Biology - Genetics Unit Test
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Allele
A variant form of a gene found at a specific location on a chromosome that can influence traits.
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
A theory that explains how genes are inherited through chromosomes from parents to offspring.
Codominance
A genetic scenario where both alleles in a heterozygous individual are fully expressed, resulting in a phenotype that shows both traits.
Complete Dominance
A situation where one allele completely masks the effect of another allele at the same gene locus in a heterozygous individual.
Cross-fertilization
The process of fertilizing an ovule with pollen from a different flower, enhancing genetic diversity.
Dihybrid
An organism that has two different alleles for two traits.
Dihybrid Cross
A genetic cross that examines the inheritance patterns of two different traits at the same time.
Dominant
An allele that expresses its trait in the phenotype even when only one copy is present.
Gene Locus
The specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
Gene Map
A representation that shows the arrangement and relative positions of genes on a chromosome.
Genetic Linkage
The tendency of genes located close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an individual, including all the alleles present for a particular trait.
Hereditary
Referring to traits or characteristics that are passed down from parents to offspring through genes.
Heritable
Describing traits that can be transmitted from one generation to the next through genetic inheritance.
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a specific gene.
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a specific gene.
Hybrid
An offspring resulting from the crossbreeding of two different species or varieties.
Incomplete Dominance
A genetic situation where neither allele is completely dominant, resulting in a blended phenotype in heterozygous individuals.
