LS 1-4
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
when the environment (nature) chooses (selects) which things survive
what is natural selection?
when the environment changes, those that survive and reproduce pass on genes that are suitable for that environment, this leads to significant changes in the populations over time
how does life change through time?
variety, advantage, inherited traits, reproduce more
what are the 4 conditions necessary for populations to change?
when there are different characteristics within the population
what is variation in natural selection?
when environmental pressure makes it easier for some individuals to survive over others
what is an advantage in natural selection?
a change in the environment that has a significant impact on living things
what is environmental pressure?
the advantaged/disadvantaged characteristics must be able to be passed down to offspring
what is inheritance in natural selection?
the individual with the advantage reproduce more than the individual that do not have the advantage, OR the ones with the disadvantage reproduce less
what does reproduction's role in natural selection?
the darker moth population would decrease, and the lighter colored moth population would increase
imagine there is a population of light and dark moths in a forest: what would happen to the populations if all of the dark trees are cut down?
the short-toed lizard population will increase, the long-toed lizard population will decrease
A species of lizard lives on a rocky island. Some have long toes that help them grip rocks, while others have short toes that are better for walking on smooth surfaces. If a volcanic eruption covers most of the rocks with smooth lava, what might happen to the lizard population over generations?
the fish population with mouths suited for catching small prey will increase, and the fish with mouths adapted for eating algae will decrease
In a lake, some fish have mouths adapted for scraping algae off rocks, while others have mouths suited for catching small prey. If pollution kills most of the algae in the lake, how might the fish population change over time?
birds with small beaks will decline in population, while birds with larger, stronger beaks will increase in population over time
A population of birds eats either small, soft seeds or large, hard seeds. Some birds have small beaks suited for soft seeds, while others have large beaks that can crack hard seeds. If a drought kills off plants that produce small seeds, how might this impact the bird population?
heredity
The passing of genetic information from parents to offspring
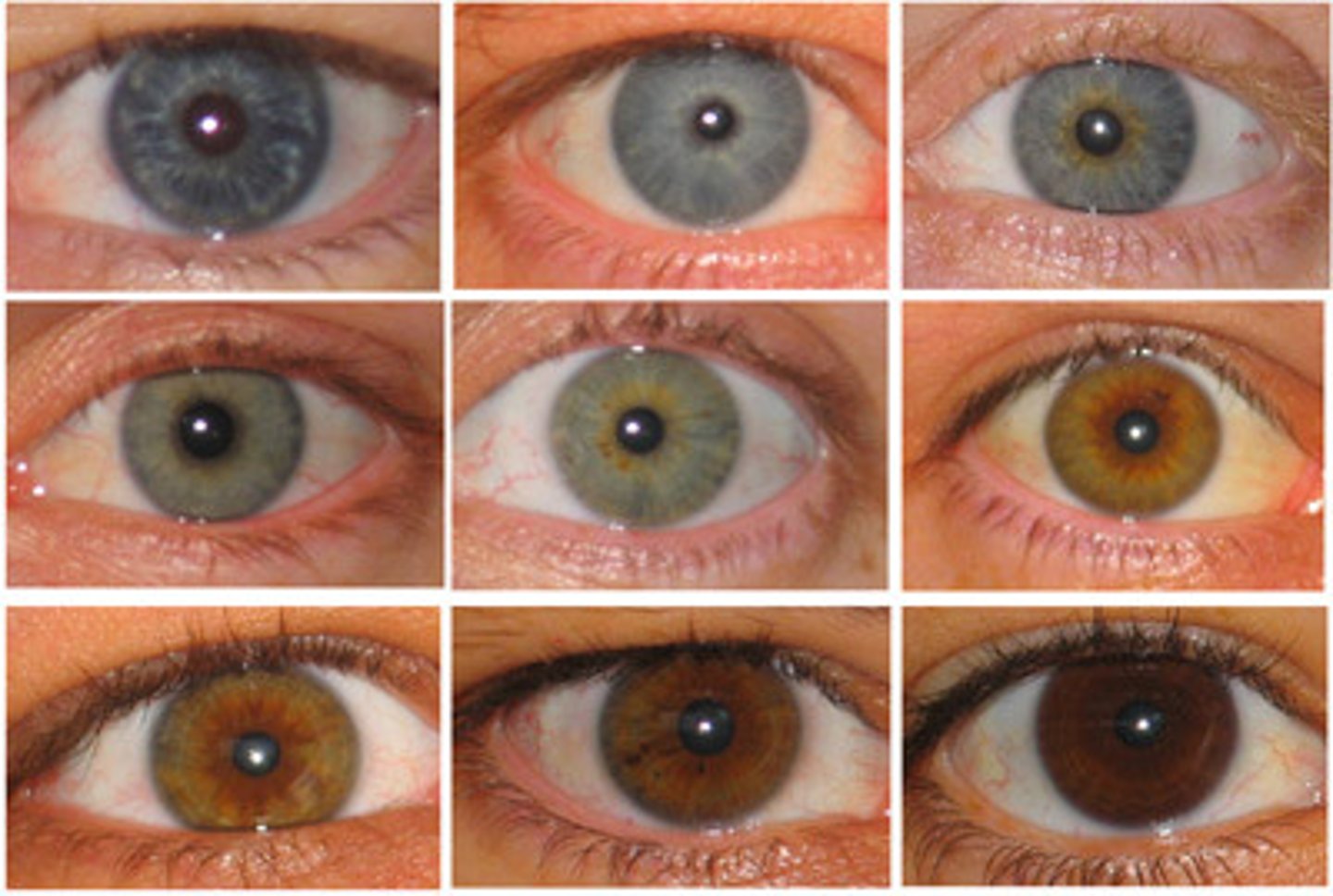
trait
A specific characteristic that can vary from one individual to another
ie. eye color, hair color, height
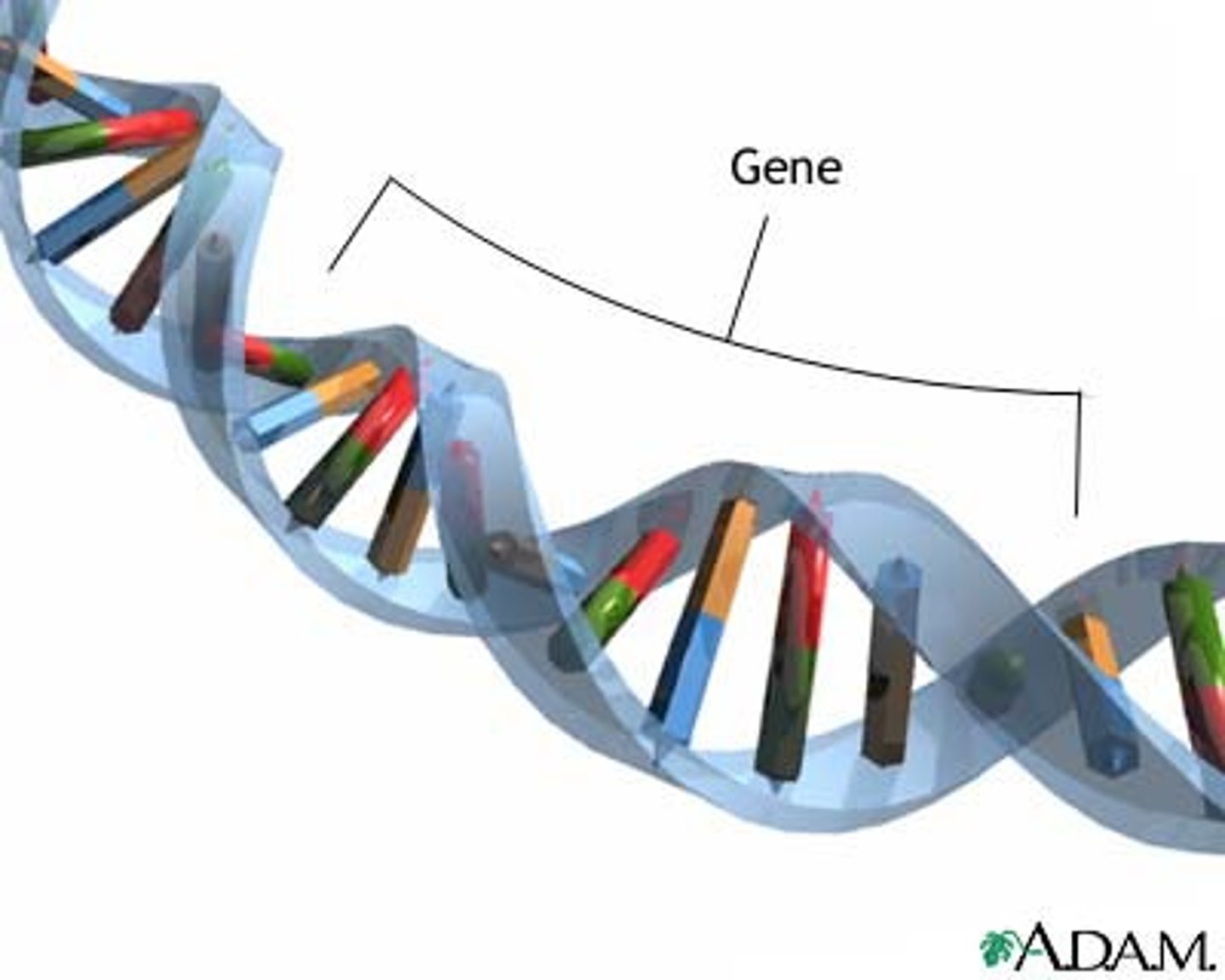
gene
Basic unit of heredity, a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building proteins that form an organism's traits
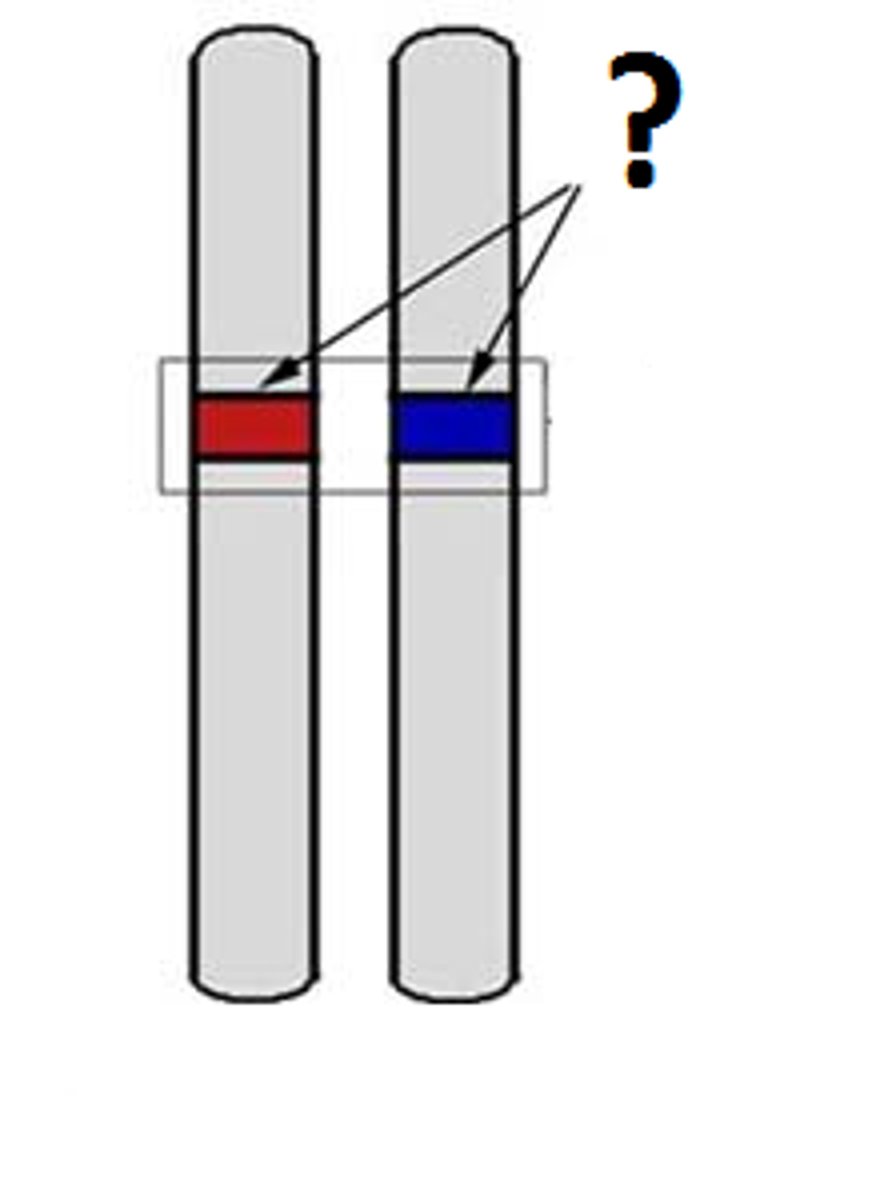
allele
A version of a gene, can determine a specific trait, represented as a individual letter
Ie. white fur or no fur
Dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present. Represented with UPPERCASE letters.
