Horticulture Exam 2
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Sport
mutation on branch
Hybrid
manipulated sexual reproduction of two plants
Hybrid Cultivar
if you try to breed from, will not get the hybrid again
Hybrid Notation
Hy. Cultivar: [species] x [cultivar epithet]
Hy. Species: [genus] x [specific epithet]
Hy. Genus: x [species]
Inflorescence
flowers in clusters; ex: hydrangeas
Emasculating
Removing parts of the flower
Registered Trademark names
name given to plant to market the plant or group of similar
classify plants in 2 categories
Edible & Ornamental
Edible
Vegetables & Fruits
Ornamental
Trees, Shrubs, Vines, Ground Covers
Tree
ornamental plant that has an exposed trunk and canopy
Allee
trees bordering a path or greenery (tree alley)
Shrub
multi-stemmed with branches to the ground
“Limb up”
removing lower limbs from shrub to look like tree
Shrub & Tree confusion example
tsuga canadensis-hemlock trees can mature at 150 ft but sold and pruned to be sold as small shrubs/trees
Habit
natural shaped (vs pruned)
Vine vs Ground Cover
called based off how they grow; vines have extending branches
Growth Events
Flush, Flower, & Set Buds
Flush
Sudden growth in short time (springtime)
Flower (the growth event)
when flowers flower (shocker)
Set Buds
Buds becoming flowers or vegetative (leaves)
Winter Appearances (2)
Evergreen & Deciduous
Evergreen
