SAPPECO quiz 1 (modules 1a, 2a, 2b)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Microeconomics
The study of the economic
behavior of individuals and
firms.
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a
whole, looking at economy-wide
factors such as interest rates,
inflation, growth, and
unemployment.
Applied Economics
Reduction of abstraction
a. Attaching labels to variables and
concepts in the core theory
b. Applying additional structure to
the theory
c. Providing numerical values for
key parameters
d. Interpret specific real events
Applied Economics
The reduction of abstraction:
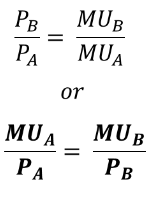
formula for marginal rate of substitution

formula for inflation rate
consumer price index
CPI
Applied Economics
combination of macroeconomics and microeconomics
Laws of Demand and Supply
The Price Theory
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Cournot Equilibrium
Nash Equilibrium
economic laws and theories
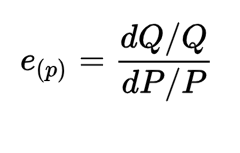
Formula to calculate the economic price
consumers
the people who buy goods and services
producers
create or provide a certain good (product) or
service. Producers can be individuals or
companies.
Demand
a schedule or curve that shows the various
amounts of a product that consumers are
willing and able to purchase at
each of a series of possible
prices during a specified
period of time.
Supply
a schedule or curve showing the various
amounts of a product that producers are willing and able to make available for sale at each of a series of possible prices during a specific period, other things equal.
increase in demand
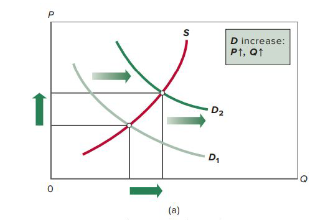
decrease in demand
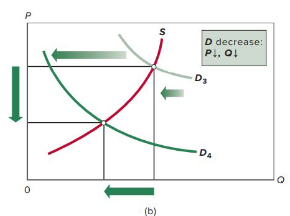
increase in supply
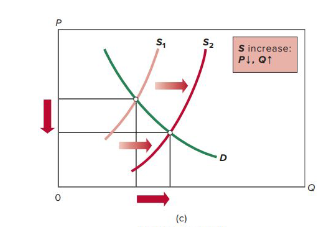
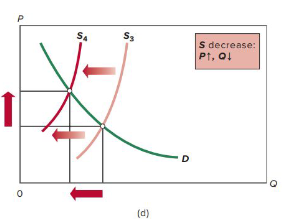
decrease in supply
Commodity
A raw material, such as oil or copper, that is
usually traded in bulk. Changes in commodity
prices can have significant economic effects by, for example, feeding through into consumer prices.
Utility
In economics, utility is a term used to determine
the worth or value of a good or service. More
specifically, utility is the total satisfaction or
benefit derived from consuming a good or
service
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce?
3. For whom to produce?
4. What provisions (if any) are to be made for
economic growth?
4 Basic Economic Problems
traffic congestion
cartel
Remittance Dependency
Natural Disaster Vulnerability
Environmental Sustainability
Socioeconomic Problems
Traffic Congestion
cartel
Agreement where a group of producers
collaborate to fix the price, or restrict the
supply, of a good or service. Cartels among
companies are often outlawed by government
antitrust regulations because they restrict
competition.
Remittance Dependency
play a crucial
role in supporting many Filipino
families, over-reliance on this
income source exposes the
economy to global economic
fluctuations and uncertainties in
foreign employment conditions.
Diversification strategies are
essential to mitigate risks
Natural Disaster Vulnerability
According to the Asian Development Bank,
the Philippines is among the world’s most
disaster-prone countries, experiencing an
average of 20 typhoons annually.
Environmental Sustainability
The Philippines placed 158th out of 180 countries in the 2022 edition of
the biennial Environmental Performance Index. Deforestation, pollution,
and habitat destruction are significant environmental challenges.
scarcity
Limited supply
shortage
temporary loss of supply
Self Actualization
Esteem
Love and Belonging
Safety needs
Physiological needs
Maslow’s Hiearchy of needs
Law of Demand
the claim that, other
things being equal, the
quantity demanded of a
good falls when the price
of the good rises
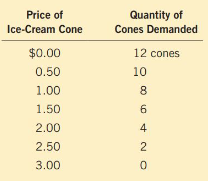
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantity demanded at each price. It illustrates the quantity demanded of the good changes as its price varies.
income
When this is lower, it means that you
have less to spend in total, so
you would have to spend less
on some—and probably
most—goods.
it becomes higher
When the peso rate is lower what happens to the dollar rate
normal good
good where the demand for a good falls when
income falls
inferior good
the good where the demand for a good rises when income falls
substitutes
complements
price of related goods
substitutes
When a fall in the price of one good
reduces the demand for another good
complements
When a fall in the price of one good
raises the demand for another good
tastes
Economists normally do not try
to explainthis because
they are based on
historical and psychological
forces that are beyond the realm
of economics. Economists do,
however, examine what
happens when tastes change.
number of buyers
In addition to the preceding
factors, which influence the
behavior of individual buyers,
market demand depends on this
Law of Supply
the claim that, other things being equal,
the quantity supplied of a good rises when the
price of the good rises.
