Lab 6 - permanent maxillary incisors
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
purpose of permanent maxillary incisors
mastication
phonetics
esthetics
cutting and shoveling food
universal numbers for permanent maxillary central incisors
8 and 9
universal numbers for permanent maxillary lateral incisors
7 and 10
where maxillary CI are located in the mouth
2 adjacent teeth in center of maxillary arch
maxillary CI share ______ contacts with each other
mesial
maxillary CI share ____ contact with laterals
distal
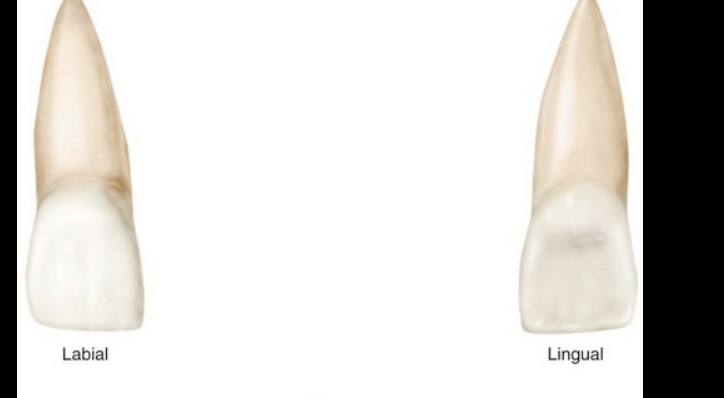
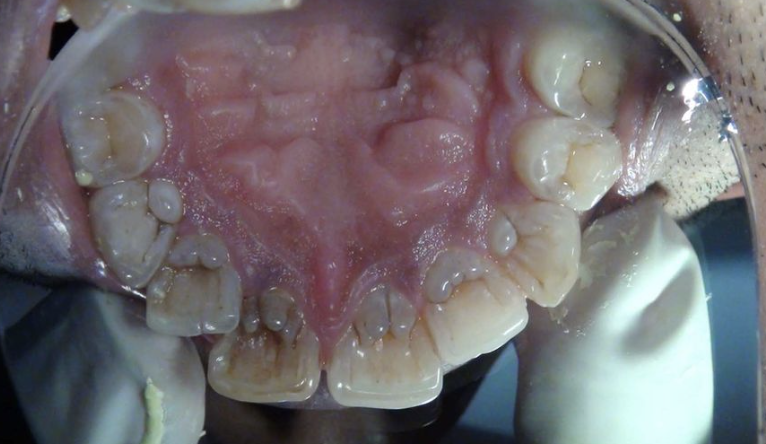
maxillary CI shape from labial or lingual
trapezoidal
maxillary CI is widest
mesiodistally
maxillary CI shape from proximal
triangular

maxillary CI initiation of calcification
3-4 months
maxillary CI eruption
7-8 years
maxillary CI completion of root
10 years
maxillary CI shape from labial view
trapezoidal
maxillary CI convexity is greatest in (from labial view)
cervical third
maxillary CI approaches flatness toward (from labial view)
incisal third
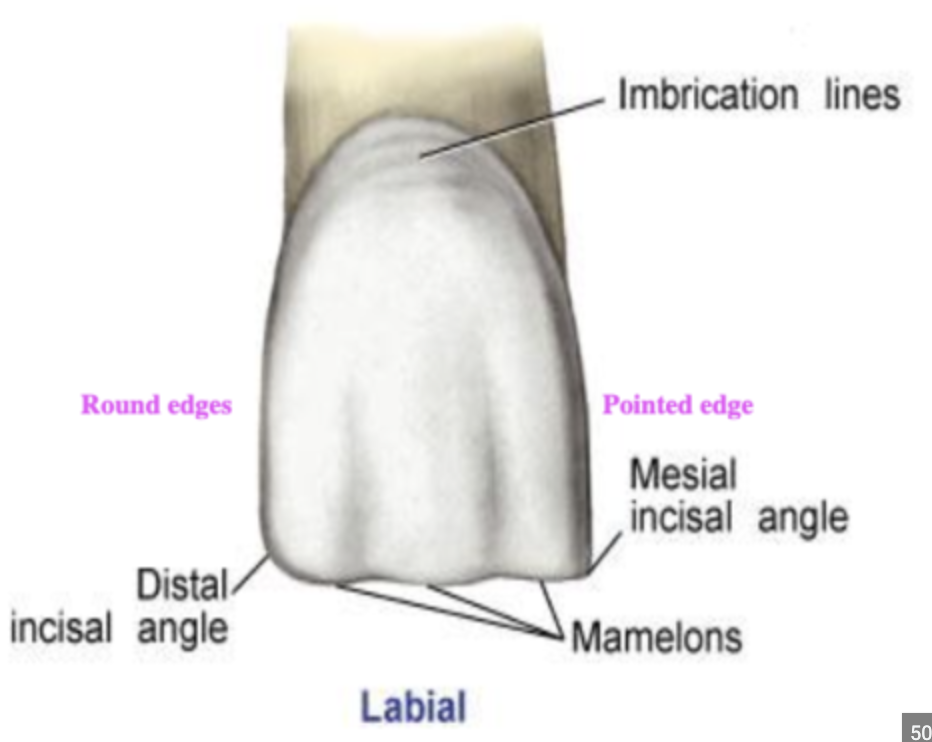
maxillary CI mesial outline (from labial view)
meets the incisal ridge at the right angle
mesioincisal angle on CI is sharp or rounded
sharp
maxillary CI distal outline (from labial view)
distoincisal angle more rounded
maxillary CI incisal margin (from labial view)