Inheritance Patterns
The predictable ways in which traits are passed from parents to offspring based on genetic principles.
Law of Independent Assortment
A principle stating that the alleles for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes.
Law of Segregation
A principle that states that during the formation of gametes, the two alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
Monohybrid
An organism that has two different alleles for one trait being studied.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics or traits of an organism, resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
Probability
The likelihood or chance of a particular genetic outcome occurring in offspring.
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict the genetic combinations resulting from a cross between two individuals.
Recessive
An allele that does not manifest in the phenotype unless two copies are present.
Sex-linked Gene
A gene located on a sex chromosome, which often leads to traits that are expressed differently in males and females.
Test Cross
A breeding experiment used to determine the genotype of an individual exhibiting a dominant trait by crossing it with a homozygous recessive individual.
Prophase I
Nucleus dissolves at this stage. Crossing Over (exchange of genetic material) occurs at this phase.

Metaphase I
pairs of homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. The centromere of each chromatid pair attaches to one spindle fibre.
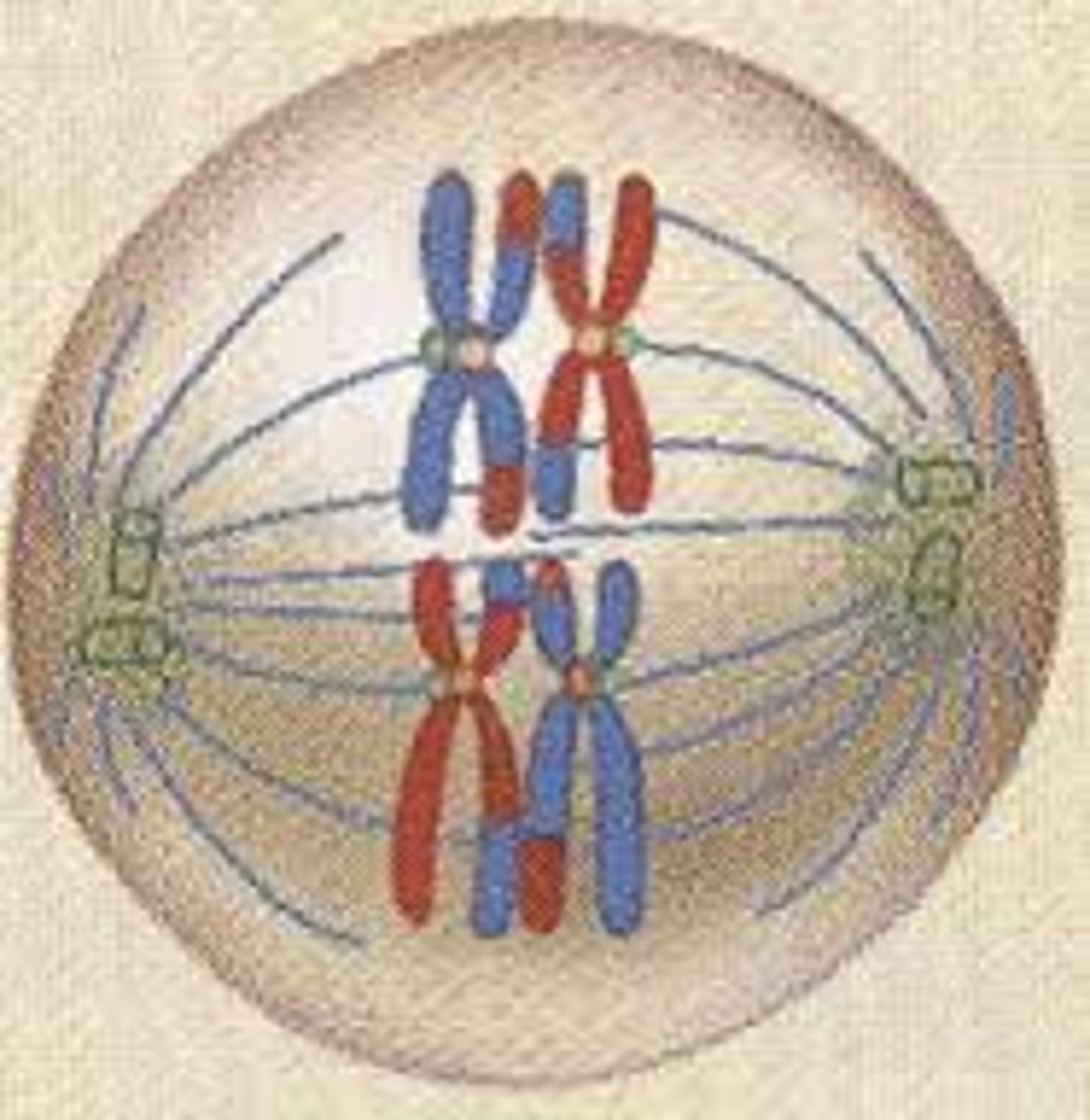
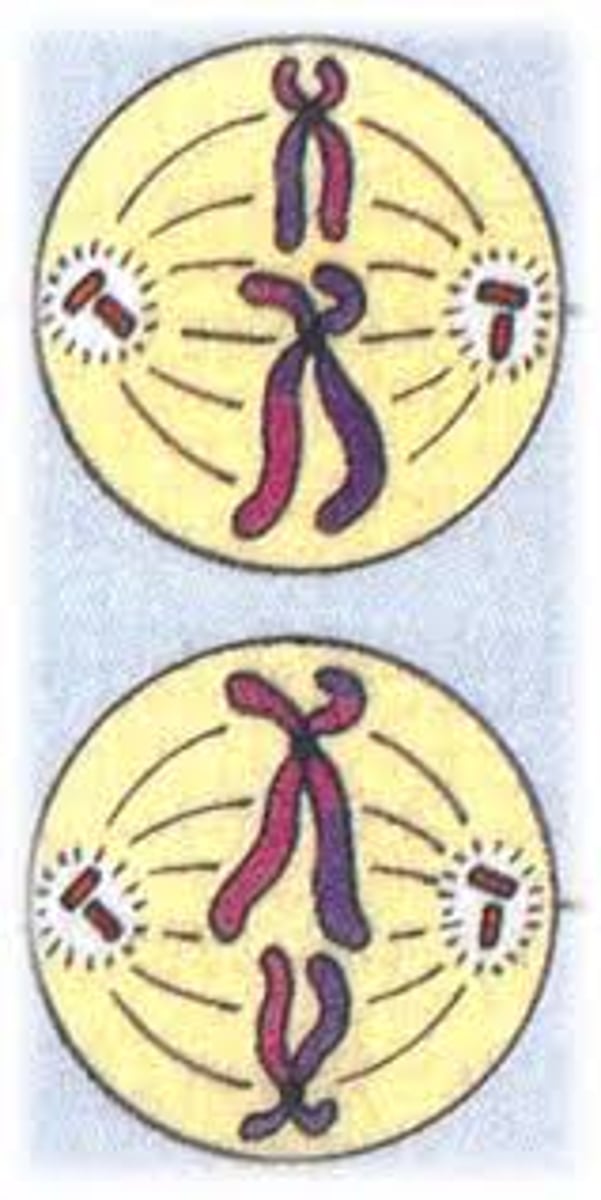
Anaphase I
stage of meiosis I where homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell. Note that chromatids do not separate - each duplicated chromosome still has two chromatids.
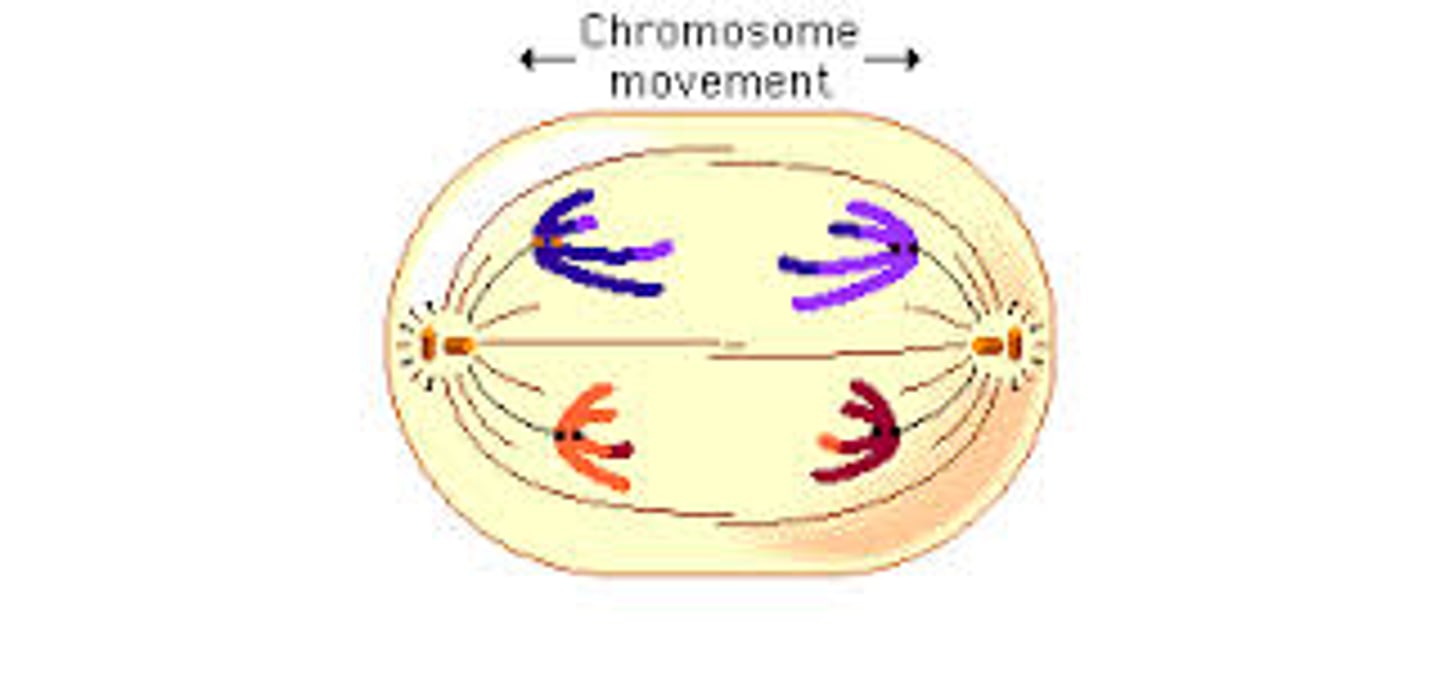
Telophase I
stage of meiosis I where the cytoplasm divides and two new cells form. Each new cell has one duplicated chromosome from each similar pair.