Plants that retain each year’s set of leaves for 3-5 years, they die and fall off but its usually inside (like xmas tree)
Deciduous
Loses all its leaves every autumn
Growth Kind (2)
Woody & Herbaceous
Woody
tissue composed of hard permanent tissue (wood)
Herbaceous
soft, tender, succulent tissue
Temperature Tolerance (3)
Tropical, Subtropical, & Temperate
Tropical
will not tolerate freezing (32*F) and are often injured in cold
ex. bananas (which is in Musa genus) and tomatoes
Chilling Injury
between 33 & 55*F can get injured
First Frost Free Date (FFFD)
date after chance of frost decreases
Last Frost Free Date
date after chances of frost increases
Subtropical
tolerate short periods of freezing but not for prolonged periods of time
citrus (orange and lemons)
Temperate
tolerate long periods of freezing and below for prolonged periods of time (days)
ex. apples, pears, cherries
Length of Life (3)
Annual, Biannual, & Perennial
Annuals
plants that only live for one growing season, usually killed by freezing temperature; aka “bedding plants”
Biannual
completes its life cycle in two years; first year is vegetative growth, second is reproductive growth
ex. carrot; if you pulled out a wild carrot (Daucos carota) with flowers on it, it would not have carrot since the plants energy is all in the flower and not the root that year
Perennial
plants that live for 3 or more years; they go dormant in the cold
Volunteers
