Chemistry Fall FINAL EXAM Study Guide
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
What are the steps to the scientific method?
Make an observation
Ask a question
Form a hypothesis
Record data
Draw a conclusion
What is a way of writing large or small numbers in an easier form known as...
Scientific notation

SI units (kg,ml,cm,ect) are used because they...
Are not easily converted

List examples of units
Kilograms, Gram, millimeters
The symbols for units of length in order from smallest to largest order are ...
Mm, cm, m, km
A measurement that closely agrees with accepted value is said to be...
Accurate

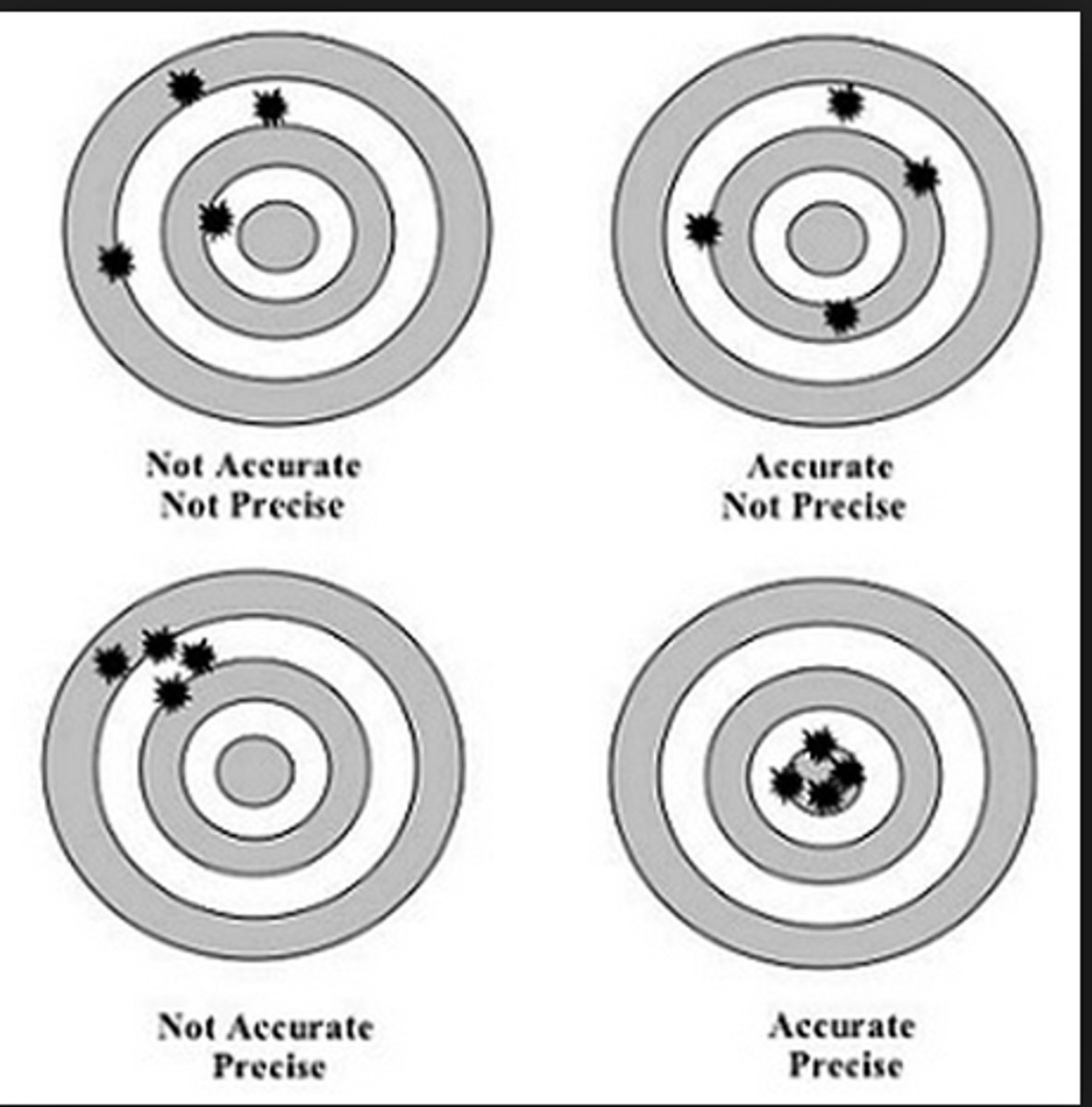
The following image shows which of the following?
Accurate and Precise

These values were obtained as the mass of products from the same reaction: 8.83g, 8.84g and 8.82g. The known mass of products from that reaction is 5.60g. The values are...
Precise
Put the measurement of .0225g to two significant figures:
0.022g

