7A
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biologicla factors, motivation, personality and disorders
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the behaviorist perspective? How does it differ from the social cognitive perspective?
It believes that behavior is learned through conditioning. Overall they are dependent only on external stimuli.
Social cognitive perspective says that people mold their environments based on their personality while the environment also molds them.
What is the humanistic perspective?
centered on the use of free will and how to best apply it
How would you label a therapist that helps a patient to replace destructive attitudes with positive ones?(basically correcting faulty thinking)
Cognitive therapist
How would you label a therapist that uses a token economy to replace negative coping responses with positive ones?
Behavioral therapist
How would you label a therapist that helps a patient uncover unconscious roots to their issues?
Psychoanalytical therapist
How would you label a therapist that lets a patient share their negative experiences and express their feelings in a safe environment, otherwise known as catharsis?
Psychodynamic therapist
Why is the anterior cingulate cortex important?
Regulates impulse control and descision making
Why would a fMRI be preferred over a PET? What situation would this be found
fMRI detects brain activity in real time so this best fro when we want to look at brain activity while someone is doing a task.
What characterizes Cluster A disorders?
“Weird”
Paranoid (distrust, suspicion)
schizoid (detached)
schizotypical (magic/ghosts)
Think Willy Wonka
What characterizes Cluster B disorders?
“Wild”
Antisocial (inconsiderate... makes sense if you think of an attention whore with a big ego)
Borderline (neurotic/unstable)
Histrionic (attention whore)
Narcissistic (big ego)
Think American Psycho!
What characterizes Cluster C disorders?
“Worried”
Anxious
Dependent (anxiety --> safety behaviours (maladaptive coping strategy, but latch on to a person)
OCPD (if your in control, avoid anxiety... like sensitization/rehearsal)
Think Charlie Brown
What’s the difference between drive and regular factors of motivation like needs?
Drives are PURELY biological not psychological while a need can be biological and psycholigical
What are the most known psychoanalytic psychologists?
Freud and Carl Jung
What are the main humanist psychologists? What even is humanistic for each?
Humans are inherently good and we should look at them as a whole
Malsow - Self-actualization
George Kelly-Info collection, processing and interpretation
Kurt Lewin: Look at current situation to look at driving and restraining forces of change
Carl Rogers- Therapist is guide for patient to define and solve their problems
What is the trait perspective? What model is this related to?
Look at pattern of patient’s thought, feelings behavior focusing on those that are stable or not
OCEAN
O-openness
C-Conscientiousness- Orderly or disciplined
A- Agreeableness- How moral you are/trusting
E- Extroversion
N-Nerutoism- anxiety/depression
What is the trait perspective according to Gordon Alloport?
Cardinal- Dominate personality(Not common, usually archetype like villian or hero)
Central-Main traits
Secondary- Depends on situation
Who is the main behaviorist? Who is the main social cognitist?
BF Skinner
Social Cognitive -Bendura which show cognition, behaviors and environment (locus of control) interact
What’s the difference between Bipolar I disorder and Bipolar II disorder?
I- At least one MANIC episode
II- One DEPRESSIVE episode and one HYPOMANIC episode
What is cyclothymic disorder?
Having manic and depressive symptoms but they’re not severe enough to be an episode
What is a somatoform disorder?
they have symptoms of a condition but not actually diagnosed and they are also very concerned about it
Not only does GABA _____ you, but it also ____ over inappropriate behavior
Calms, DECREASES CONTROL
Describe:
Delusion of persecution:
Delusion of reference:
Delusion of grandeur
Persecution: Believe they’re discriminated against
Reference: Believe everything is directed towards them
Grandeur: Think they are famous
What is reciprocal determinism? What perspective is this related to?
There are personal and environmental motivations that influences behavior.
Social cognitive perspective!
What is dysthymia?