Input Prices
Technology
Expectations
Number of Sellers
Shifts in the Supply Curve
input prices
When the price of one or more
of the inputs rises, producing
the good is less profitable, and
firms supply less ice cream
Technology
Reduces the amount of labor
necessary to produce the good.
(e.g. Bibingka Oven)
Bibingka Oven
Traditional Bibingka Equipment
Expectations
The amount of product a firm
supplies today may depend on
its expectations about the
future
Number of Sellers
Market supply depends on the
number of sellers. Generally,
with more sellers, there is more
supply. With fewer sellers, there
is less supply.
Equilibrium
a situation in which the market price has
reached the level at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
Equilibrium Price
the price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded
Equilibrium Quantity
the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium price
The Price Theory
an economic theory that states
that the price for a specific good
or service is determined by the
relationship between its supply
and demand at any given point.
Price Elasticity of Demand
measures how much the quantity demanded
(Qd) responds to a change in price.
elastic
quantity demanded responds significantly to
changes in the price
Inelastic
quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price.
elastic
close substitutes tend to
have more______ demand
inelastic
necessities
elastic
luxuries
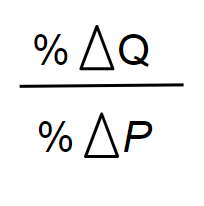
basic formula of Economy price
Infinity
calculated price elasticity of perfectly elastic
Perfectly Inelastic
result of change in price that declines to zero
greater than 1
calculated price elasticity of elastic
1
calculated price elasticity of unitary elasticity
Unitary Elasticity
result of change in price that is equivalent percentage change
less than 1
calculated price elasticity of inelastic
inelastic
result of change in price with insignificant change
0
calculated price elasticity of Perfectly Inelastic
Perfectly inelastic
result of change in price with no change
Elastic
result of change in price that has a significant change in demand
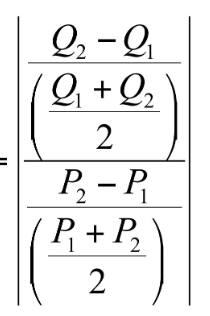
Midpoint formula
Price Elasticity of Supply
measures how much the quantity supplied (Qs)
responds to a change in price.
This elasticity is usually positive because a
higher price gives producers an incentive to
increase output.
Firms operating close to full capacity.
Firms have low levels of stocks, therefore there
are no surplus goods to sell.
With agricultural products, supply is inelastic in
the short run
Supply could be inelastic for
the following reasons:
If there is spare capacity in the factory.
If there are stocks available.
If it is easy to employ more factors of
production.
If a product can be sold from the internet which
increases the scope of international competition
and increases options for supply
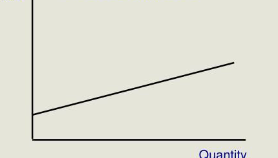
Supply could be elastic for
the following reasons:
perfectly elastic

Elastic
Perfectly Inelastic
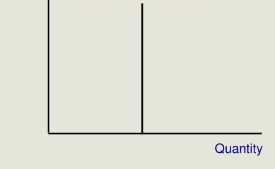
Inelastic
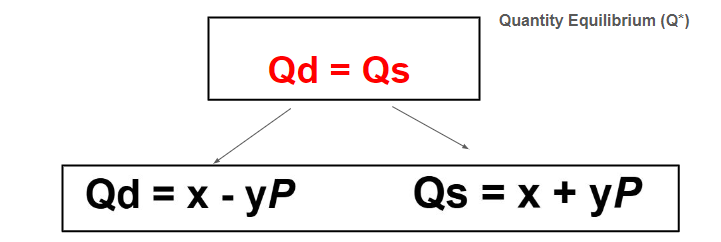
Equilibrium Formula
Equilibrium
balance between supply of and demand for a good at a market clearing price
All else being equal
What does Cetris Paribus mean
MPPa/MPPb
If MPPa and MPPb represents the marginal physical products of two inputs, then the marginal rate of substitution would be