Appendicular skeleton
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
First stage of muscle contraction
excitation
Which tissue types are electric
nervous and muscle
What is resting membrane potential?
positive charge outside of the cell (Na+), negative charge inside of the cell (PO4 3-)
What steps occur in excitation step
Frontal lobe sends signal through motor neuron, secretes ACh (neurotransmitter), attaches to sarcolema receptor
What is the second stage of contraction
excitation contraction-coupling
ACh ligand does what once it attatched to ACh receptors?
opens channel proteins causing depolarization by letting in Na+ ions
What happens in excitation: contraction-coupling stage?
depolarization, Na+ ions travel through t-tubules of cell to sarcoplasmic reticulum, SR releases Ca+, and Ca+ attached to troponin on actin
What is the third stage of contraction
contraction
What happens in the contraction stage
troponin removes tropomyosin, exposing active site on actin, allowing myosin to attach to actin.
ATP is required during which step of the contraction phase?
when the myosin pulls on actin, causing motion
When actin and myosin attach, that’s called forming a
crossbridge
When myosin pulls on actin, that’s called a
powerstroke
When all myosin fibers pull on actin simultaneously, that’s called a
contraction
The fourth stage of contraction is
relaxation
What happens during the relaxation stage
Frontal lobe stops motor neuron, AChE enzyme removes ACh from sarcolemma, closing channel protein. ATP breaks cross bridge, releasing actin from myosin, Ca+ gets reabsorbed into SR
Which step(s) of relaxation stage require ATP
breaking of actin-myosin crossbridge and re
What are the rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
What are the functions of the rotator cuff muscles
holds the ball and socket joint stable
When someone injures their rotator cuff, it’s usually the
supraspinatus
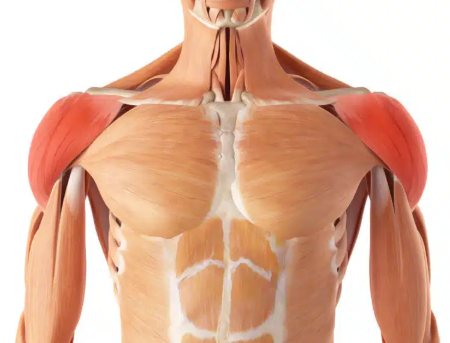
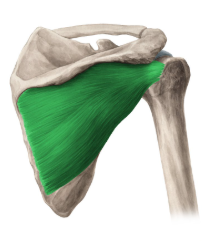
deltoid
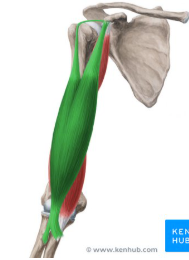
biceps brachii
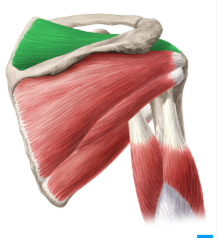
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
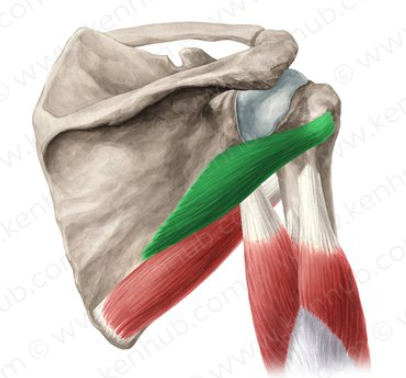
teres minor
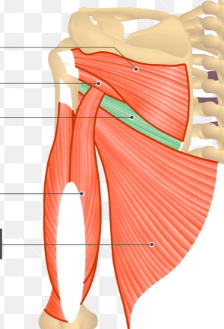
teres major
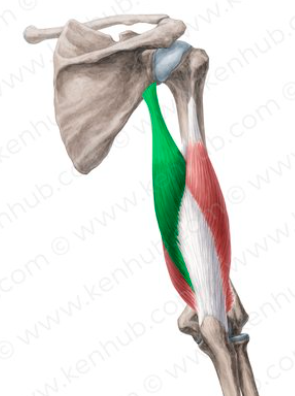
triceps brachii
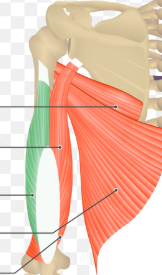
