Pharmacology of Oral Contraceptives
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
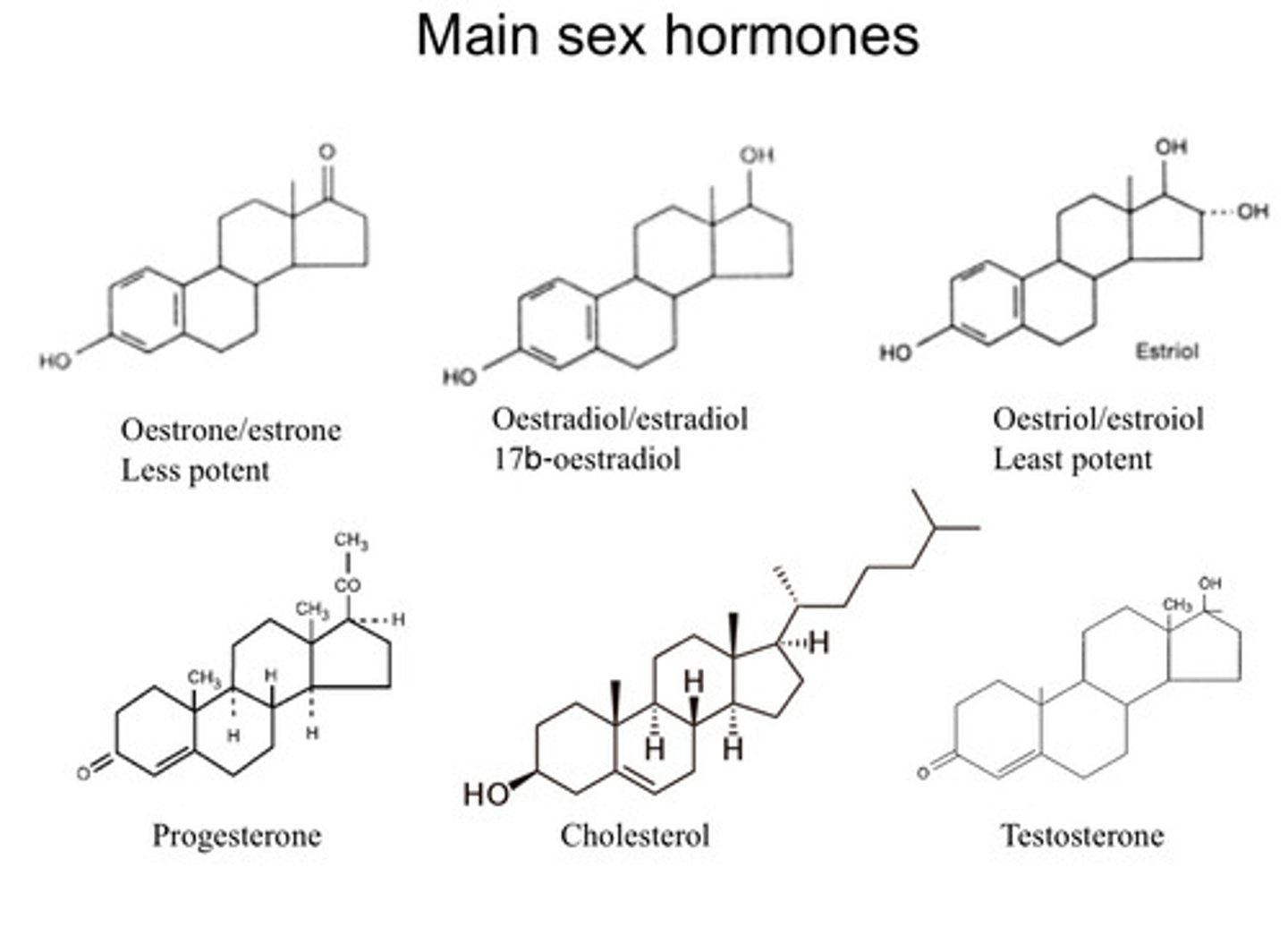
What are the main sex hormones?
