Sec+ Messer Practice Exams (Ones I got wrong)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
DKIM vs DMARC
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) verifies email integrity and authenticity by using digital signatures.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) provides instructions to receiving email servers on how to handle unauthenticated messages (authorized devices list also)
Security Content Automation Protocol
RTOS
Real time operating system - an operating system (OS) for real-time computing applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints
What is regulated data?
information that is protected by local, national, or international statute or regulation mandating certain restrictions
On path attack?
cyberattack where an attacker intercepts and possibly alters communication between two parties who believe they are communicating directly with each other
What is federation?
process that allows users to authenticate to multiple systems using a single set of credentials, often across different organizations
What is MOA?
non-binding document that outlines the terms of a collaborative relationship between parties. It's a more formal agreement than a verbal understanding but less binding than a formal contract
Deterrent in regard to security control?
attempt to prevent incidents by discouraging individuals from causing security incidents
What is a record encryption?
helps organizations maintain compliance with data security standards with an additional layer of protection for sensitive data
What is journaling?
he practice of logging and recording information for various purposes, such as auditing, compliance, or data recovery
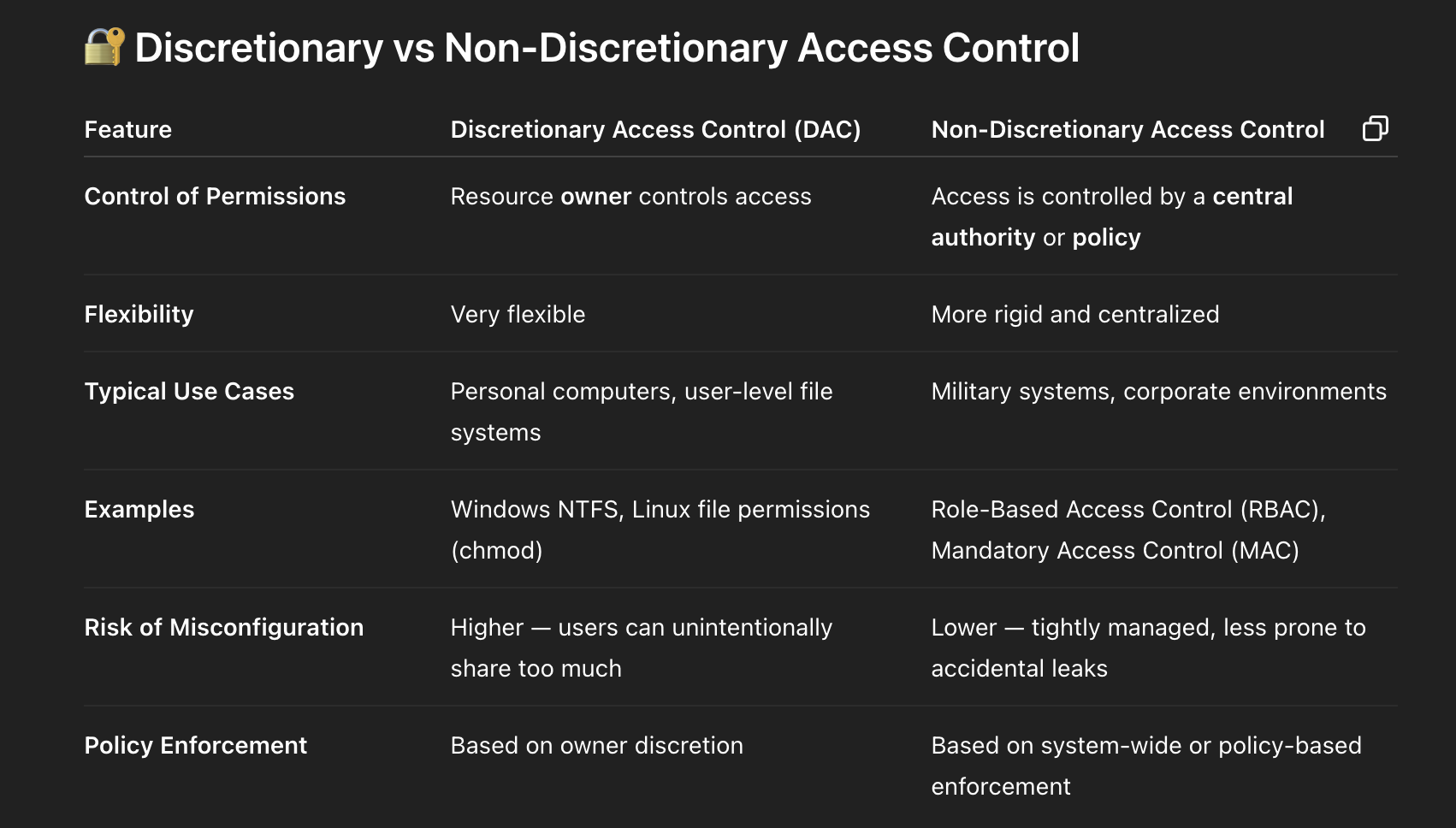
What is discretionary access control?