How many significant figures are in the measurement 0.000305kg is
3
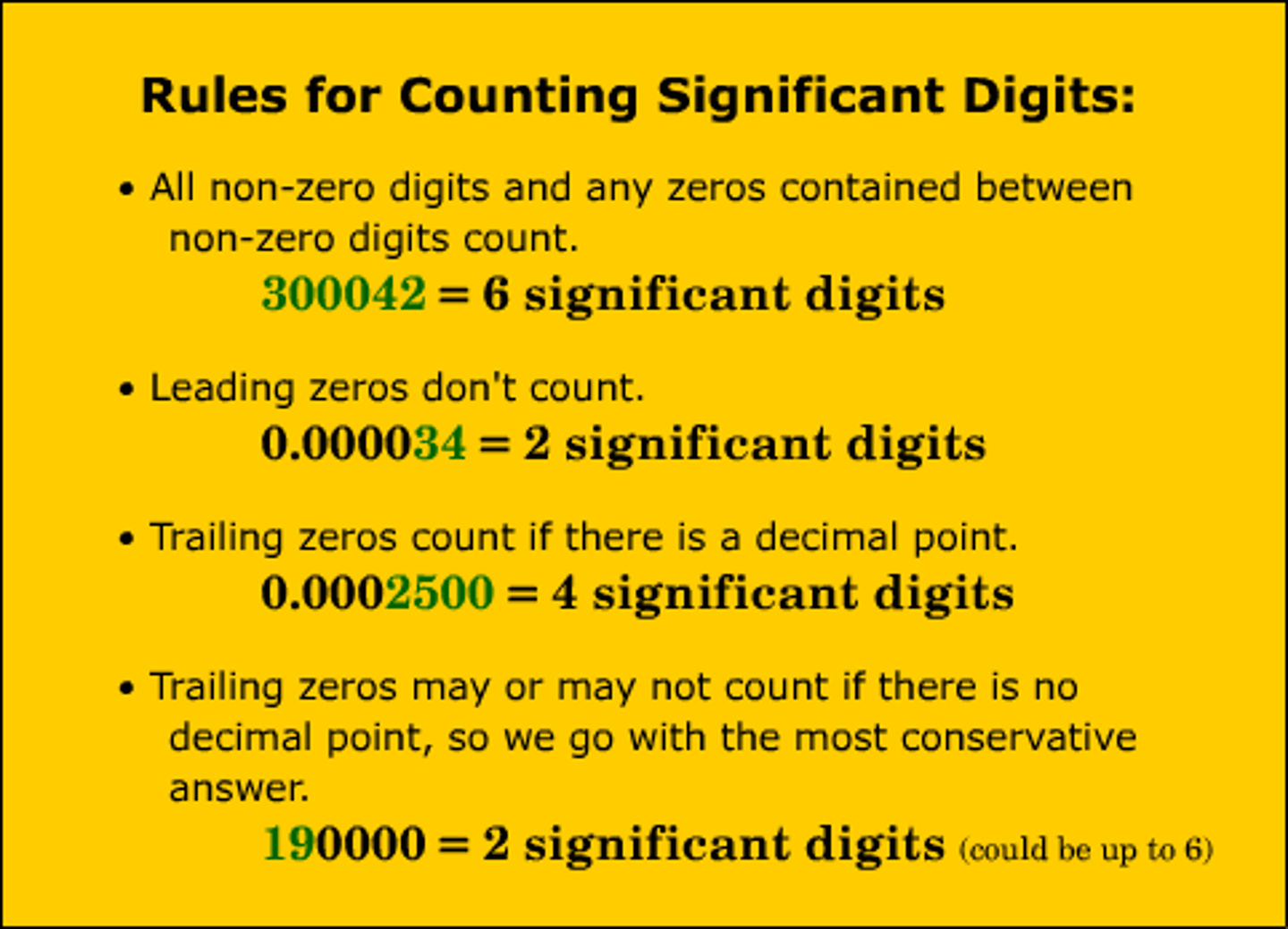
How many significant figures are in the measurement 170.040km is...
6
The measurement that has been expressed to four significant figures is...
402.10mm
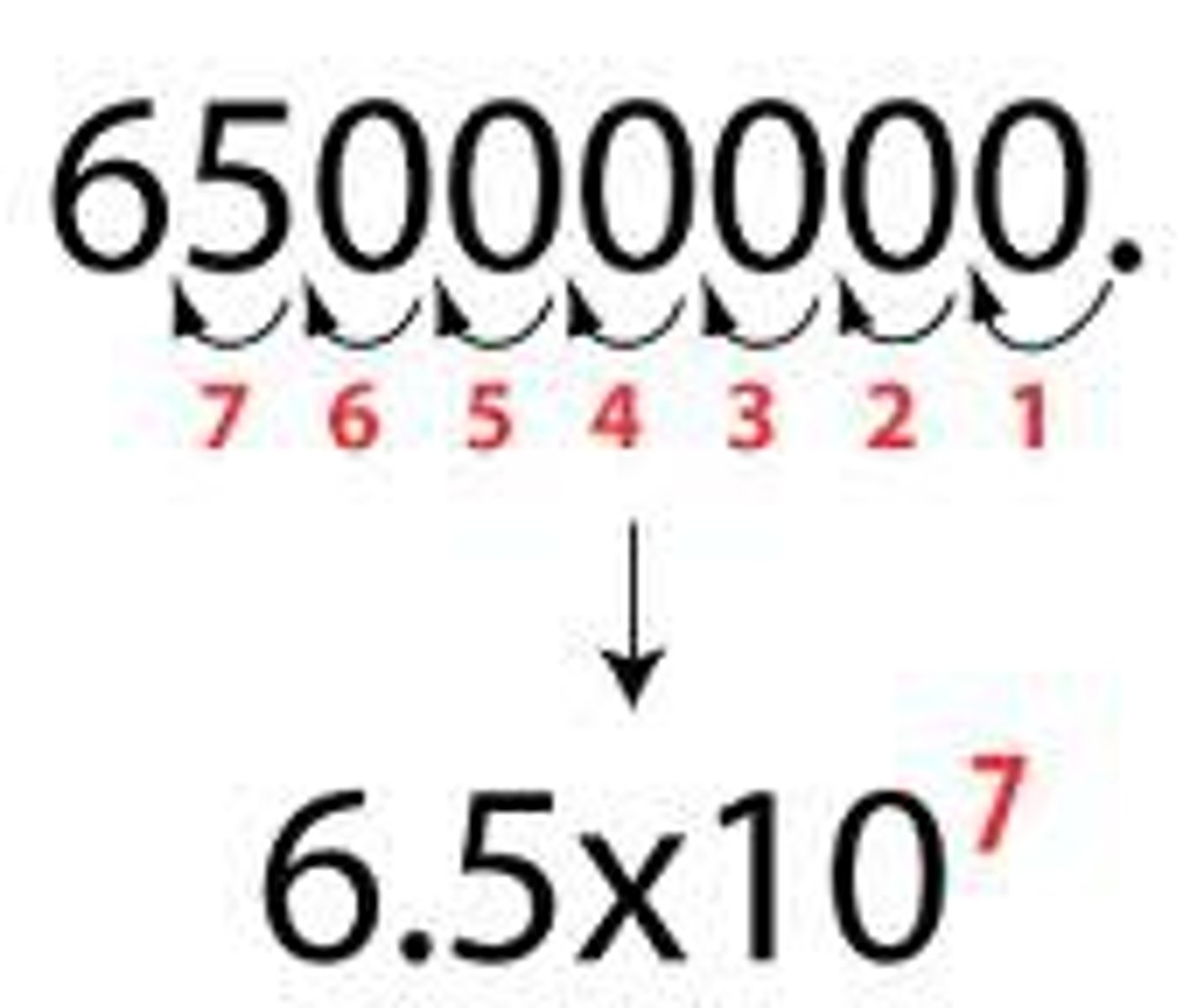
Written in scientific notation the measurement 0.000065 is ...
6.5 x 10^-5 cm
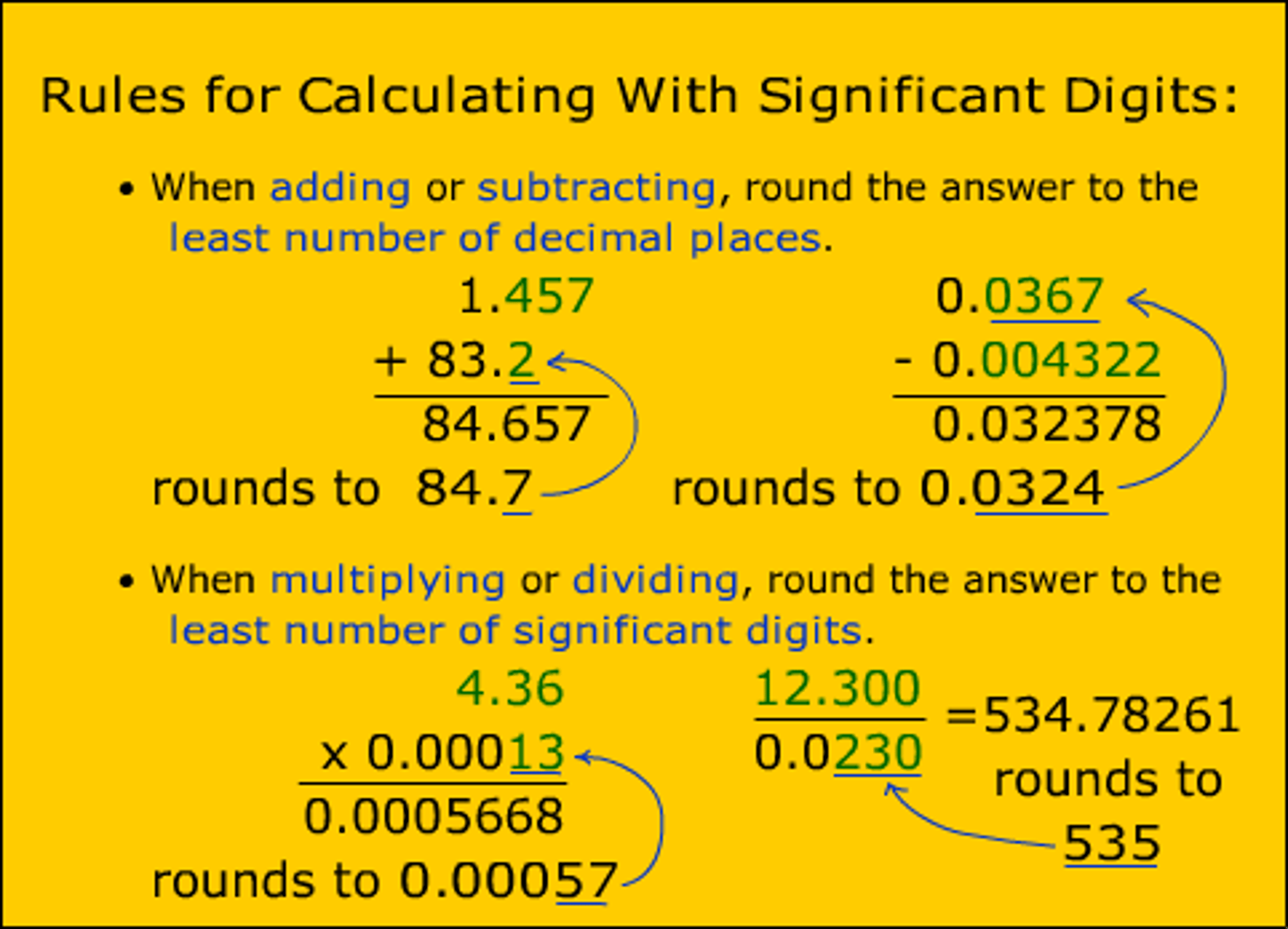
When 78.5 is divided by 1.40, the correct number of sig figs in the answer would be...
3
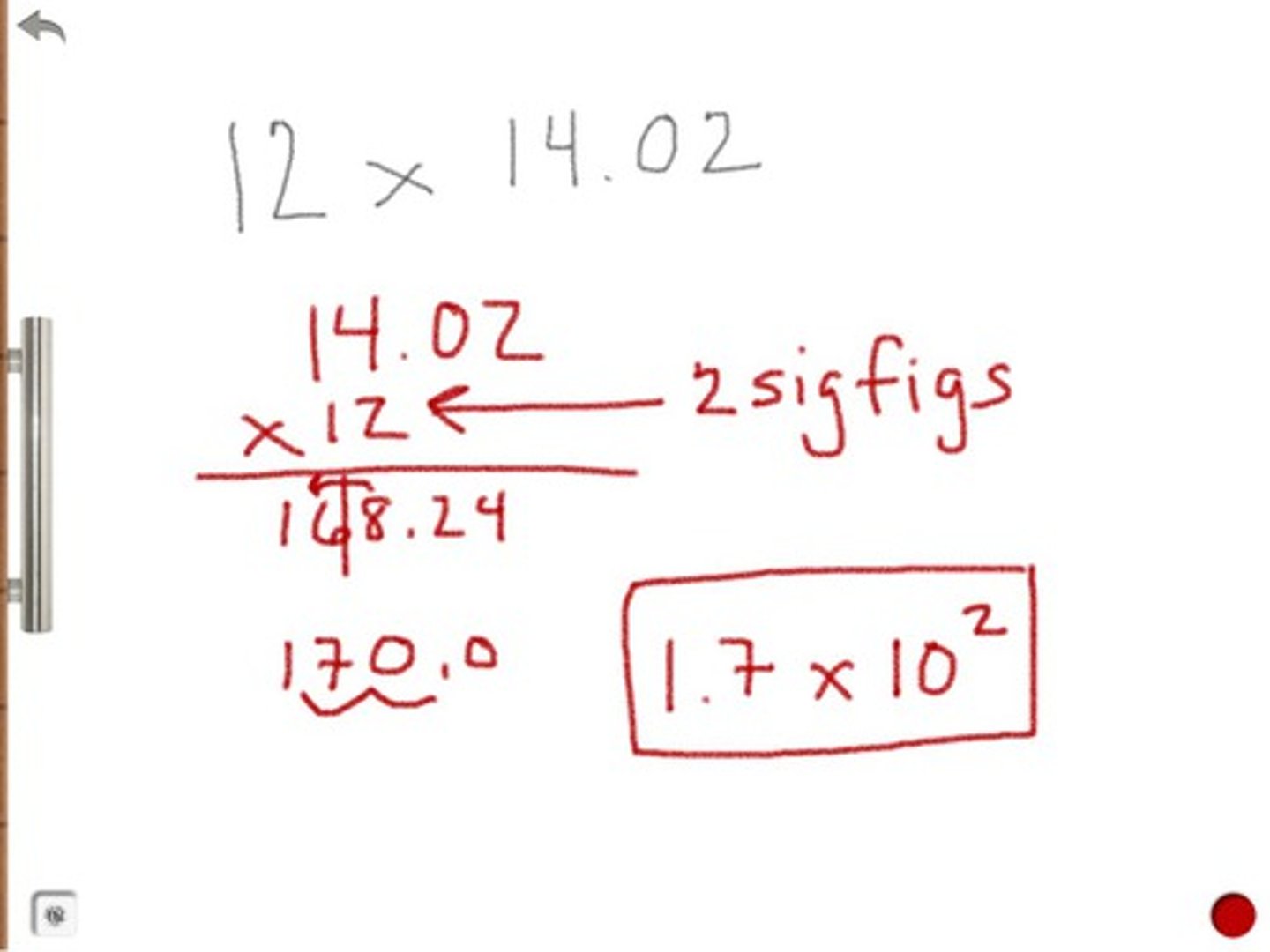
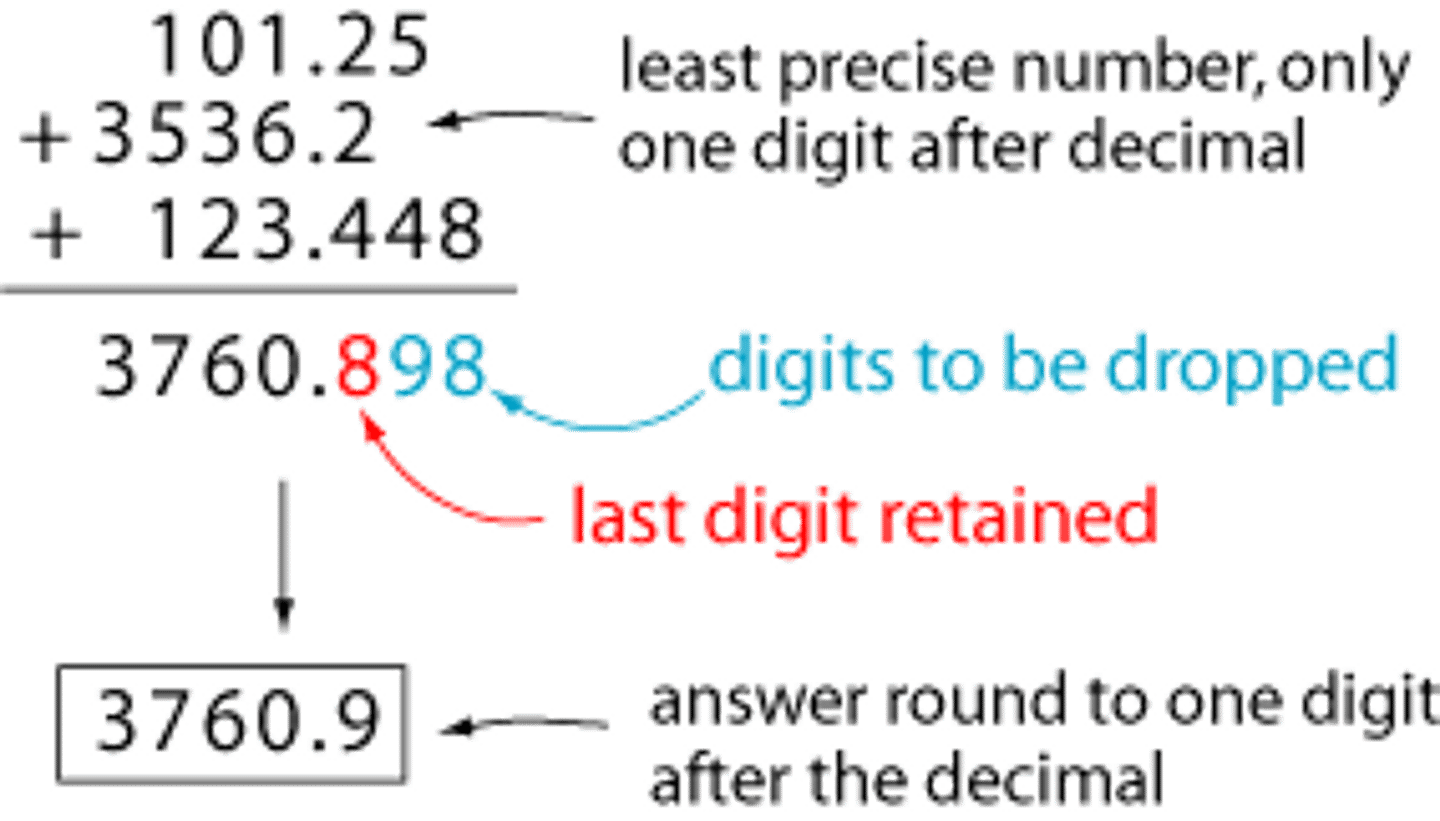
The sum of 295.3km and 65km is correctly expressed as...
360km
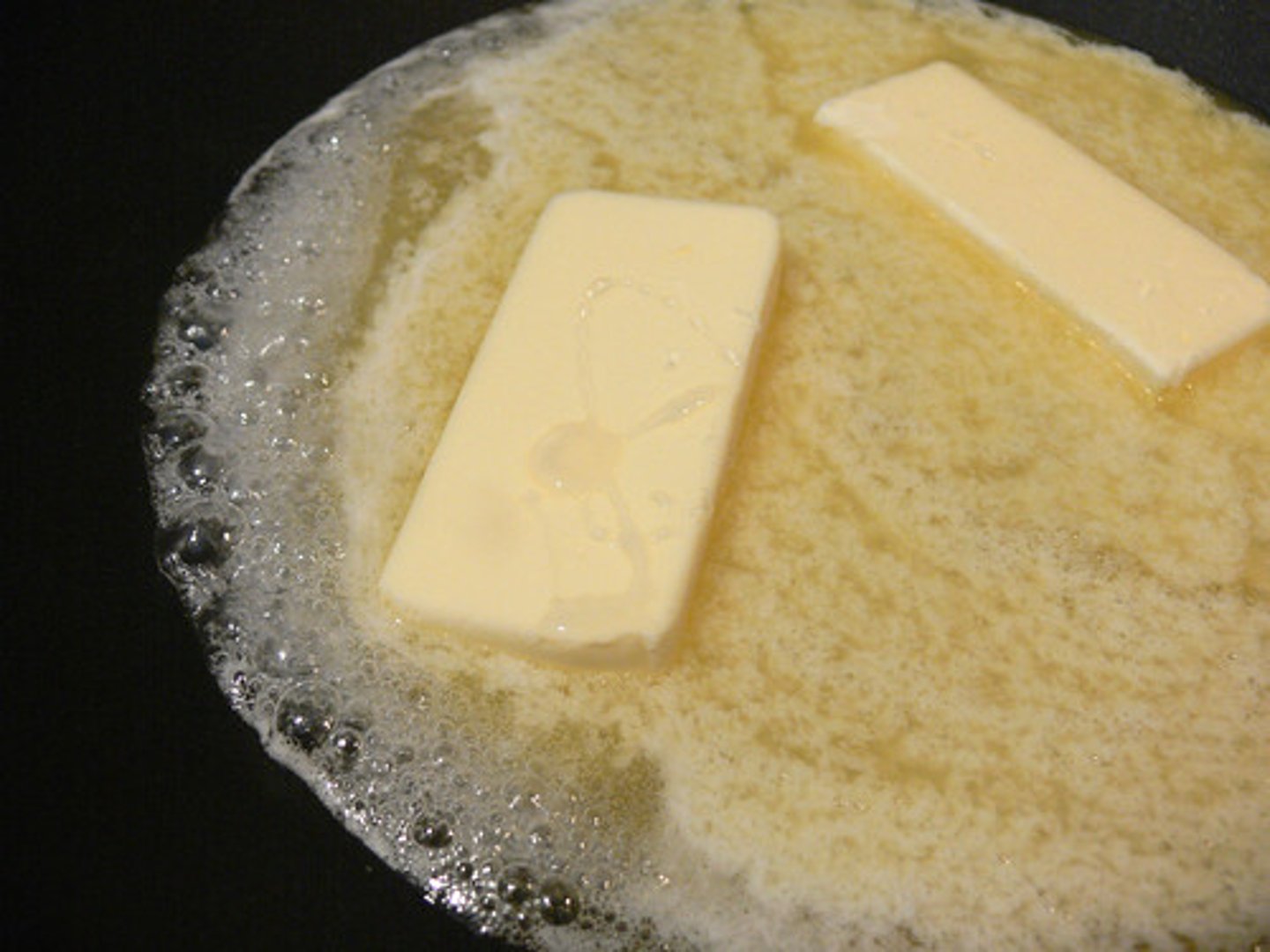
Is this a physical change or chemical change?
Melting butter
Physical Change