annuals that appear to act like perennials; plants that actually die but have “set seed” that is able to “over-winter” and germinate next season
ex. begonias & ferns; species specific
Mass Planting
using 3 or more plants to create a mass of plants
Temperate Plant Hardiness
based on average annual minimum winter temperature; broken up into 10*F zones
Plant Taxonomy
identification & classification
Nomenclature
names
Anatomy
internal structure
Morphology
external structure
Physiology
what is going on inside
Classic Plant Parts (6)
Vegetative: Roots, Stems, Leaves
Reproductive: Flower, Fruit, Seed
Functions of Roots
Absorption, Anchorage, Transportation, Storage
Primary Root
first root to emerge from seed
Secondary Root
roots emerging from primary or secondary roots
Adventitious Roots
roots emerging from abnormal places; ex. root coming out of a branch cutting
Root Hairs
single cell extensions of the epidermal cells
most found closest to root tips
increases surface area, 100x absorptive power
gives off root exudates
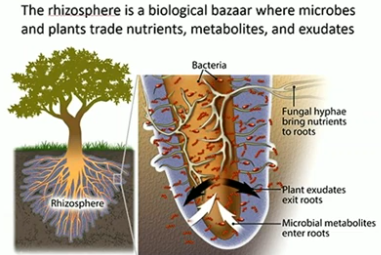
Root Exudates
attract beneficial microbes
improve the chemical & physical properties of the soil
improve the amount & availability of nutrients to the plants
contains sugars, carbs, & protein
improves Rhizosphere
Rhizosphere
2-3 mm zone around growing roots, very important for microbial activity
Specialized Roots (3)
Tap, Tuberous, & Aerial
Tap Root