may exhibit mamolens , generally straight otherwise
mamolens
rounded protuberances of incisal surface on newly erupted incisor teeth
CEJ of CI
crown is narrower mesiodistally at cervical than incisal
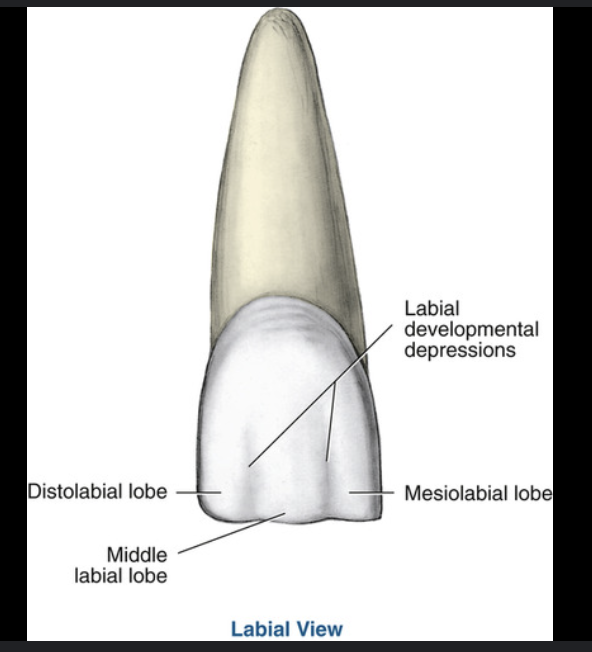
developmental depressions on labial surface of CI
2 straight shallow depressions from incisal ridge towards gingival and fade in middle 1/3
developmental depressions on labial surface of CI location
mesiolabial and distolabial
developmental depressions on labial surface of CI represent
divisions of 3 labial lobes
imbrication lines on labial surface of CI
faint curved lines, parallel to the CEJ (not always present)
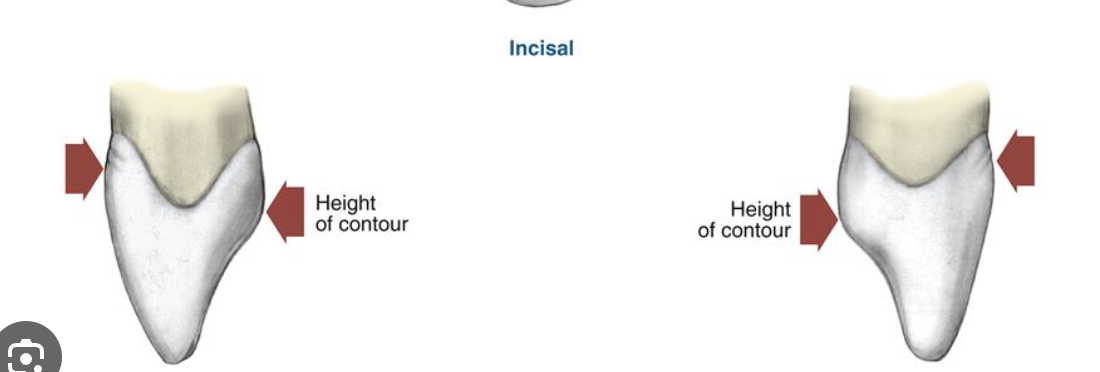
Height of contour on labial surface of CI
on cervical third
Shape of CI from lingual view
trapezoid
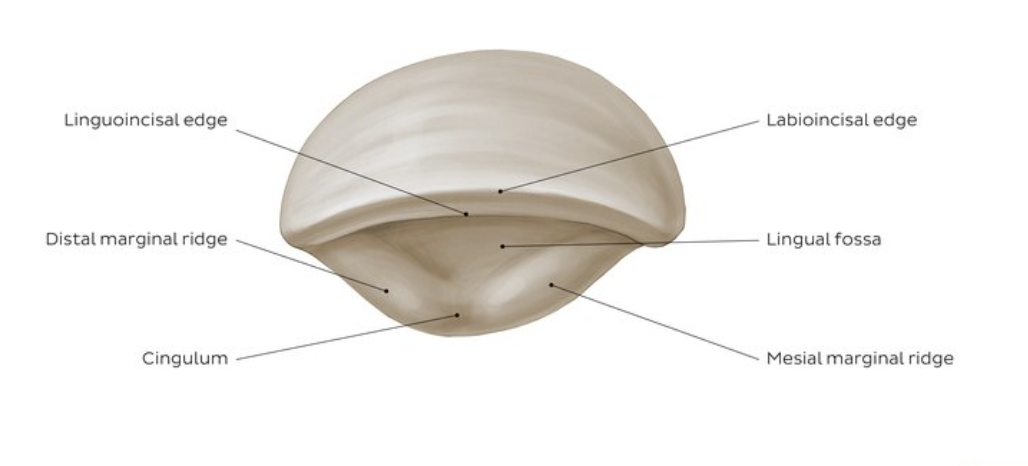
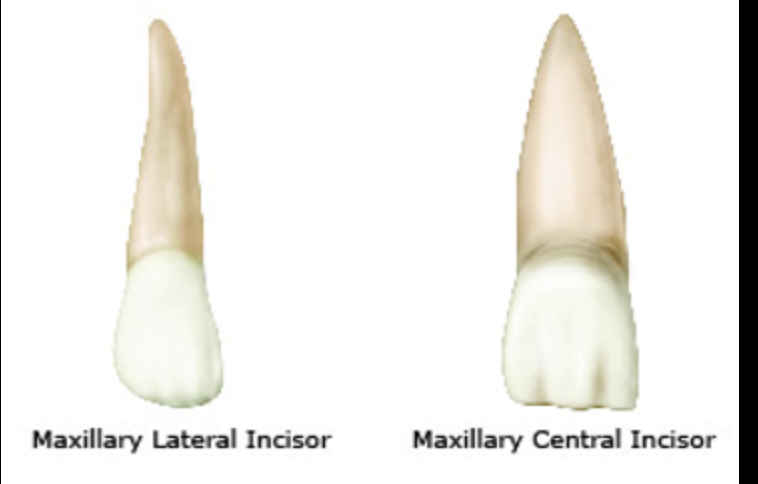
lingual fossa
large shallow conavity on lingual surface if CI
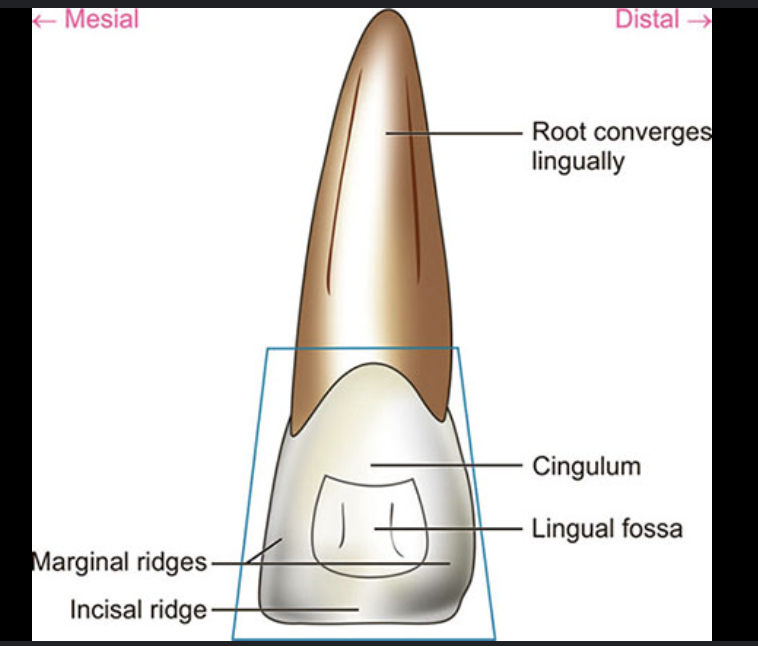
what is CI from lingual view bordered by
mesial marginal ridge
distal marginal ridge
incisal ridge
cingulum
Cingulum on lingual view of CI
bulky convexity in cervical third
what does cingulum on lingual view of CI correspond with
lingual lobe
cingulum on lingual view of CI may be offset
to distal
what sometimes occurs on the lingual aspect of CI