Depressed mood that doesn’t meet the criteria for major depressive disorder
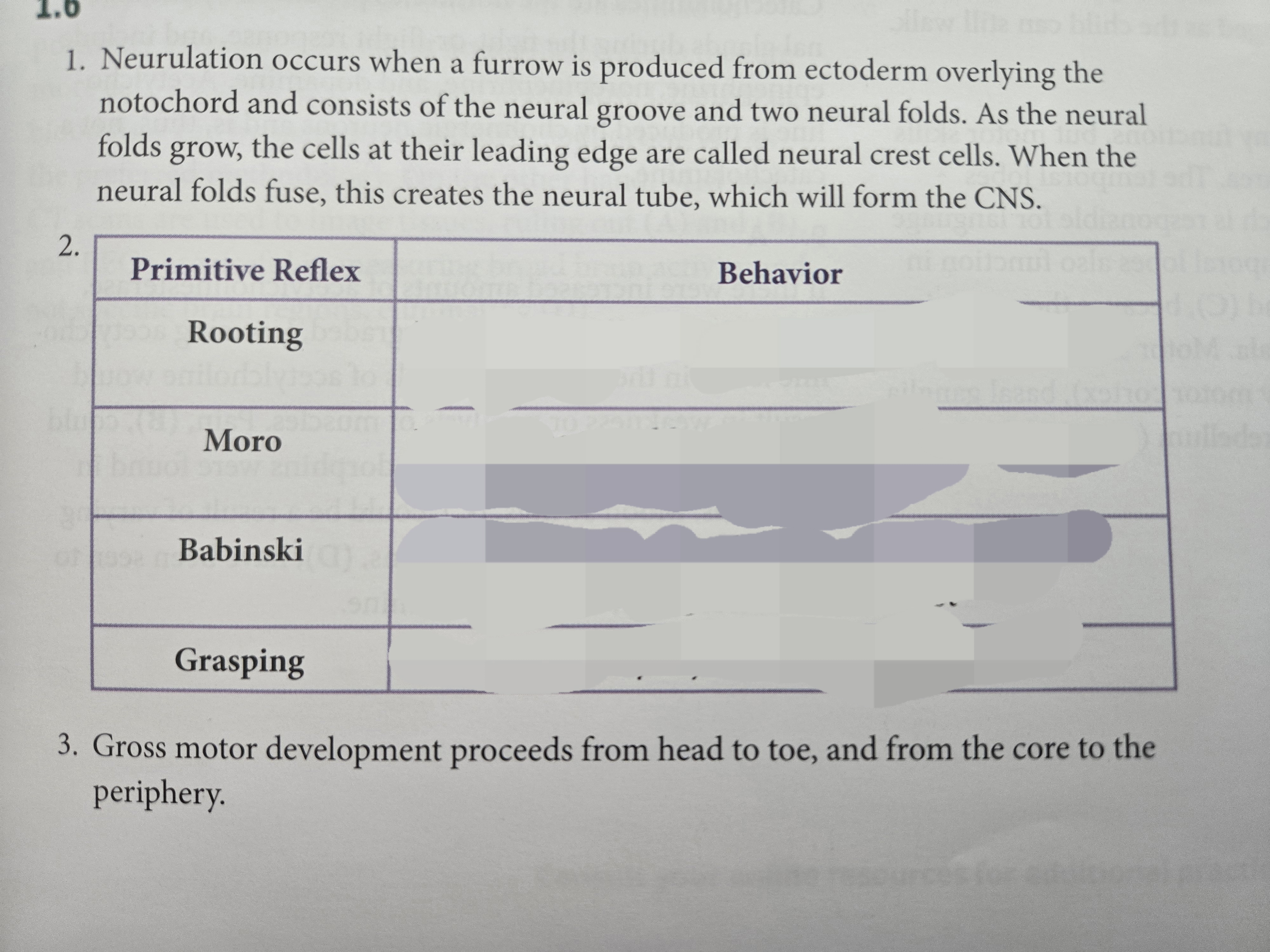
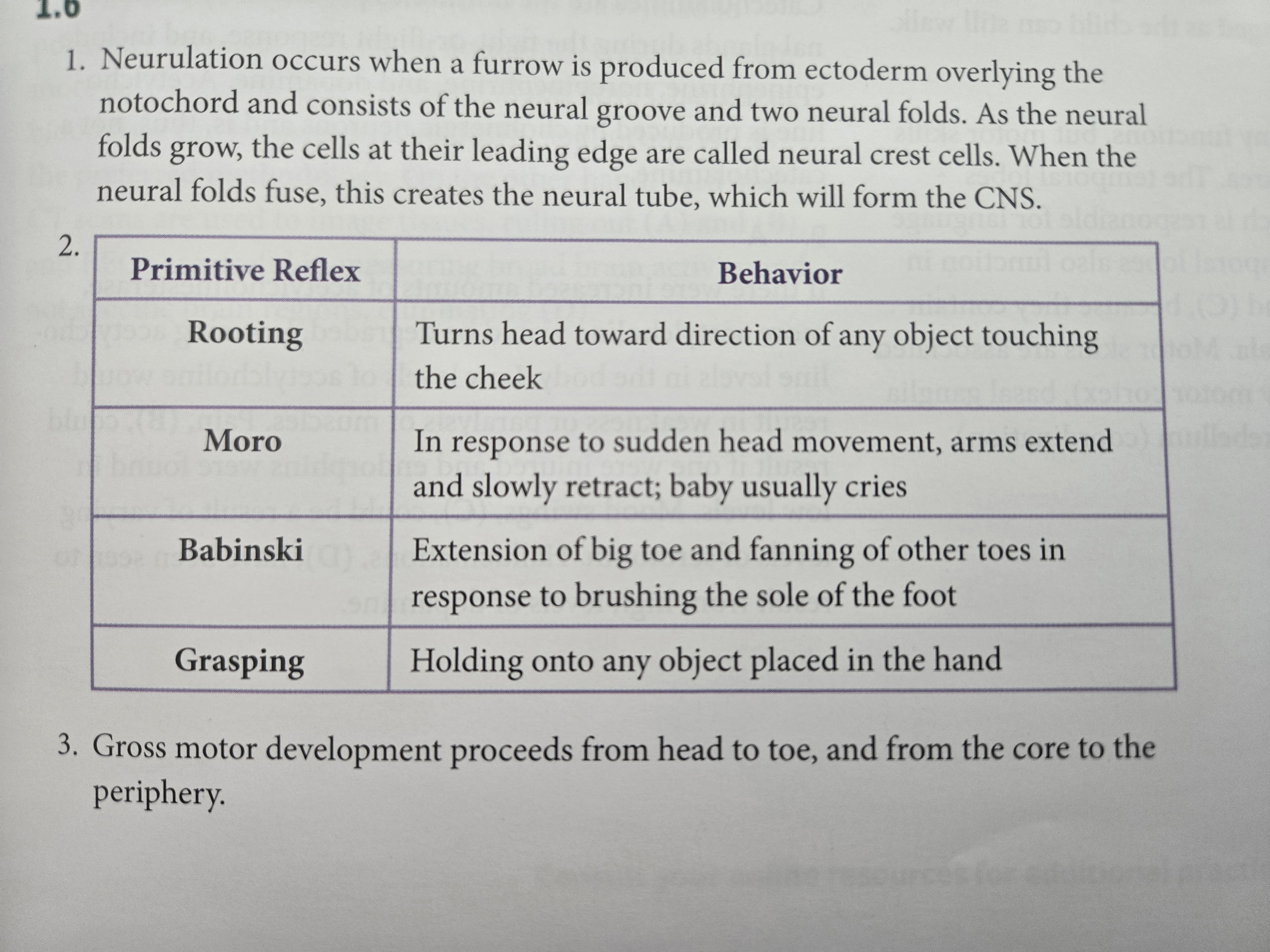
Fill dis out