large swollen primary root; ex. carrot
Tuberous Root
large swollen secondary root; ex. potatpes
Aerial Root
roots growing above ground, often adventitious but not always
Epiphyte
plants with aerial roots that grow on other plants, gets water from atmosphere
ex. 70% of all orchids have epiphytic roots which is why you put it in bark
Parasitic Plants
takes energy and nutrition from plant host
ex. mistletoe and Cuscuta americana (steals sugar since it doesn’t have it’s own chloroplast

Functions of Stems
Storage, Transportation, Support, Food Production
Stem Anatomy (2)
Terminal/Apical Bud & Lateral/Axillary Bud
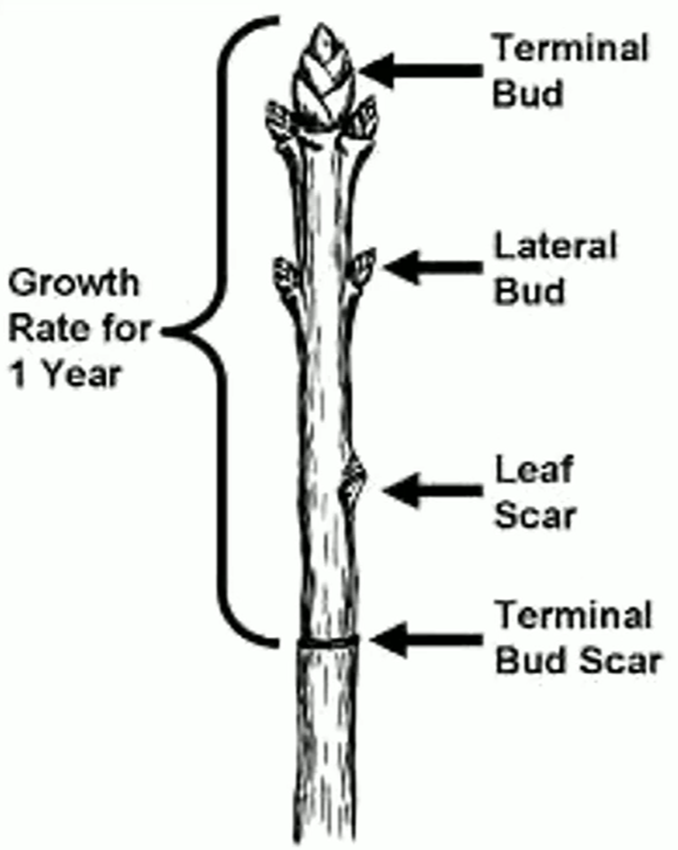
Terminal/Apical Bud
comes out of the terminal (the end)
Lateral/Axillary Bud
comes out of the sides/axis
What do Buds do
they “break” (open up) and stem and leaves come out
Meristem
zone of active cell division, occurs in specific areas in a plant (geographic)
primary/apical: at tip & length
secondary/vascular: circular & girth
growth is episodic (periodic)
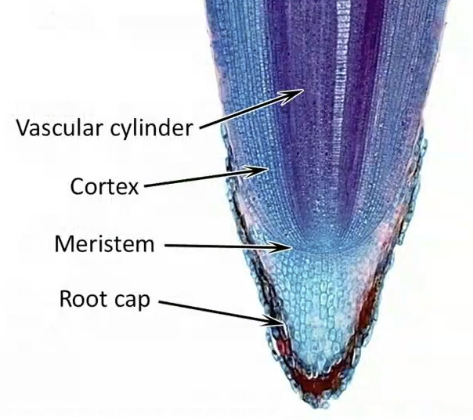
Apical Dominance
when apical meristem is present then the lateral buds don’t break; the farther the secondaries are the better they break, if you cut off the apical then the lateral buds all break (making bushier shrub)
Types of Stems
Prostate, Stolon, Rhizome, & Large Swollen Underground Stem
Prostate Stem
stems that runs along the ground
Stolon