- Androgens can be converted to oestrogens
- Androgens come from Pregnenolone
- Basic building block of steroid hormones is Cholesterol
- Enzyme which converts cholesterol to Pregnenolone =
20, 22 desmolase
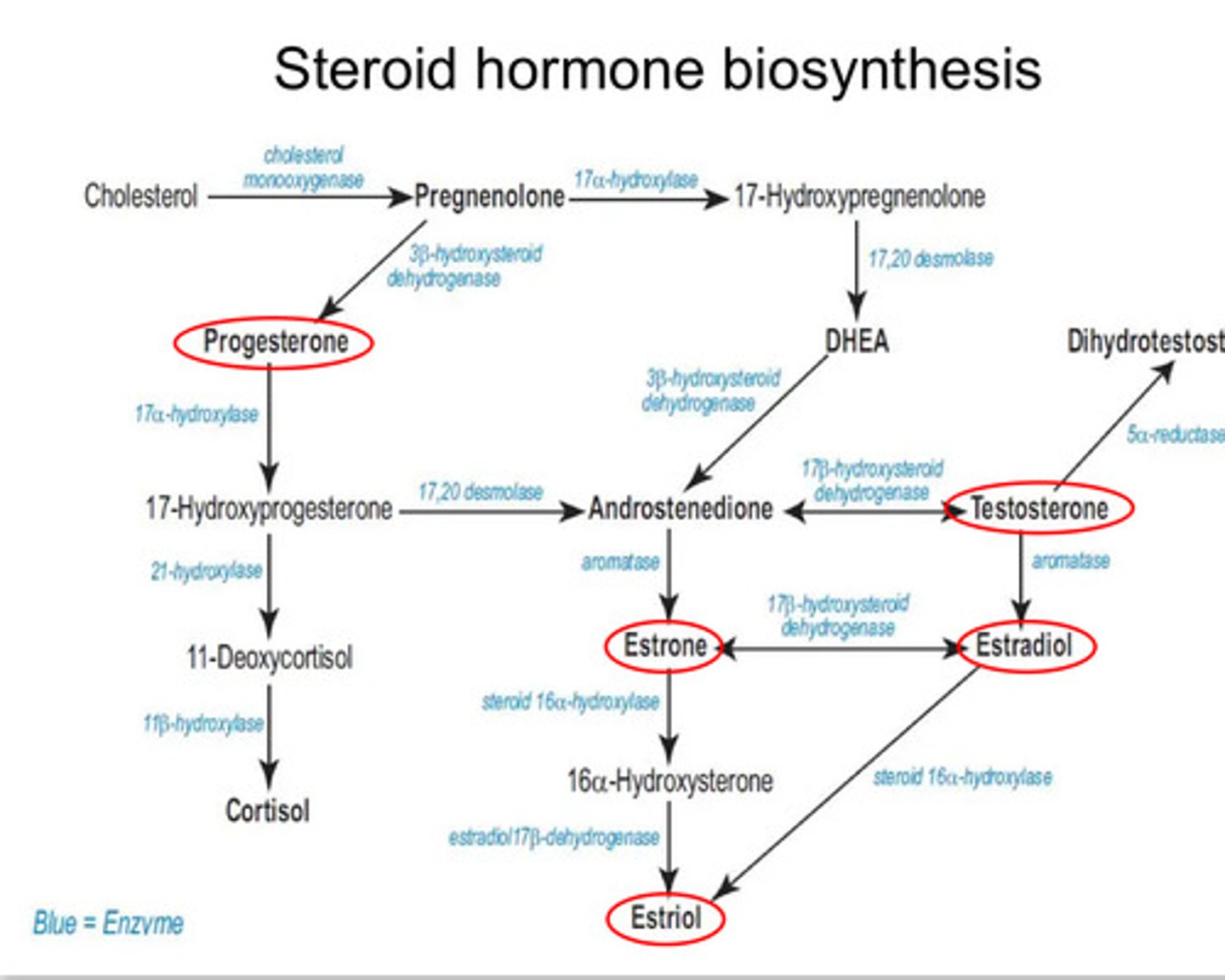
Steroid hormone biosynthesis flow chart
Remember the top row and be familiar with it but don't have to memorise everything
Which hormones prevent the release of FSH and LH?
