HSC Engineering In depth
1/373
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
374 Terms
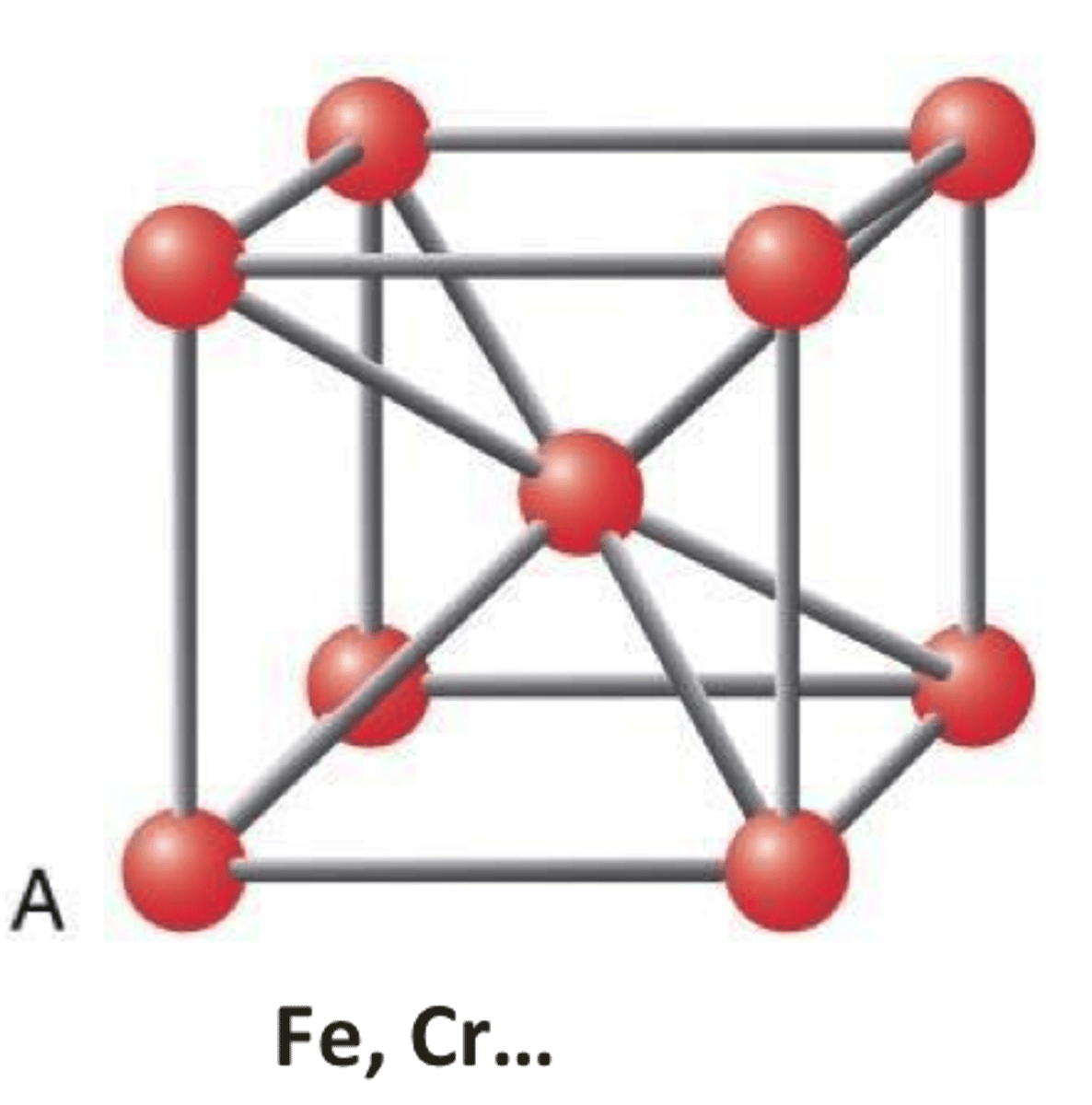
Body centred cubic
A type of crystal structure in metals. This structure can be seen as a gathering of cubes with atoms at the edges and an atom in the center of every cube.
Cast Iron
Iron carbon that is hard, brittle and weak in tension.
