last cases of VL were reported by who in Algeria?
French forces
Western armies on duty/in training are regularly confronted with what disease?
Lyme disease
Soldiers of different armies have been exposed to what mostly in US forces in Europe? (Scientific name for a Lyme disease variant)
B.burgdoferti
What disease is a rickettsial disease that is prevalent in areas where military training takes place and is lethal?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
In the spring of what year were the members of a military unit trained in Arkansas and Virginia (where 15% and 2%) of soldiers were infected by R. rickettsia and Ehrlichia canis respectively?
1989
All western armies have developed what because of the fact that vector-borne diseases on armed forces can have significant burden?
Vector-control strategies
Medical intelligence allows for the _ _ _ before deployment and for the planning of preventative countermeasures
Assessment of risks
Military operations in rural and urban areas have permitted the creation of what models and maps?
Entomological and epidemiological
What are the personal protection measures?
Proper use of uniforms, application of repellent to exposed skin, application of permethrin to battledress uniforms, and use of insecticide-impregnated bed nests, curtains, tents, and window screens.
What are the unit protection measures?
Base camp selection, environmental management, larviciding space spraying, aerial spraying, and indoor residual spraying
What institutes investigate disease threats and develop effective countermeasures to protect and sustain US troops?
Navy Medical Research Command (NMRC), Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR), US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRID), Biosafety Level 4 Research Facility