linguogingival groove which separates cingulum from lingual fossa
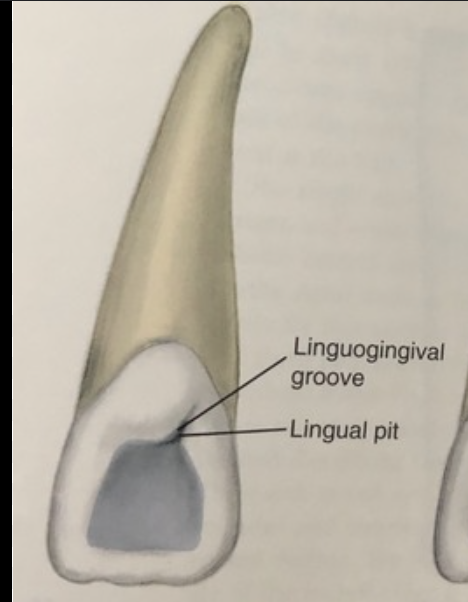
what borders the lingual fossa of CI
mesial and distal marginal ridges
height of contour on lingual view of CI
cervical third at greatest convexity for cingulum
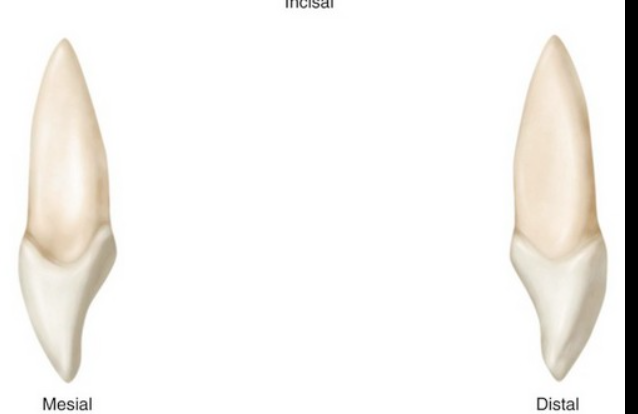
describe the labial outline on the mesial view of CI
convex, greatest at gingival third
describe the lingual outline on the mesial view of CI
greatest convexity at cervical third at the prominence of cingulum, concave toward middle and incisal thirds
on the mesial view of CI, the CEJ curves slightly toward
incisal
on the mesial view of CI, the CEJ curves deeper toward
mesial
Is the CEJ on mesial of on the mesial of CI the greatest curvature of any tooth surface in mouth
yes
incisal outline of CI from mesial view
pointed or slightly rounded, flattens with wear and slopes
distal view of CI resembles
mesial
The CEJ on the distal of CI is
NOT as deep or curved as mesial
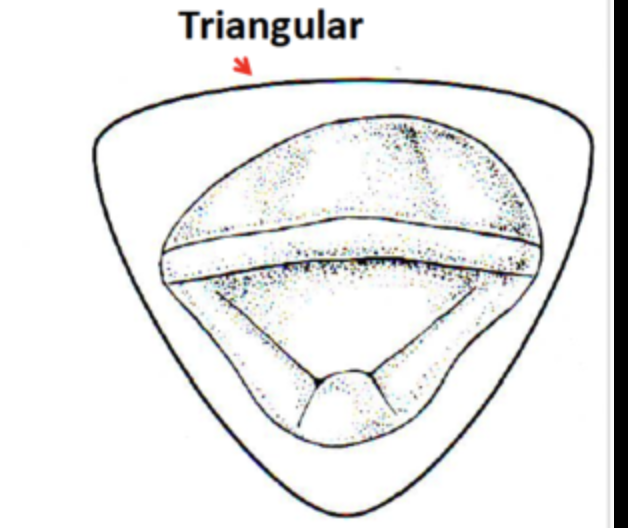
where is Incisal ridge from incisal aspect of CI stright
mesiodistally
where is the incisal aspect widest
mesiodistally
shape of CI from incisal ascept
triangular
Root of CI
single root
conical
relatively straight
tapers to rounded apex
tapers toward lingual
why are CI at risk for truamtic fractures (clinical considerations)
due to position in arch