type of access control where the owner of a resource (like a file or directory) decides who can access it and what they can do with it
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
enforces access based on centrally defined policies and user clearance levels
What is a responsibility matrix?
who is accountable for specific cybersecurity tasks and responsibilities within an organization. It clarifies roles and responsibilities, ensuring accountability and efficient resource allocation, especially during incidents.
What is SASE?
a cloud-delivered cybersecurity framework that integrates networking and security functions into a single, unified platform
Containerization
a lightweight virtualization method that packages applications and their dependencies into self-contained units called containers, which run on a shared host operating system
What is OSINT?
Open source intelligence (gather info about company from outside sources, like social media)
What is tokenization?
the process of replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive, unique placeholders called tokens
What is a WAF?
Web Application Firewall - cybersecurity solution designed to protect web applications from a variety of cyber threats and attacks
What is a replay attack?
A replay attack in cybersecurity is an attack where an attacker intercepts legitimate data transmission, typically an authenticated message, and then retransmits it to trick the recipient into performing an unauthorized action or gaining access
What is secure enclave?
a hardware-based, isolated environment within a CPU that's designed to protect sensitive data and cryptographic keys. It's like a secure "black box" that isolates critical operations, preventing unauthorized access to protected data even if the main operating system is compromised
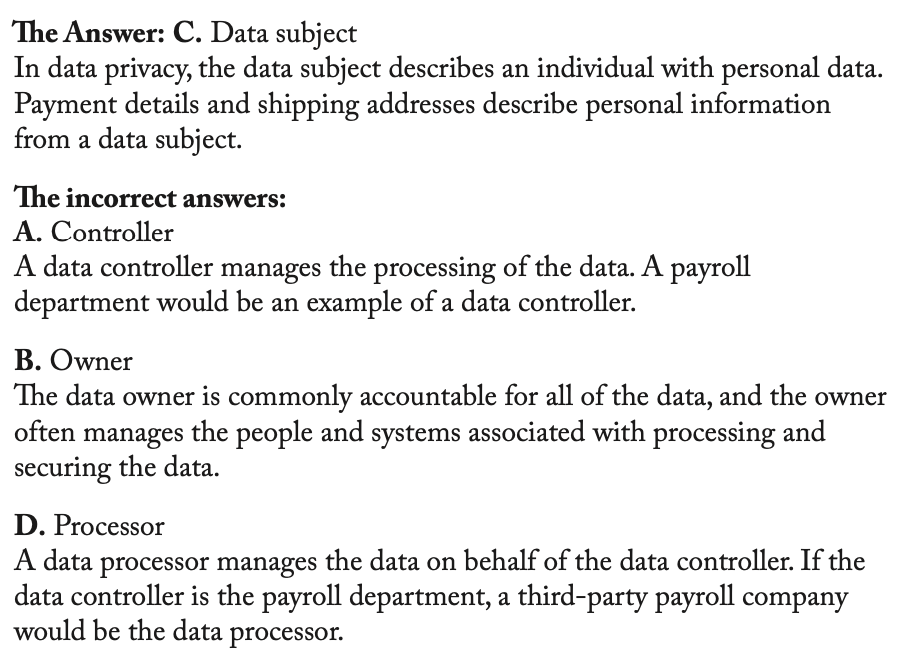
What is a data subject?
data subject is an individual whose personal data is being processed, meaning it is being collected, used, or stored by an organization
What is detective in terms of security control?
security controls that are designed to detect, log, and alert after an event has occurred
AAA have a big focus on centralizing authentication.