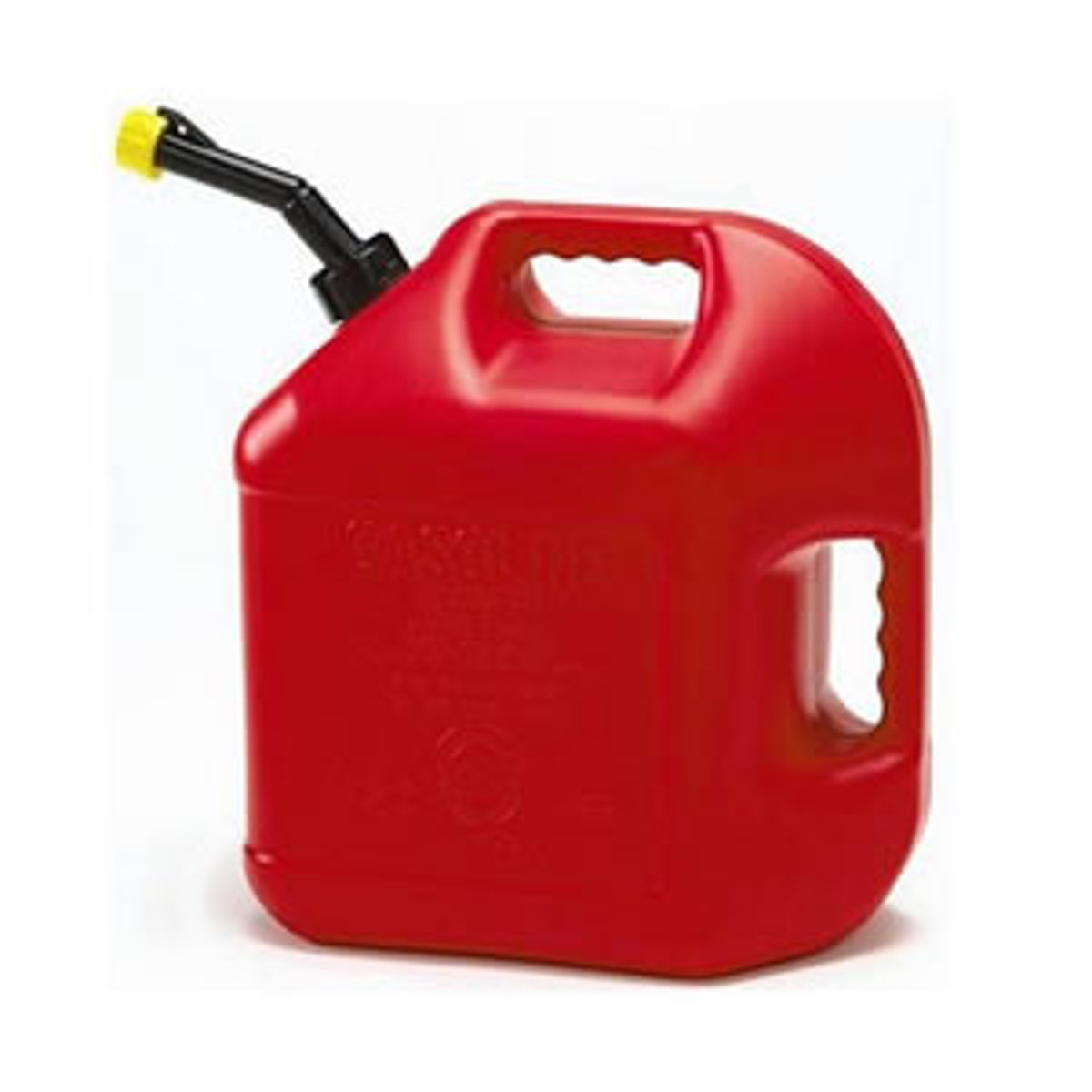
Is this a physical change or chemical change?
Burning gasoline
Chemical Change

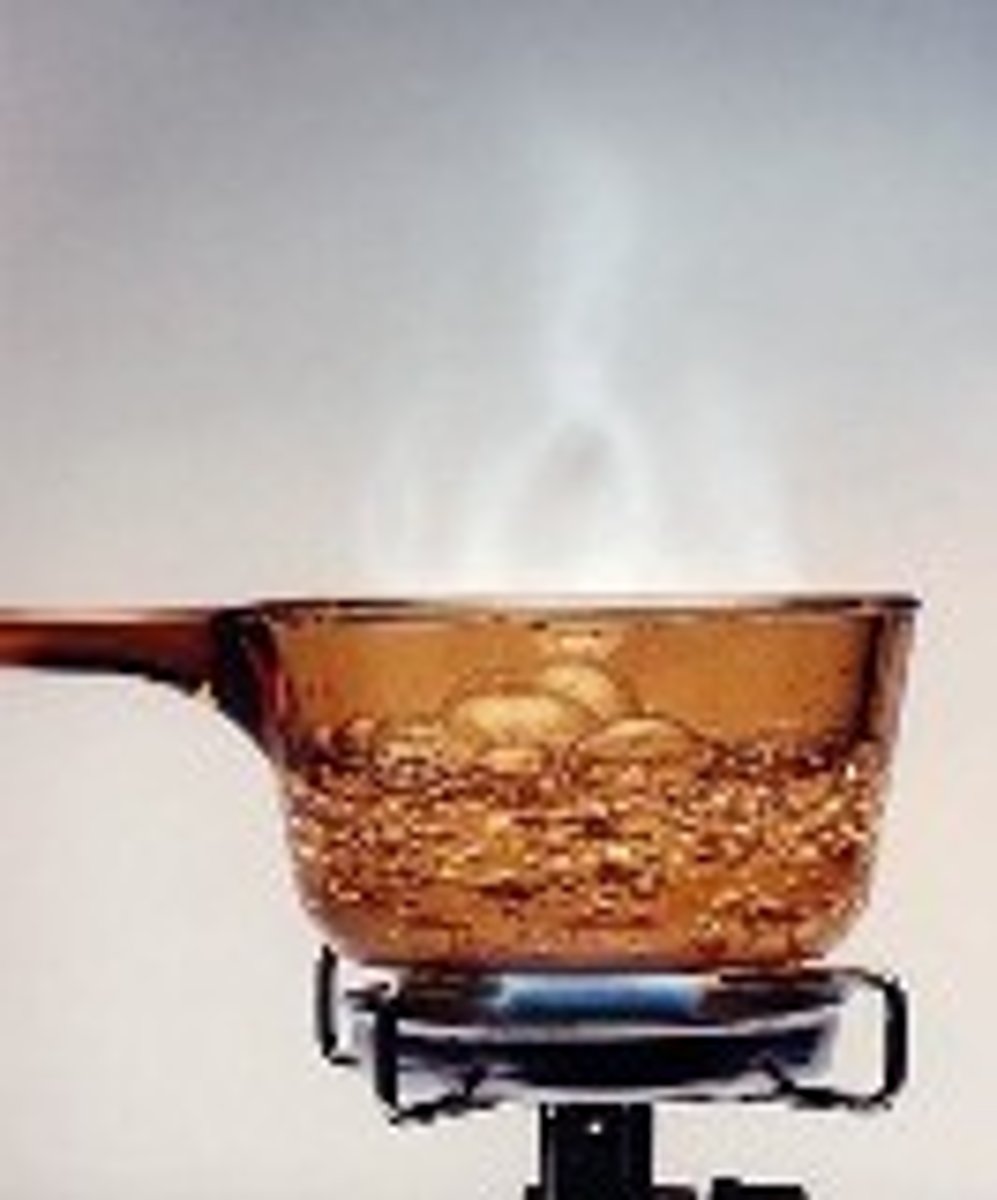
Is this a physical change or chemical change?
Boiling water
Physical Change