Oestrogen and progesterone
What are glycoprotein hormones? what do they include - give examples? What is the purpose of the alpha chain and the beta chain?
- Include LH, FSH, hCG and TSH
- All GHs consist of alpha and beta chains
- Alpha chain is common to all four and beta chains are
responsible for specificity
Note:
- LH, FSH and TSH from anterior pituitary and hCG from placenta
What does sustained and pulsatile release of GnRH cause?
Pulsatile: promotes LH and FSH release
Sustained: inhibits LH and FSH release
How do LH and FSH act on the reproductive hormones?
LH and FSH induce testosterone, oestrogen and progesterone which feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary
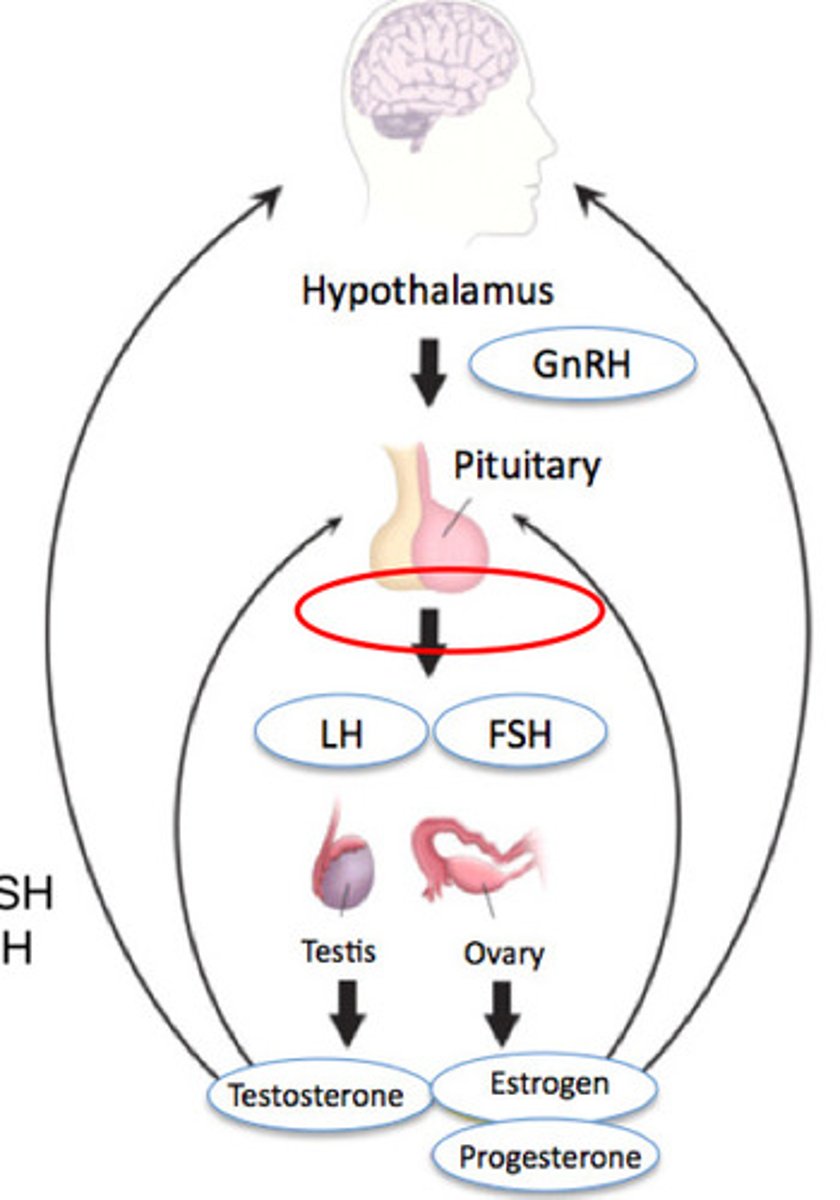
How are female hormones produced?
