Genetics exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1
New cards
effects of mutations on evolution
Increases genetic variation.
2
New cards
Codon
Any sequence of three adjacent nucleotides in a messenger
RNA molecule, specifying either an amino acid or a stop
signal in protein synthesis.
RNA molecule, specifying either an amino acid or a stop
signal in protein synthesis.
3
New cards
Gene
Parts of DNA that code for making proteins
4
New cards
Genome
An organism’s complete set of DNA
5
New cards
Polymorphisms
The presence in a population of two or more relatively
common forms of a gene, chromosome, or genetically
determined trait.
common forms of a gene, chromosome, or genetically
determined trait.
6
New cards
Proteome
The complete set of proteins encoded in the genome.
7
New cards
Transcript
An RNA strand that is produced from, and is
complementary in base sequence to, a DNA template
strand.
complementary in base sequence to, a DNA template
strand.
8
New cards
Nitrogenous bases of DNA
adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine
9
New cards
Central dogma
DNA codes for RNA, and RNA codes for protein. The DNA → RNA step is transcription, and the RNA → protein step is translation.
10
New cards
Locus
The site or position of a particular gene on a chromosome.
11
New cards
Allele
Any of the alternative forms of a given gene.
12
New cards
testcross
Cross an unknown dominant with a known recessive trait.
13
New cards
true-breeding
When offspring produced are same as the parent.
14
New cards
Differentiate between homozygote recessive, homozygote dominant, heterozygote
An organism can be homozygous dominant, if it carries two copies of the same dominant allele, or homozygous recessive, if it carries two copies of the same recessive allele.Heterozygous means that an organism has two different alleles of a gene.
15
New cards
Chargaff’s Rule
In double-stranded DNA, the amount of A equals that of T,
and the amount of G equals that of C.
and the amount of G equals that of C.
16
New cards
codominance
type of inheritance in which two alleles of the same gene are expressed separately to yield different traits in an individual
17
New cards
Variable expressivity
Range of phenotypic expression
18
New cards
Incomplete penetrance
Condition in which a mutant phenotype is not expressed in
all organisms with the mutant genotype.
all organisms with the mutant genotype.
19
New cards
sex-linked trait
Related to a trait determined by a gene on a sex
chromosome, usually the X.
chromosome, usually the X.
20
New cards
Mendel's Principle of Segregation
each individual that is a diploid has a pair of alleles (copy) for a particular trait.
21
New cards
Centromere
Region of chromosome that contains spindle fibers. It is a specialized DNA sequence between sister chromatids, where mitotic spindle attaches.
22
New cards
chiasma
site of crossing over
23
New cards
Independent Assortment
the alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another.
24
New cards
How is DNA packaged?
Tightly wrapped with histones without breaking
25
New cards
What is cell division?
The parent cell divides into two "daughter" cells. The process then repeats.
26
New cards
What is the purpose of cell division
the production of gametes and growth in eukaryotes.
27
New cards
genetics
study of biologically inherited traits
28
New cards
genomics
study of all genes in an organism
29
New cards
trait
a characteristic coded for by genes
30
New cards
mutation
any heritable change in a gene
31
New cards
mutant
the result of a mutation
32
New cards
polymorphic
a gene that has two or more variants, or alleles
33
New cards
pleiotropy
The ability of a single gene to have multiple effects
34
New cards
preotome
totality of proteins coded for in a genome
35
New cards
nucleoside
a nitrogen base joined with a deoxyribose molecule
36
New cards
nucleotide
a nucleoside combined with a phosphate group
37
New cards
transposable element
a DNA sequence capable of moving from one site to another within a genome
38
New cards
particulate gene
the concept that a gene is unchanged as it is passed from one generation to another
39
New cards
pedigree
family tree diagram that shows the phenotype of each individual
40
New cards
penetrance
the proportion of people with the at-risk genotype that express traits of the disorder