What is OCSP stapling?
a technique that enhances the efficiency and security of SSL/TLS connections by streamlining the certificate validation process
Whats a wildcard in cybersecurity?
a wildcard SSL/TLS certificate, which allows you to secure multiple subdomains under a single certificate
What is CSR creation?
creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), a digital file used to request a digital certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This CSR contains information about the entity requesting the certificate
What is exposure factor?
the percentage of an asset's value that would be lost if a specific threat or vulnerability were to be exploited. It's a key component in calculating potential losses and prioritizing security efforts
What is conflict of interest?
when an individual's personal interests or obligations potentially conflict with their professional duties, potentially compromising the organization's security
What is chain of custody?
a meticulously documented record of who handled, when, and why digital evidence was accessed, modified, or transferred from its point of collection to its final destination
What is E-discovery?
e-discovery refers to the process of identifying, preserving, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) for legal purposes, such as in investigations or as evidence in lawsuits
What is a legal hold?
a legal hold is a formal notice that organizations send to employees (custodians) when litigation or a potential legal dispute arises. It instructs them to preserve all potentially relevant information, including physical documents and electronically stored information (ESI), for a period of time
What is an air gap?
an air gap refers to the physical or logical separation of a computer or network from other systems, particularly the internet or other networks. This isolation is a security measure intended to protect sensitive data and systems from cyber threats like malware and ransomware
What is a fail-open?
a system's behavior where, in the event of a failure or malfunction, it reverts to an open state, allowing unrestricted access or functionality
What is mandatory access control?
an access control model where the system, not the individual user, dictates who can access a resource based on predefined security policies. It's a nondiscretionary access control, meaning the user can't override the system's restrictions.
What is ARO?
Annual Rate of Occurrence. It represents the estimated frequency with which a particular risk or threat is expected to occur within a given year.
What does XDR stand for?
XDR stands for Extended Detection and Response. It's a technology that collects and analyzes security data from multiple sources (like endpoints, networks, and cloud) to improve threat detection, investigation, and response.
What does HA stand for?
High Availability - ensuring continuous operation of critical security systems, even during failures or outages, by implementing redundant systems and failover mechanisms
What does ALE stand for?
Annual Lost Expectancy - metric used to estimate the potential financial loss an organization might experience from a specific security risk over a one-year period
What does SLE stand for?
Single Loss Expectancy - represents the monetary value of a single loss that can occur if a specific asset is compromised or vulnerable
What does EDR stand for?
Endpoint Detection and Response - A technology that continuously monitors endpoints (devices like laptops, desktops, and mobile devices) to detect and respond to cyber threats.
What does CRL stand for?
certificate revocation list (CRL) - a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing certificate authority (CA) before their actual or assigned expiration date
Admin vs Owner vs Group vs System — Rights/Permissions Control
Pic attached
SSO vs Federation
single organization vs multiple
Active Reconnaissance
where an attacker or tester actively engages with a target system to gather information
What is an injection?
The unwanted injection of data into a database, library, or any other data flow
Forgery Attack
cross-site request forgery commonly uses malicious links to take advantage of the trust a site might have for a user's browser. Packet captures are not necessary to perform a forgery attack.
SD-WAN
SD-WAN network allows users to efficiently communicate directly to cloud-based applications
What is Non-repudiation?
the assurance that someone cannot deny the validity of their actions or communications.
