experimental psych exam 1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Heider called nonscientific data gathering commonsense psychology
this approach uses scientific sources of data and nonscientific inference
Scientific mentality
Behavior and though follow a natural order and can be predicted – the assumption is essential to science.
There is no point in using the scientific data
if there Is no implicit order.
When we research, we must gather measurable evidence;
You make things measurable by operationally defining the research.
A law consists of
statements generally expressed as equations with few variables that have overwhelming empirical support
Theory is
broad and can be supported by a hypothesis well supported over a course of many tests. Ex; bystander effect, cognitive dissonance theory,
Theory is an interim explanation
a set of related statements used to explain or predict a phenomenon; They can be tested. The hypothesis must fail to support or support a theory
Good thinking is critical to scientific methods
we engage in good thinking when data collection and interpretation are systematic- equal or the same throughout the experiment, objective- , rational-what is your study telling you based on what you measured.
Replication
is an exact or systematic repetition of a study
There are 3 forms of replication
direct, conceptual, and operational
direct replication
- which is copy pastes of a study
Conceptual replication
- uses the same variables and operationalizes them differently
Operational
4 objectives of science
description, prediction, explanation and control
Description
is happening when we encounter something brand new; we know nothing about it is a systematic and unbiased account of characteristics of behaviors.
Prediction
is the capability of knowing in advance when certain behaviors should occur.
Explanation-
is knowledge of the conditions that reliably produce a behavior. Why a behavior is happening.
Control-
is where we interfere or act to do something or produce a certain outcome. - scientific knowledge to influence behavior
Basic research
test theories and explain psychological phenomena like helping behavior- done by academics
Applied research
address real-world problems like how to improve student graduation rates- business or corporation-based research
Observation
is the systematic noting and recording of events
Systematic means
means that the procedures are consistently applied, The events of their signs must be observable. Observations must be objective so that there can be strong agreement among rates
Measurement assigns
assigns numbers to objects, events or their characteristics. This is and inherent feature of quantitative research.
Experimentation
is the process we use to test the predictions we call hypotheses and establish cause and effect relationships
Experimentation is not always possible
because our predictions must be testable
Ethics prevents things from being
testable, resources, some things may not be measurable.
Confound
when you accidentally manipulate another variable when manipulating another – your study may be confounded when random assignment is not done well
In psychology experiments
we control extraneous variables so we can measure “what we intend to measure”- we can remove a confound by adding and variable or levels
Experiments establish
a temporal relationship because causes must precede effects; however, not all prior events are causes.
An experiment
attempts to establish cause- and effect relationship between the antecedent conditions iv and dv
Bidirectional causation
two variables, insomnia and depression- may affect each other
Third variable problem
not the same things as confounds- a third variable is a family conflict- may create the appearance that insomnia and depression are related to each other. Example- ice cream and murder - causality related to temperature
Researchers use multiple regression
to predict behavior measured by one variable based on score on two or more other variables. They can never rule out other explanations but only rule out if an explanation that you think of.
What variables do I control for in predictors
EX, SES, gender, age,
Causal modeling
- two types- we do them in an instant when we cannot do an experiment but use experimental methods to find causality.
Path analysis
when a researcher test models of possible sequences using multiple regression analysis where two or more variables are used to predict behavior on a third variable
3 rules
1. Every variable that is receiving (arrow is going to a variable) an arrow is a dependent variable or outcome variable.
2. There is the same amount of regression equations as there are dependent variables.
Every variable that is giving (going from) an arrow is the predictor
multiple regression equations describing arrows
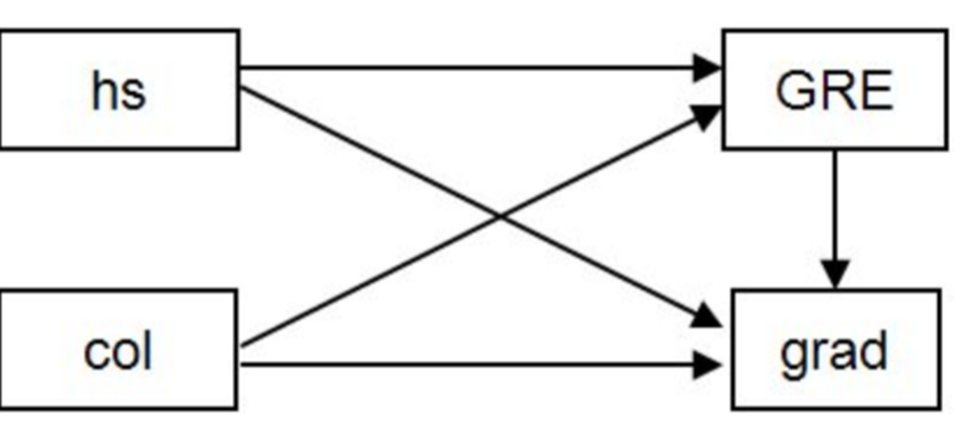
Htg- atg
Atg- sre
A path model is combing and putting together different regression models
Variables can be predictors or dependent variables but they cannot be both.
