HIstory Final Exam Multiple Choice
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms

The Enlightenment
a European intellectual movement of the late 17th and 18th centuries emphasizing reason and individualism rather than tradition. It was heavily influenced by 17th-century philosophers.

Philosophes
the influential French Enlightenment intellectuals of the 18th century, like Voltaire, Rousseau, and Locke, who championed reason, individual rights, and social reform, using their writings to critique tradition

Natural Rights
basic rights that include the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. Every citizen is entitled to these rights and they are to be protected from encroachment by the government or society. It is both illegal and morally wrong for a person to be denied natural rights.
everybody has these - born with them
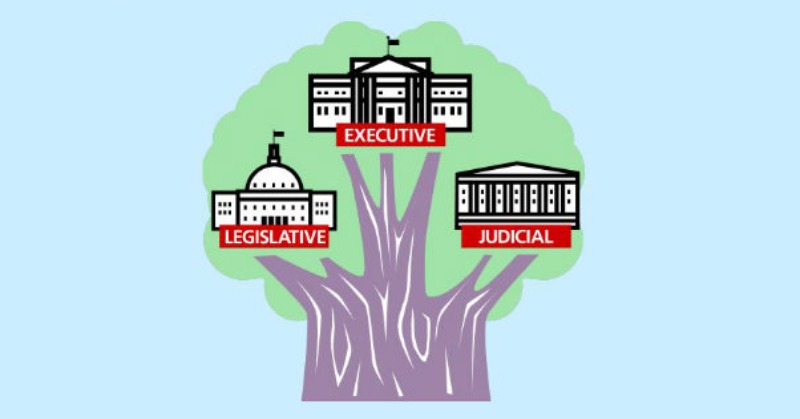
Separation of Powers
splitting government functions so no single person or group holds absolute control.

Social Contract
an implicit agreement among the members of a society to cooperate for social benefits, for example by sacrificing some individual freedom for state protection.
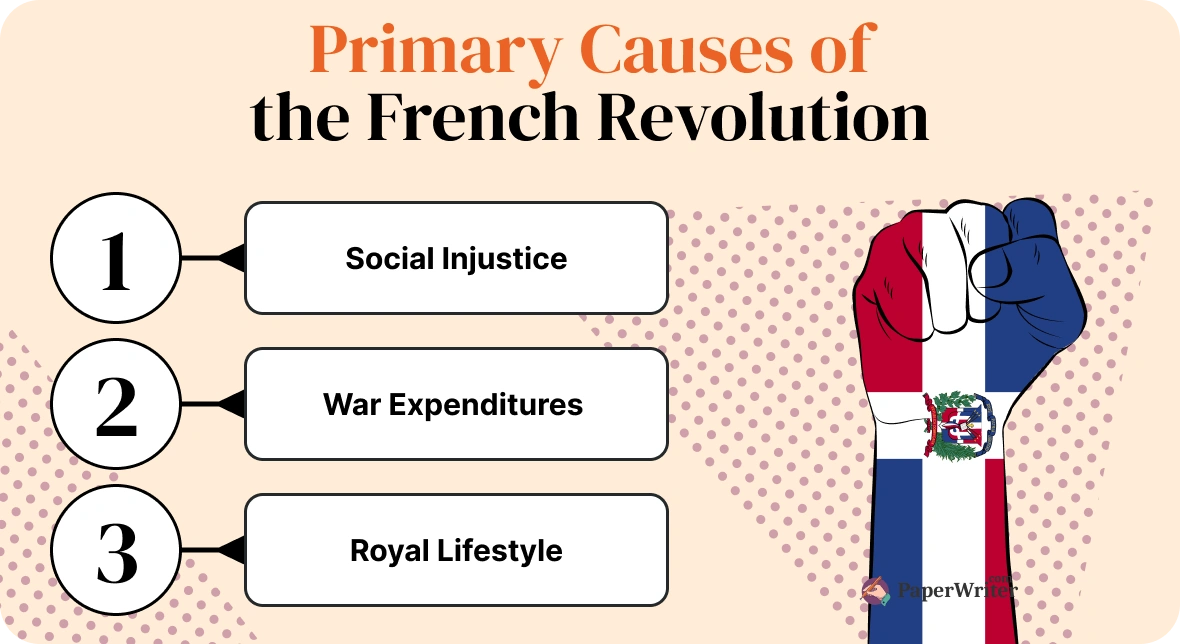
Causes of the French Revolution
-Enlightenment ideas (natural rights, equality)
-economic hardship (debt, high taxes, famine)
-social inequality (unequal rights for commoners vs. elites)
These elements combined to create widespread unrest, fueling demands for fundamental political and social change.

Robespierre
one of the most radical leaders of the French Revolution. He was in charge of the government during the Reign of Terror, when thousands of persons were executed without trial.

Reign of Terror
a period of remorseless repression or bloodshed, in particular the period of the Terror during the French Revolution.
LED BY Robespierre

Napoleon
a French military general and statesman. Napoleon played a key role in the French Revolution (1789–99), served as the First Consul of France (1799–1804), and was the first emperor of France (1804–14/15).

Congress of Vienna
this constituted a major turning point – the first genuine attempt to forge an 'international order', to bring long-term peace to a troubled Europe, and to control the pace of political change through international supervision and intervention.