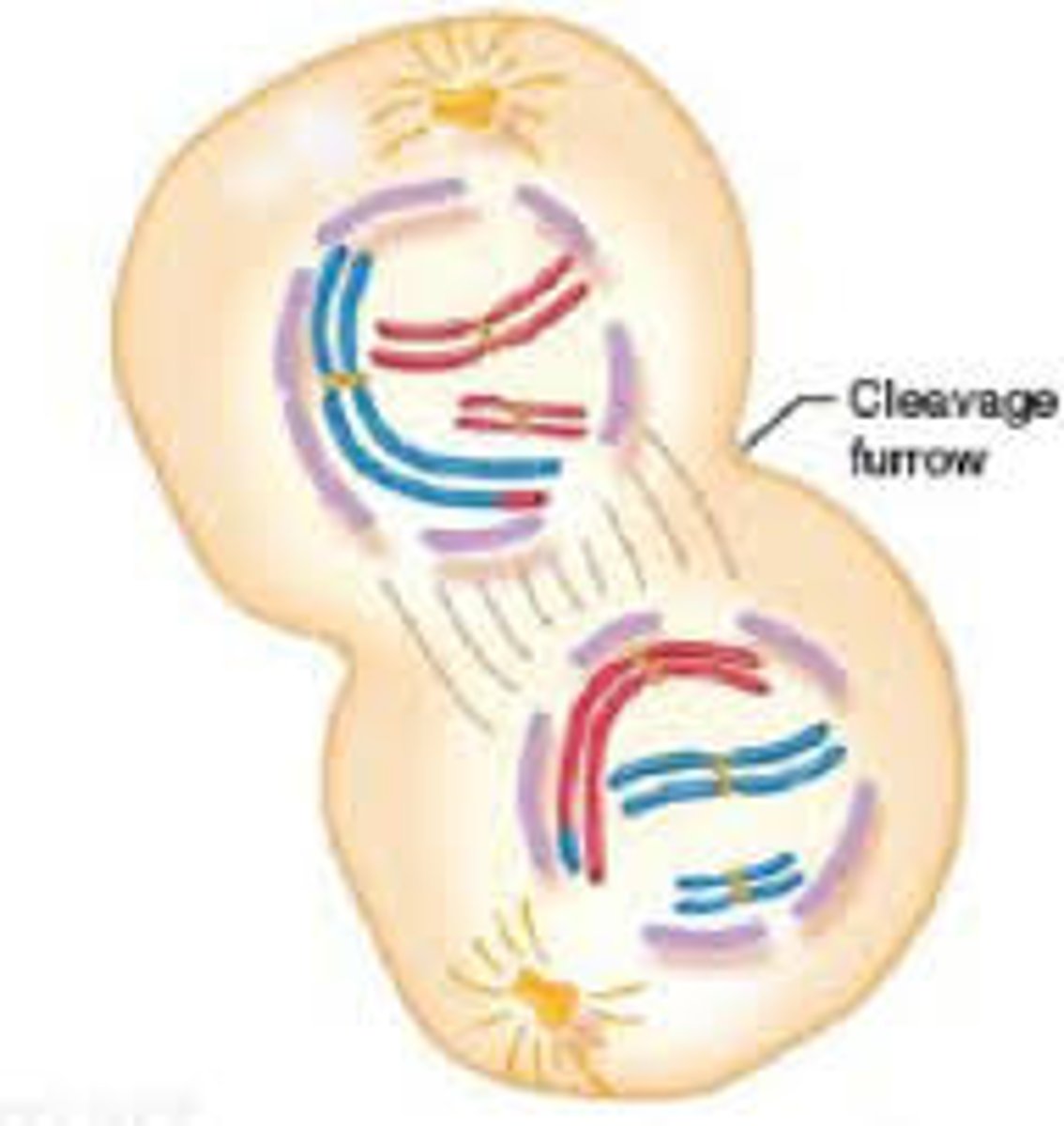
Prophase II
stage of meiosis II where duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell.
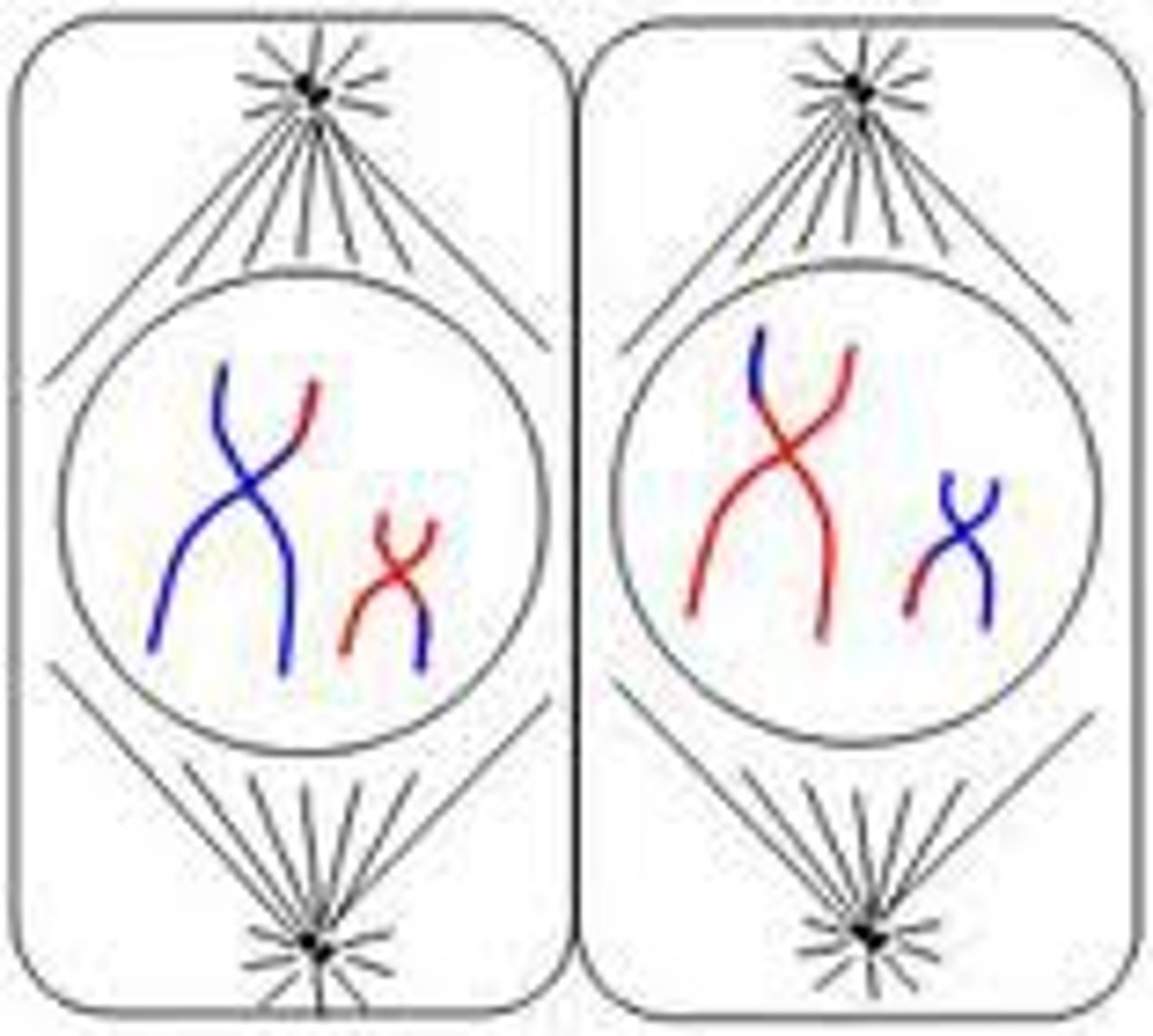
Metaphase II
stage of meiosis II where the duplicated chromosomes move to the centre of the cell. Each centromere attaches to two spindle fibres instead of one.