Ie. the white fur/white bead

Recessive allele
An allele that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present. Represented with lowercase letters. (ie. the no fur trait/red bead)
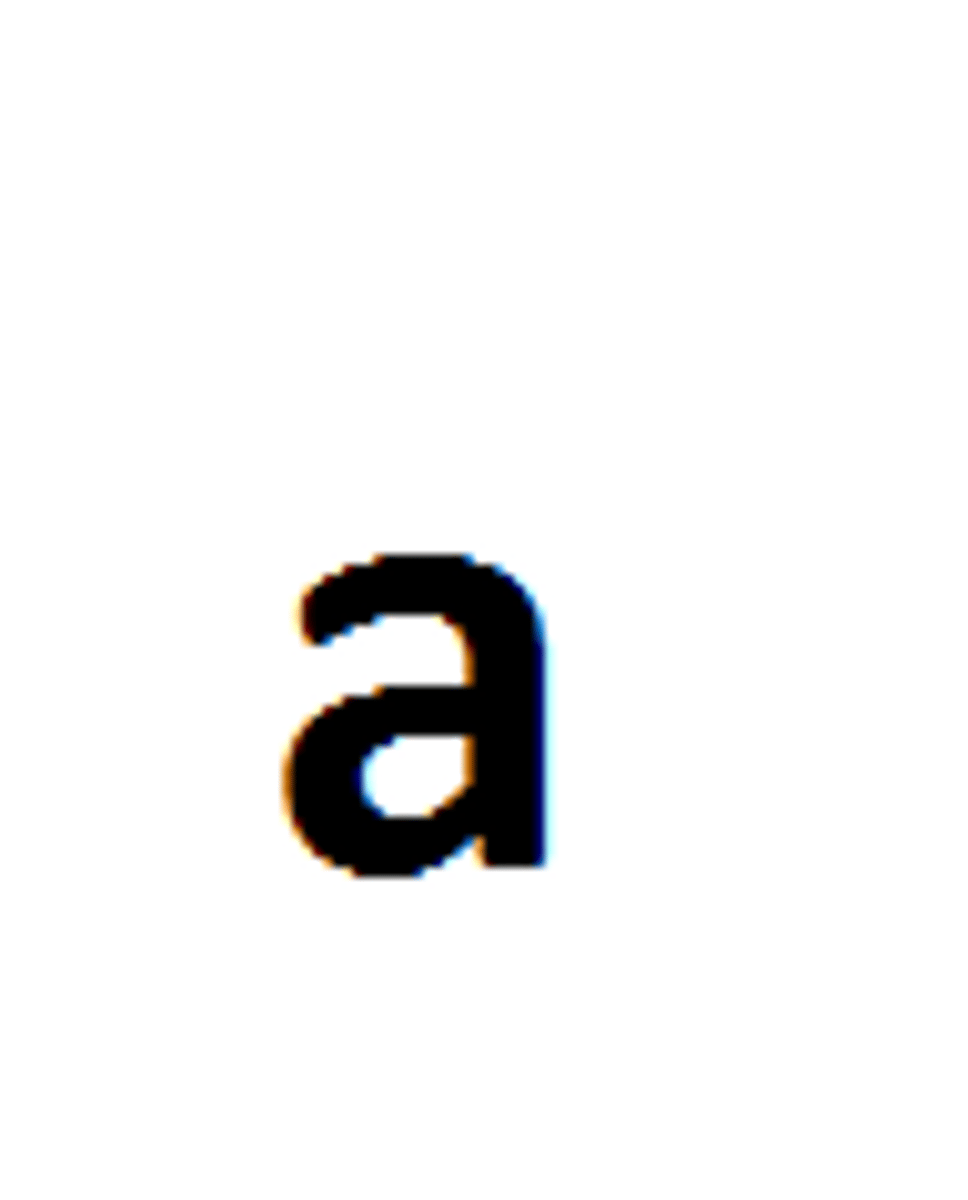
Genotype
The combination of alleles inherited for a particular gene, written as a pair of letters Example: WW, for two white fur/beads
