pre-malignant lesions + PE
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what are the layers of the epithelium from most superficial to deep
stratum corneum → stratum lucidum →stratum granulosum → stratum spinosum → stratum basale
dysplasia refers to what layer
epithelium
definition of premalignant lesion
morphologically atypical tissues which appear abnormal under microscopic examination, and in which cancer is more likely to occur
definition of dysplasia
the presence of cells of an abnormal type within a tissue, which may signify a stage preceding the development of cancer - premalignant stages
what are the 6 criteria of dysplasia
inc and/or abnormal mitosis
abnormal keratinization
inc nuclear/cytoplasmic ratios
cellular disorientation
hyperchromatic (inc in nuclear staining)
pleomorphism (many different shapes)
what are the stages of dysplasia
mild → moderate → severe → carcinoma in situ
mild dysplasia is limited to…
atypical morphology in the bottom 1/3 of the epithelium
moderate dysplasia is limited to…
atypical morphology up to 2/3 of the epithelium
severe dysplasia is limited to…
atypical morphology above the mid 2/3 to entire thickness of the epithelium
carcinoma in situ is limited to…
atypical morphology of the entire epithelium
management of mild dysplasia
close follow up
moderate dysplasia management
close follow up or surgical removal/laser ablation and close follow up
severe dysplasia management
surgical removal and close follow up
carcinoma in situ management
surgical removal and close follow up
what are the high risk sites of dysplasia and oral cancer
floor of the mouth
lateral/ventral border of the tongue