- Hypothalamus releases GnRH
- GnRH acts on the pituitary to release LH/FSH
- LH acts on thecal cells to make androgens (via
conversion of cholesterol) from Pregnenolone
- These androgens act on granulosa cells = low oestrogen which feeds back to on hypothalamus
and pituitary = Low oestrogen level restricts more LH/FSH
- Granulosa cells make small amounts of oestrogen which increases oestrogen = positive feedback =hypothalamus and pituitary produce more LH/FSH
- More LH/FSH made = LH surge triggers ovulation
- Corpus luteum (through FSH/LH effects) continues to make oestrogen and progesterone until their levels fall which stops GnRH production and all hormone levels return to basal level
Which ovarian cells do LH cells act on to make?
LH acts on thecal cells to make androgens from pregnenolone
Which ovarian cells do FSH act to make?
FSH acts on granulosa cells which turn androgens to oestrogen
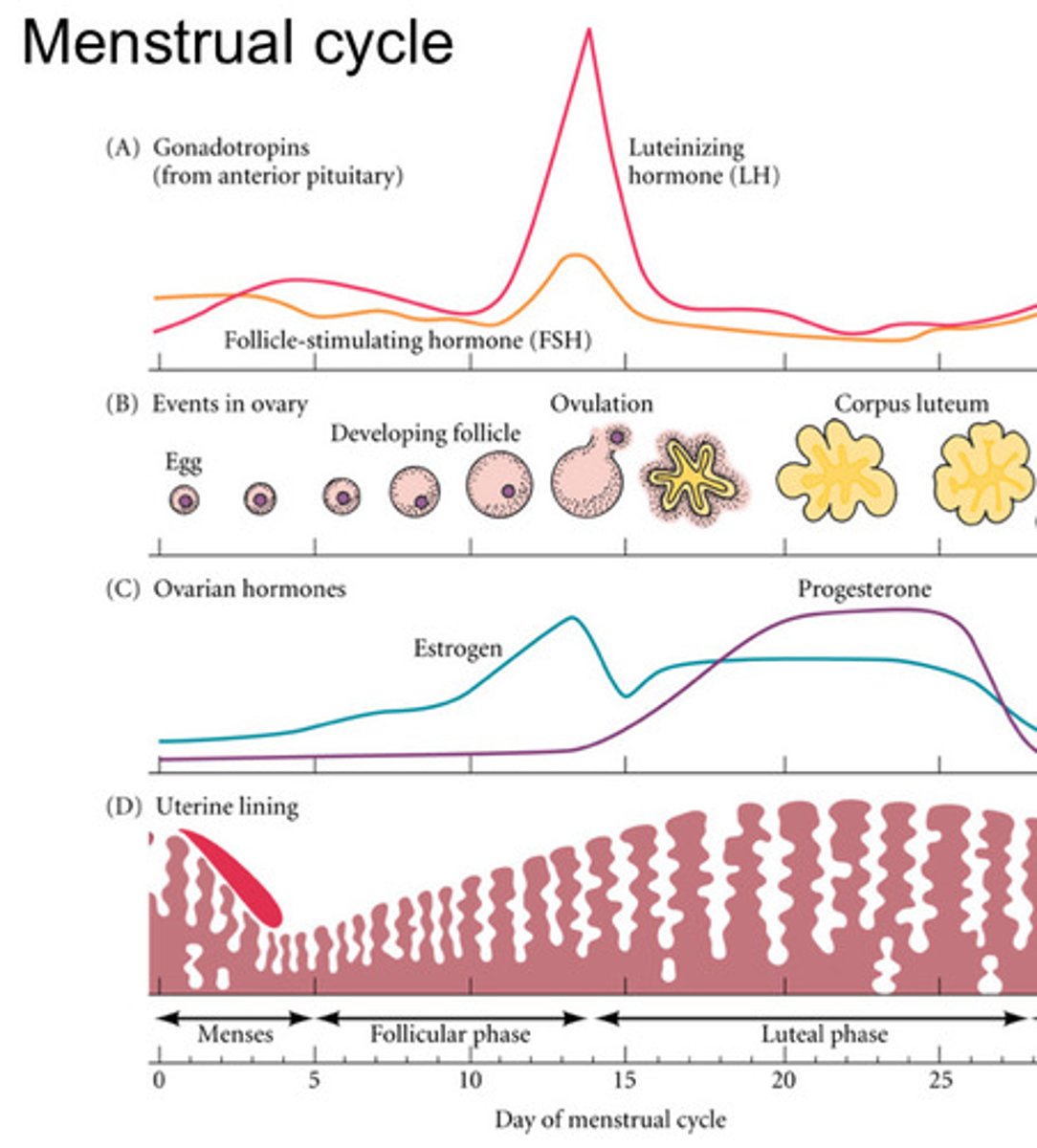
Menstrual cycle Diagram
What is the Steroid receptor activation mechanism
See LECTURE ON THIS
How does the combined oral contraceptive pill work?
- Oestrogen + Progestogen
(emulate late luteal phase processes)
- 3 weeks on 1 week off
- Normal menstruation usually starts fairly quickly after cessation
- Oestrogen stops FSH secretion which stops follicular development
- Progestogen stops LH secretion which stops ovulation
- Oestrogen and progestogen alter the endometrium to discourage implantation
- Cervical mucus more hostile to discourage implantation
What type of oestrogen and progestins (synthetic progesterones) is used in COC?
-Oestrogen