BB, for two blue flower alleles
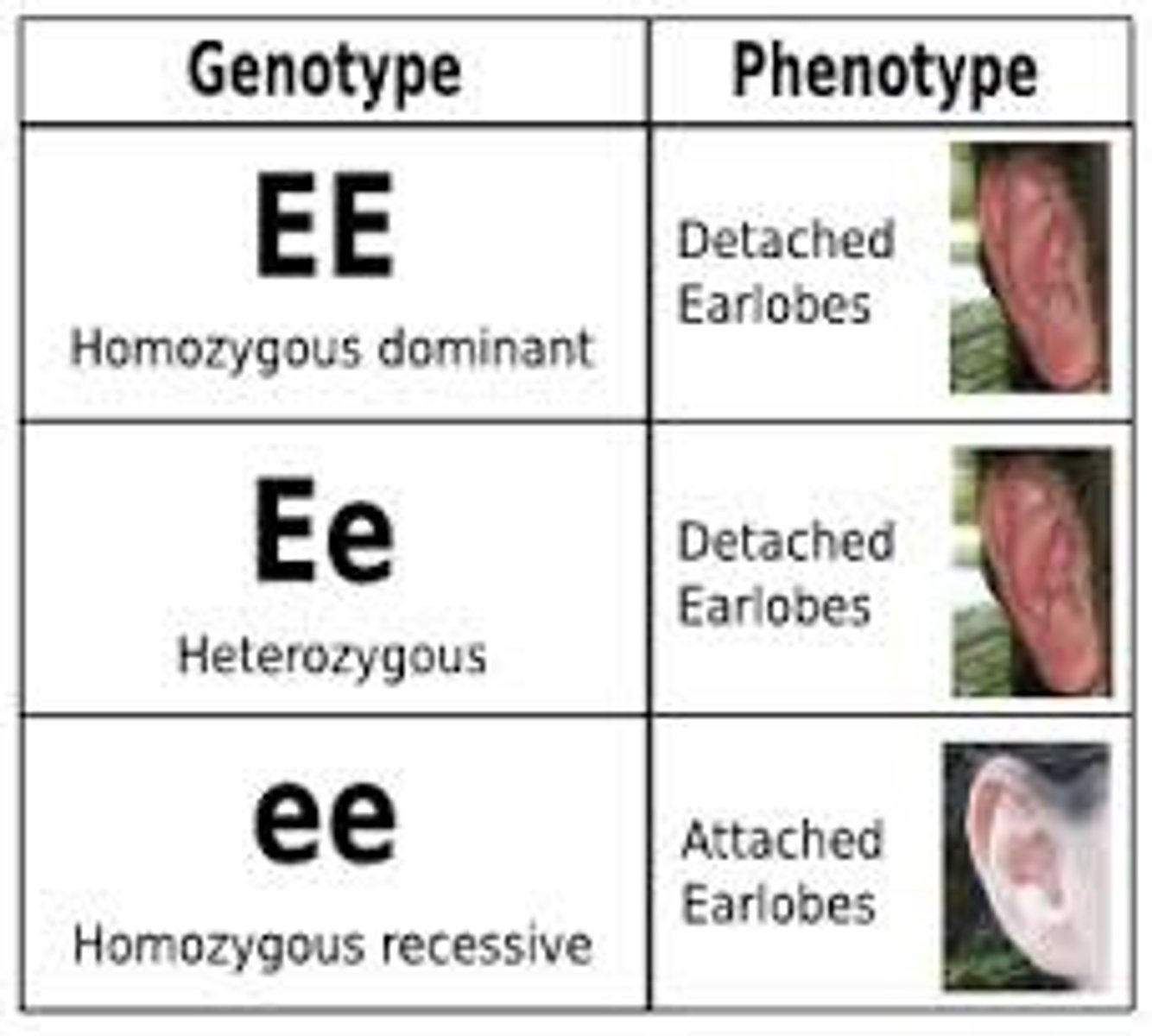
Phenotype
The physical expression (observable trait) due to inherited alleles. Example: Blue flower color
Homozygous
To have two of the same alleles for a gene
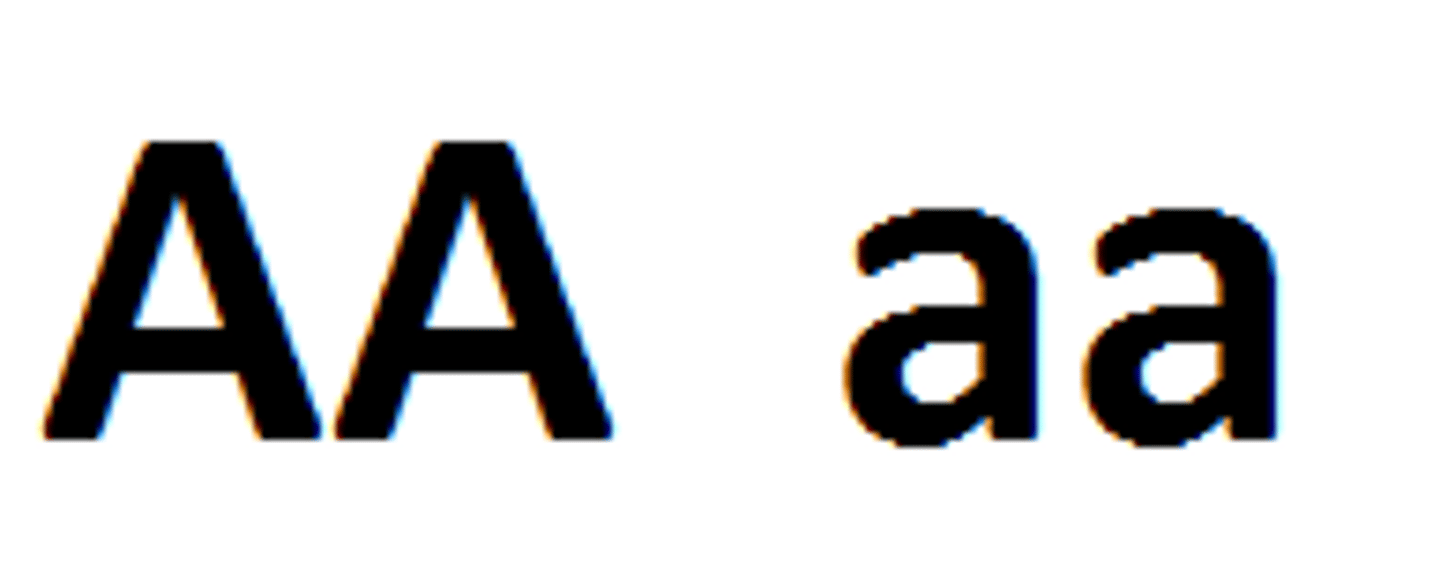
Heterozygous