alvulsion (clinical considerations)
complete displacement of tooth from socketpulp
pulpal pathology (clinical considerations)
disease of pulp usually caused by caries or trauma
diastema (clinical considerations)
space between teeth
lingual pit (clinical considerations)
pit occasionally present on lingual
susceptible to caries
linguolateral groove extends from pit
more common in max. lateral incisors******
shovel shaped incisors (clinical considerations)
deep lingual fossa
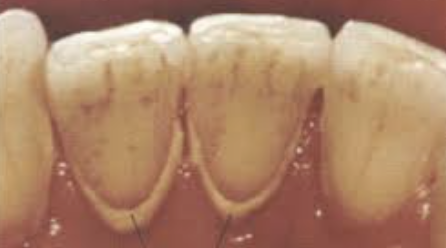
supragingival lingual deposits on CI (clinical considerations)
plaque build up on lingual surface
Dens in dente on CI (clinical considerations)
pit may be entrance when enamel and dentin have become invaginated in the pulp cavity, due to developmental deviation from normal
where are maxillary LI located
2nd from midline
LI have _____ contact with CI
mesial
LI are similar to CI except they are
smaller
LI are narrower
mesiodistally
features, curvatures, concavities, and convexities are ___ ____ and ____ than CI
more prominent and distinct
initiation of development of LI
1 year
eruption of LI
8-9 years
completion of root of LI
11 years
mesial outline of LI from labial view
mesioincisal angle is sharp
distal outline of LI from labial view
more rounded than distal of CI, distoincisal angle is more rounded