Solute
dissolves in solvent
Austenite
FCC, appears at 1000 degrees, 2% carbon
limestone
formed when shells and other plant and animal matter are subjected to extreme heat and pressure
Clays
Chemical weathering of silicate minerals with water
Polymerisation
a chemical reaction joining monomers in long chains to form a polymer.
addition polymerization
a type of polymerization in which the monomers simply add together to form the polymer, with no other products
Boundary layer
The point on the surface with a layer of air next to the wing
Transition point
When the air on the boundary layer becomes turbulent
Equation of continuity
A1V1=A2V2
mean camber line
An imaginary line between the leading and trailing edges and halfway between the airfoil's upper (curved) and lower (flat) surfaces
Elevators
the hinged rear section of the horizontal stabilizer as part of the tailplane
concentration cells
occurs when there is a difference in concentration of electrolyte
VR of a bicycle
diameter of pedal/ Diameter of wheel x Number of revolutions(teeth front/teeth rear)
Copper zinc alloy as connectors
harder and stronger than pure copper, while having good corrosion resistance they will however tarnish. Can be plated to resist conductivity issues caused by oxidation
Geostationary Satellite
a satellite that orbits above the equator and is commonly used to broadcast TV signals
Vitrification
the process that is applied to dried clay for it to obtain the required compressive strength for use as a common brick (firing)
Amorphous
Random and non crystalline atomic structure.
Asphalt
Composite material of aggregate in a matrix of bitumen.
Truss
supportive structure consisting of beams or girders in triangular formation
Yield point
The first point at which the specimen yields and increases stain occurs without an increase in stress
Yield strength
the ability to bear gradual progressive force without permanent deformation
Hydraulic cements
hardened when mixed with water
pre-stressed concrete
Concrete is preloaded with stresses to help strengthen it for tensile loads
Post-tensioned concrete
primary reinforcement is tensioned after concrete placement and cure
compression moulding
The manufacturing process generally used for processing thermosetting polymers.
Bernoulli's Principle
as the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases
Critical Mach number
the speed where airflow reaches the speed of sound
Disc Brake
A brake in which pressure squeezes the brake pads against a flat metal wheel disc, producing the friction needed to stop the wheel from turning.
VA of a pulley system
= number of ropes across
Diode and transistor
electronic components semi-conductors
Drag and thrust
the forces oppose each other during level flight
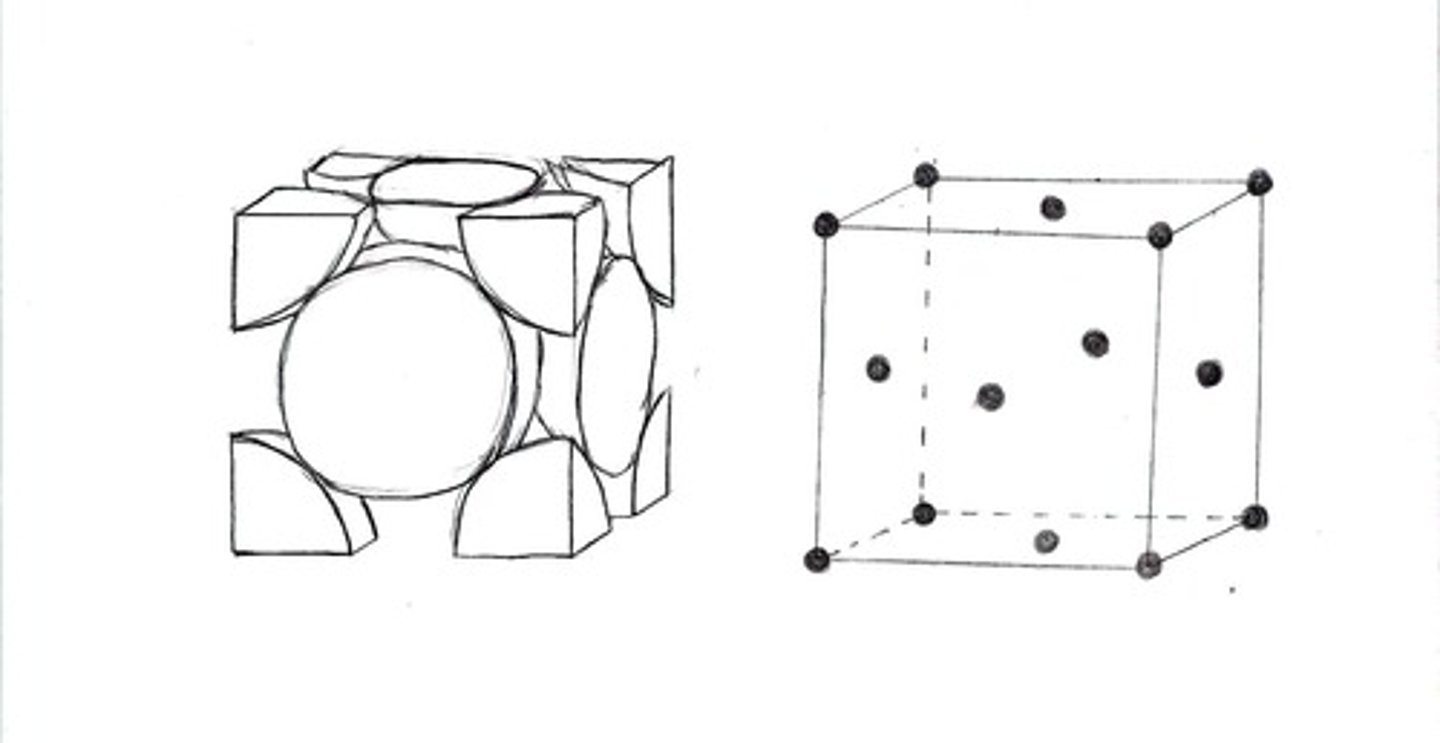
Face centred cubic
A cubic lattice with the face positions fully equivalent to each of the eight corners.