soft palate
lower lip

out of these, in which direction is it most concerning for malignant transformation potential to oral cancer

which is the management for mild dysplasia:
surgical removal
incisional biopsy
follow-up
laser removal
follow-up
atypical morphology involving the entire thickness of the epithelium:
mild dysplasia
severe dysplasia
squamous cell carcinoma
moderate dysplasia
severe dysplasia
leukoplakia represents what percent of precancerous lesions
85%
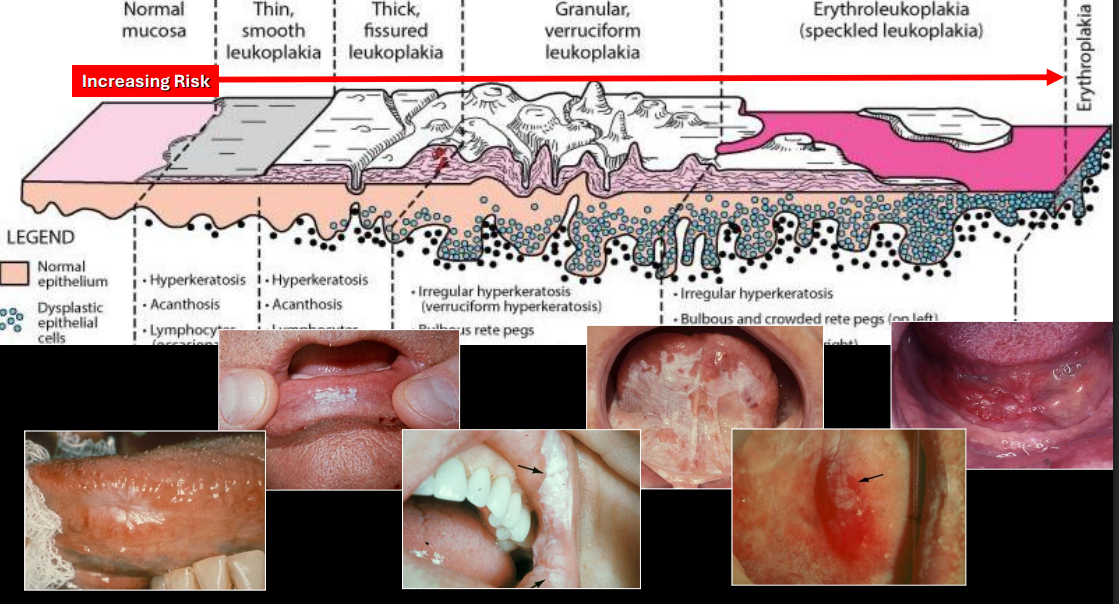
common age affected by leukoplakia
adults, inc w age
common location of leukoplakia
anywhere in oral mucosa; 70% are found on lip, B mucosa, gingiva
tx for leukoplakia
incisional biopsy, follow up, surgical excision, laser
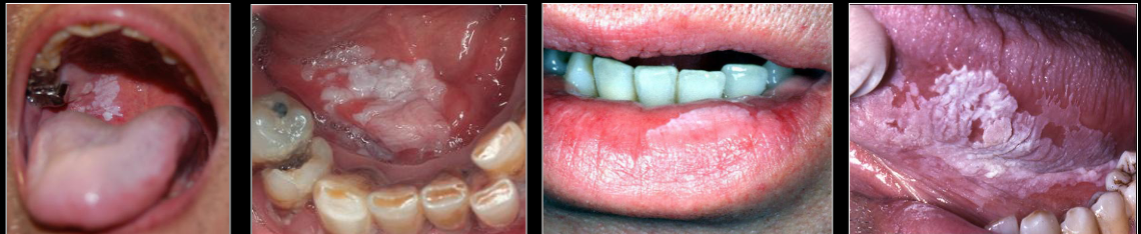
dx
leukoplakia
which is leukoplakia, which is chewing trauma
left leukoplakia
right chewing trauma
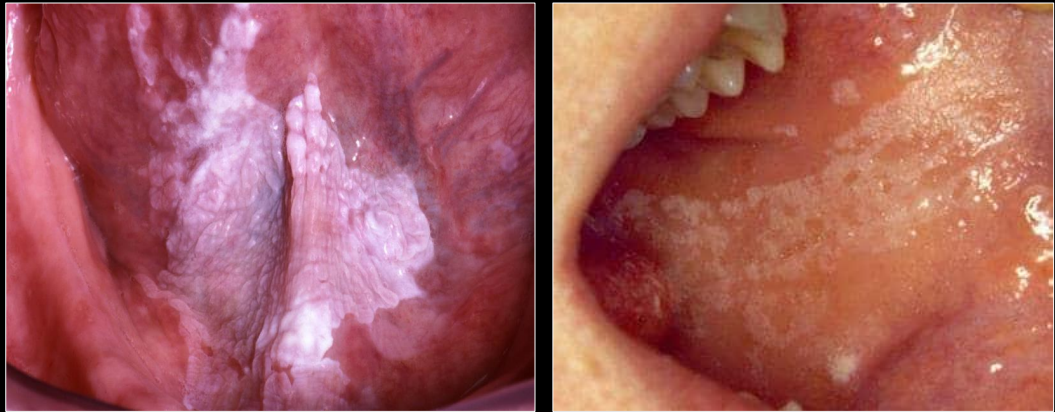
what is proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
very high risk form of leukoplakia; multiple slowly spreading keratotic plaques w rough surface, persistent growth that will eventually develop into dysplasia and cancer
cancer risk of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
50-80%
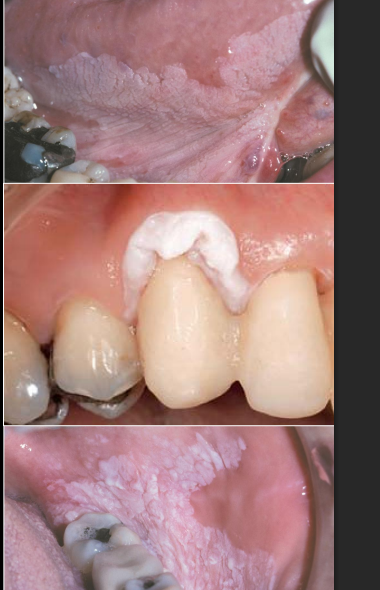
what is leukoplakia
white plaque which will not rub off and which cannot be dx as a specific disease; exclusion of other entities
gender association w proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
strong female predilection (4:1)
common age affected by proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
adults
common location for proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