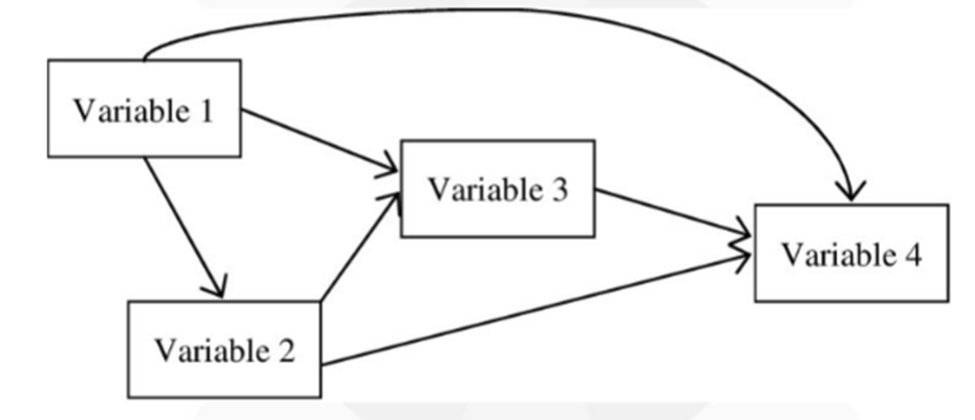
V3 is predicted by V1 and V2
V2 is predicted by V1
V4- is predicted by V1,V2,V3
3 EQUATONS- 6 arrows means 6 total predictors
Cross-lagged panel design- where you are taking a 1-2 variable design- measure them at least two time points- the idea with this design is to give you the knowledge of which one came first. A researcher measures relationships over time, and these are used to suggest a causal path. When making a judgment on the way the effects are going, you look at the cross and see which correlation is stronger, bigger in absolute value, and furthest from zero.
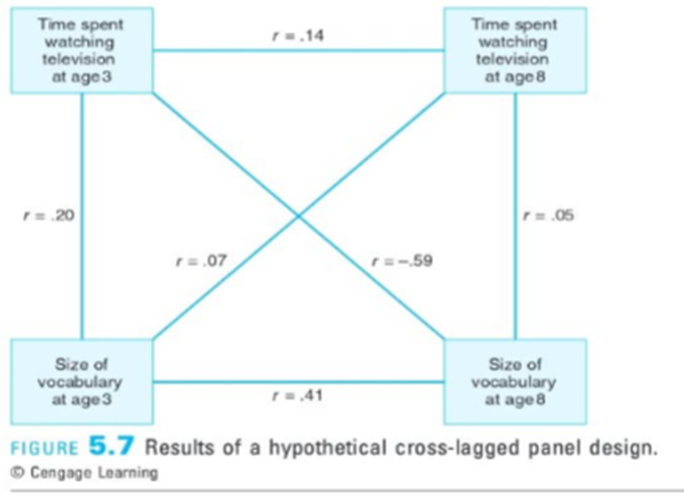
Time spent watching tv- my vocabulary goes down. If I watch less my vocab goes up.
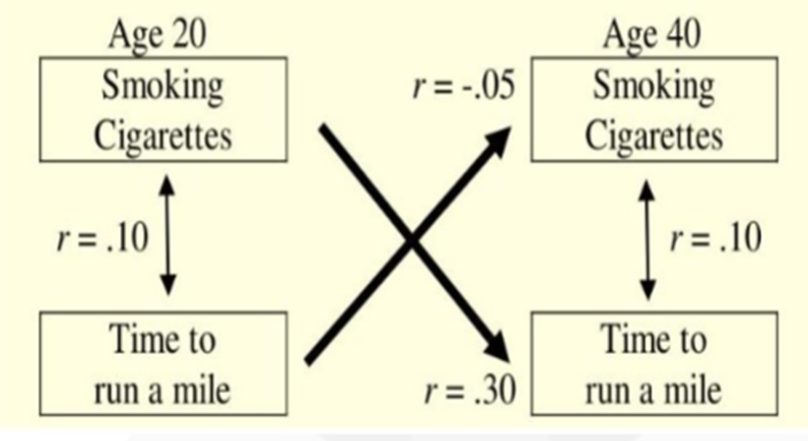
Another example of a cross-lagged design
Smoking cigarettes – makes your time to run a mile longer- positive correlation
No causation either direction
Correlation would be close to zero or non-directional.\
A hypothesis
is an explanation/prediction of a relationship between two variables
Your hypothesis should communicate what the dependent and independent variable is, and a direction
which way the relationship is going
CBT and antidepressants
Treatment is the independent variable with CBT and antidepressants are the two levels of it and amount of relapse Is the dependent variable
How do you determine if a hypothesis is experimental and non-experimental?
you determine that if the independent variable and if it is manipulated.
Example of non-experimental
red hair patients receive less relief from pain medication than blonde patients.
another example of non-experimental study
iv- hair color; red or blonde, dv- relief. There is no manipulation within the study on who receives treatment and you cannot manipulate who has what hair
example of continuous IV ($) and continuous DV (death count)
The more ice cream that is sold, the more people will get killed
example of categorical IV (s) x continuous DV (height, inches)
men will be taller than women
Categorical IV (s) X Continuous DV (hair color, blonde y or N)
More men will report having blonde hair than women or men are more likely to have blonde hair than women
Always mention all categories of IV
do not need to mention all categories of DV.
Testable
ethics, resources, time, money, feasibility (cannot measure) prevents things from being testable.
Parsimony
means that we prefer a simple hypothsis over one requiring many supporting assumptions- simple hypothesis or better
Induction
is where we go specific to general principles to form a hypothesis; used to build theories. Build with induction; refine with deduction. Specific to broad.
Deduction
is reasoning from general principles to specific predictions; this approach is used to test the assumptions of a theory. Where it applies and where it does not- broad to specific