Elastic limit
the maximum extent to which a solid may be stretched without permanent alteration of size or shape.
Aerofoils
a structure with curved surfaces designed to give the most favourable ratio of lift to drag in flight, used as the basic form of the wings, fins, and tailplanes of most aircraft.
Stiffness
the ability to resist defamation under stress
Total Thrust
F1 + F2
Basic oxygen steel making
High purity oxygen is blasted through the molten scrap to aid oxidation and remove impurities as part of steel recycling.
Cantilever
Beams anchored at only one end.
Cement
Constituent of concrete made from a mixture of clay and lime like materials.
Ceramic
Multi phase material containing compounds of metals and non-metals, typically hard and good insulators.
Composites
Multi-phase materials formed from a combination of materials with different compositions or forms. These combinations improve upon the original properties of the constituent materials.
Compression
Squashing or clamping force.
Concrete
Cement, sand, aggregate and water chemically bonded over time, good in compression but poor in tension without steel reinforcement.
Corrosion
The deterioration or breakdown of a material brought about by its interactions with the environment that cause chemical change.
Elastic
Deforms under stress but returns to the original shape when the stress is released.
Factor of safety
Guides engineers to design structures within safe limits.
Fatigue
A cyclic load with the force often well below the yield strength.
Geotextile
Natural and synthetic materials used to create a barrier between different materials in contact with the earth; can be porous or impermeable.
Glass
A ceramic produced through a fusion of inorganic materials cooled to a solid state with an amorphous structure.
Hooke's law
Stress is directly proportional to strain.
Life cycle analysis
A tool used to assess the impact a product or process has on the environment.
Plasticity
The ability to resist permanent deformation without failure
Shear
Cutting force in which parallel internal surfaces slide past each other.
Strain
The amount of deformation an object experiences compared to its original length.
Stress
The relationship between a force and the a materials cross sectional area (N/mm2 or MPa).
Superstructure
Includes roadways, footpaths, railing and supporting structural members of a particular structure.
Tension
Stretching or pulling force.
Timber
A naturally occurring composite made up of cellulose and lignin.
Ultimate tensile strength
The maximum stress a material can withstand before failure.
Wrought iron
Iron and large inclusion of slag (stony waste) elongated by the forming process
Yield stress
The maximum stress in MPa at which permanent, non elastic deformation will occur.
Young's modulus
The ratio of stress to strain with the elastic region.
Allotropic
different atom arrangements based on temperature
Intrinsic semiconductor
Non- doped semiconductor
Extrinsic
Doped semiconductor
Amplitude modulation
Encodes a radio carrier wave by varying its amplitude
Amplifier
A device which boost a signal
Attenuation
the reduction in amplitude of an electrical signal
Bandwidth
The amount of data transfer in a given period of time
Carrier wave
an electromagnetic wave that can be modulated in frequency or amplitude
Channel
Any path a communication may take from a transmitter to receiver
Conductor
A substance, body or device capable of transmitting electricity, heat, sound, etc.
Conductivity
The ease that free electrons in a material move.
Diode
an electric component that allows current to flow in one direction only
Direct wave
An electromagnetic wave that travels from transmitter to receiver by line of sight
Dispersion
Act or process of scattering light, electricity or waves.
Fibre optics
The transmission of light signals via fibre optics
Fidelity
The degree at which an electronic system accurately reproduces the sound or image of its input signal
Frequency modulation
Encodes a radio wave by varying its frequency
Brittle
easily cracks
Creep
permanent deformation when subjected to prolonged stress
Ductile
able to be drawn into thin wires or deformed without losing toughness
Elasiticty
being able to return to their original shape after being deformed
Hardness
the ability to resist permanent change by force, scratching
Malleability
being able to be rolled into thin sheets
Resilience
the ability to obsorb energy and resist soft impact loads
Toughness
amount of energy required to break it
Elements
most basic of matter and cannot be broken down
Solution
result of solvent and solute mixing
Solvent
able to dissolve other substances
Compounds
are two or more elements that are bonded chemically in a fixed proportion
Mixture
are two or more substances (elements of compounds) mixed together mechanically in a random proportion
Biological materials
a result of the life cycle of a plant or animal
Composite materials
materials combined together to capitalise on their desireable properties
Alloys
mixtures of two or more metals
Thermosetting polymer
non reversible with links between polymer chains, high tensile strength
Thermosoftening polymer
reversible when heated, malleable, recyclable
Tensile strength
ability to withstand a stretching force