Earth Science: Weathering, Erosion, and Water Distribution
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Endogenic processes
Internal geological forces within Earth that shape its structure through plate boundaries, volcanism, and more.
Exogenic processes
External forces at Earth's surface that wear down rocks and reshape landscapes.
Weathering
The physical breakdown (disintegration) and chemical alteration (decomposition) of rocks at or near Earth's surface.
Erosion
The removal of weathered rocks and minerals by moving water, wind, glaciers, and gravity.
Mass wasting
Movement of earth materials (soil, rocks, etc.) downslope primarily under the influence of gravity.
Angle of repose
Maximum slope or steepness at which loose material remains stable without sliding.
Suspension
Particles carried in water.
Solution
Dissolved minerals.
Traction
Rolling along the riverbed.
Saltation
Bouncing of particles.
Chemical Weathering
Decomposition of rocks through chemical reactions.
Physical/Mechanical weathering
Breaks rocks into pieces without changing chemical composition.
Frost wedging
Rainwater enters cracks, freezes, expands, and causes cracks to widen.
Dissolution
Slightly acidic rainwater dissolves minerals, such as in limestone dissolution.
Abrasion
Particles like sand strike rock surfaces, wearing them down.
Temperature
Cause rocks to expand and contract, leading to cracking and breaking.
Biological Activities
Plants, animals, and microorganisms contribute to weathering.
Root wedging
Plant roots grow into cracks and break rocks.
Mining
Deep rocks exposed; machinery causes physical disturbance.
Deforestation
Removes protection from water/wind and increases exposure to erosion.
Salt Crystal Growth
Salty water in cracks evaporates, crystals grow, and put pressure on rock.
Exfoliation
Large rock masses exposed to lower pressure expand and crack into thin layers.
Oxidation
Oxygen reacts with minerals, forming oxides like rust on iron-rich rocks.
Hydrolysis
Water reacts with minerals, forming new minerals and breaking down rock.
Biological Weathering
Caused by living organisms, can be physical (root wedging) or chemical (acids from decaying matter).
Acidic Rain
Dissolves minerals, roughening surface (solution/dissolution).
Relative Dating
Sequencing rock layers (which formed first).
Absolute Dating
Determining actual age of rocks/fossils using radiometric methods.
Faunal Succession
Fossils succeed one another in a predictable order → useful for relative dating.
Geologic Time Scale (GTS)
Timeline of major Earth events from formation (~4.6 billion years ago) to present.
Water cycle
Movement of water between oceans, land, and atmosphere through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
Brackish water
Mix of salt and freshwater; found in estuaries, deltas, mangroves, coastal wetlands.
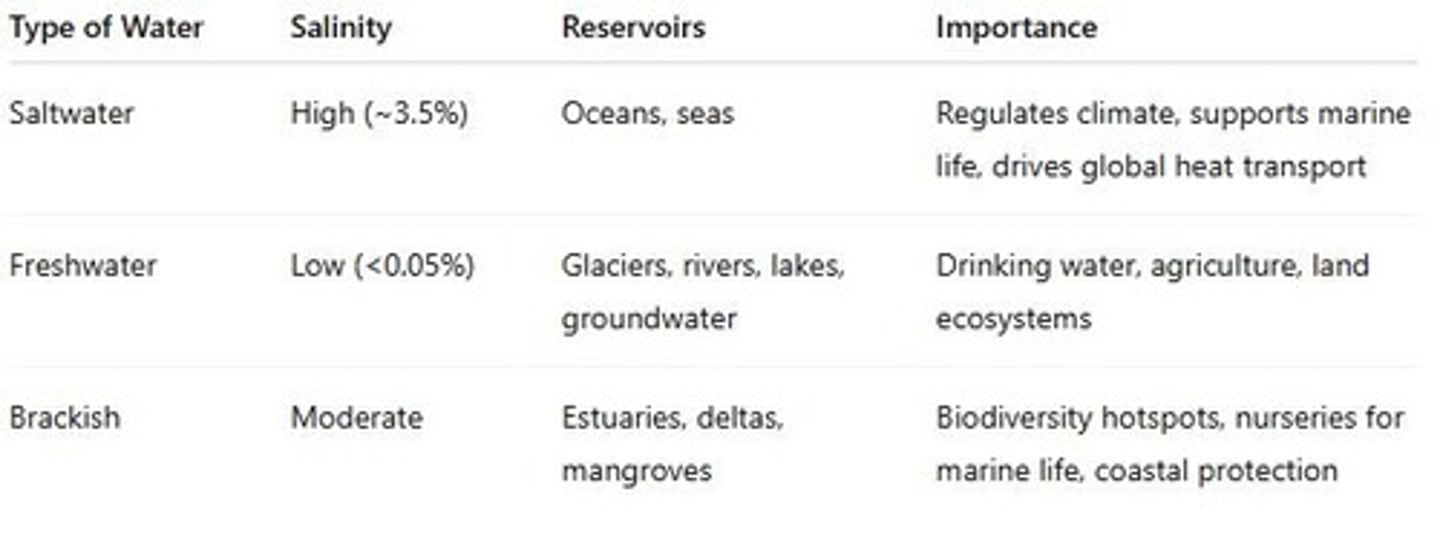
Paradox of plenty
Earth looks water-rich, but usable freshwater is scarce.
Polarity
Oxygen slightly negative, hydrogen slightly positive → allows hydrogen bonding.
Cohesion
Water sticks to itself → droplets.
Adhesion
Water sticks to surfaces.
High specific heat
Resists temperature changes.
Universal solvent
Dissolves many substances.
Capillary action
Movement through narrow spaces without gravity; essential for water transport in plants.
Evaporative cooling
Heat loss through evaporation → regulates temperature in organisms.