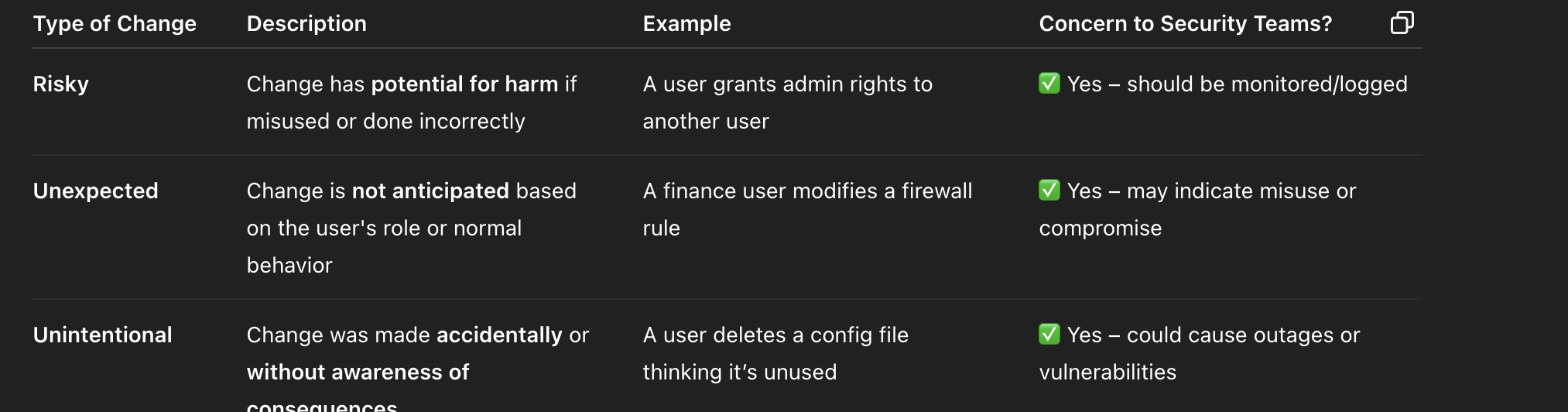
User Changes to system: Risky vs. Unexpected, vs Unintentional
image attached
Shared Session Key ~ Asymmetric Encryption
The Diffie-Hellman algorithm can combine public and private keys to derive the same session key. This allows two devices to create and use this shared session key without sending the key across the network.
What is a dependency?
Modifying one part of a system may first require changes to other components. In this example, the application upgrade is dependent on an updated version of a device driver.
802.1x info
When 802.1X is enabled, devices connecting to the network do not
gain access until they provide the correct authentication credentials.
This 802.1X standard refers to the client as the supplicant, the switch
is commonly configured as the authenticator, and the back-end authentication server is often a centralized user database.
Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP)
standardize how security software identifies, assesses, and reports vulnerabilities and configurations in computer systems
OSINT meaning?
Open Source Intelligence - It refers to the process of collecting and analyzing publicly available information to gather intelligence
Cross-site scripting
allows an attacker to inject malicious scripts into websites viewed by other users. These scripts run in the victim's browser, often without their knowledge…leading to stealing data
Domain Hijacking
gains control over a domain name, effectively stealing ownership from the legitimate domain holder
Note: An on-path attack is often associated with a third-party who is actively intercepting network traffic. This entity in the middle would not be able to provide a valid SSL certificate for a third-party website, and this error would appear in the browser as a warning.
—
Note: Federation would allow members of one organization to authenticate using the credentials of another organization.
Note: An MOA (Memorandum of Agreement) is a formal document where both sides agree to a broad set of goals and objectives associated with the partnership.
—-
Note: Integrity refers to the trustworthiness of data. A digital signature allows the recipient to confirm that none of the data has been changed since the digital signature was created.
—
Note: A race condition occurs when two processes occur at similar times, and usually with unexpected results. The file system problem can often be fixed before a reboot, but the reboot is occurring before the fix can be applied. This has created a race condition that results in constant reboots.
—
Platform Diversity
Using different operating systems and platforms can help mitigate issues associated with a single OS, but it wouldn't provide any mitigation if the primary Internet connection was no longer available.
Journaling writes data to a temporary journal before writing the information to the database. If power is lost, the system can recover the last transaction from the journal when power is restored.