To have two different alleles for a gene

Punnett Squares
genetic diagrams that are used to work out the probability (likelihood) of possible offspring genotypes.
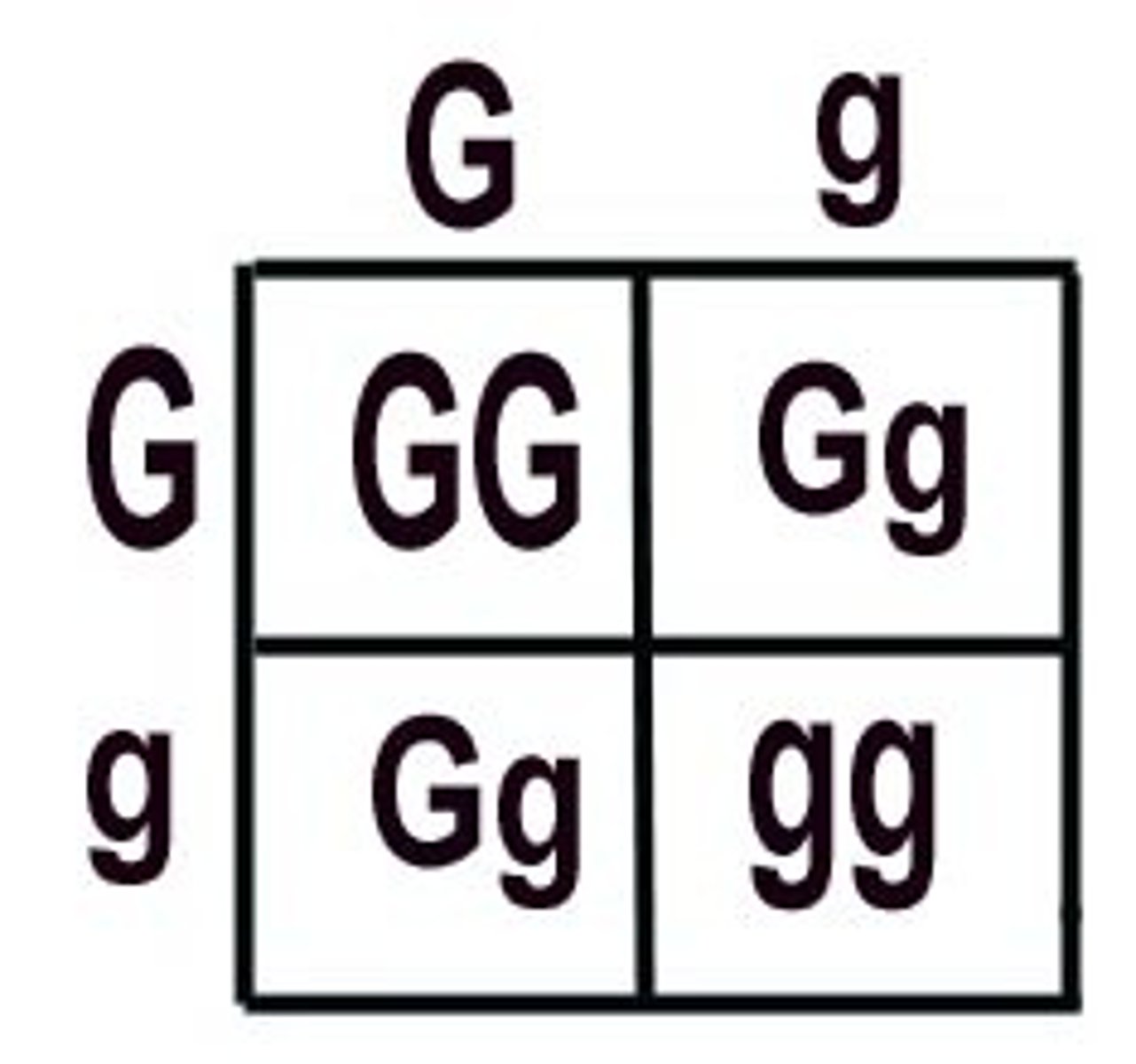
Purebred
another name for a homozygous trait in an organism that has two of the SAME alleles for a gene (XX or xx)
hybrid