Babinski-toes spread when foot stroked
Moro- Arms extend and start crying because of sudden head movement
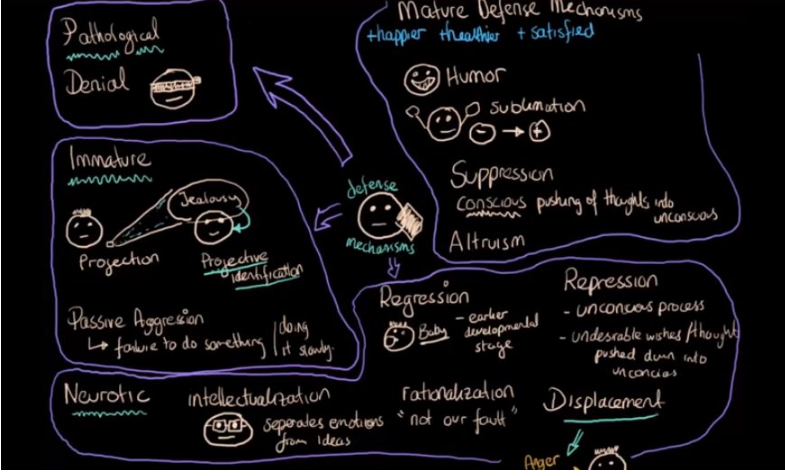
Defense mechanisms, draw it out?