Is this a physical change or chemical change?
Dissolving sugar in water
Physical Change

Is this a physical change or chemical change?
Toasting bread
Chemical Change

Is this a physical property or a chemical property?
Malleable
Physical Property

Is this a physical property or a chemical property?
Combustibility
Chemical Property

Is this a physical property or a chemical property?
Freezing Point
Physical Property
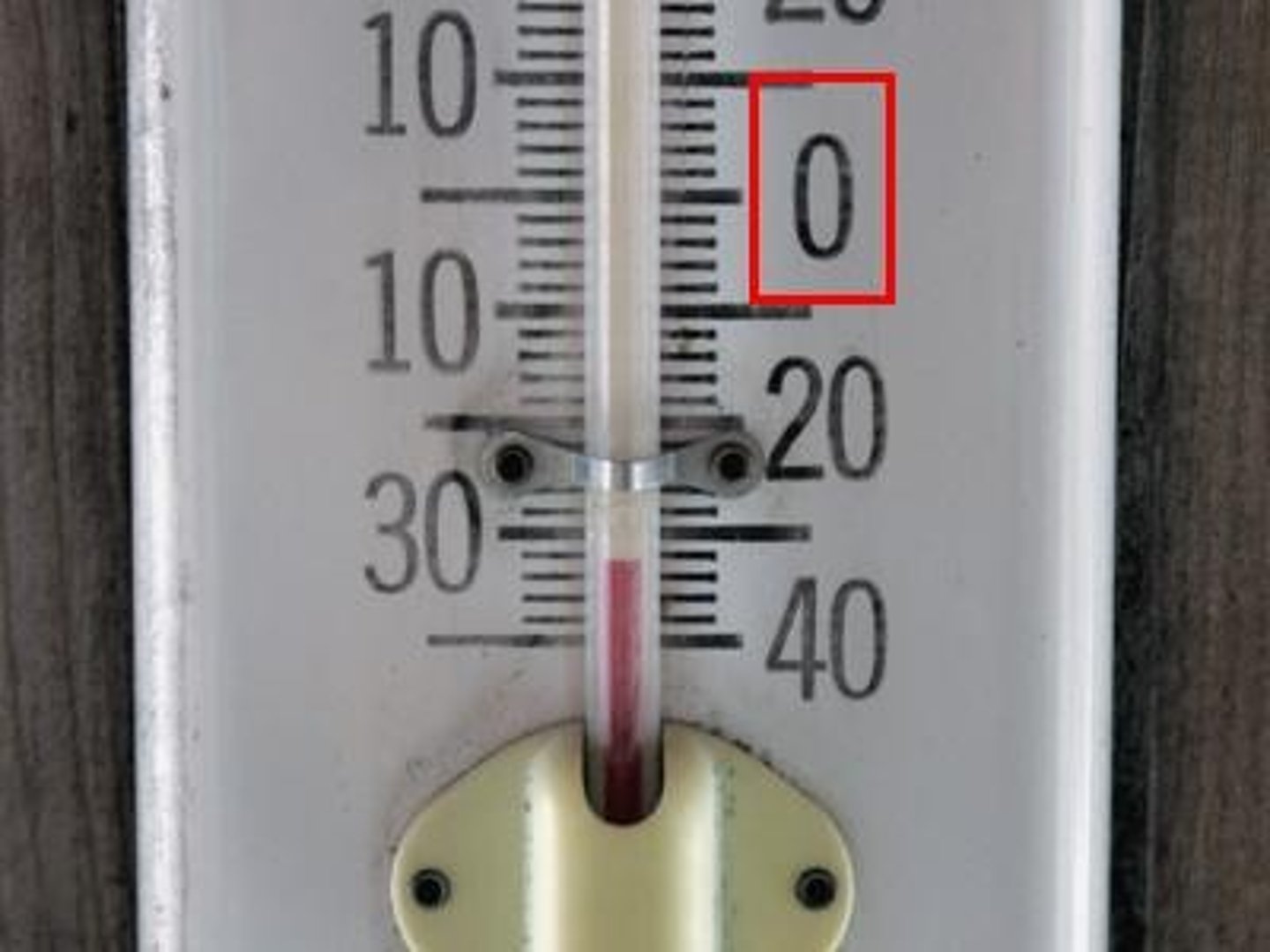

Is this a physical property or a chemical property?
Corrosion
Chemical Property

Is this a physical property or a chemical property?
Strong Smell
Physical Property

Are the following mixtures Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Vegetable soup
Heterogeneous

Are the following mixtures Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Blood
Homogeneous
Are the following mixtures Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Chocolate chip cookie dough
Heterogeneous

Are the following mixtures Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Black coffee
Homogeneous

Are the following mixtures Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Plain Yogurt
Homogeneous

Are the following Pure substances or mixtures?
Oxygen
Pure Substance
Are the following Pure substances or mixtures?
Concrete
Mixture

Are the following Pure substances or mixtures?
Water
Pure Substance

Are the following Pure substances or mixtures?
Sugar(C6H12O6)
Pure Substance

Are the following Pure substances or mixtures?
Multi-grain bread
Mixture

Are the following an Intensive property or an extensive property?
Color
Intensive Property

Are the following an Intensive property or an extensive property?
Volume
Extensive Property

Are the following an Intensive property or an extensive property?
Mass
Extensive Property

Are the following an Intensive property or an extensive property?
Boiling point
Intensive Property

Are the following an Intensive property or an extensive property?
Density
Intensive Property
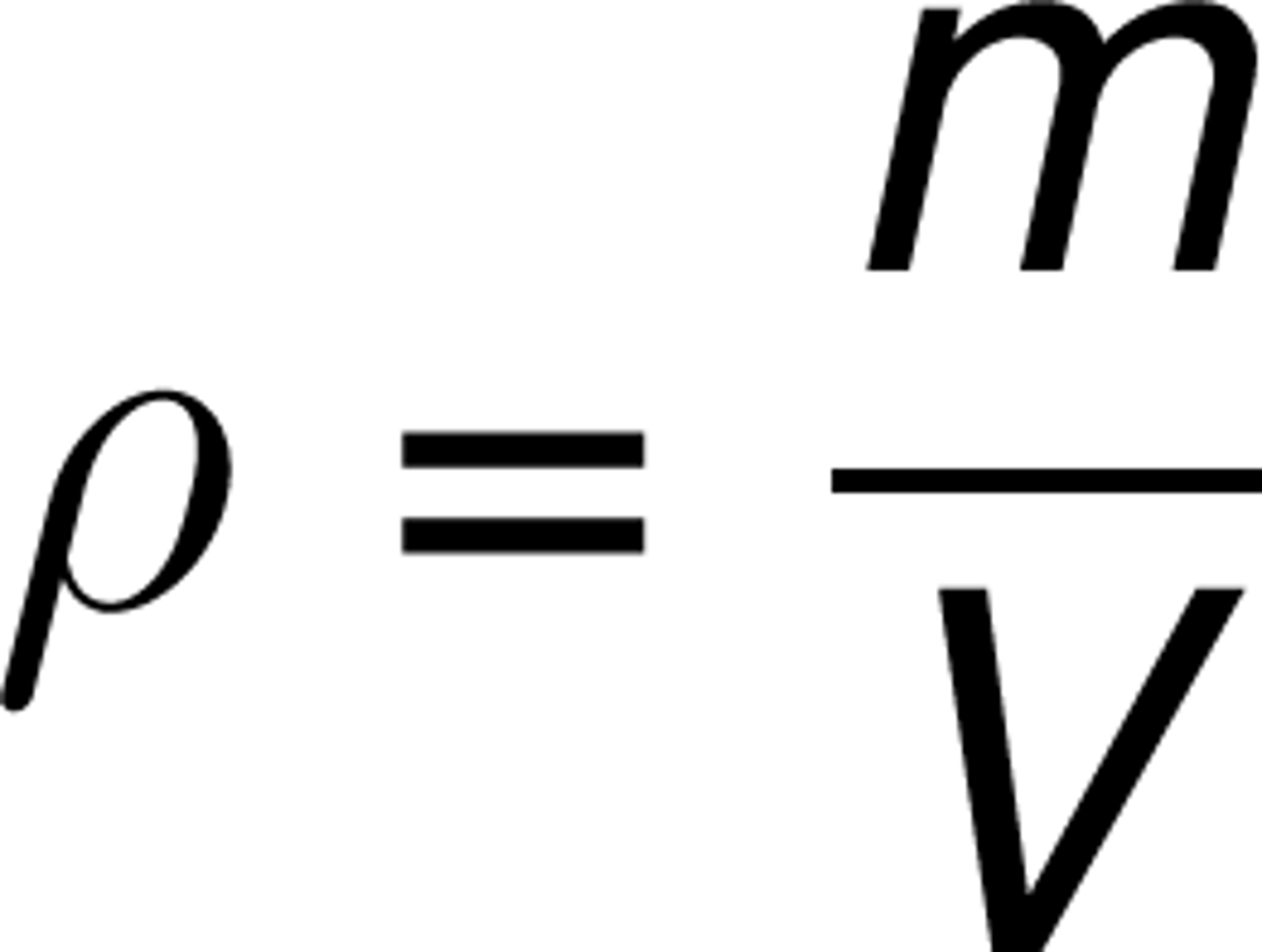
The mass of a sample of clay is 11g. To find the volume, 5.0ml of water was measured in a graduated cylinder. When the clay was added the total volume in the cylinder rose to 10.0 ml. What is the density of the clay?
D=m/v
D=n11/5.0 = 2.2
2.2 g/mL is the density of the clay
The density of pure diamond is 3.5 g/cm^3. Find its volume .
D=m/v
V x 3.5 = 0.25/V x V
V x 3.5/3.5 = V = m/d = 0.25/3.5 = 0.071g/cm3
The volume of the diamond is 0.071g/cm3
Convert 1.06L to mL
KHD(m,g,l)dcm
1.06 L (move the decimal point all the way to the right) = 1,060 mL = 1.06 L
1,060mL
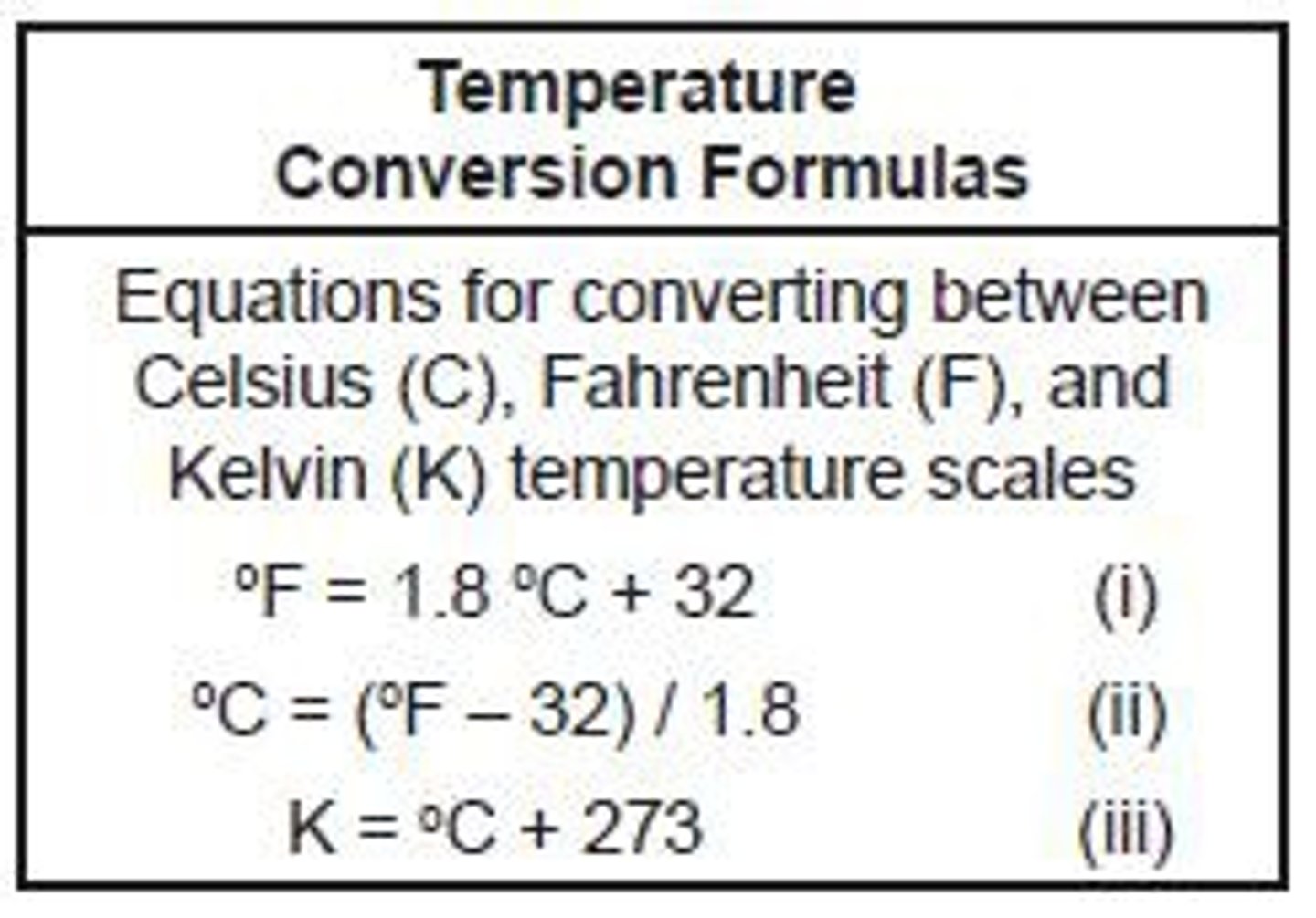
Convert 25C into K
K = C + 273
K = 25 + 273
K = 298
298K
What is the atomic number of Xe?
The atomic number is 54.