Usually ethinylestradriol (20-35mg)
Sometimes mestranol
-Progestin (synthetic progestogen)
First/Second generation norethisterone or levonorgestrel
Third/Fourth generation
desogestrel or gestodene (3rd) nomegestrol, dienogest & drospirenone (4th)
What is the main difference between first/second vs third and fourth generation progestins
The main difference between first/second vs third and fourth generation progestins is that the latter has less of an effect on lipoprotein levels, but an increase in the risk of thrombosis
What type of drugs can decrease the efficacy of the combined oral contraceptive (COC)?
Drug efficacy decreased by drugs which induce liver enzymes like some
antibiotics (rifampicin) and some anti-epileptic drugs (phenytoin,
phenobarbital)
What are the monophasic/biphasic/triphasic forms of COC?
- Monophasic COC: fixed oestrogen and progestogen dose
- Biphasic COC: one or two doses of oestrogen but two different doses of
progestogen
- Triphasic COC: one or two doses of oestrogen but three different doses of
progestogen
What are the main SE of COCs?
Hypertension, increases thromboembolism risk, increased breast cancer risk, weight gain, depression, amenorrhea
What conditions can COCs cause?
Breast and cervical cancer
What are the advantages of COC?
decreases: irregular periods, intermenstrual bleeding, iron
deficiency, anaemia, premenstrual tension, risk of benign breast disease,
uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, ovarian and endometrial cancer, pelvic
inflammatory disease
What types of cancers is COC associated with decreased levels of?