Fill dis out

Fillll

What is Alzheimer’s disease associated with?
Decreased levels of acteylcholine
The prefrontal cortex communicates with the _____ to regulate ____ depending on the situation.
reticular formation
arousal and alertness
If a patient has been diagnosed and treated with Parkinson’s disease, and they suddenly develop hallucinations what cpuld be the cause?
We treat with L-DOPA which increases dopamine levels, which can cause hallucinations similar to how schizophrenia is caused by excess dopamine.
What’s the difference between the incidence and the prevalence of a condition in a population?
Incidence is the number of new cases within a specific time while prevalence is the total amount of people with the condition
What’s the difference between dissociative amnesia and dissociative identity disorder?
amnesia- Sudden unexpected move and are confused about identity and may assume a new one.
Identity: Experience multiple personalities that control their behavior
What neurotransmitter can be associated with manic episodes?
High levels of norepinephrine
What are positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
Positive: delusions, hallucinations, and CATATONIC behavior
Negative: AVOLITION
Define these different aspects of attitude:
Cognitive:
Affective:
Emotional
Behavioral:
Cognitive: Comprise our thoughts and beliefs
Affective: Our emotional reaction to a specific thing
Emotional: Very general may or may not be tied to attitude
Behavioral: our action because of the attitude
Central and Peripheral route processing are involved with the processing of ____. What do they each mean?
Persuasive info (ads)
Central: Thoughtful decision
Ex: This has great nutritional value
Peripheral: Superficial decision
Ex: It looks like it tastes good or I was recommended this
What is the dominant and nondominant hemisphere? What do they include?
Dominant(LEFT): Math, language, logic
Nondominant(RIGHT): Music, tone, creativity
What is the diencephalon?
Part of embryonic forebrain that becomes the thalamus, posterior pituitary, and pineal gland
In order to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, what needs to be observed?
Positive symptoms
If a gene is likely to be expressed, it has _____ but if it accounts for only a small amount of variation, then ____.
Has high penetrance, low heritability
What’s the difference between the foot-in the door technique and door-in the face technique?
Foot In: Accept small request first
Door: asking a favor and getting denied but the asking for a SMALLER favor
Where is cerebrospinal fluid located?
In the skull
What is incongruence?
The gap between a person’s actual self and ideal self
What is the difference between distress and maladaptiveness?
Distress: Unusual or prolonged levels of stress
Maladaptive: Negative impacts person’s life and poses a threat to others
Incentive theory?
how factors outside of individuals, including community values and other aspects of culture, can motivate behavior.
Which part of the psychodynamic theory resolves conflict?
Ego
What is the difference between fMRI and PET scans?
fMRI: reveals increases in blood flow
PET: Measures increase in glucose
What are the basic things we need to know about an action potential especially when a neurotransmitter exits the presynaptic cell??
First the neurotransmitter bind to their SPECFIC receptors on the postsynaptic cell
Ligand gated cation channels open
Depolarization exceeds our threshold which causes the action potential
If we say a certain word that was shown in our visual field and we somehow have a brain split, what would happen?
If ball was presented on the right and room on the left we would only be able to describe ball as describing ball happens on the left hemisphere and we dont have access to the left when room is on the left.
When we have cognitive dissonance, our goal is to ___ by ___.
Minimize it by conforming to them or questioning their validity
Changing their opinion than actually changing their behavior!
What are common example of first favors in the foot in the door technique?
Signing a petition
Wearing a pin
Completing a short survey
Making a small donation
Allowing a sign to be hung