What is the atomic mass of Xe?
The atomic mass is 131.293.

How many neutrons are in the element Xe?
The number of neutrons present in the element are 77. (You subtract the mass number from the atomic number to find the neutrons.)
List 3 Lab Safety Rules:
No eating food, or drinking beverages allowed.
No horseplay allowed.
Always tie your hair up before using fire in an experiment. (There are many others you can use as well.)

Describe characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloids are semiconductors with having some characteristics of metals and nonmetals.
The Number of Neutrons in this isotope of silver-109 is:
62 ( How to Solve: 109 - atomic number = 62)
Daltons' atomic theory helped to explain the law of conservation of mass because it stated that atoms
Could not be created or destroyed
The basic principles of atomic theory that are still recognized today were first conceived by:
Dalton

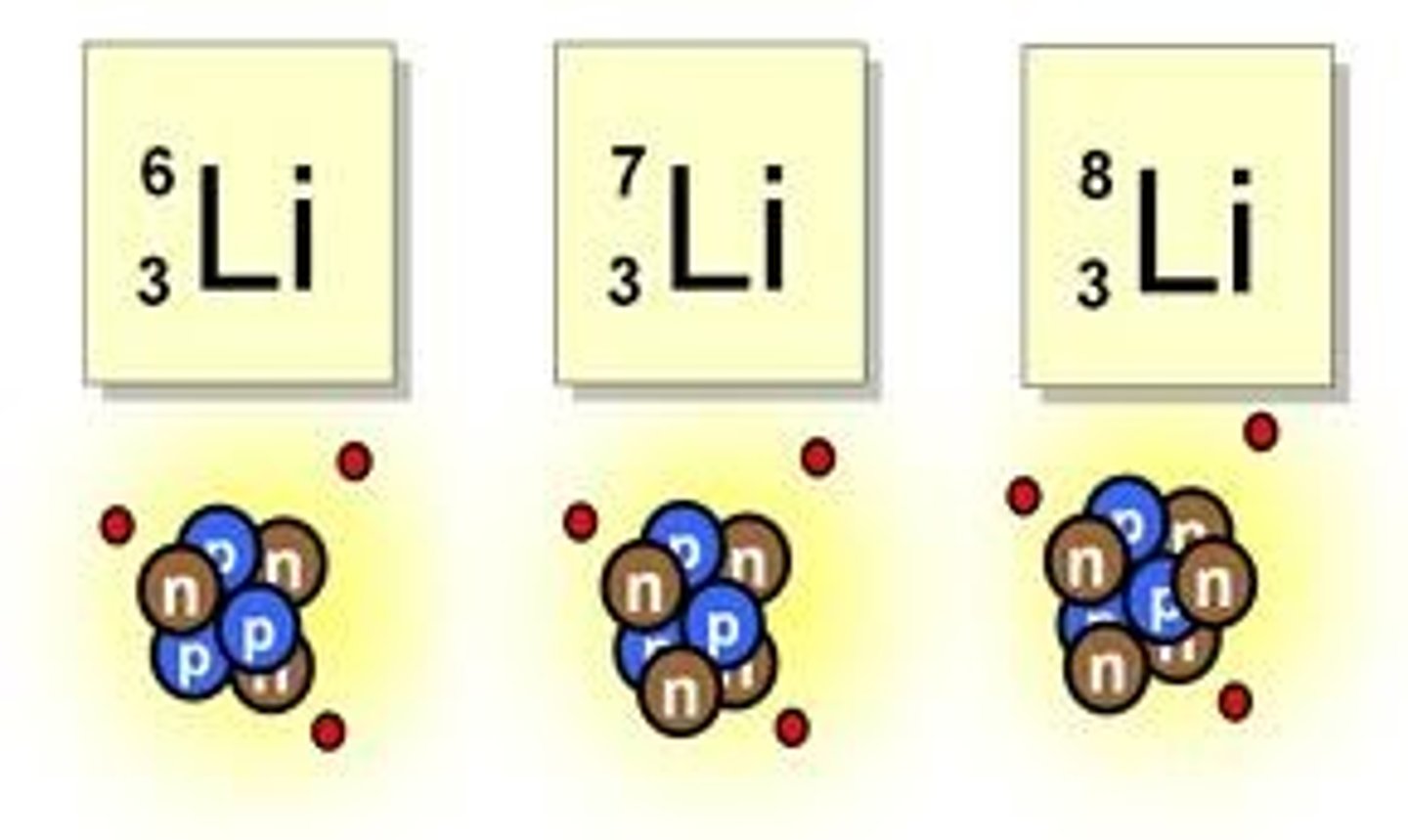