anywhere but gingiva is highly involved
tx of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
incisional biopsy, follow up, surgical removal, laser
dx
proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
what is erythroleukoplakia “speckled”
one of the highest risks for cancer
color of erythroleukoplakia
red/pink/white patches
how does erythroleukoplakia show on a biopsy
advanced dysplasia
tx for erythroleukoplakia
incisional biopsy, surgical excision, follow up
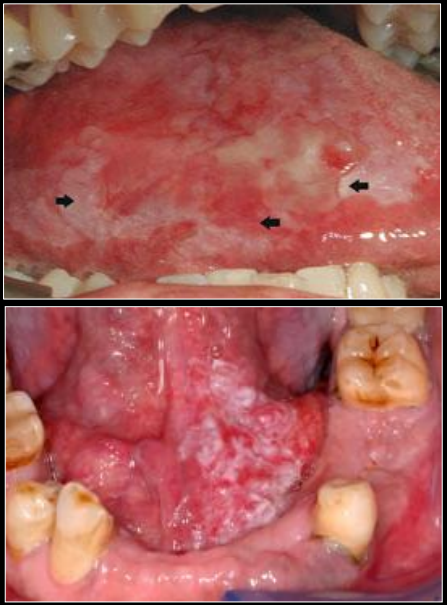
dx
erythroplakia “speckled”
what is erythroplakia
a red patch of plaque that cannot be dx clinically as any other condition
cancer risk of erythroplakia
90% show dysplasia, majority are carcinoma in situ
high risk sites of erythroplakia
lateral/ventral tongue, FOM, soft palate
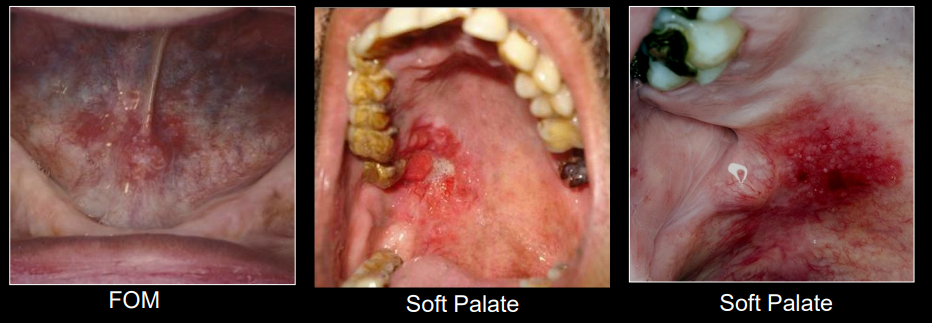
tx for erythroplakia
incisional biopsy, surgical excision, follow up
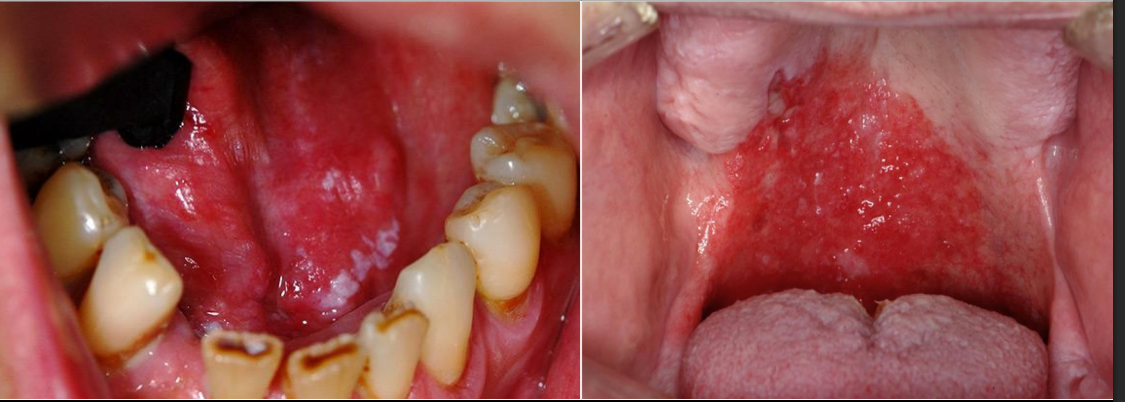
dx
erythroplakia
what is oral submucous fibrosis
chronic, progressive scarring due to betal quid use (tobacco, lime, areca, but, betal leaf)
where is oral mucous fibrosis most commoon
southeast asia and india
onset of oral submucous fibrosis
takes years to develop
cancer risk of oral submucous fibrosis
19x more likely
clinical manifestations of oral submucous fibrosis
trismus, fibrous bands (buccal, soft palate), stomatopyrosis (general oral burning from spicy food)
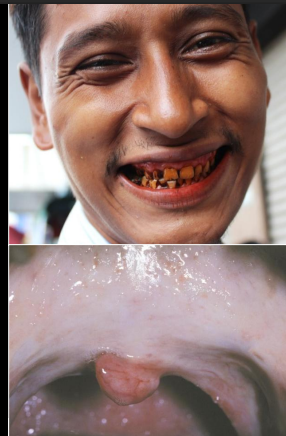
tx for oral submucous fibrosis
intralesional steroid injection mild lesion, surgical splitting of fibrous bands, physical therapy lifelong, close clinical follow up
what is actinic cheilosis