41
New cards
incomplete dominance
a type of inheritance when the heterozygote shows an intermediate form of both the dominant and recessive phenotypes
42
New cards
codominance
a type of inheritance when neither trait dominates over the other, and the heterozygote shows both the dominant and recessive phenotypes
43
New cards
epistasis
one gene will mask expression of the other
44
New cards
chromatin
the unwound form of DNA; "beads on a string"
45
New cards
centrosome
organelles which serve as the main microtubule organizing centers
46
New cards
centromere
specialized DNA sequence between sister chromatids, where mitotic spindle attaches
47
New cards
nucleosome
structural unit of DNA packaging, consisting of DNA wrapped around histone proteins
48
New cards
apoptosis
programmed cell death as a part of controlled cell division
49
New cards
proto-oncogenes
genes that stimulate cell division or apoptosis at division checkpoints
50
New cards
oncogenes
mutated porto-oncogenes, cause unregulated cell division
51
New cards
cytogenetics
the field of genetics that involves the microscopic examination of chromosomes
52
New cards
cancer
unregulated cell division
53
New cards
karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
54
New cards
histone
group of basic proteins found in chromatin
55
New cards
tumor-suppressor genes
genes that promote apoptosis in cell division
56
New cards
gain of function mutation
a mutation that allows for enhances expression of a gene
57
New cards
loss of function mutation
a mutation that inhibits the expression of a gene
58
New cards
contact inhibition
a process that stops additional cell growth when cells become crowded
59
New cards
tumor
mass of cells or tissue with no function
60
New cards
benign
tumor that stays in one place
61
New cards
malignant
tumor that invades other tissues
62
New cards
angiogenesis
the development of new blood vessels
63
New cards
anchorage dependence
the requirement that to divide, a cell must be attached to a solid surface.
64
New cards
telomere
protective cap at the end of the chromosome that regulates cell death
65
New cards
pyrimidine bases
thymine and cytosine
66
New cards
purine bases
adenine and guanine
67
New cards
chromomeres
localized contractions with a characteristic number, size, and position in a given chromosome
68
New cards
longest stage in meiosis
Prophase I
69
New cards
leptotene period of meiosis I prophase I
when the DNA is visible only as a thin thread in the nucleus
70
New cards
zygotene period of meiosis I prophase I
when homologous chromosomes synapse together at the ends
71
New cards
pachytene period of meiosis I prophase I
when chromosomes shorten & thicken and crossing over occurs
72
New cards
diplotene period of meiosis I prophase I
when synapsed chromosomes pull apart but are held together by the chiasma
73
New cards
diakinesis of meiosis I prophase I
when the nuclear envelope breaks down, spindle fibers form, and the DNA is fully condensed
74
New cards
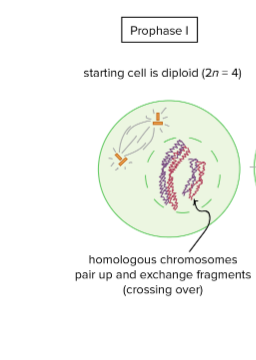
Meiosis I Prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs.
75
New cards
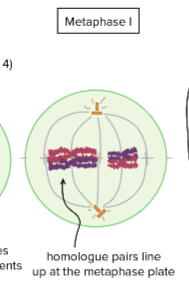
Meiosis I Metaphase I
homologue pairs line up at the metaphase plate for separation.
76
New cards
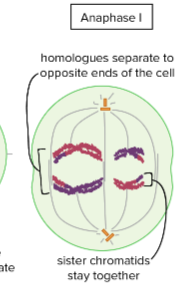
Meiosis I Anaphase I
the homologues are pulled apart and move apart to opposite ends of the cell.
77
New cards
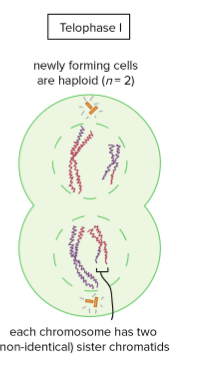
Meiosis I Telophase I/Cytokinesis
the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles of the cell and nuclear membrane reassembles.
78
New cards
chiasma
site of crossing over
79
New cards
Chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome
80
New cards
Identify the cell cycle checkpoints
G1, G2, M
81
New cards
G1 phase
the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecular building blocks it will need in later steps.
82
New cards
S phase
the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus. It also duplicates the centrosome.
83
New cards
G2 phase
the cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, and begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis.
84
New cards
The daughter cells from mitosis are called
diploid cells
85
New cards
What are the steps in cell division for mitosis?