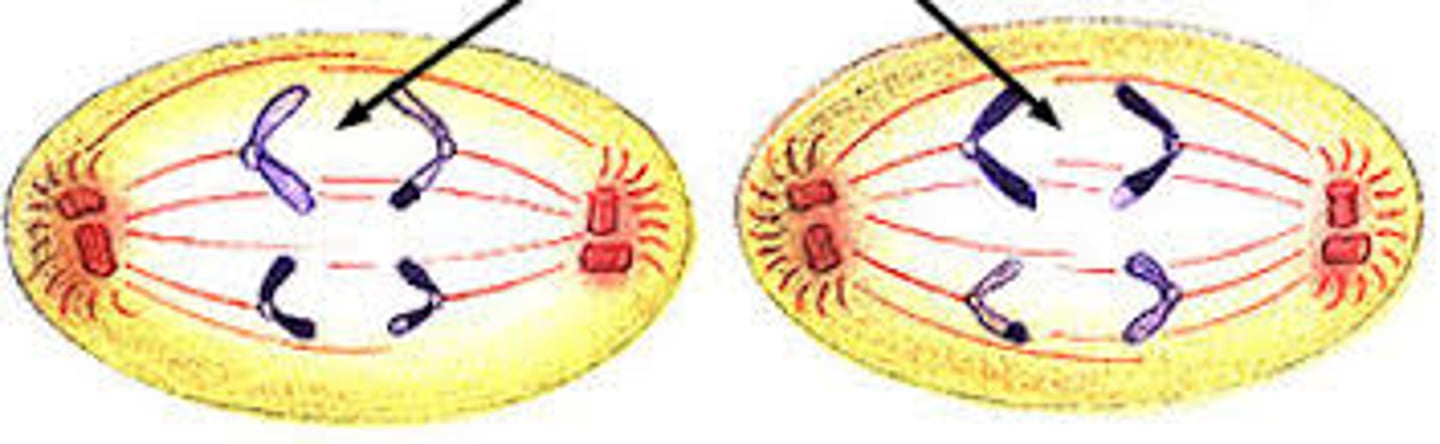
Anaphase II
stage of meiosis II where the chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Each chromatid is now an individual chromosome.
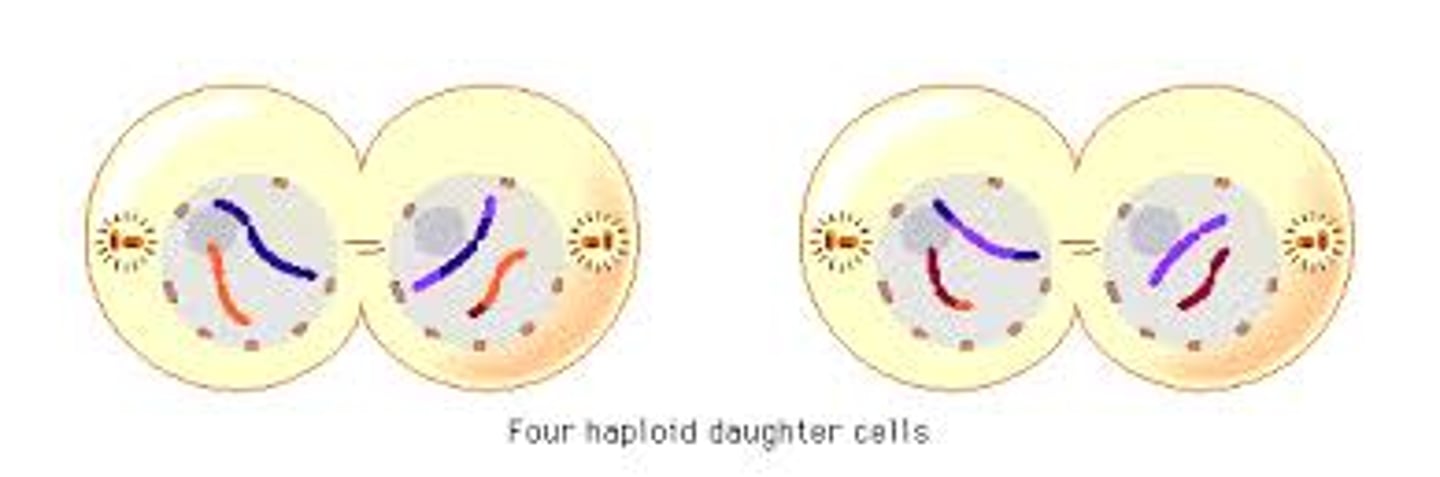
Telophase II
stage of meiosis II where spindle fibres disappear, and