lateral head of triceps brachii
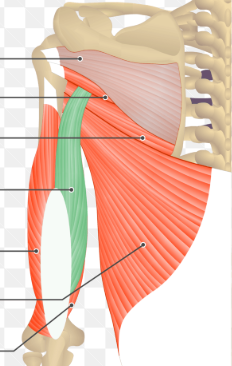
long head of triceps brachi
Mvmt of deltoid
abducts, flexes and extends arm
Mvmt of biceps brachii
supinates and flexes forearm
Mvmt of supraspinatus
stabilizes joint and assists abduction
Mvmt of infraspinatus
laterally rotates and stabilizes joint
Mvmt of teres minor
laterally rotates and stabilizes joint
Mvmt of subscapularis
adducts and rotates medially and stabilizes joint
Mvmt of teres major
adducts, extends, and rotates arm medially
Mvmt of triceps brachii (both lateral and long head)
extends forearm
Mvmt of ilacus
flexes thigh
Mvmt of psoas major
flexes thigh, flexes and laterally flexes vertebral column
Mvmt of sartorius
flexes abducts, and laterally rotates thigh/leg
Mvmt of Vastius lateralis
extends leg
Mvmt of rectus femoris
extends leg
Mvmt of Vastus medialus
extends the leg
Mvmt of gracilis
abducts, flexes, and rotates thigh medially
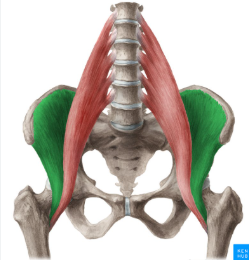
iliacus
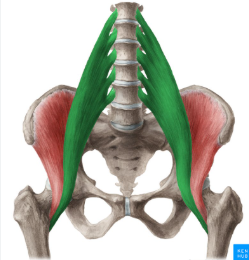
psoas major
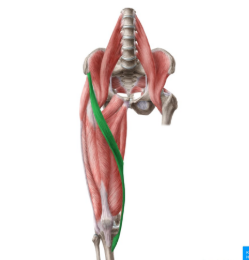
sartorius
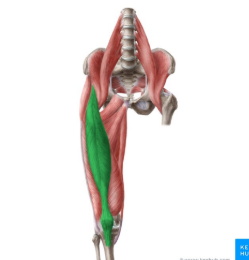
rectus femoris
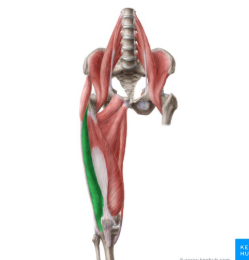
vastus lateralis
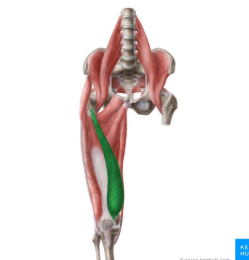
vastus medialus
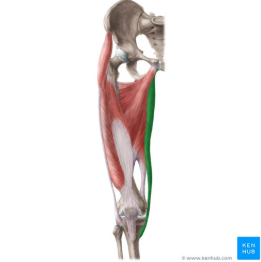
gracilis
mvmt of gluteus maximus
extends, laterally rotates, abducts thigh
mvmt of biceps femoris
extends thigh, flexes leg
mvmt of semitendinosus
extends and flexes leg
mvmt of semimembranosus
extends and flexes leg
mvmt of iliotibial tract
abducts, flexes, and rotates thigh medially
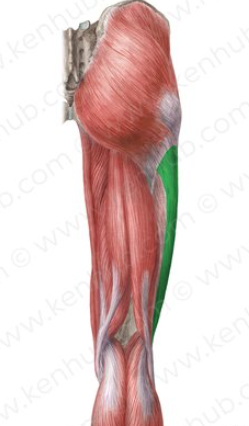
iliotibial tract
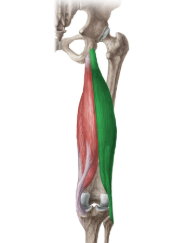
biceps femoris
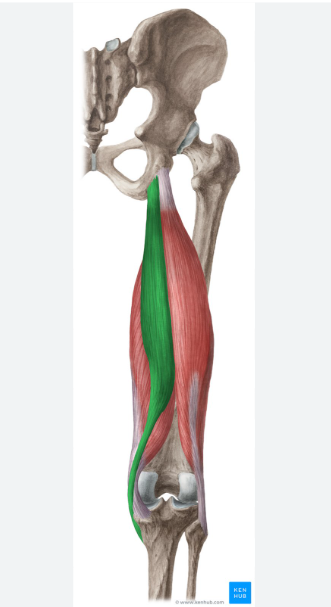
semitendinosus
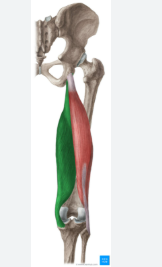
semimembranosus
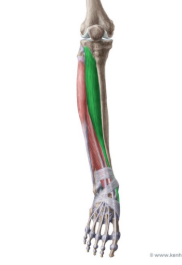
tibialis anterior
mvmt of tibialis anterior
dorsiflexes foot
mvmt of gastrocnemius
plantarflexes foot + flexes leg
mvment of soleus
plantarflexes foot
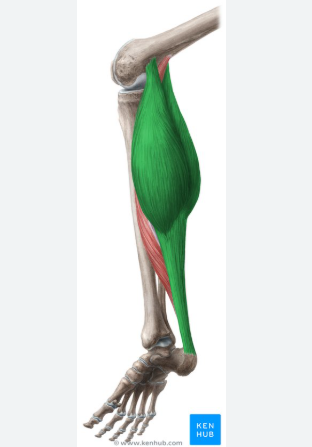
gastrocnemius
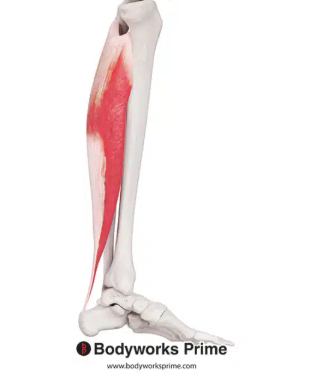
soleus
What is rigor mortis
when you die, muscles contract and can’t relax
Why does rigor mortis happen
No breathing, no ATP, Ca+ spills out causing contraction and muscle is stuck in that state
What kind of paralysis is rigor mortis
spastic