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
86
New cards
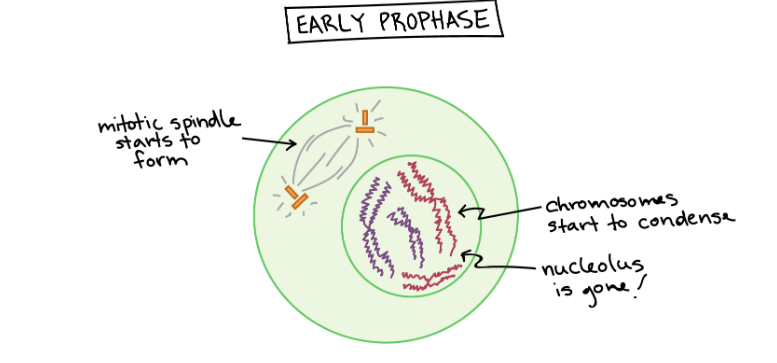
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and are visible under a microscope. Each chromosome made of 2 sister chromatids. Spindle fibers form that radiate from the centrioles on either side of the cell
87
New cards
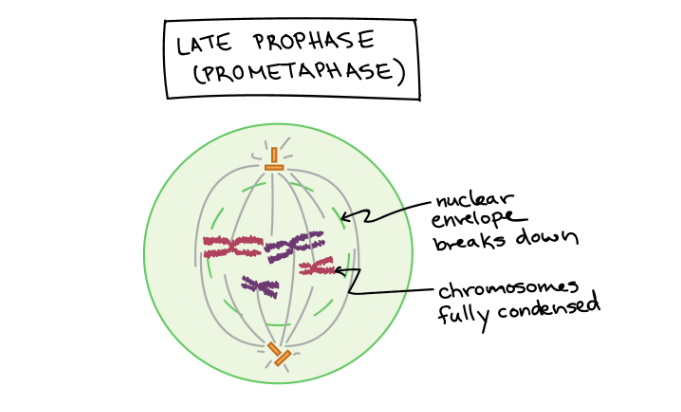
Prometaphase
The mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. The chromosomes become even more condensed, so they are very compact. The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes.
88
New cards
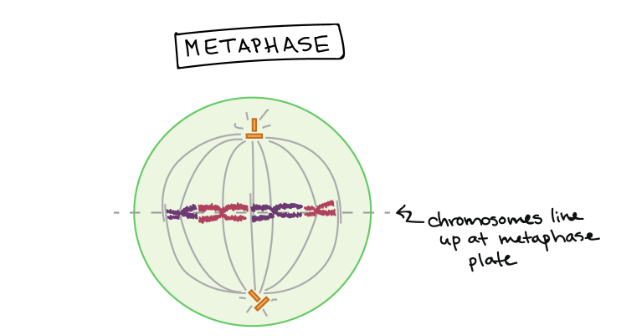
Metaphase
Chromosomes meet on the metaphase plate. They are most highly condensed during this stage
89
New cards
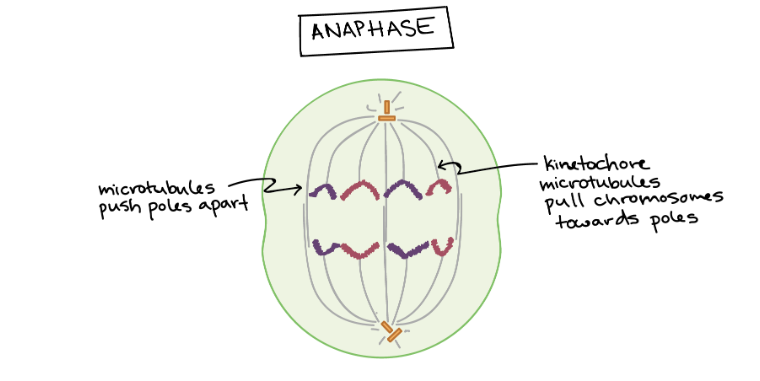
Anaphase
Centromere of each chromosome splits that allow sister chromatids to separate. Microtubules not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart, separating the poles and making the cell longer.
90
New cards
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
1. Mitosis: Two diploid (2n) somatic cells that are genetically identical to each other and the original parent cell.
2. Meiosis:four haploid (n) gametes that are genetically unique from each other and the original parent (germ) cell.
3. Mitosis involves one cell division, whereas meiosis involves two cell divisions.
91
New cards
Describe how meiosis creates genetic variation
Random alignment increases the number of possible chromosome combinations in the gametes.