a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes. End result=4 haploid cells
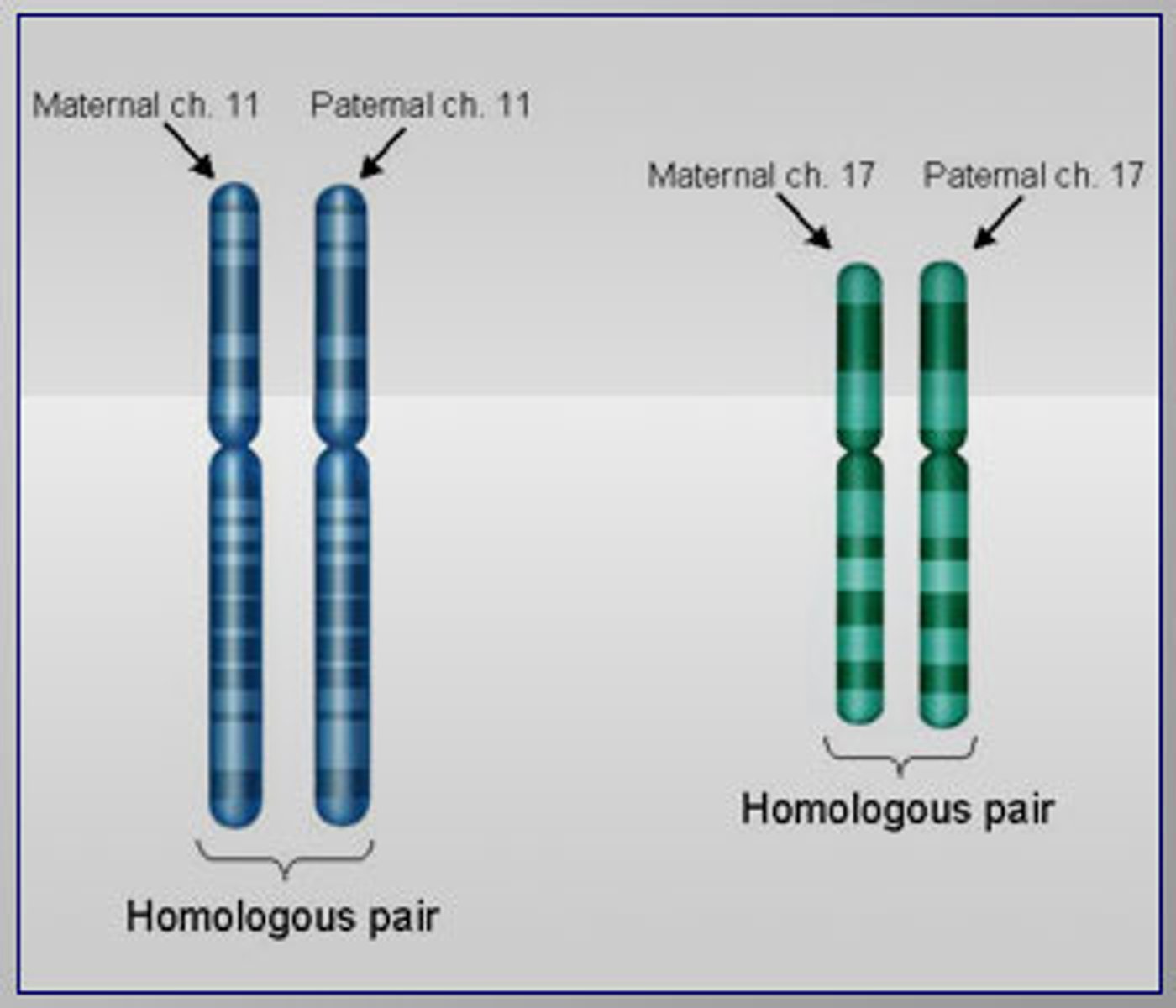
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
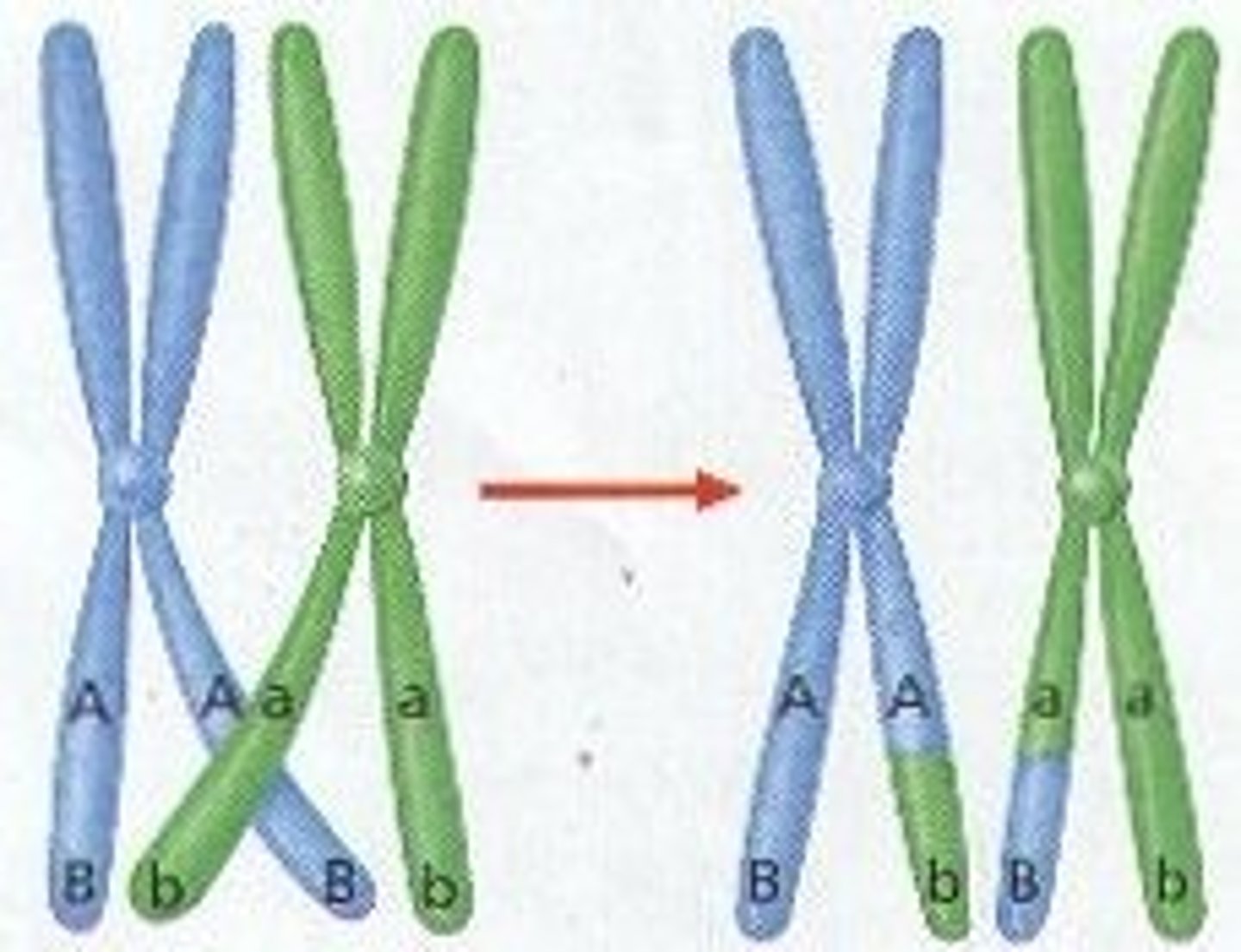
Crossing Over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis. This increases genetic variation.