a prostate stem that runs along the ground and produces a plantlet at tip
ex. strawberry & spider plant
Plantlet
a little plant that comes from the main plant
Rhizome
prostate stem that runs below ground and produces plantlet at tip
ex. bamboo & Polygonatum ordoratum “Variegatym” Varigated Solomon’s Seal
Tuber
large swollen underground stem
ex. Tuber Irish Potato, the eyes potatoes have are its nodes
how to distinguish root from stem
stems have nodes (where the buds and leaves come out of)
Function of Leaves
Food Production & Storage
Types of Leaves for Dicot & Angiospermae (2)
Simple & Compound
Simple Leaf
one blade & petiole/leaf stem
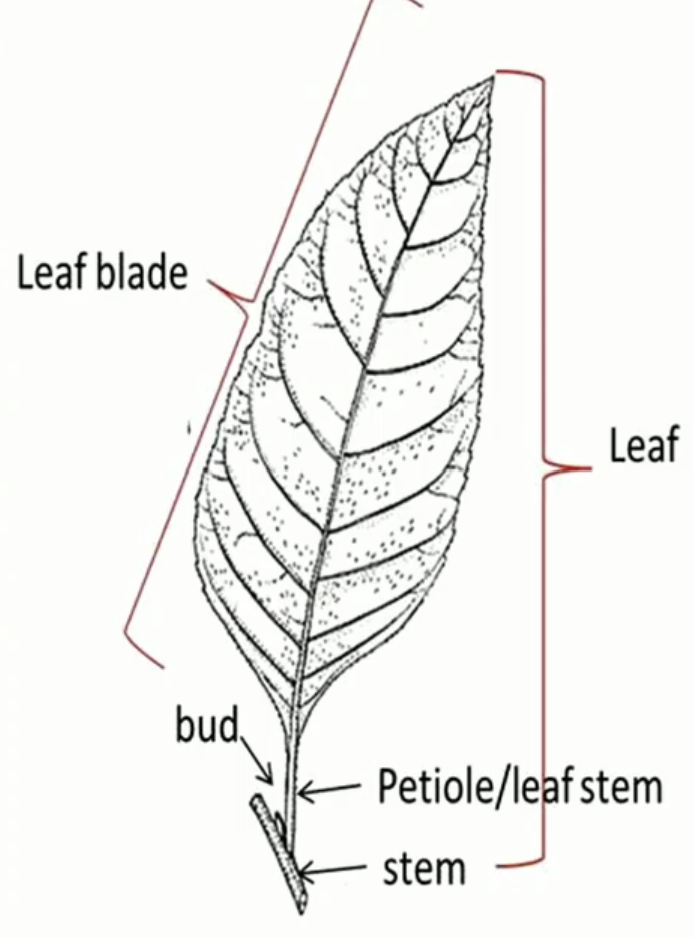
Compound Leaf
leaflets and petiole/leaf stem
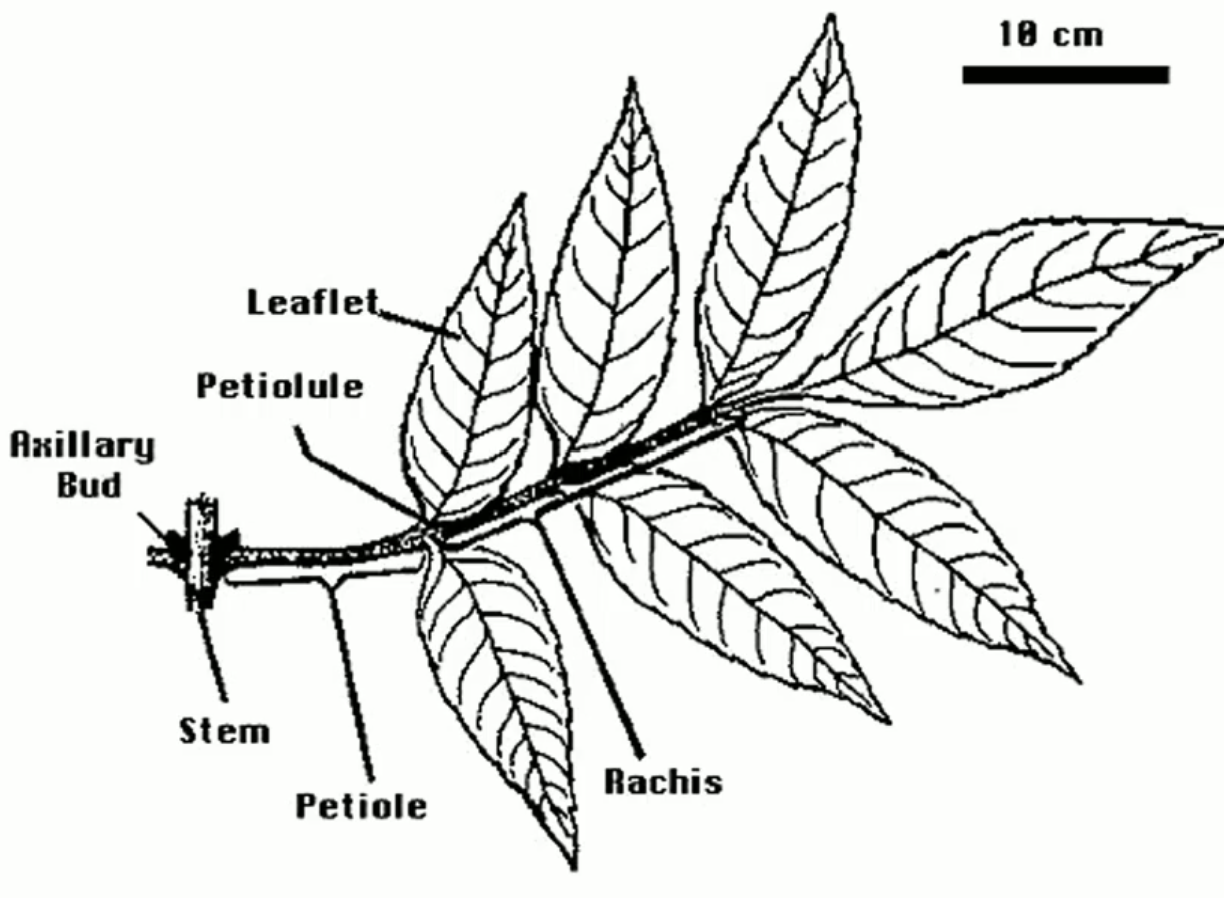
Types of Leaves for Gymnospermae (3)
Needle, Scale, & Awl
Needle-like Leaves
needly leaves
Fascicle
bundle of needle-like leaves
Scale-like Leaves
very small scaly leaves that overlap each other
ex. cypress
Awl-like Leaves
awls are spikes that are used to puncture leather
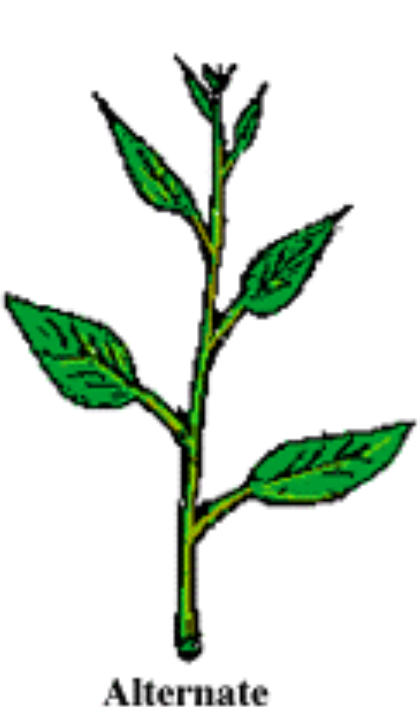
Leaf Arrangement (3)
Opposite, Alternate, Whorld
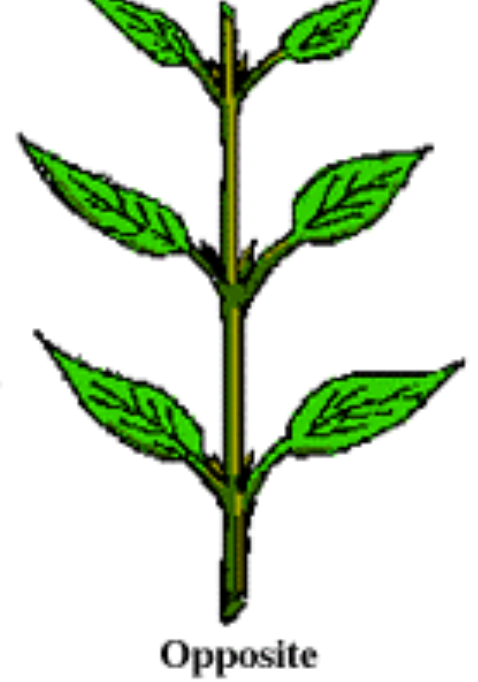
Opposite Leaf Arrangement
ex. all acer (maple) & boxwood
Alternate Leaf Arrangement
ex. all quercus (oak), holly

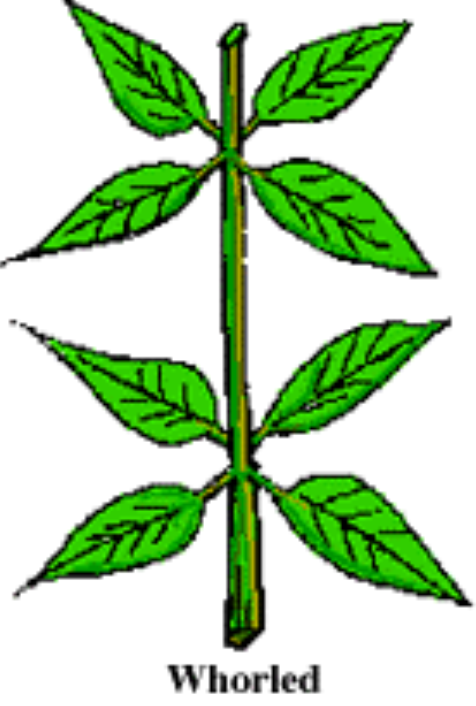
Whorld Leaf Arrangement
3 or more at a node
Plant Failure caused by (2)
poor light relations (sugar)