Use of pill is associated with decreased endometrial cancer, decreased
ovarian cancer risk (50%)
How does a contraceptive patch work? give an example
Example: Combined contraceptive patch (Evra)
750mg ethinylestradiol
6mg norelgestromin:
Similar to the pill, there is 21 days of drug exposure in the form of 3 consecutive patches that are worn for 7 days each. This is followed by 7 days without a patch. These patches contain an estrogen such as ethinyl-estradiol, and a pregestin such as norelgestromin
Why are COC patches promoted to be brought back to the pharmacy to be disposed of ?
It's worth mentioning that 80% of the drug is still present in the patch after 7 days of use, and this has raised some concerns about an increase in the environmental levels of estrogen which is linked to a decrease in sperm count in men. Therefore it is now recommended that the used patches are returned to the pharmacy for proper disposal
Give an example if a COC vaginal ring and how to use it
-Combined contraceptive vaginal ring (NuvaRingÒ)
15mg ethinylestradiol
120mg etonogestrel
-Applied for 21 days, new ring 7 days later similar effectiveness to COC pill
How does the progestogen-only pill work? give example
Examples: Desogestrel 75 mcg, Etynodiol 500 mcg, Levonorgestrel 30 mcg,
Norethisterone 350 mcg
- Same time each day
Note:
-3 hr POP: traditional must be taken within 3 hours of same time each day
- 12 hr POP: Desogestrel- must be taken within 12 hours of same time each
day
-MOA: Inhibits LH, prevents ovulation, makes cervical mucus more hostile
- Better for those who get hypertension from COC, older women, VT history, smokers
What are the main SEs of POPs?
Irregular bleeding
What type of drugs can decrease the efficacy of the Progestogen only pill (POP)?
Drug efficacy decreased by drugs which induce liver enzymes like some
antibiotics (rifampicin) and some anti-epileptic drugs (phenytoin,
phenobarbital)
How does emergency contraception work? give 2 examples
- Take within 12 to 72 hours