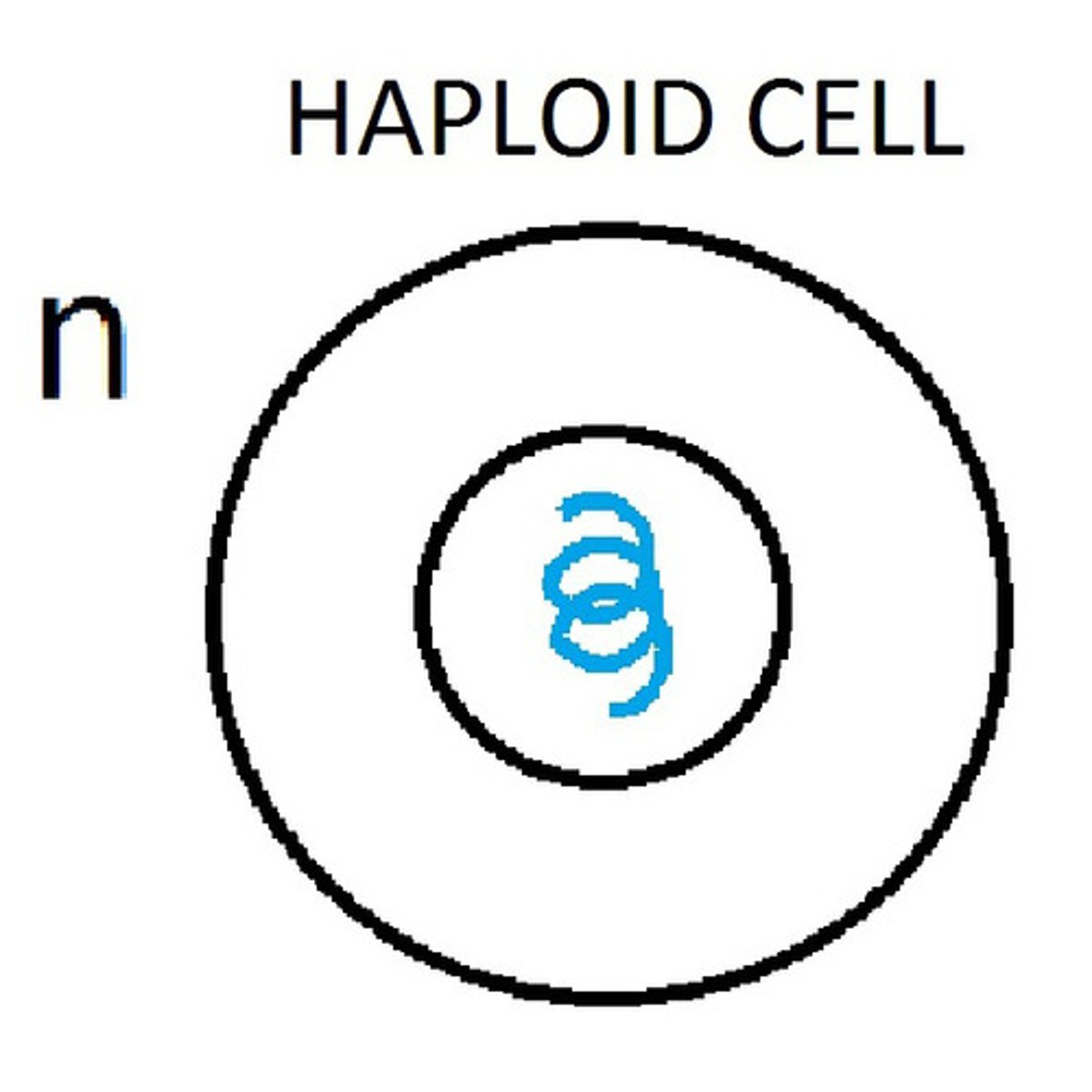
Haploid
A cell that contains only one set of chromosomes instead of the normal pair.