Atoms of the same element can differ in:
Mass Number
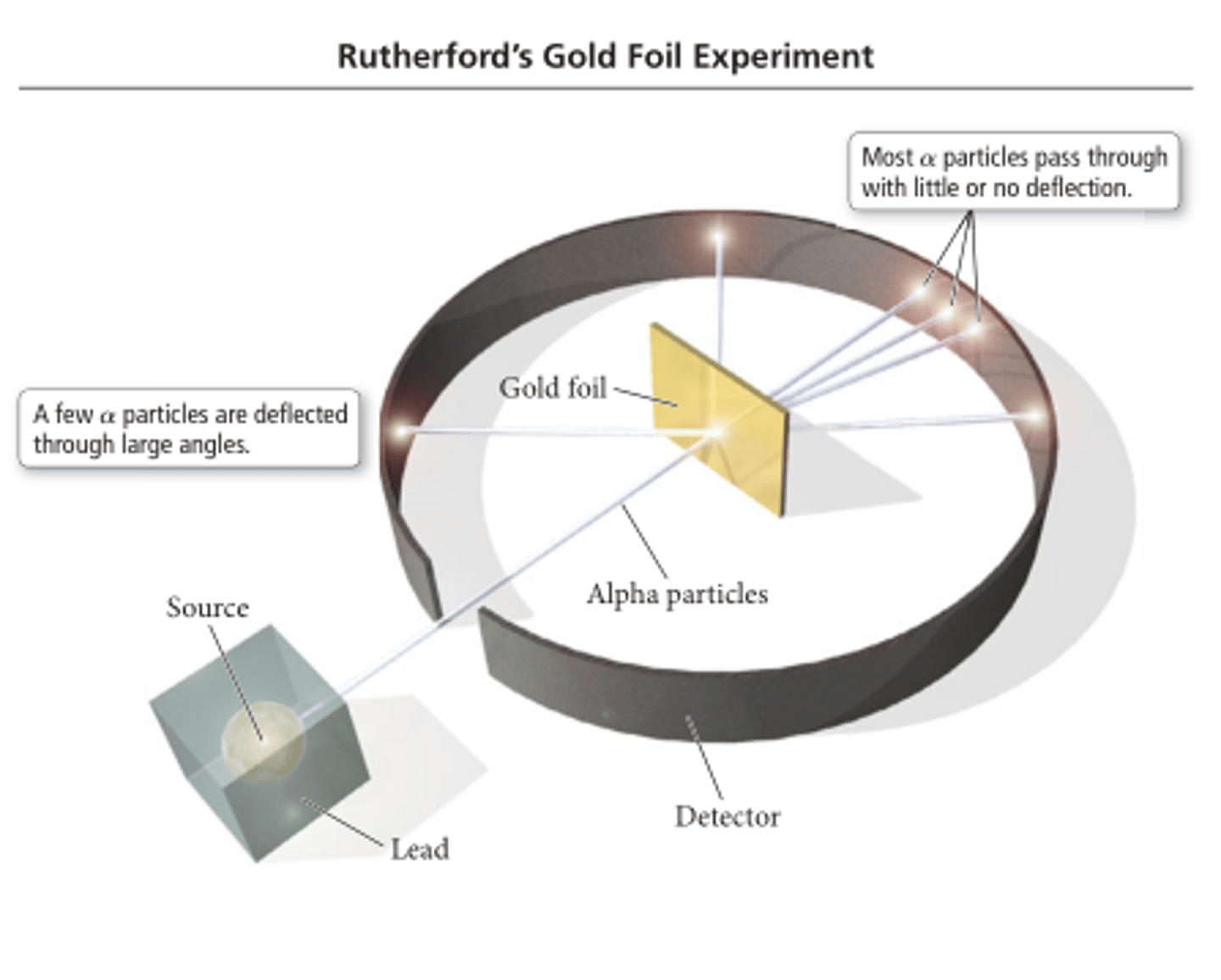
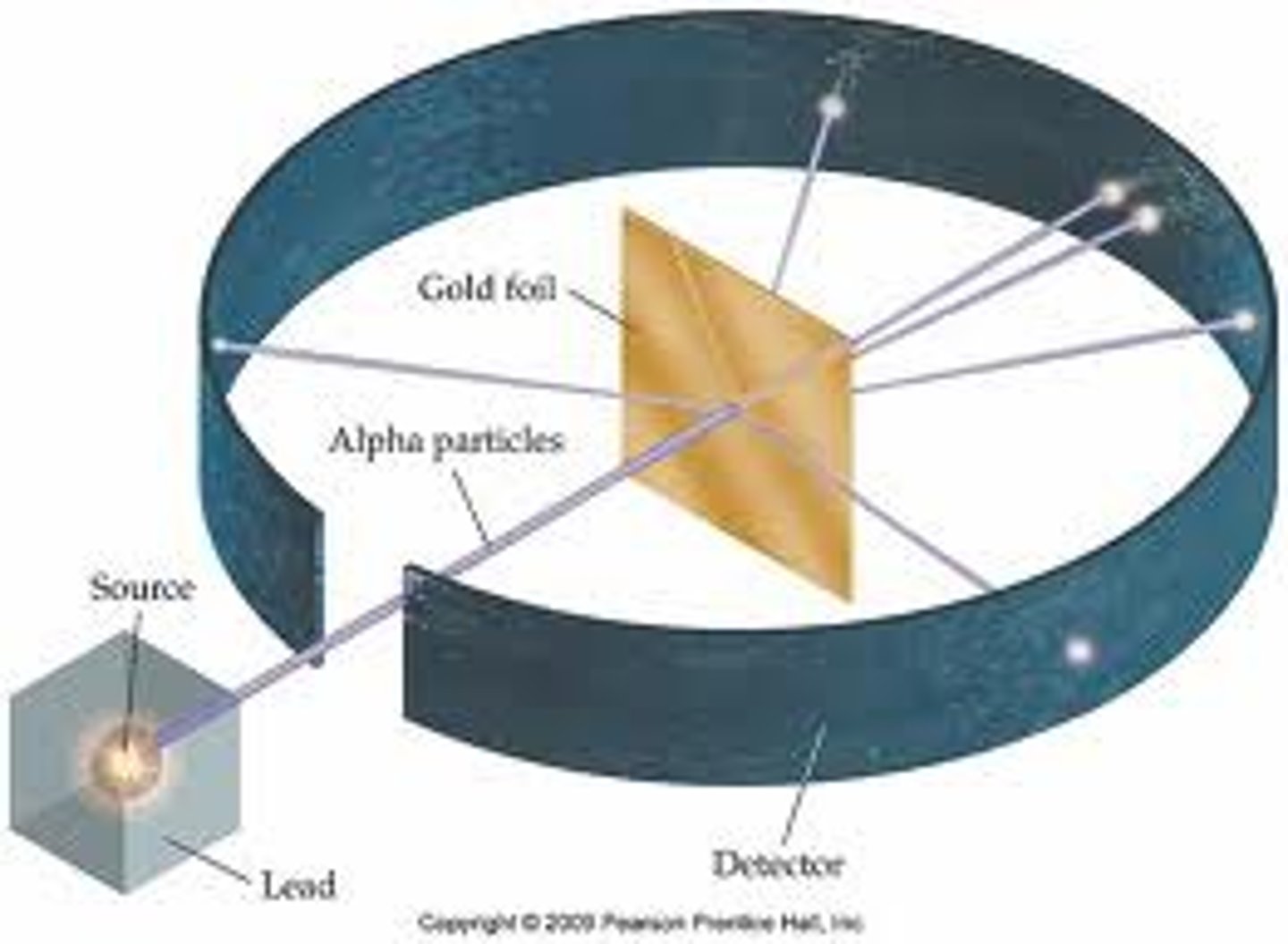
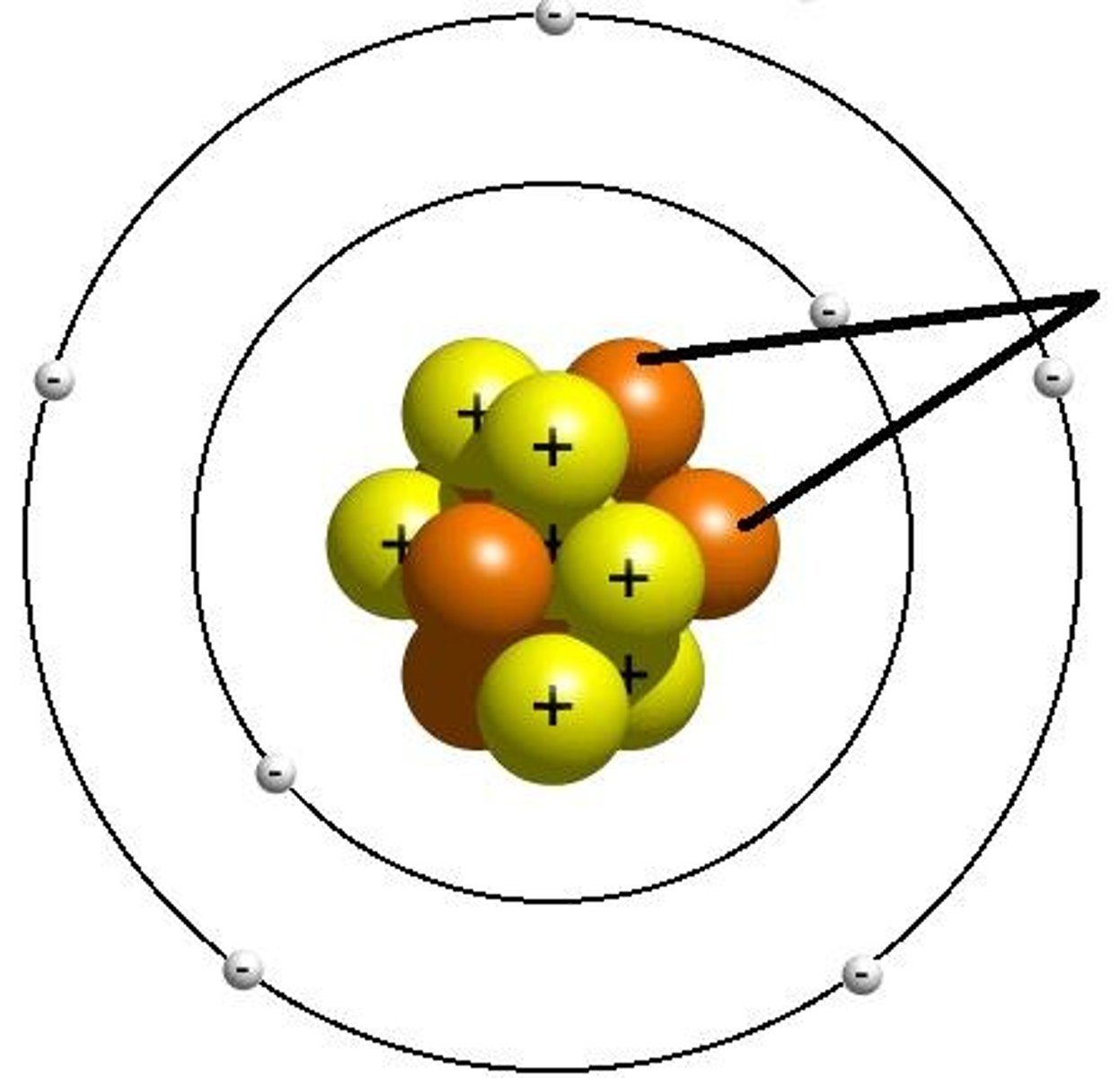
In Rutherford's Gold Foil experiment which happened:
Most of the alpha particles travel through the foil undeflected. Occasionally, an alpha particle travel back from the foil. Some alpha particles are deflected by small angles.
Most of the mass of an atom is in the:
Nucleus
According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms:
Of each element are identical in size, mass, and other properties
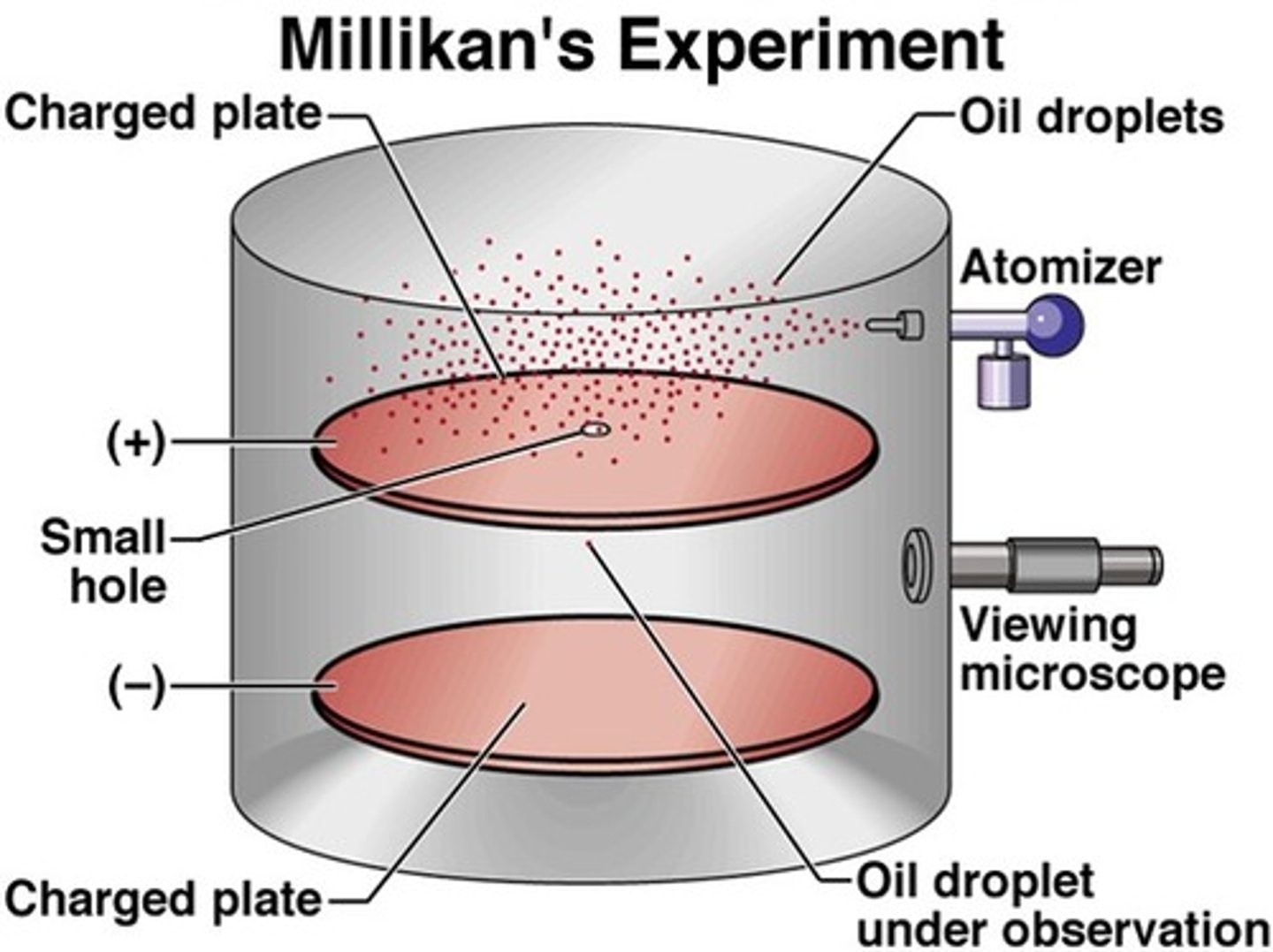
Millikan's experiments determined:
The approximate value of the electron's mass and charge
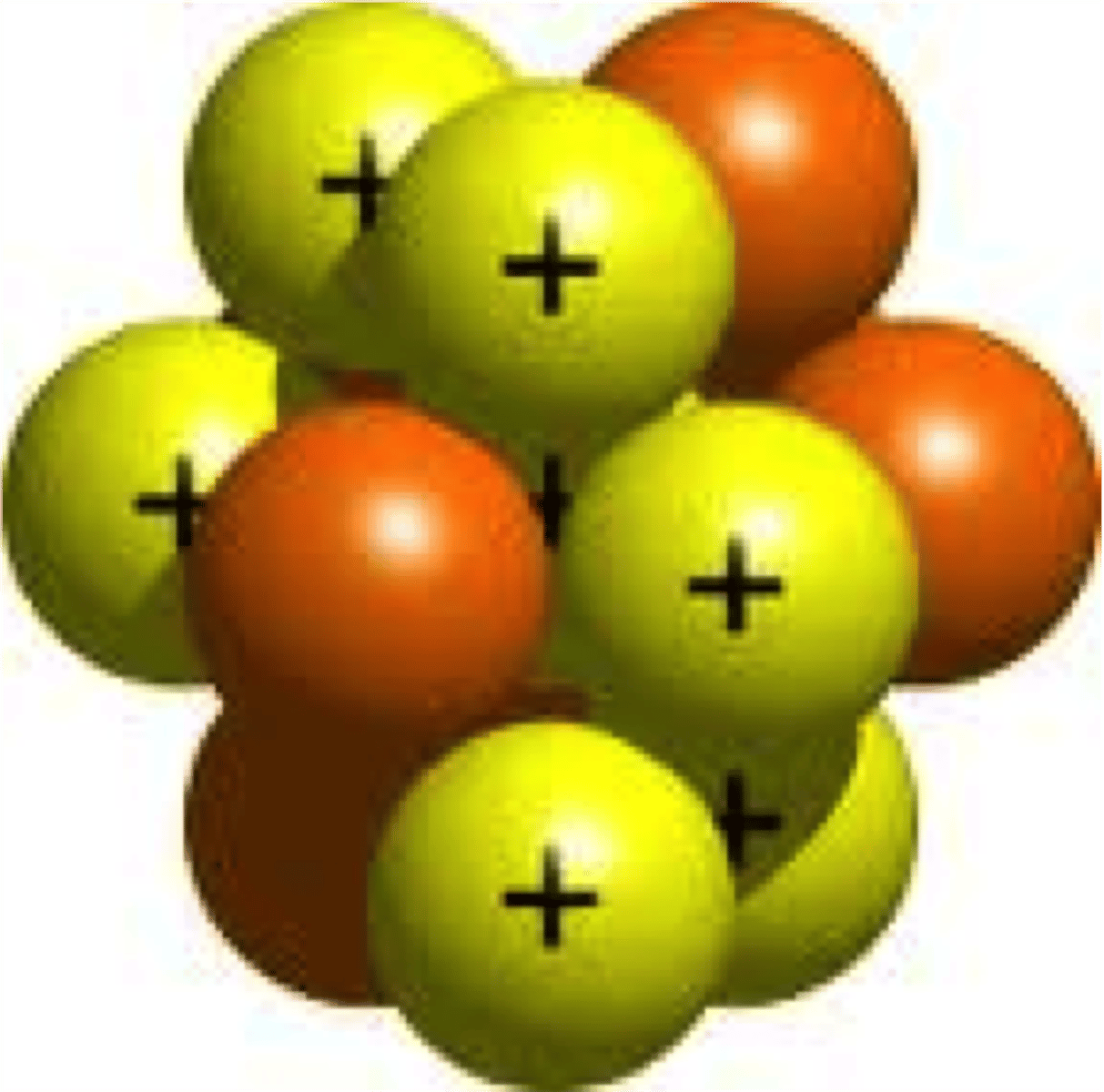
Which of the following ideas was NOT part of Dalton's atomic theory?
Atoms can be divided into smaller parts
The nucleus of an atom contains:
Protons and neutrons
Who said atoms are indivisible?
Democritus