incisal surface of LI from labial view
may exhibit mamelons, more rounded incisal angles than CI
Cervical margin (CEJ) of LI from labial view
curves slightly toward root, less curved than CI
developmental depression and imbrication lines of LI from labial view
sometimes present
height of contour of LI from labial view
cervical third
mesial outline of LI from lingual view
similar to mesial of CI
distal outline of LI from lingual view
similar to CI, distoincisal angle is much more rounded than mesiodistal angle
incisal of LI from lingual view
may exhibit mamelons, more rounded incisal angles than CI
cervcial margin of LI from lingual view
CEJ curves toward the apical
mesial and distal marginal ridges and cingulum of LI from lingual view, are more _____ than CI
prominent
Cingulum is ______ in LI from lingual view
centered
lingual fossa in LI is _____ than CI
deeper
lingual pit is ___ ___ on LI than CI
more common (potential site for caries)
linguogingival groove of LI from lingual view
starts are lingual pit and extends distally to cingulum
height of contour of LI from lingual view
at the greatest curvature of cingulum in cervical third
mesial CEJ of LI
deeper than on distal
distal CEJ of LI
not as deep as mesial
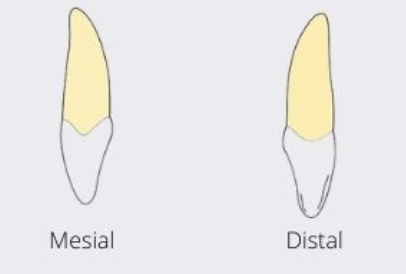
incisal aspect of LI
resembles CI but with more prominent cingulum