premalignant alteration of the lower lip
causes of actinic cheilosis
UV light exposure
common gender affected by actinic cheilosis
M>F 10:1
common age affected by actinic cheilosis
>45 yrs
prevalence of actinic cheilosis
more common is rural areas
cancer risk of actinic cheilosis
2-6% develop into cancer if not removed
pleomorphism:
abnormal # of cells
abnormal architecture
abnormal shape and size of cell
abnormal miotic figures
abnormal shape and size of cell
tx for actinic cheilosis
incisional biopsy, surgical excision
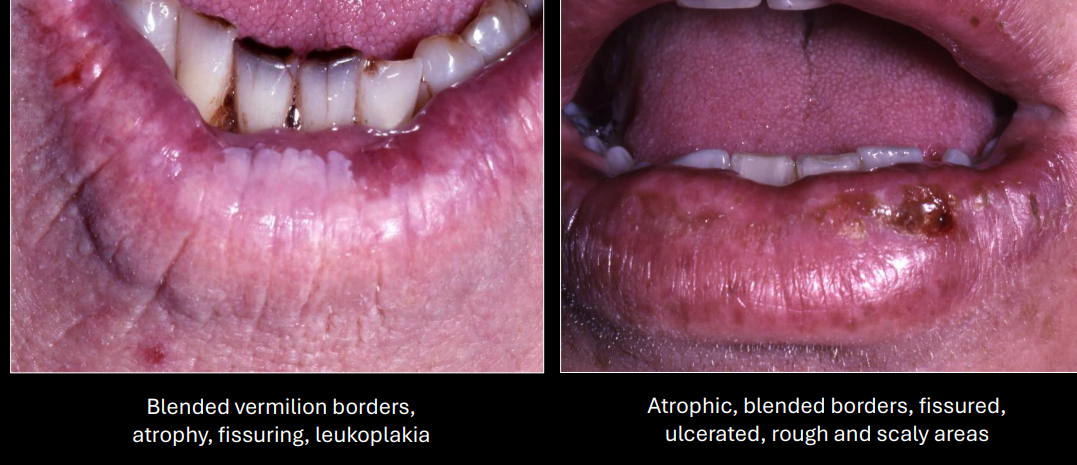
clinical manifestations of actinic cheilosis
blended vermillion borders, atrophy, fissuring, leukoplakia, ulcerated, rough and scaly area
what is actinic keratosis
a premalignant skin lesion
what can cause actinic keratosis
long-term sun exposure
clinical manifestations of actinic keratosis
rough, scaly patches on face, ears, neck, scalp, and other areas
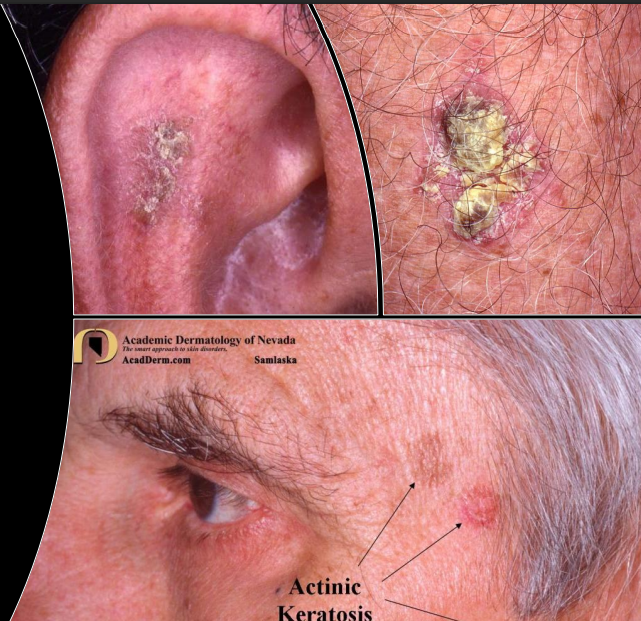
cancer risk for actinic keratosis
5-10% can become cancer
tx for actinic keratosis
biopsy and surgical excision
what is smokeless tobacco keratosis
6% in US are due to chewing tobacco
common location for smokeless tobacco keratosis
mandibular vestibule
what is the controversy w smokeless tobacco keratosis
precancerous white macule
clinical manifestations smokeless tobacco keratosis
leathery white fissured plaque or fissures, gingival recession
what can inc caries risk for a pt w smokeless tobacco keratosis
if sweeter is added
tx for smokeless tobacco keratosis
stop habit → keratosis will be gone in 2-4 mo
when would you do an excisional biopsy