92
New cards
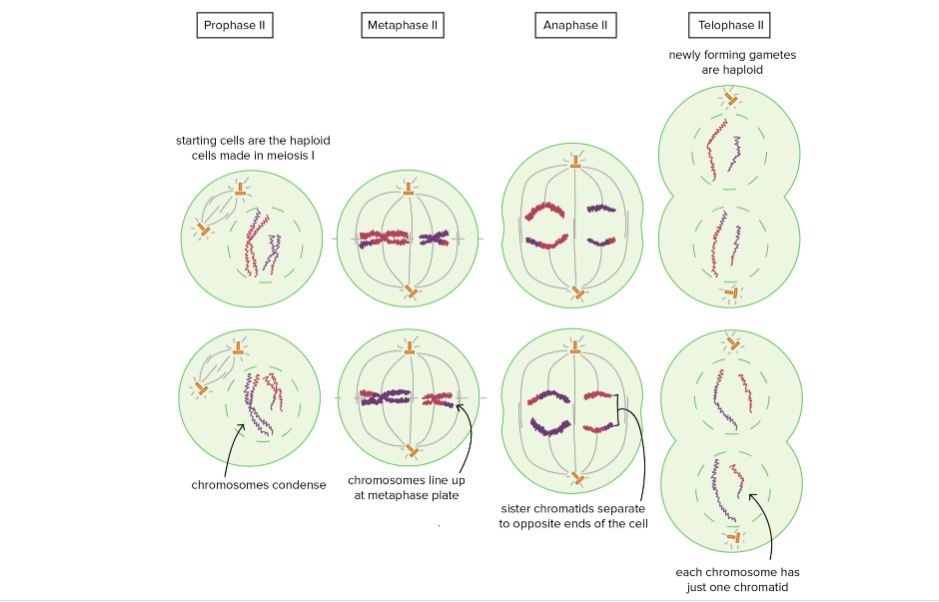
Meiosis II phases
Prophase II: Starting cells are haploid cells made in Meiosis I. Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope breaks.
Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II: Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes decondense. Newly forming gametes are haploid. Each chromosome has one chromatid.
Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II: Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes decondense. Newly forming gametes are haploid. Each chromosome has one chromatid.
93
New cards
Cancer v normal
Cancer keep duplicating and normal cells stop.
Normal cells have contact inhibition.
Normal cells have contact inhibition.
94
New cards
Wild type
natural un mutated form
95
New cards
role of mutations in evolution
Creating genetic variation.
96
New cards
Causes non disjunction
Metaphase
97
New cards
Nondisjunction
Unequal distribution of chromosome
98
New cards
Chromosome
One or more unique pieces of DNA
99
New cards
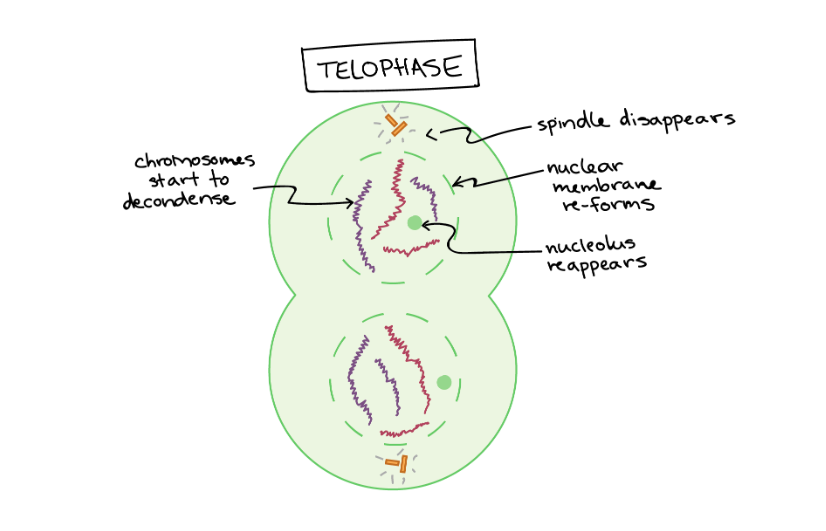
Telophase
Ends with 2 daughter cells. Each have a full set of chromosomes. The mitotic spindle is broken down into its building blocks. The chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their “stringy” form.