in incisal aspect, the LI is more ____ labially and lingually than CI
convex
shape of LI from incisal aspect
rhomboidal
root of LI
single root
conical shape
may curve toward distal
sharp apex
dilaceration (clinical consideration of LI)
distorted shape bend in crowns and usual root curvatures more common than any other incisor
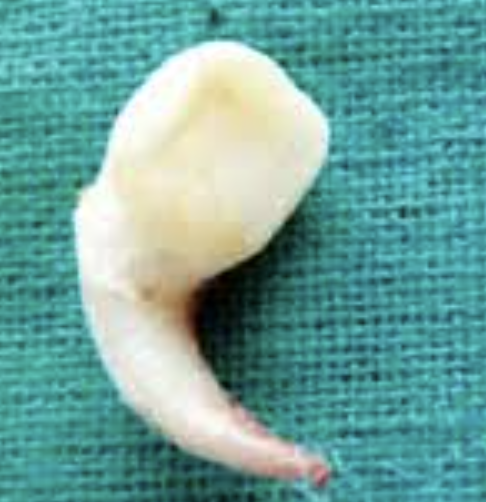
Talon’s cusp (clinical consideration of LI)
incisal portion of cingulum may exhibit tubercle (accessory cusp)
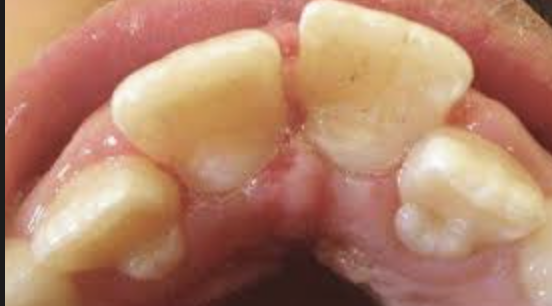
microdontia (clinical consideration of LI)
smaller in size, most common in LI
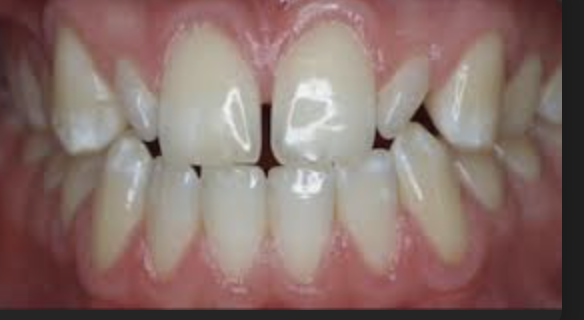
linguogingival groove may accumulate ___ and it may ________ (clinical consideration of LI)
deposits and it may extend all the way onto root surface
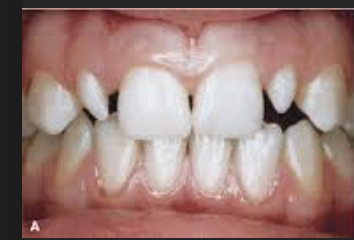
peg lateral (clinical consideration of LI)
lack of development of mesial or distal portions of crown (can be uni or bilateral, relatively common)
congenitally missing LI (clinical consideration of LI)
tooth does not form
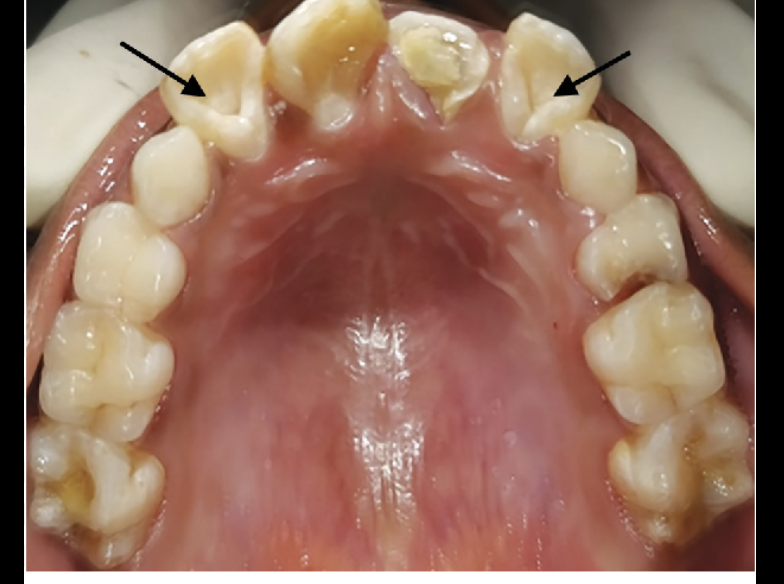
Dens in dente in LI (clinical consideration of LI)
more common in lateral because of lingual pit
maxillary lateral incisor 7 replaces baby tooth
D
maxillary central incisor 8 replaces baby tooth
E
maxillary central incisor 9 replaces baby tooth
F
maxillary lateral incisor 10 replaces baby tooth
G