The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it:
Contains nearly all of the atom's volume
Protons within a nucleus are attracted to each other by:
Nuclear forces
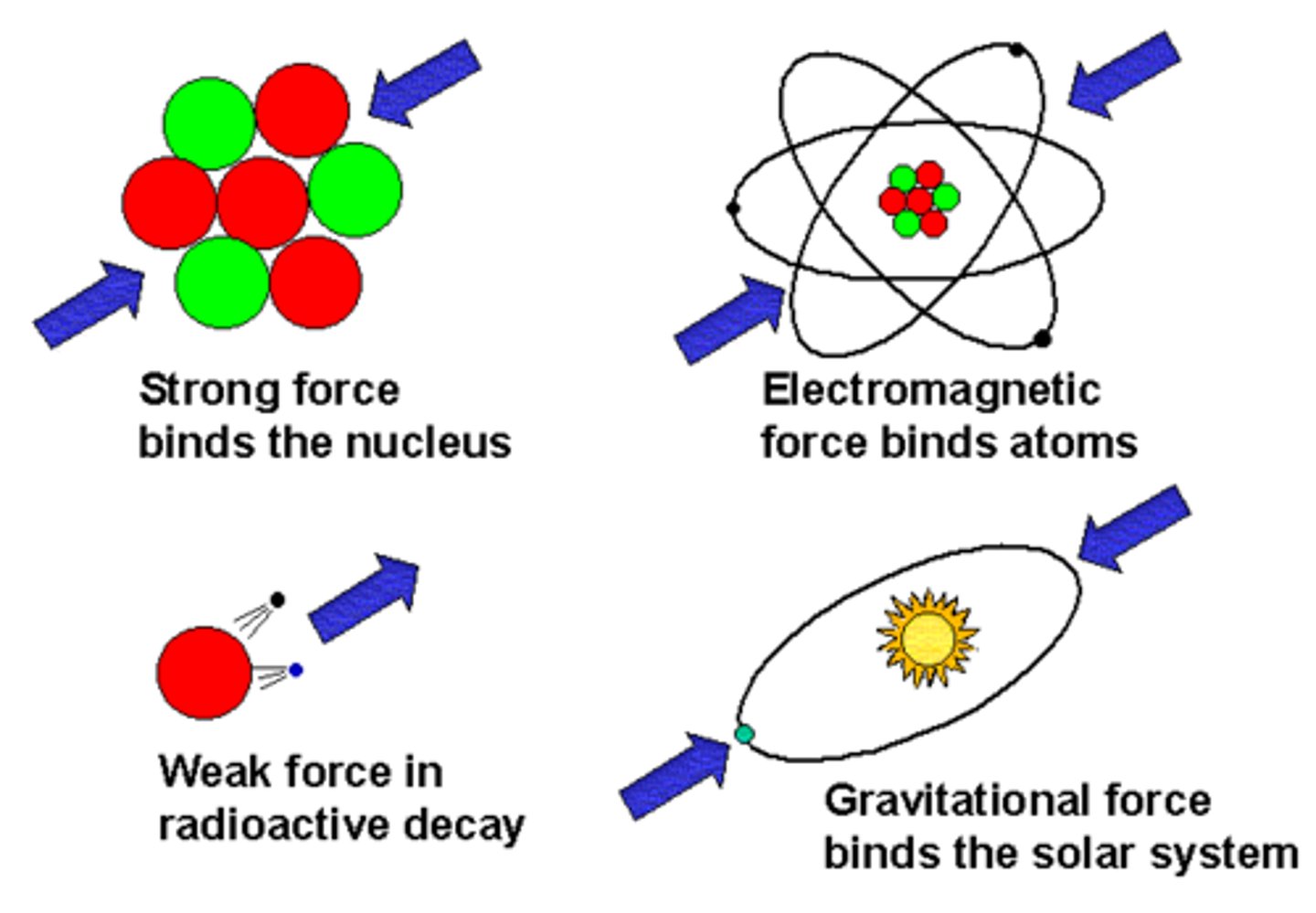
Atoms contain a unique number of __________________. It determines the element and never changes.
Protons
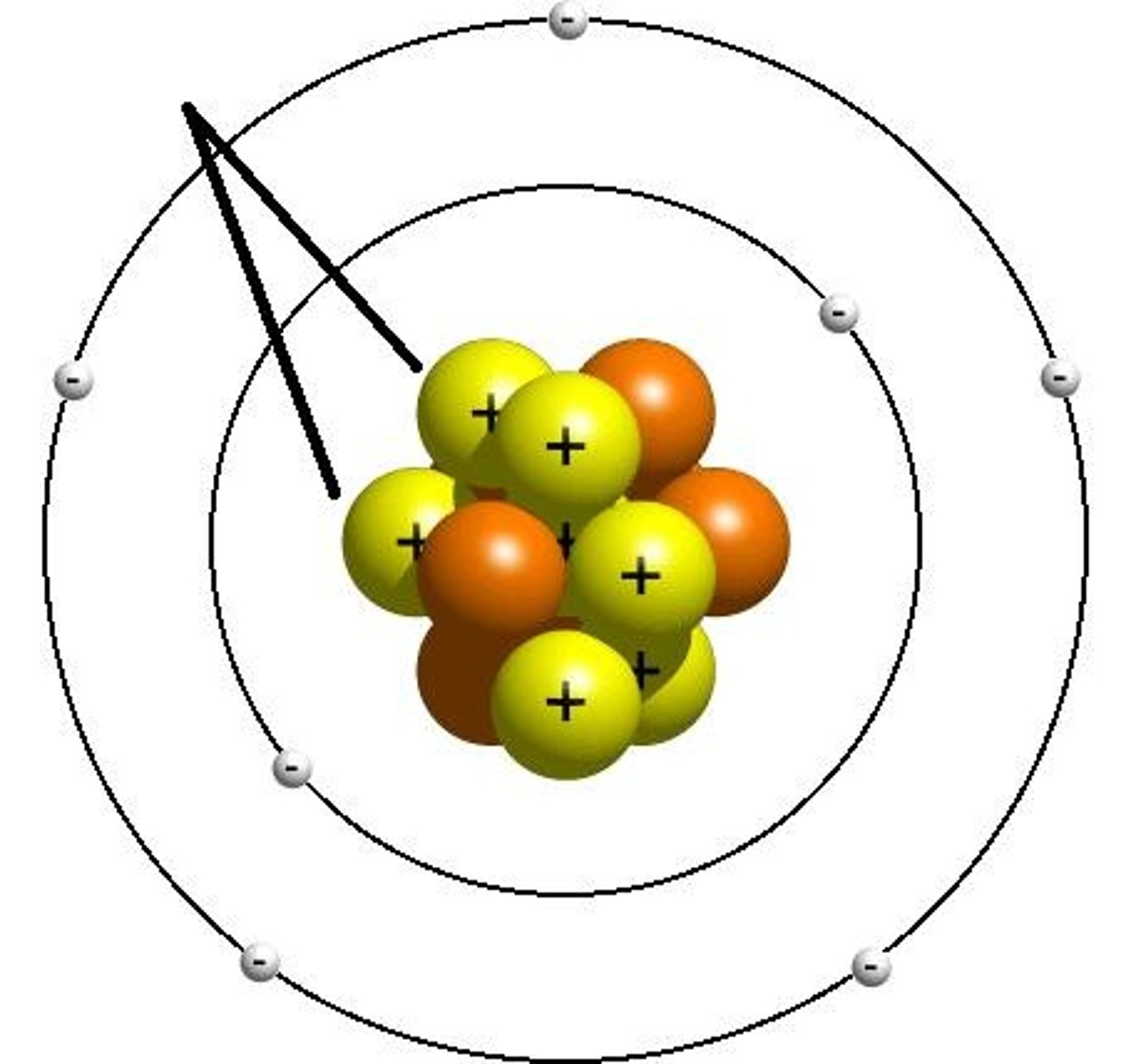
Who discovered the nucleus by bombarding gold foil with positively charged particles and noting that some particles were widely deflected?
Rutherford
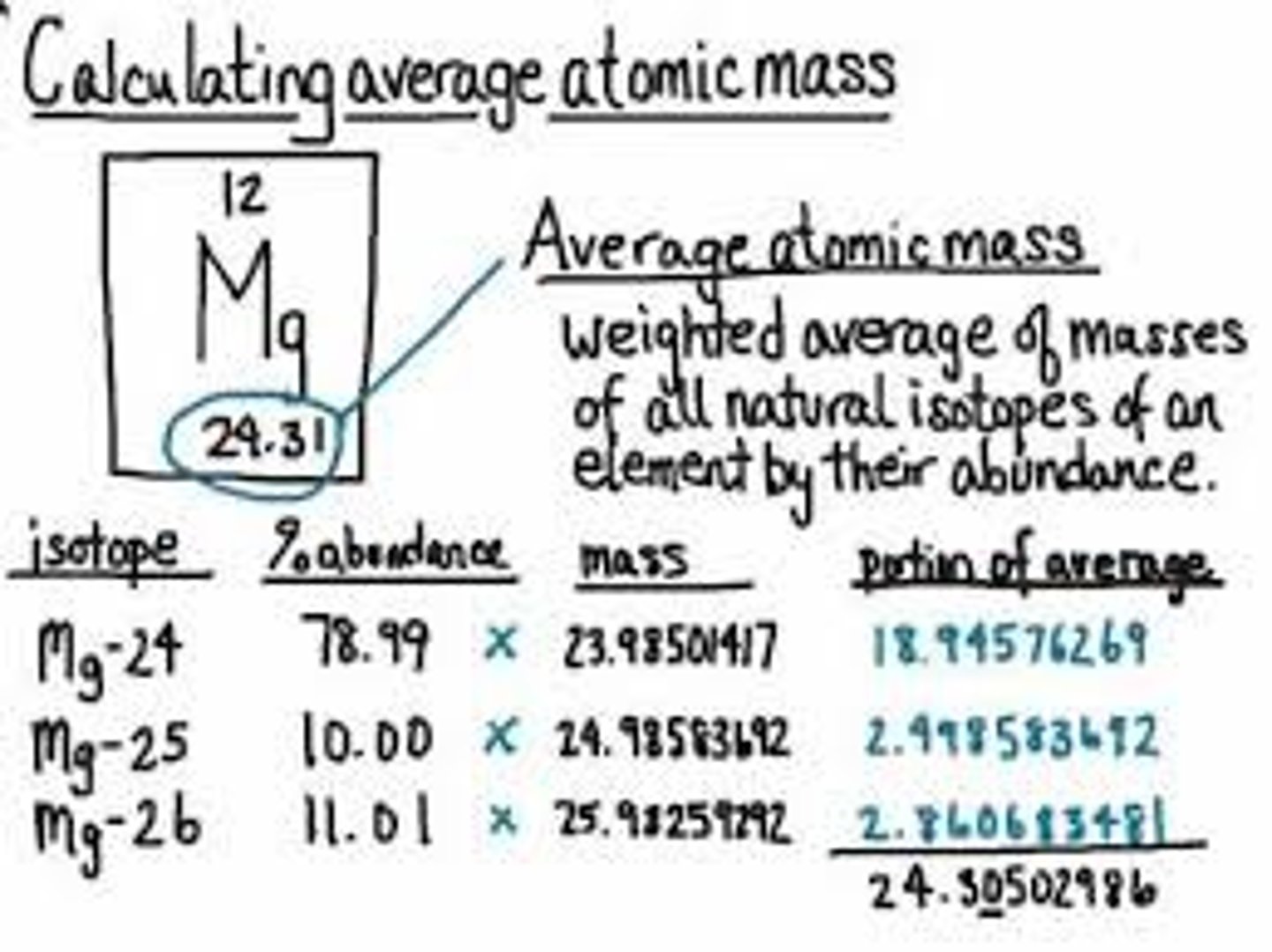
The average atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of its:
Naturally occurring isotopes
Dalton's model of the atom is called which of the following?
Billiard Ball Model