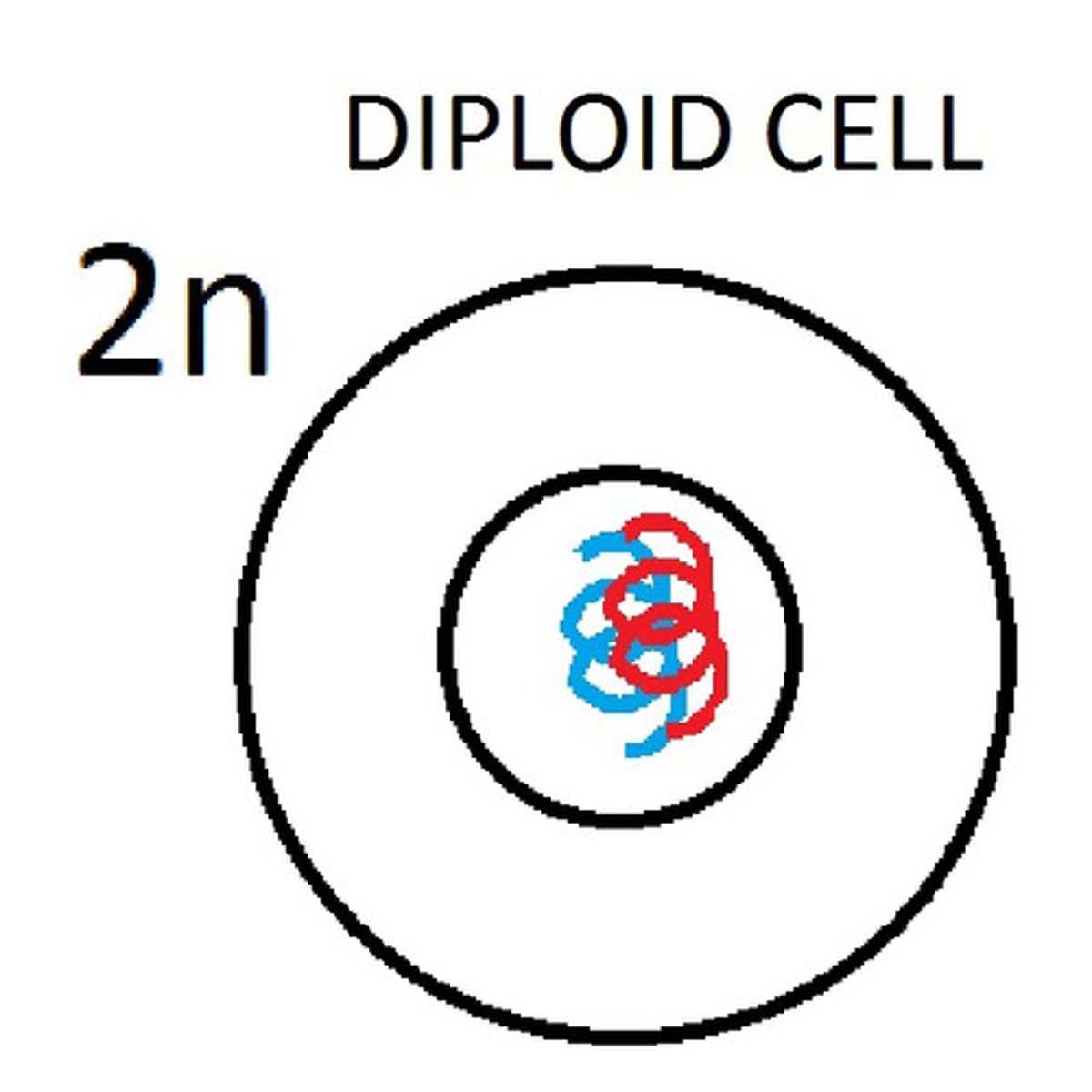
Diploid
A cell that contains two sets of chromosomes; one inherited from the mother and one inherited from the father. Most body cells (nerve, brain, muscle, skin, etc.) are considered diploid cells.
Sperm
Male gamete (sex cell)
Egg
Female gamete (sex cell)

Gamete
The result of meiosis is 4 gametes, or sex cells, that each contain half of the genetic information in the parent organism.
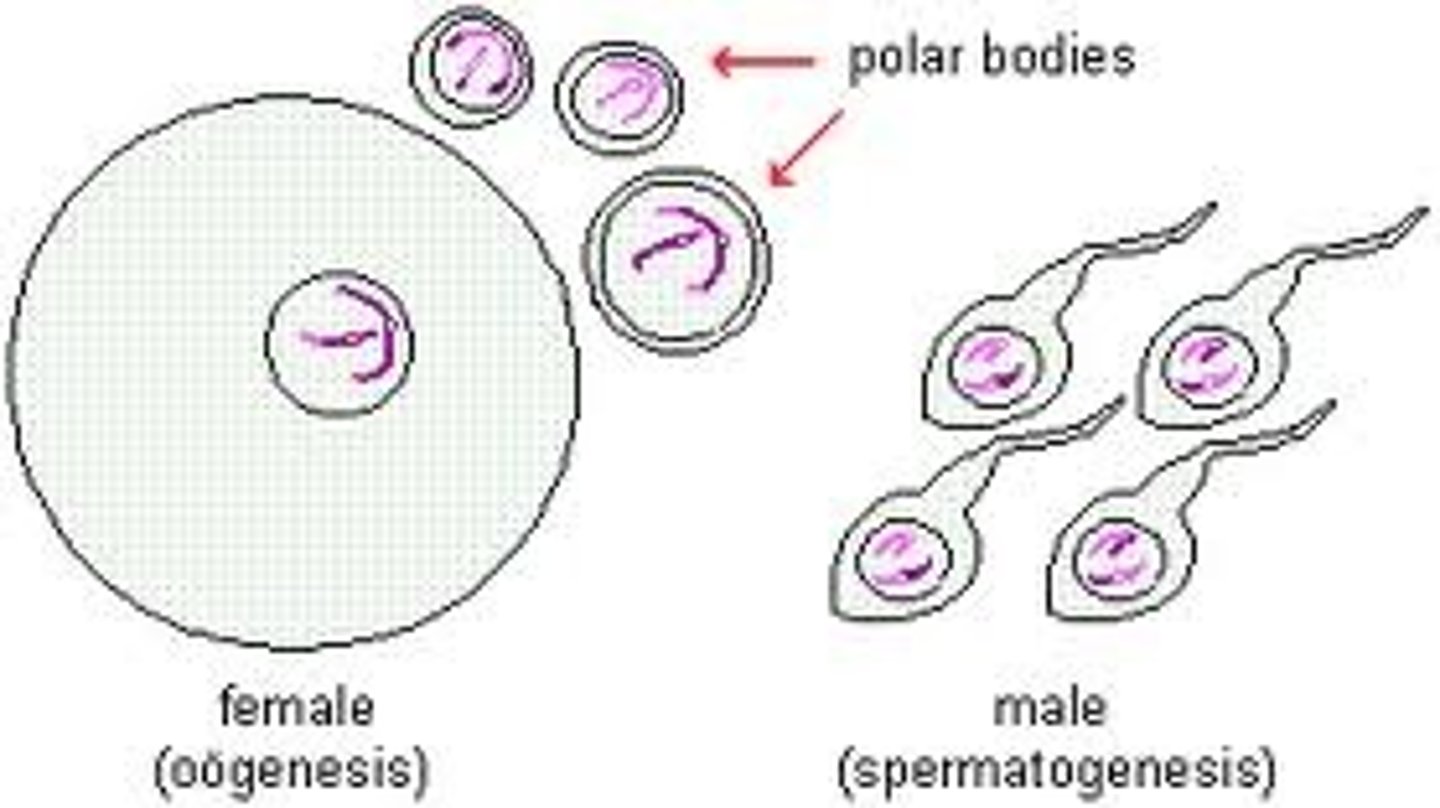
Meiosis
A process in cell division that results in the production of 4 unique sex cells (gametes).
Fertilization
Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female gametes join to form a new diploid cell
the purpose of this process is to create genetically unique gametes with half the original DNA for sexual reproduction
meiosis
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, genetic information carrier.