Another name for a heterozygous trait in an organism that has two different alleles for a trait
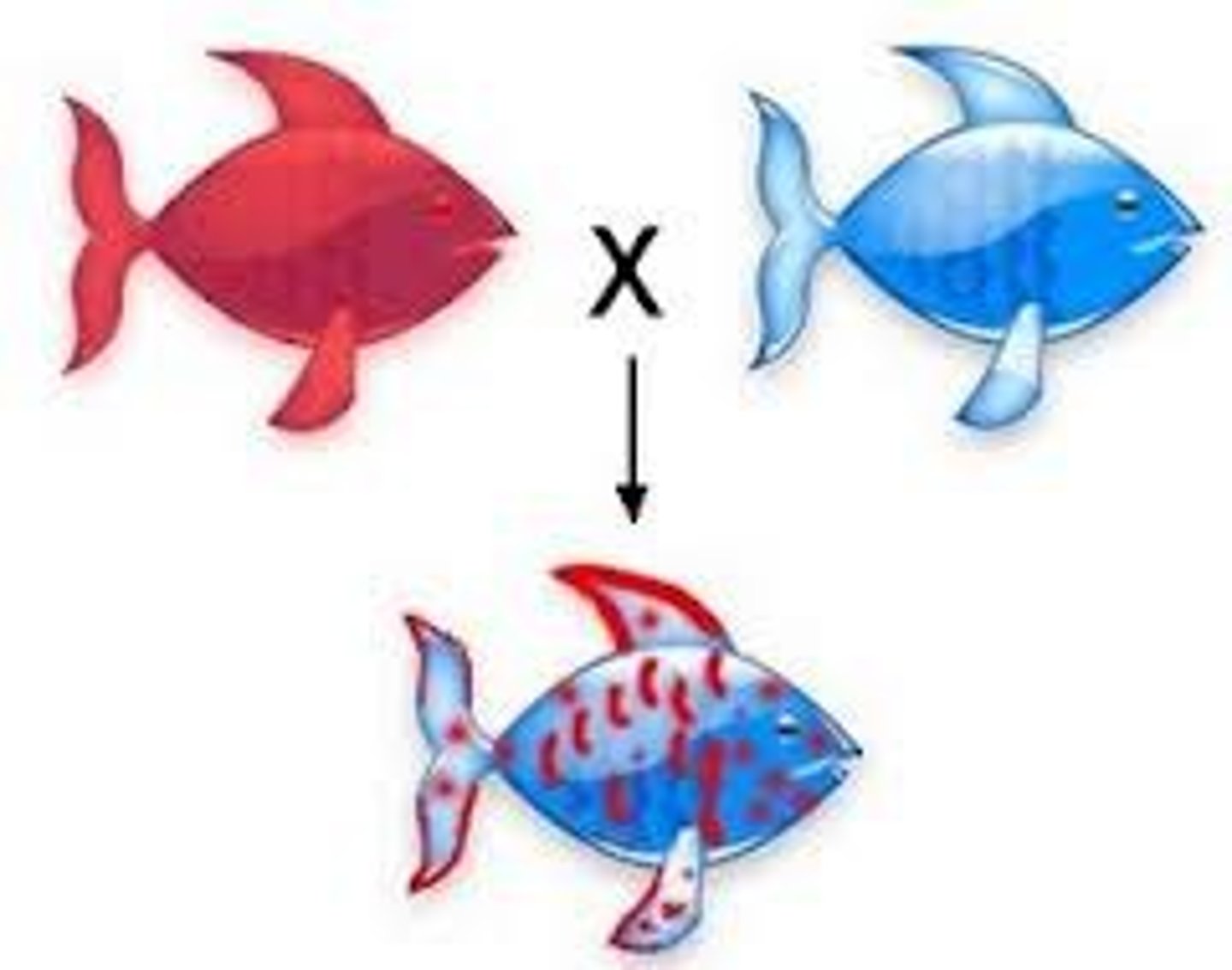
codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are dominant and are fully expressed
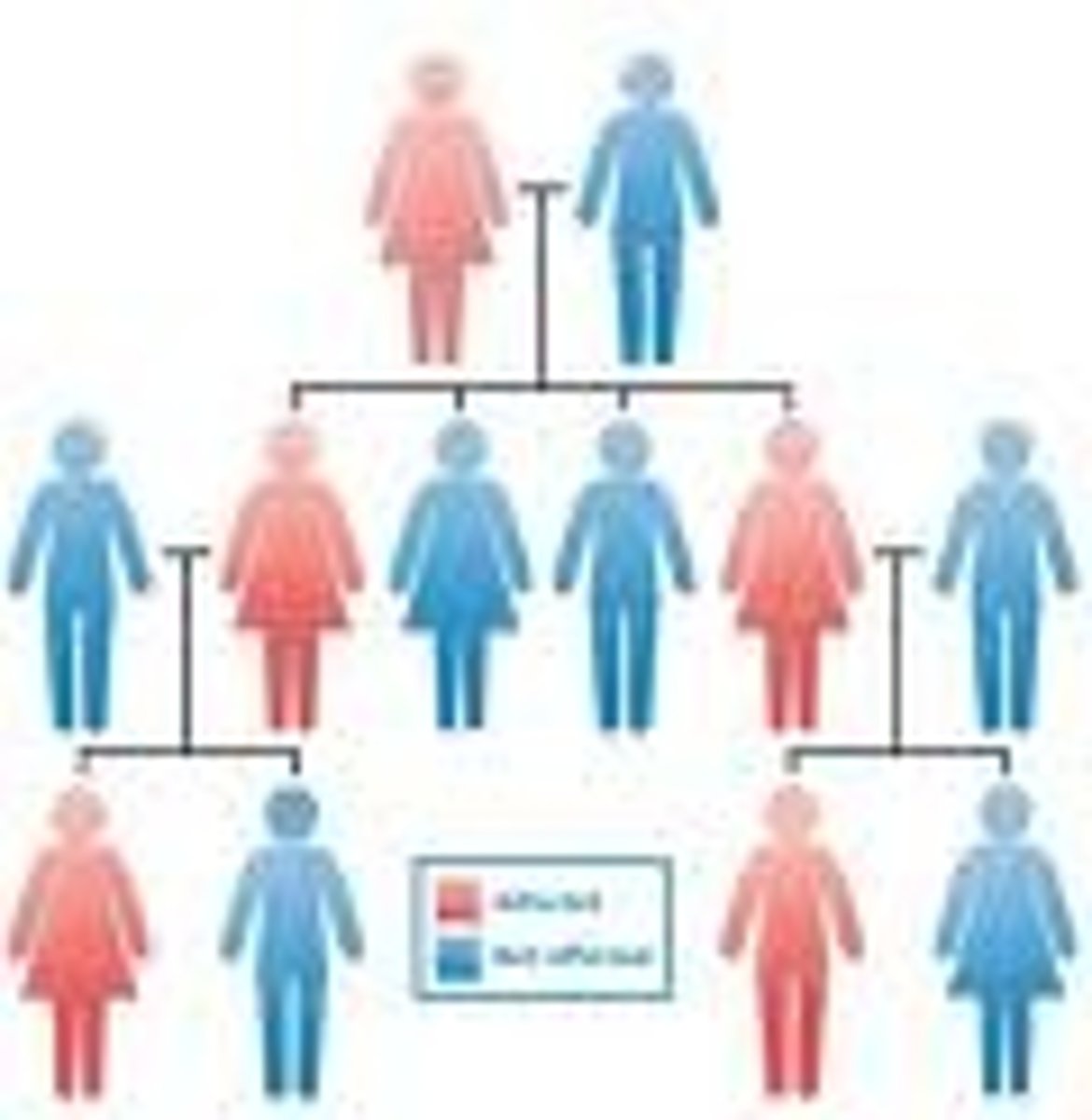
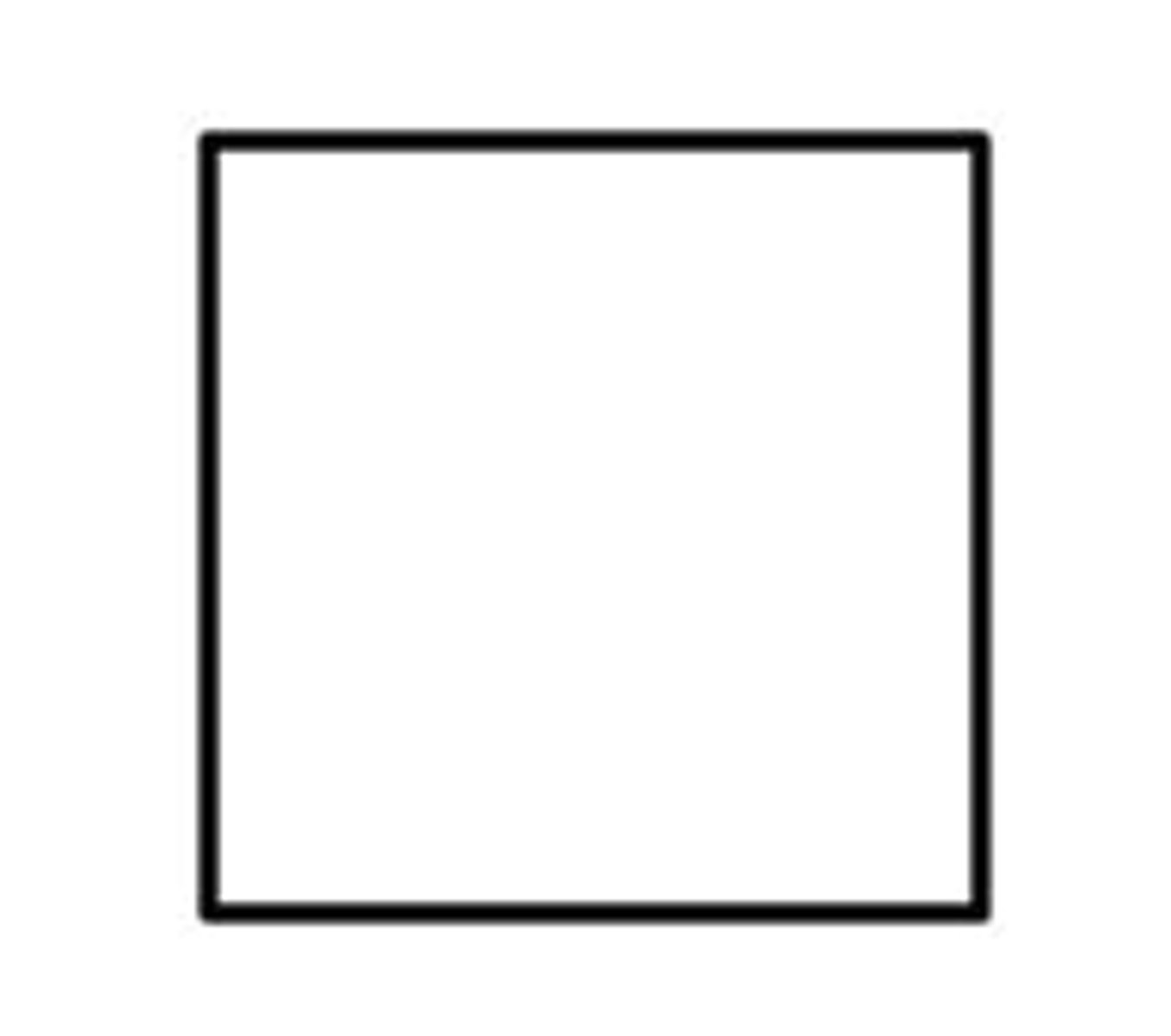
square
what shape represents males on a pedigree?