- Levonelle One Step = single 1.5 mg pill (85% success rate if taken within 72
hours)- some nausea incidence
- Ulipristal - selective progesterone receptor modulator = 30 mg (97% success
rate if taken within 120 hours)
How can an individual get an emergency contraception?
Available in pharmacies, walk-in's, minor injuries unit
What are the long-acting contraceptives?
-Levonorgestrel/Ethinylestradiol = 84 days active pill 7 days placebo- only 4 periods/year
- Lybrel = every day 28 pill/pack- no periods
- Segesterone (Annovera)= insert for three weeks off for 1
- I.M injections every 8 (Norethisterone) or 12 weeks (Medroxyprogesterone)
- Subcut implant (Etonogestrel) = effective for 3 years
-Copper-containing device which interferes with implantation: - Effective for 3-5 years
More suitable for older;
-IUD is impregnated with Levonorgestrel
How does an IUD work?
- Copper device interferes with implantation
- Works 3-5 years
- Older women
Main SEs for everyone on this: pelvic inflammatory disease which can lead to infertility
-can be added w/ levonorgestrel
List some male contraceptions
- Condoms, Vasectomy (a surgical procedure that permanently prevents pregnancy by cutting or sealing the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles), IVD - physical plug in the vas deferens , reversible inhibition of sperm under guidance
(RISUG), vasalgel, NES/T gel
Not licensed yet but been through clinical trials:
- Androgen e.g., testosterone- weekly injection/implants
- Androgen + progestogen- weekly injection, daily oral progestogen
- Androgen + GnRH antagonist- daily antagonist injection
- Testosterone + Norethisterone- injection every 8 weeks
- Takes up to 8-12 weeks for maximum spermatogenesis suppression
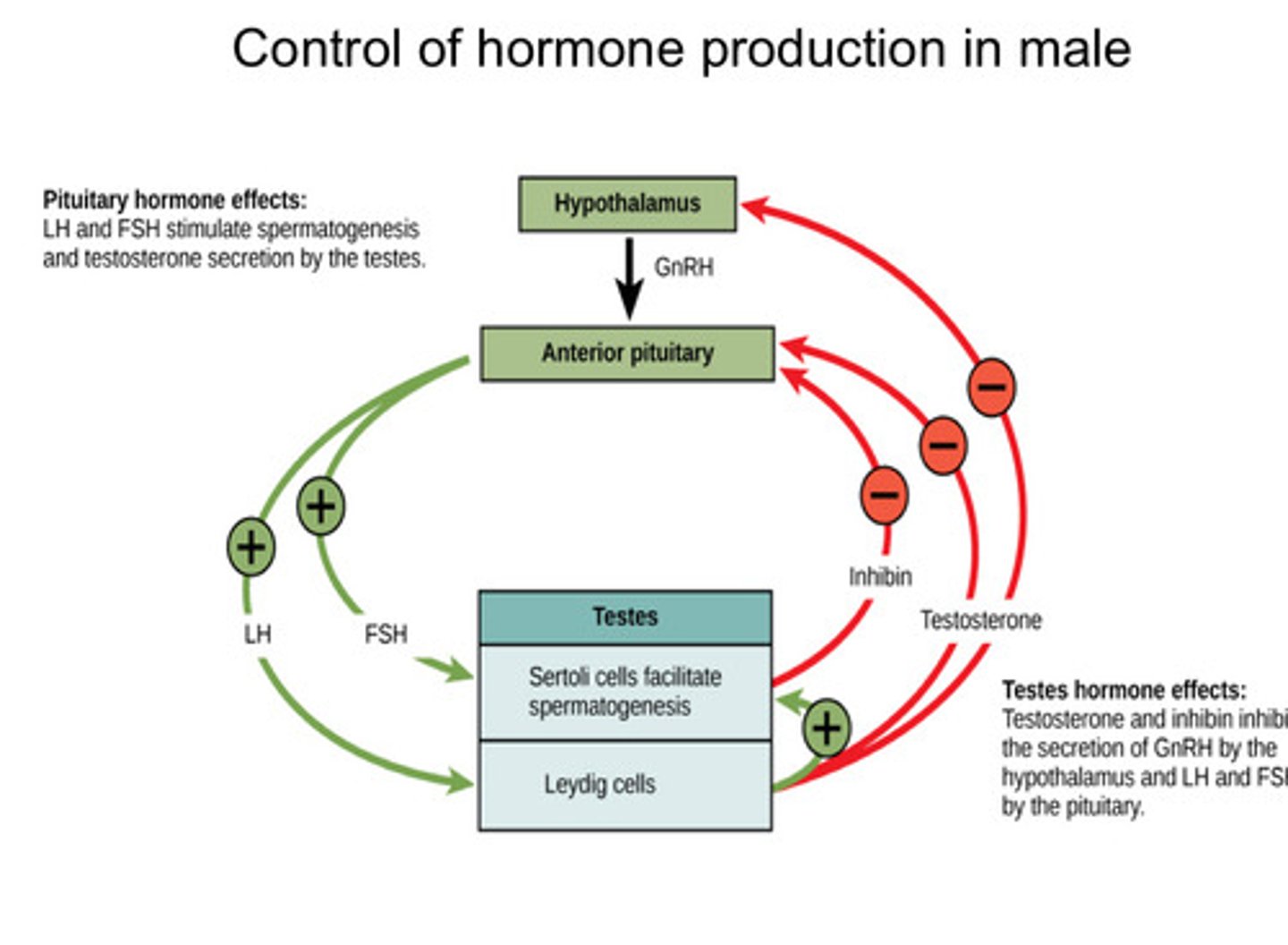
How is hormone production controlled in males?
- Hypothalamus makes GnRH
- GnRH acts on anterior pituitary to make LH and FSH
- LH acts on Leydig cells
- FSH acts on Sertoli cells for spermatogenesis
- Testosterone and Inhibin act on pituitary to stop LH/FSH and hypothalamus to stop GnRH