Nucleic acids and dna
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what makes a nucleic acid
a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a sugar molecule
what r group does dna have
What R group does rna have
OH
What effect does the H give dna
dna is more stable which is important for long term storage
What effect does OH give Rna
RNA is more tractive and less stable than dna, this is impoertant for its functianal roles
what are the five nitrogenous bases
denine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U)
what are the three pyramidine, or one ringed bases
Cytosine, Thyamine, and Uracil
What is Thymine used in and what properties does it have
DNA, it has amethyl group, and is more stable
What is Uracil used in
Rna and it is less stable
why isnt cytocisne used in dna
It can have a spotndeus deanimation into Uracil and can lead to mutations
what are the two purine bases
adedine and guanine
how are nucleotides joined
through phosphodiester bonds and a nucleotidal transfer reaction
which is stronger the bond between A-T or C-G
C-G becasue it forms three bonds instead of 2
what does protonated mean
To be protonated means a molecule has gained a proton (a positively charged hydrogen ion, H+).
what is the central dogma of molecular biology
Dna transcribed to Rna translated to protein
what kind of backbone does dna have
dna has a sugar phosphate backbone
what are the properties of the magor groove in Dna
large and info-rich; can be ”read” by proteins
without having to unwind helix
what are the properties of the minor groove in dna
smaller and more uniform; some interactions for structural stabilization and drug binding
what does antiparallel mean
that dna strands run in opposite directions
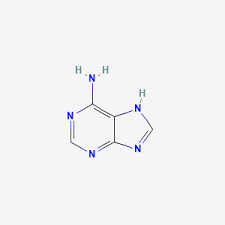
what does adenine bond with
Thymine
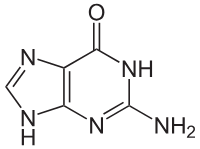
what does guanine bond with
cytosine
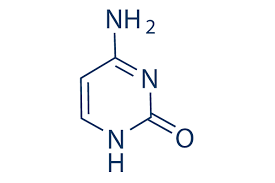
what is the width of a strand of dna
2 nm
what stabilises the double helix
hydrogen bonding and and base stacking
where does the hydrogen bonding occur
between bases across strands
base stacking is prmarily driven by
van der walls forces and hydrophobic forces (bases are very hydrophobic)
what enzyme copies dna
dna polymerase
what does semiconservative replication mean
it means replicated dna has one parent and one daughter strand
what are some major things about rna
nucleotides are linked my phosphdiester bonds
polarity is 5-3
it uses uracil instead of thiamine
it is much shorter than dna
it is single stranded but can fold in interesting patterns
what is the byproduct of a nucleotidal transfer reaction
pyro phosphate
At what sequence in DNA does RNA transcription begin?
Transcription begins at the promoter sequence
At what sequence in DNA does RNA transcription stop?
transcription stops at the termination sequence
What is the template strand of DNA?
The template strand is the strand that RNA polymerase uses to create a complimentary RNA transcript
What is the role of the nontemplate strand of DNA?
the nontemplate strand is not transcribed but its sequence matches the the transcribed RNA with the replacment of U with T
what strand of DNA is usually shown in textbooks
the template strand
Does DNA stay unzipped indefinitely during transcription?
No. Only a short section of DNA is unwound at a time. As RNA polymerase moves forward, the DNA re-anneals behind it.
What are the three main steps of transcription?
Initiation, elongation, and termination
what happens during initiation
RNA polymerase (with accessory proteins such as sigma factors in prokaryotes or
transcription factors in eukaryotes) binds to the promoter sequence. The DNA double helix is
unwound at this region, and transcription of the template strand begins
what happens during elongation
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand in the 3′ → 5′ direction, adding
complementary ribonucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing RNA transcript. The transcript is
thus synthesized in the 5′ → 3′ direction
what happens during termination
When RNA polymerase reaches a terminator sequence in the DNA, transcription
stops. The RNA transcript is released, and the DNA helix reforms.
how many types of RNA polymerase to prokaryotes have
one
How many types of RNA polymareas to eukaryotw have
Three RNA polymerases (Pol I, II, III), each for different RNA types
where do transcription and translation happen in prokaryotes
Transcription and translation are happen simultaneously in the cytoplasm
where to transcription and translation happen in Eukaryotes
Transcription occurs in the nucleus; translation in the cytoplasm (spatial separation).
mRNAs in prokaryotes ore often
polysitronic( they code for multiple protiens)
eukaryotes often have what on their promotoers
enhancers
promoter
where the rna polymerase binds to the dna
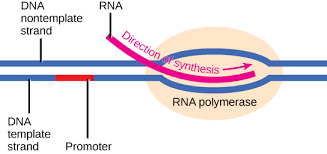
whaat is this
transcription bubble
what are protien coding genes transcribed by in eukaryotes
POL II
What does mRNA do
carries the genetic material from the DNA to the ribosome
what does the ribosome do
translates the message into protien
what direction does rna polymerase move on the template strand
3-5
what direction is the rna transcript built
5-3