—
Compensating controls
Compensating controls are used to mitigate a vulnerability when an optimal security response may not be available. For example, if a company can't deploy a patch for a vulnerability, they can revoke or limit application access until a patch is provided.
—
Guard rails:
Guard rails are used by application developers to provide a set of automated validations to user input and behavior.
—
A posture assessment evaluates the configuration of a system to ensure all configurations and applications are up to date and secure as possible. If a configuration does not meet these standards, the user is commonly provided with options for resolving the issue before proceeding.
—
Discretionary vs Mandatory access control
Discretionary
Discretionary access control is used in many operating systems, and this model allows the owner of the resource to control who has access.
Mandatory
Mandatory access control allows access based on the security level assigned to an object. Only users with the object’s assigned security level or higher may access the resource.
Network protection mismatches
A hybrid cloud includes more than one private or public cloud. This adds additional complexity to the overall infrastructure, and it's common to inadvertently apply different authentication options and user permissions across multiple cloud providers.
—
Risk appetite
A risk appetite is a broad description of how much risk-taking is deemed acceptable. An organization's risk appetite posture might be conservative, or they might be more expansionary and willing to take additional risks
—
Impact Analysis
process of assessing the consequences that a cyber threat, vulnerability, or security incident could have on an organization’s assets, operations, or individuals.
Privilege escalation
A privilege escalation attack allows a user to exceed their normal rights and permissions. In this example, user permission escalations were not required to perform this attack.
—
Misconfiguration
There are many different configuration options when installing an access point, and it's likely one of those options allowed an attacker to gain access to the internal network.
—
Note: DNS filtering uses a database of known malicious websites to resolve an incorrect or null IP address. If a user attempts to visit a known malicious site, the DNS resolution will fail and the user will not be able to visit the website.
—-
What is a downgrade attack?
attacker forces a system, application, or communication protocol to use an older, less secure version of a protocol or software—one that is more vulnerable to exploitation.
What is configuration enforcement?
ensuring that systems, applications, or devices adhere to predefined security and operational settings
What is sanitization?
deletes data from storage media and allows the storage device to be used in the future
NOTE: A SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) solution is a next-generation VPN technology designed to optimize the process of secure communication to cloud services
—
What is an advanced persistent threat (APT)?
attacker gains unauthorized access to a network and remains undetected for a long period to steal data, spy, or cause damage
SDN
SDN (Software-Defined Networking) separates the control plane of devices from the data plane. This allows for more automation and dynamic changes to the infrastructure.
DKIM
A DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) record is a DNS (Domain Name System) entry that includes the public key associated with an email server's digital signatures. A legitimate email server will digitally sign all outgoing emails and provide the public key in their DNS for third-party validation.
Due Care
taking all reasonable, responsible, and industry-accepted precautions to protect an organization’s information systems, data, and users from threats. It's about acting prudently and proactively to prevent harm—and being able to prove it.
Exposure Factor
It represents the percentage of asset value loss that would occur if a specific threat or event were to happen.
Data Exfiltration
Exfiltration describes the removal or theft of data by a third-party.
NOTE: 802.1X is commonly used in conjunction with LDAP, RADIUS, or similar authentication services.
—

Evidence related terminology and documentation pic
—
NOTE: The secure enclave monitors the boot process, create true random numbers, store root cryptography keys, and much more.
—
Data owners, processor, etc. Pic
—

Access Control Types (mandatory, etc..) Pic
—-
NOTE: If rule is not made on firewall ACL’S, then its an implicit deny!!!
—
Orchestration
Orchestration describes the process of automation, and is commonly associated with large scale automation or automating processes between different systems.
Data hashing
Data hashing creates a unique message digest based on stored data. If the data is tampered with, a hash taken after the change will differ from the original value. This allows the forensic engineer to identify if information has been changed.

Another access/permissions related pic
—
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a system that uses public and private key cryptography to enable secure and reliable digital communications
Static analysis
view code without running it (check for vulnerabilities, weaknesses, etc.)