DNA Nucleotide
Building block of DNA, includes sugar, phosphate, base.
Deoxyribose
Five-carbon sugar in DNA nucleotides.
Nitrogen Base
Component of nucleotides; four types exist.
Adenine (A)
Nitrogen base that pairs with Thymine.
Thymine (T)
Nitrogen base that pairs with Adenine.
Guanine (G)
Nitrogen base that pairs with Cytosine.
Cytosine (C)
Nitrogen base that pairs with Guanine.
Complementary Base Pairing
Specific pairing of nitrogen bases in DNA.
DNA Replication
Process of duplicating DNA for cell division.
Chromosomes
Dense structures of DNA and protein in cells.
Codon
Triplet of nucleotides coding for an amino acid.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.
RNA Nucleotide
Building block of RNA, includes ribose, phosphate, base.
Ribose
Five-carbon sugar in RNA nucleotides.
Cell Division
Process by which cells reproduce and repair.
Mitosis
Type of cell division for growth and repair.
Sexual Reproduction
Offspring produced by fusion of two gametes.
Asexual Reproduction
Offspring produced from a single parent.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death to remove damaged cells.
Cancer Cells
Cells that divide uncontrollably and evade apoptosis.
Factors Affecting Mitosis
Environmental and chemical influences on cell division.
Protein Synthesis
Process of creating proteins from amino acids.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions in organisms.
Cell Cycle
Series of phases for cell growth and division.
DNA Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds DNA during replication.
Free Nucleotides
Available nucleotides that pair with template strands.
Mutations
Changes in DNA sequence that can affect traits.
64 Codons
Total possible combinations of three nucleotide sequences.
Interphase
Phase where the cell prepares for division.
Prophase
First stage of mitosis; chromosomes condense.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equator.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart to poles.
Telophase
Chromatids unwind; nuclear membranes reform.
Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm following mitosis.
Chromatin
Uncoiled DNA in the nucleus during interphase.
Centromere
Point where sister chromatids are joined.
Spindle Fibers
Structures that separate chromosomes during mitosis.
Diploid Cells
Cells containing two sets of chromosomes.
Haploid Cells
Cells containing one set of chromosomes.
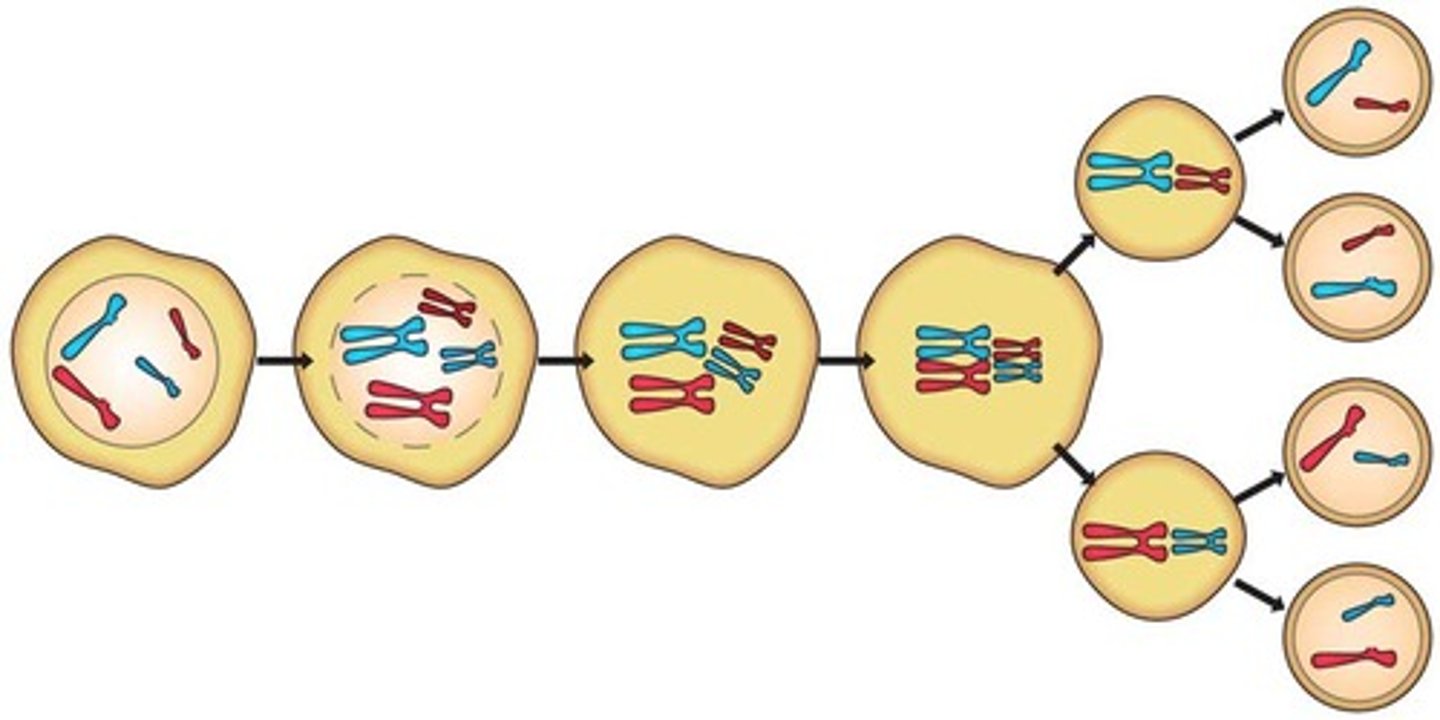
Meiosis
Process of cell division for gamete formation.
Gametes
Sex cells produced through meiosis.
Zygote
Fertilized egg formed from gamete fusion.
Chromosome Number
Constant number of chromosomes per species.
Cytokinesis in Plants
Formation of a cell plate to divide cells.
Cytokinesis in Animals
Cell membrane pinches to separate daughter cells.
Chromosome Structure
Consists of two chromatids linked by centromere.
Cell Division Stages
Includes interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
Mitosis Phases
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase (PMAT).
Meiosis I
First division resulting in two haploid cells.
Meiosis II
Second division similar to mitosis.
Spermatogenesis
Formation of sperm cells through meiosis.
Oogenesis
Formation of egg cells through meiosis.
Chromosome Preservation
Maintaining chromosome number during cell division.