complete surgical removal; small lesions <2 cm; appears benign on clinical
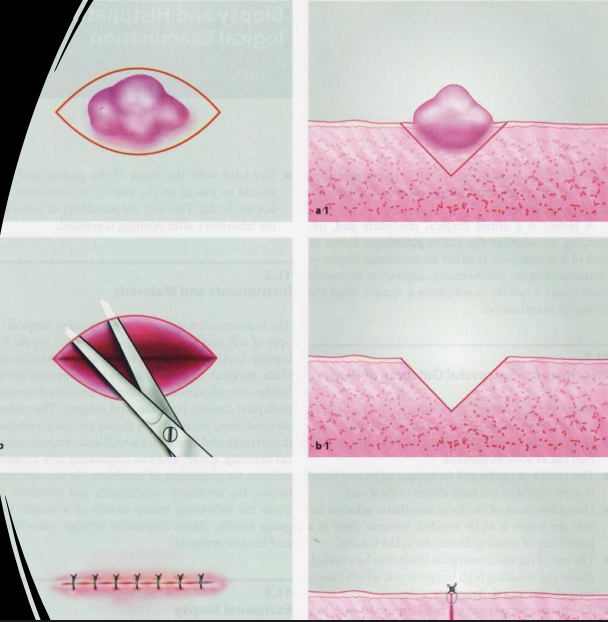
what lesions would you do an excisional biopsy
fibroma
mucocele
lipoma
papilloma
when would do an incisional biopsy
lesions are larger than 2 cm
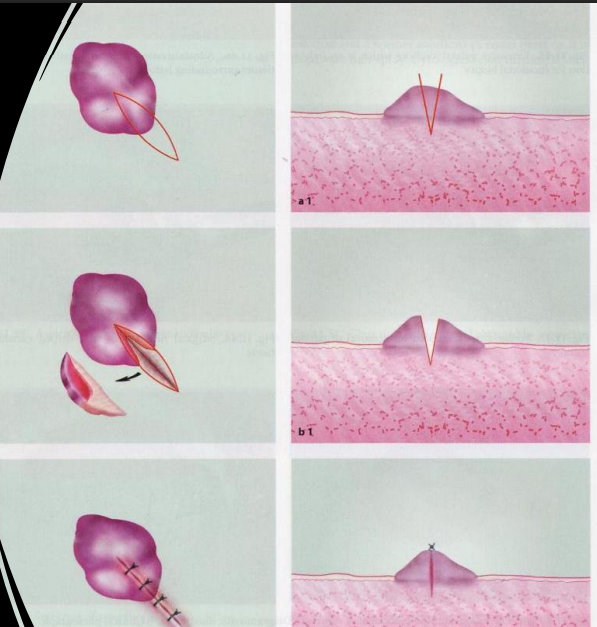
what type of lesions would you do an incisional biopsy on
leukoplakia/erythroplakia
ulcer
SCC
tumor (benign or malignant)
lichen planus or other autoimmune conditions
what are adjunct tools and what do they tell us
brush
velscope
unreliable
false results
does not provide a dx
which of the following is indicated for an excisional biopsy:
fibroma
squamous cell carcinoma
leukoplakia
actinic cheilosis
fibroma
which of the following is a clinical term used to describe a white premalignant lesion:
leukoplakia
actinic cheilosis
erythroplakia
dysplasia
leukoplakia
which is a common site for proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
dorsum tongue
soft palate
buccal mucosa
gingiva
gingiva
all of the following are premalignant lesions EXCEPT:
erythroplakia
tocacco pouch keratosis
actinic lentigo
submucous fibrosis
actinic lentigo
which of the following is NOT true regarding actinic keratosis:
due to sun exposure
occurs on the skin
can become cancerous
a smooth white lesion
a smooth white lesion
which is FALSE regarding erythroplakia:
most often are high dsyplasia or cancer
a red patch that cannot be dx clinically as any other condition
high-risk site is floor of the mouth
Excisional biopsy is indicated
excisional biopsy is indicated
all of the following are high risk sites for premalignant cancer EXCEPT:
FOM
soft palate
dorsum of tongue
lower lip
dorsum of tongue