1.1-1.5: matter and radiation
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is specific charge?
Specific charge is a value that states how much charge something has in relation to its mass
What is the equation that relates to specific charge, mass, charge
Specific charge (Kg^-1)= charge(C)/mass(kg)
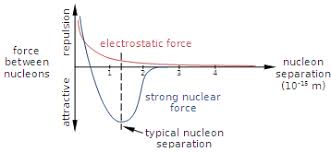
What interaction keeps protons and neutrons together in a stable nucleus?
The Strong Nuclear Force:
Acts between nucleons (p & n).
Very strong but short-range (1–3 fm).
Attractive at 1–3 fm, but repulsive below ~0.5 fm (prevents collapse).
Stronger than electrostatic repulsion between protons.
Acts equally on p–p, n–n, and p–n.
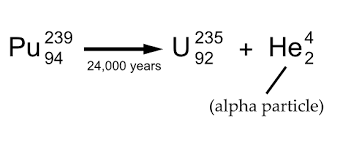
Definition of alpha decay
A type of radioactive decay in which an unstable nucleus emits alpha particles resulting in a new nucleus with its atomic number reduced by 2 and mass number reduced by 4.
define Beta minus decay
A type of radioactive decay in which a neutron in an unstable nucleus changes into a proton, emitting a beta particle (a high energy electron) and an antineutrino.
Increases the atomic number by 1 (new element formed)
Mass number stays the same (total nucleons unchanged)
What are Photons
A particle representing a quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation (smallest discrete packet of light or EM energy)
Photons are massless, and have no charge,(so can travel at the speed of light) particles of EM radiation.
They exhibit wave–particle duality, meaning sometimes they act like waves, sometimes like particles, depending on the experiment.
nature of photons
Wave-like properties
Can interfere and diffract, like light waves.
Have a wavelength (lamda) and frequency (f).
Energy related to frequency: E = hf
Particle-like properties
Can be thought of as discrete packets of energy (quanta).
Can transfer energy in collisions, e.g., knock electrons out in the photoelectric effect.
Have no mass and no charge, but carry energy and momentum.
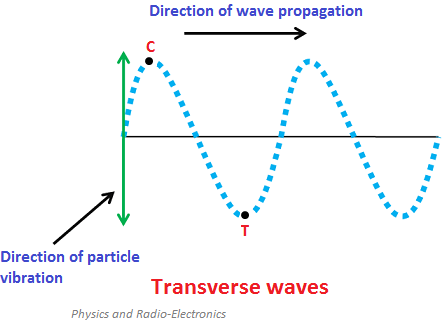
What are electromagnetic waves
EM waves are transverse waves consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation.
Transverse waves (oscillate perpendicular to the energy transfer)