Nationalism
Love, devotion, and support for your own country (it is the best)
Extreme nationalism = believing your country is the only good country and all others should be eliminated
N in MAIN

Industrialization
a social or economic system built on manufacturing industries.

Capitalism
an economic system where people and businesses own things, make products or services, and sell them to earn money.

Socialism
a system where the government or the community owns and controls major businesses and services, instead of individual people owning them

Communism
an economic and political system where everything is owned and shared by everyone, and the government controls resources to make sure people are equal; no rich or poor
Marxism
a theory about how society and the economy works
created by Karl Marx; he says that history is shaped by conflict between social classes, especially between workers and owners
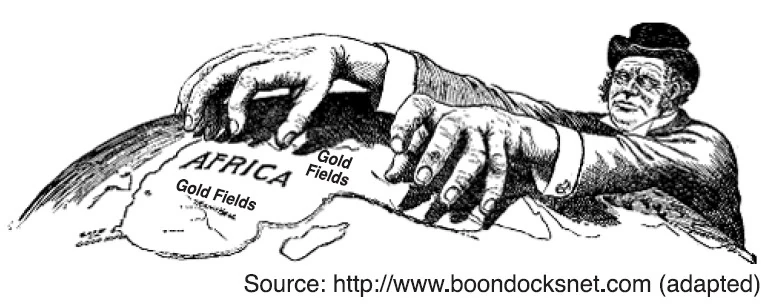
Imperialism
a policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
I in MAIN

Social Darwinism
the idea that society works like nature, where the strongest or most successful people rise to the top, and others fall behind
survival of the fittest
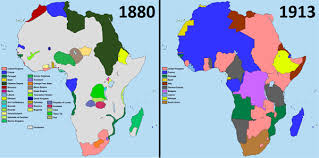
Berlin Conference
a meeting of European powers to set rules for colonizing Africa and avoid conflict among themselves; guaranteed free trade on major rivers
scramble for Africa

Militarism
the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend one’s country
M in MAIN
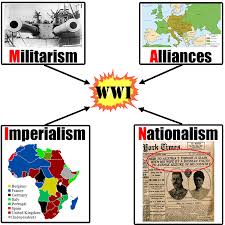
Causes of WW1 - MAIN
M ilitarism - a country should maintain a strong military to fight with and be prepared to use it aggressively
A lliances - mutual defense partners that will defend each other during war
I mperialism - extending a country’s power to to other territories
N ationalism - the belief that your country is the best/better than others
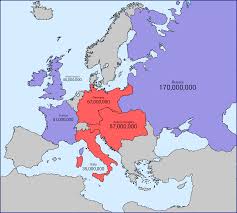
The Alliance Systems
Triple Entente - Germany, A-H, Italy
Triple Alliance - Great Britain, France, Russia

Treaty of Versailles
a peace agreement signed after WW1 that punished/blamed Germany for the war
took away Germany’s land, limited its military, and forced to pay large fines
led to WW2 - Germany broke Treaty of versailles

Weimar Republic
Germany’s government after WW1
Germany’s first democracy, struggled to survive (lasted 14 years)

Adolf Hitler
the dictator of Nazi Germany who started World War 2 and was responsible for the Holocaust, the genocide of millions of people

The Nazi Party
a political party in Germany led by Adolf Hitler that promoted extreme nationalism, racism, and antisemitism

Totalitarianism
a type of government where the leaders have complete control over everything - what people do, what they say, what they believe, and even how they think.

Appeasement
when a country gives in to the demands of another country, usually to avoid conflict or war, even if those demands are unfair or wrong
apologizing just to make things better

Munich Pact
an agreement made between Germany, Britain, France, and Italy.
Hitler wanted Sudetenland(part of Czech), Britain and France agreed to let him have it, hoping it would prevent a war
example of appeasement

Holocaust
the mass murder of 6 million Jews and millions of other people by the Nazi regime in Germany during WW2
Hitler

Nuremberg Laws
rules made in Nazi Germany that took away rights from Jewish people

Causes of Russian Revolution
-poor working and living conditions
-totalitarian rule by Czar Nicholas II (ignored the needs of the people)
-WW1 (Russia suffered huge losses)
-economic hardships
-inspiration of Revolutionary ideas (Marxism, socialism, people wanted a change)

Lenin
a Russian revolutionary political leader who led the Bolsheviks and helped bring communism to Russia

The Bolsheviks
a group of Russian revolutionaries who wanted to overthrow the government and create and communist state
believed in Marxism

Stalin
leader of the Soviet Union after Lenin died
turned the Soviet Union into a totalitarian state using fear

Stalin’s 5 Year Plan
government programs to rapidly modernize and industrialize the Soviet Union
goal was to increase productions of factories, machines, and farms in just five years
was hard on citizens

The Gulags
government prison camps in the Soviet Union under Stalin

Mao Zedong
a Chinese politician, revolutionary, and political theorist who founded the People's Republic of China (PRC) and led the country from its establishment until his death in 1976.

Cultural Revolution
A political movement initiated by Mao Zedong. It was a campaign in China ordered by Mao Zedong to purge the Communist Party of his opponents and instill revolutionary values in the younger generation

The Great Leap Forward
a plan by Mao to quickly turn China into a modern, industrial country
plan failed; caused famine - killed millions

The Red Guards
a group of young people, mostly students, in China who supported Mao during the Cultural Revolution; enforced his rules

Tiananmen Square
a protest in 1989 in China for democracy that was violently crushed by the government