soil issues (water & nutrition)
Plant Growth Necessities
Water, Nutrition, Sugar, Energy/ATP
Full Sun
min of 6 hours of direction unimpeded sunlight
anything less is partial sun
The Wholistic Plant Growth Processes (5)
Absorption, Translocation, Photosynthesis, Transpiration, and Respiration
Absorption
water and nutrition (but in different ways); dependent on good soil practice
Osmosis
diffusion of water across semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute to an area of higher solute concentration; no energy is needed
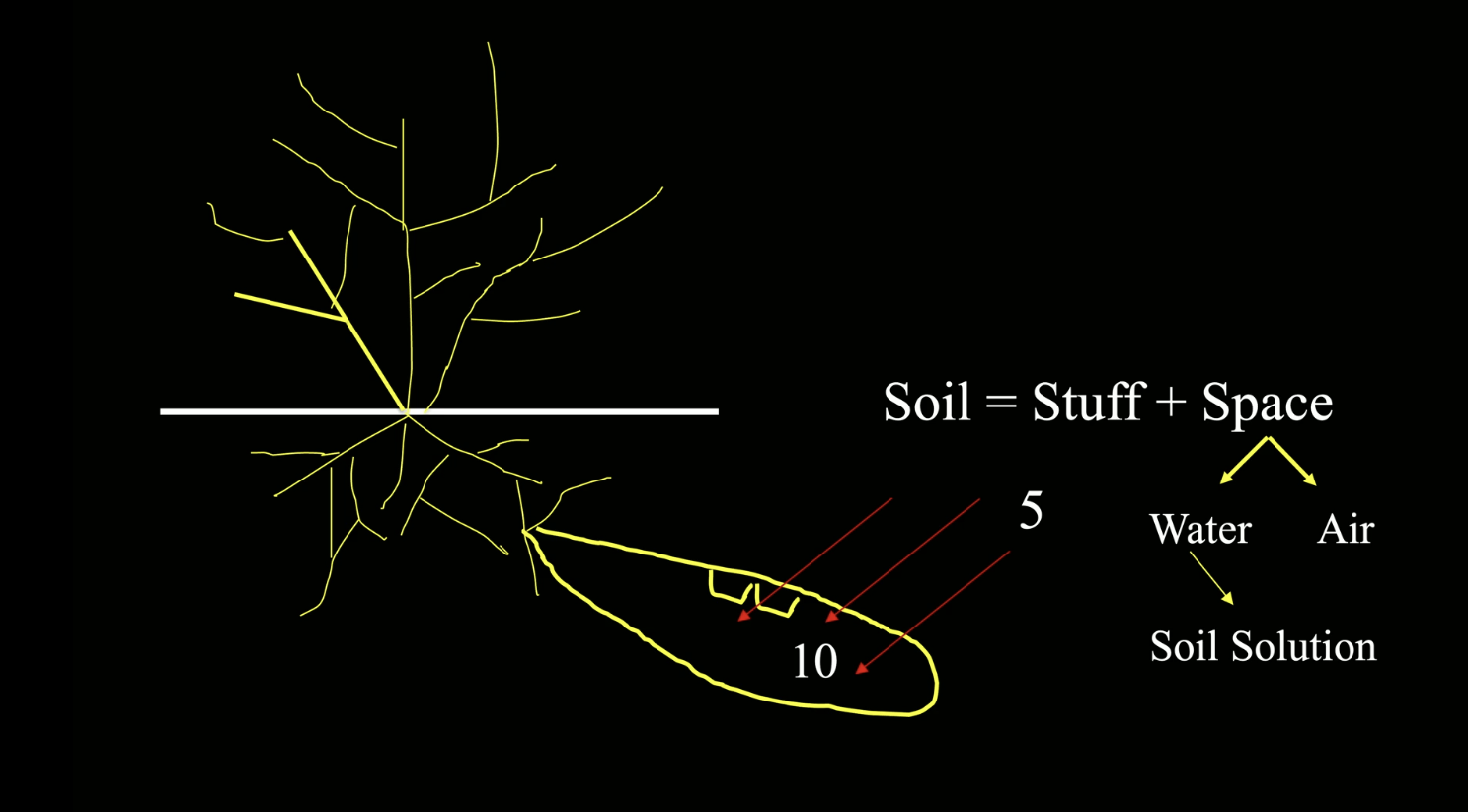
Carrier Molecule Theory
nutrients gets absorbed like how forklift come gets things
nutrient specific molecules (the forklifts) are responsible for nutrient uptake
energy is expended (active transport)
Translocation
movement of material from one location to another; specific tissues are responsible for specific movements
Translocation Vessels
Xylem Vessel: water & nutrition go up
Phloem Vessel: sugar go up and down
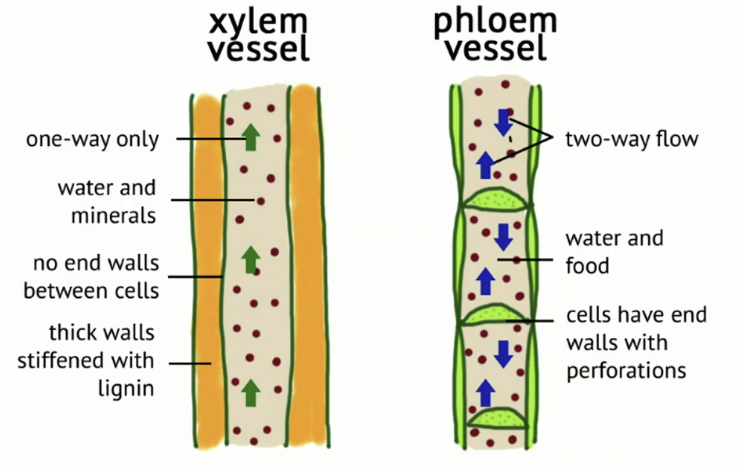
Photosynthesis
most important process on earth because it cerates oxygen and only organism that makes its own sugar, without it we do not exist; process is a lot like baking cookies
Photosynthesis Ingredients
Water (H2O) & Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Photosynthesis Energy Source
Light (not limited to sunlight)
Photosynthesis Mixing Bowl
Leaves (sometimes Stems)