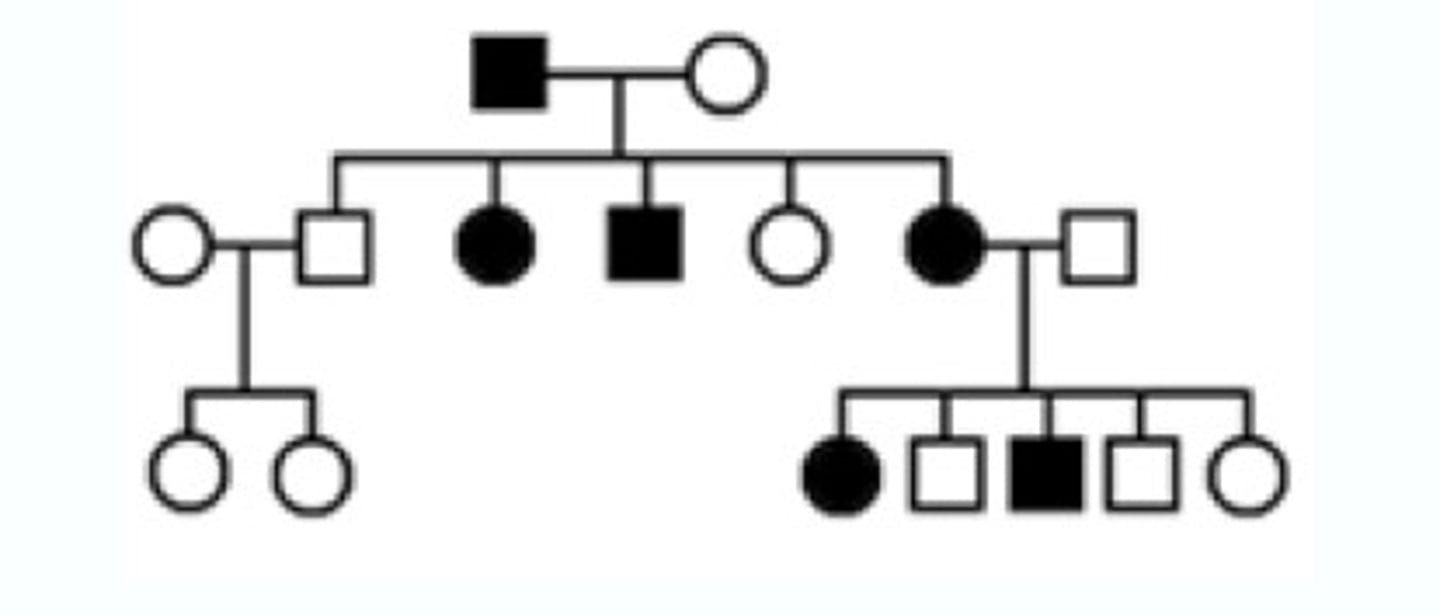
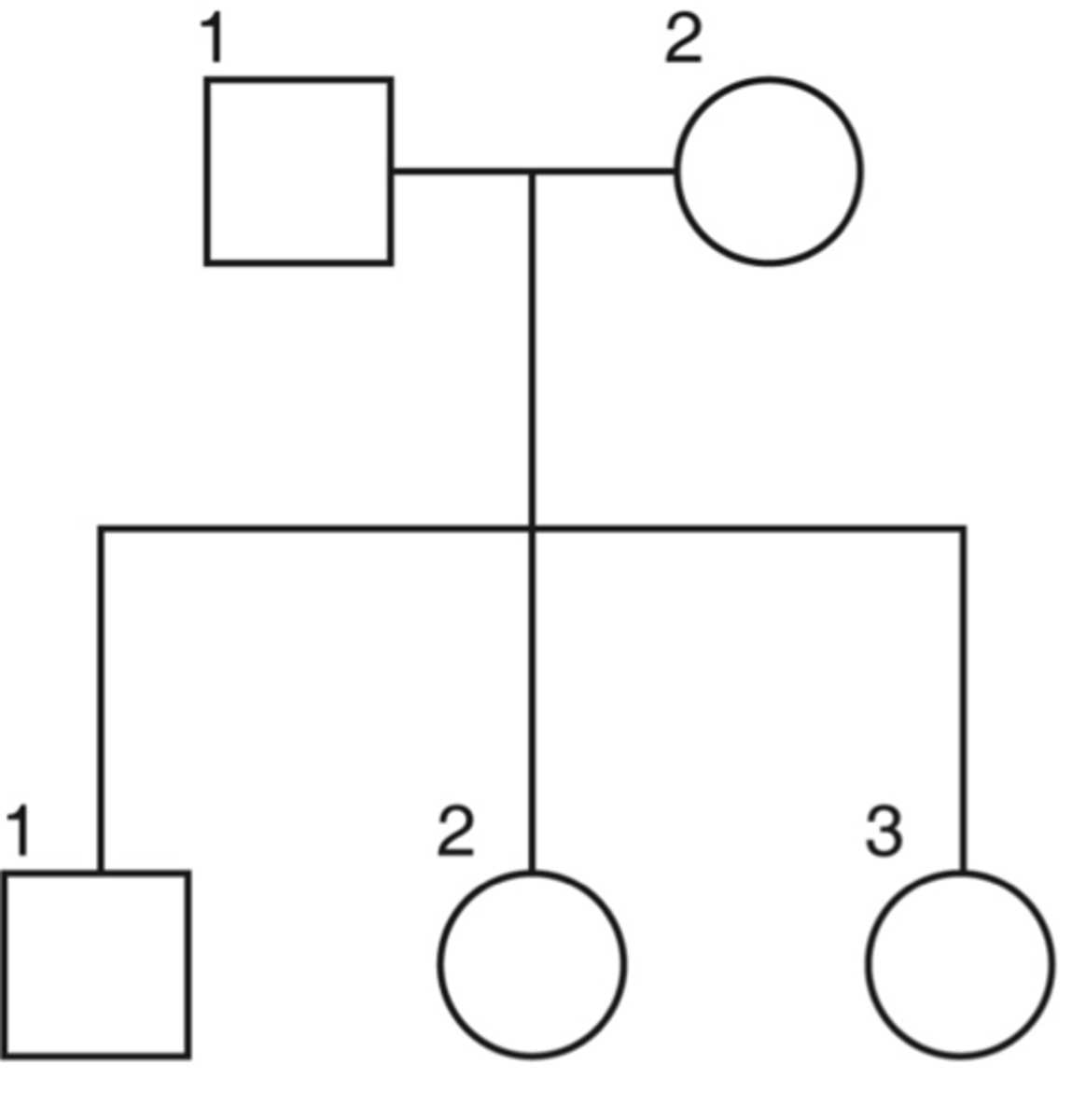
pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
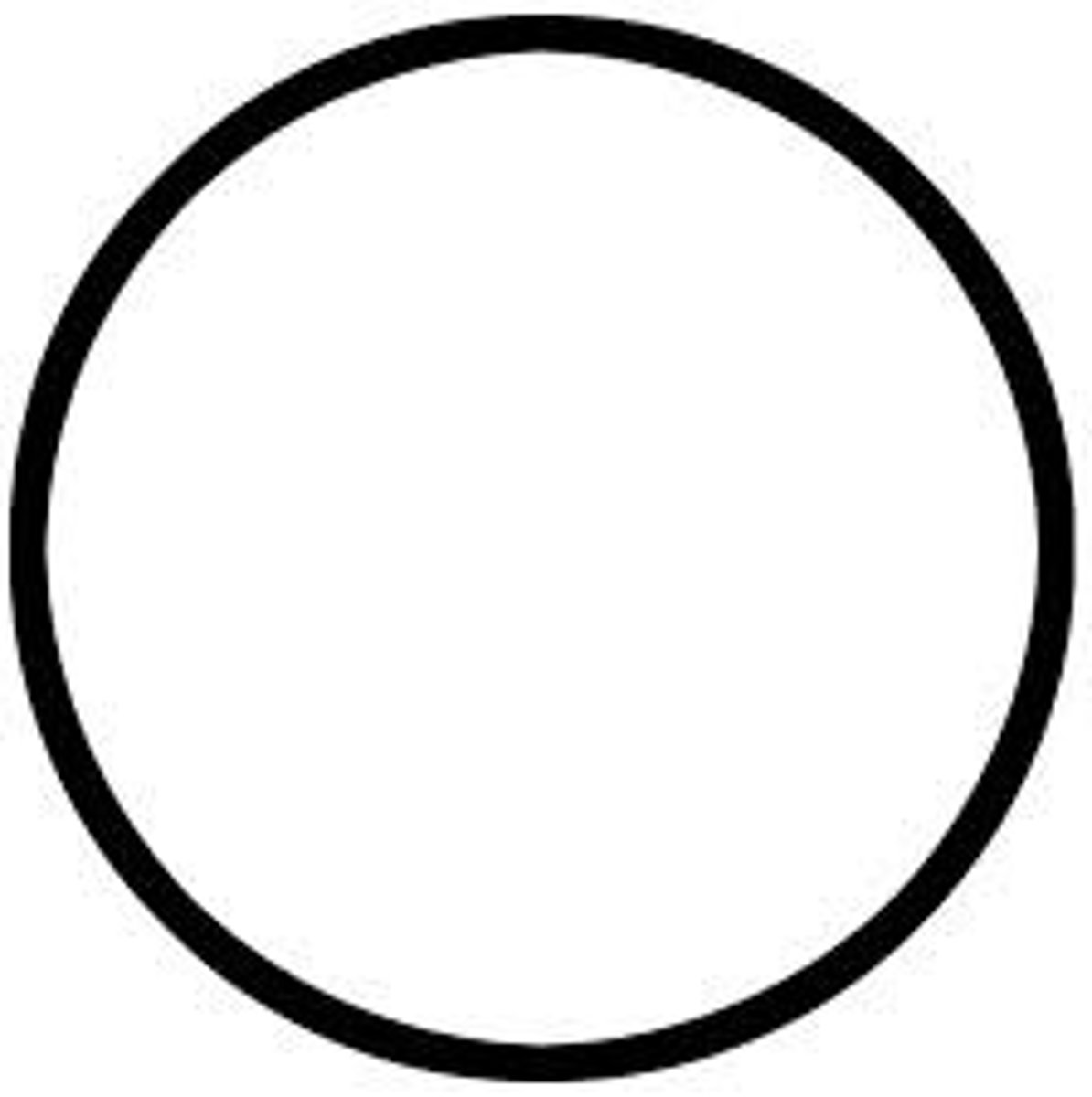
circle
what shape represents females on a pedigree?
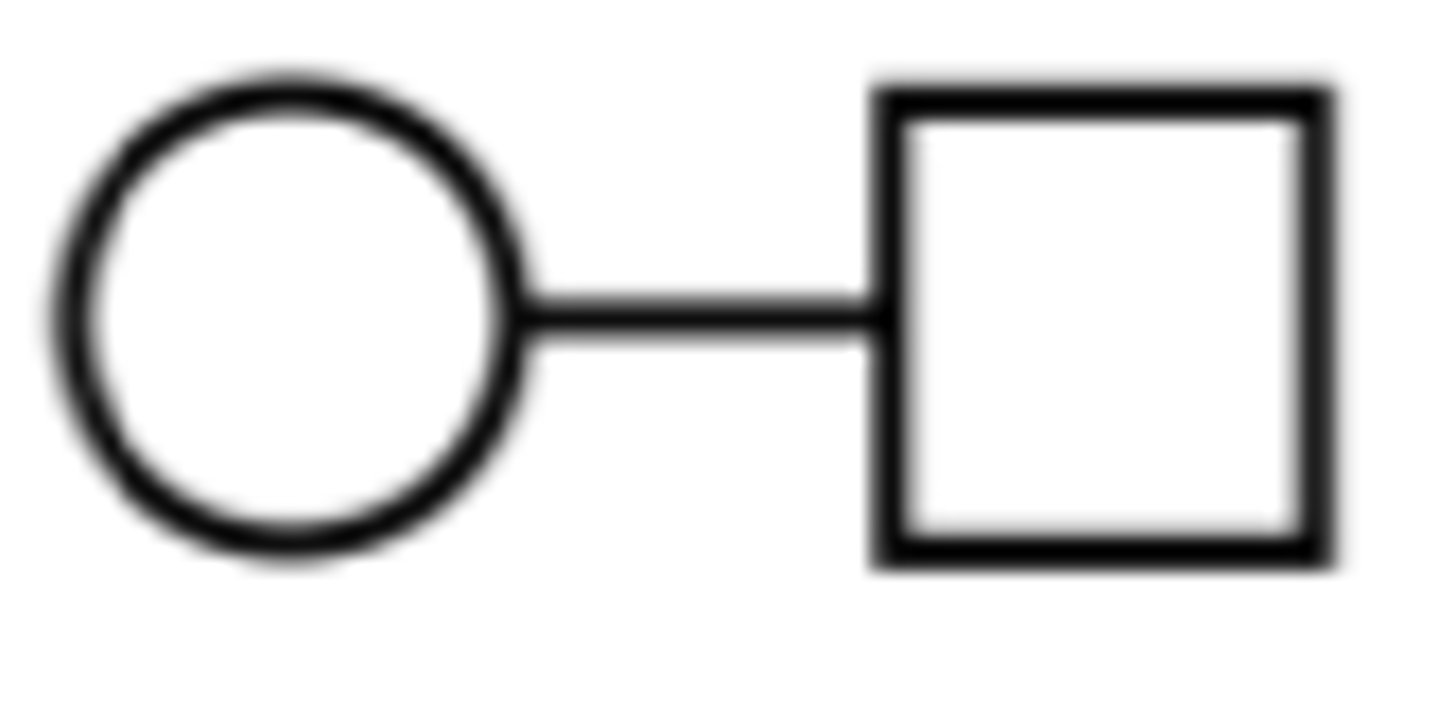
a horizontal line connecting a male and female
what represents a marriage/union on a pedigree?
a vertical line connected to a marriage/union
what represents children on a pedigree?
shaded symbols
what represents individuals that have a specific trait we're analyzing on a pedigree?

carrier
someone who is heterozygous, they “carry” the recessive trait but don’t show/express it