A magnesium isotope consists of 12 protons, 12 electrons, and 13 neutrons. Its mass number is:
25
What is the atomic number for boron?
5

A neutral atom of bromine contains:
35 electrons

An atom of chlorine has 17 protons and 18 neutrons. What is its mass number?
35 (Find what number can subtract from 17, to get 18 as your neutrons, and you will find the mass number.)

A neutral helium atom has:
2 protons and 2 electrons

Zinc-66 has:
36 neutrons (30 protons (because it is Zinc) and 36 neutrons (so that they add up to 66).

Fluorine has an atomic number of 9 and mass number 19. It has:
9 protons, 9 electrons, and 10 neutrons
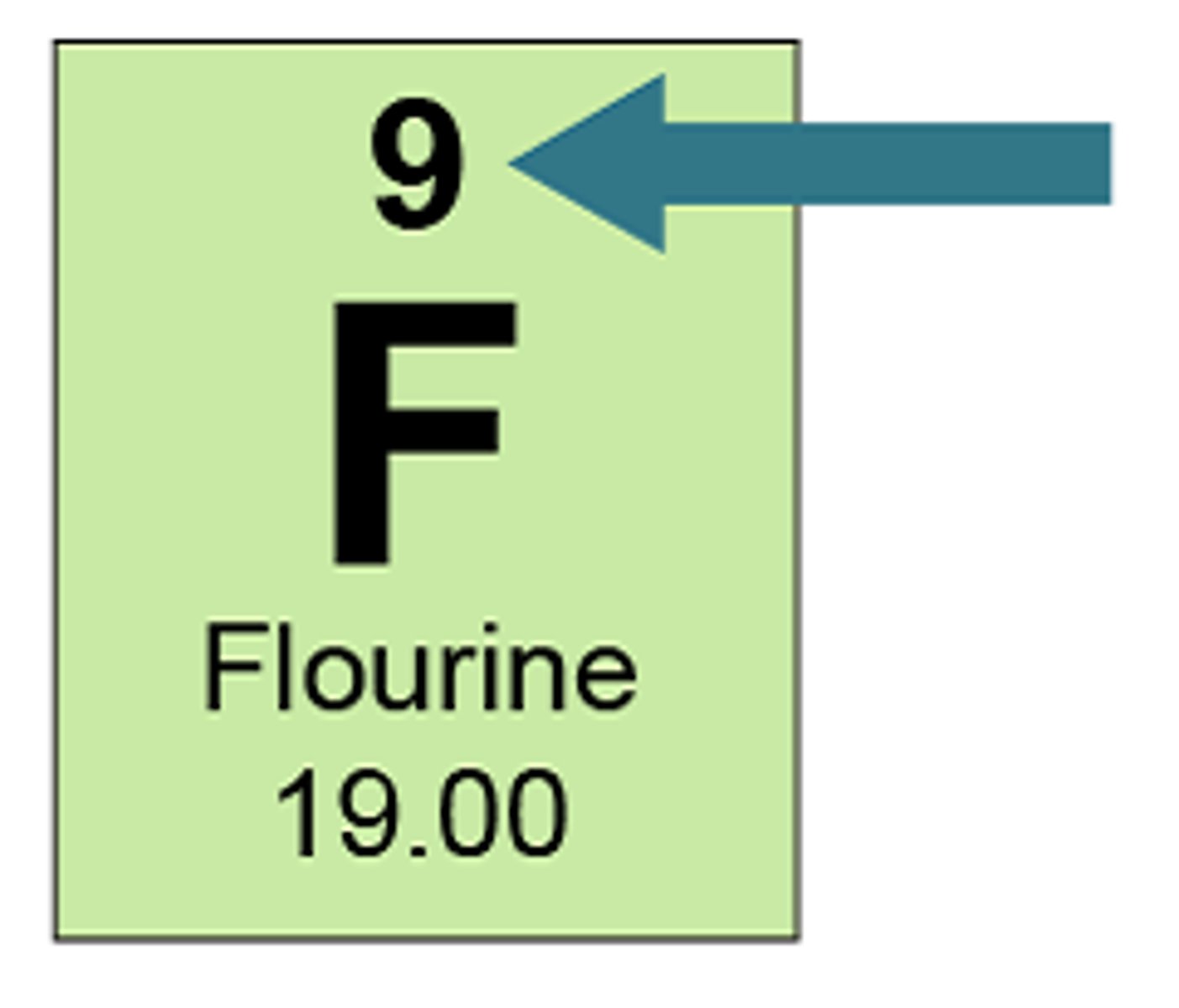
Potassium-39 has:
20 neutrons (19 protons (because it is Potassium) and 20 neutrons (so that they add up to 39).

Looking at the chemical reaction of Na + Cl -> NaCl, whose atomic theory addressed this concept?
Dalton

An electrically neutral atom of mercury (Hg) has:
80 protons and 80 electrons

Magnesium-23, Magnesium-24, Magnesium-25 are all _______________ of each other:
Isotopes
Which of the following is not true of the species O-2?
It has gained 2 protons to become an ion
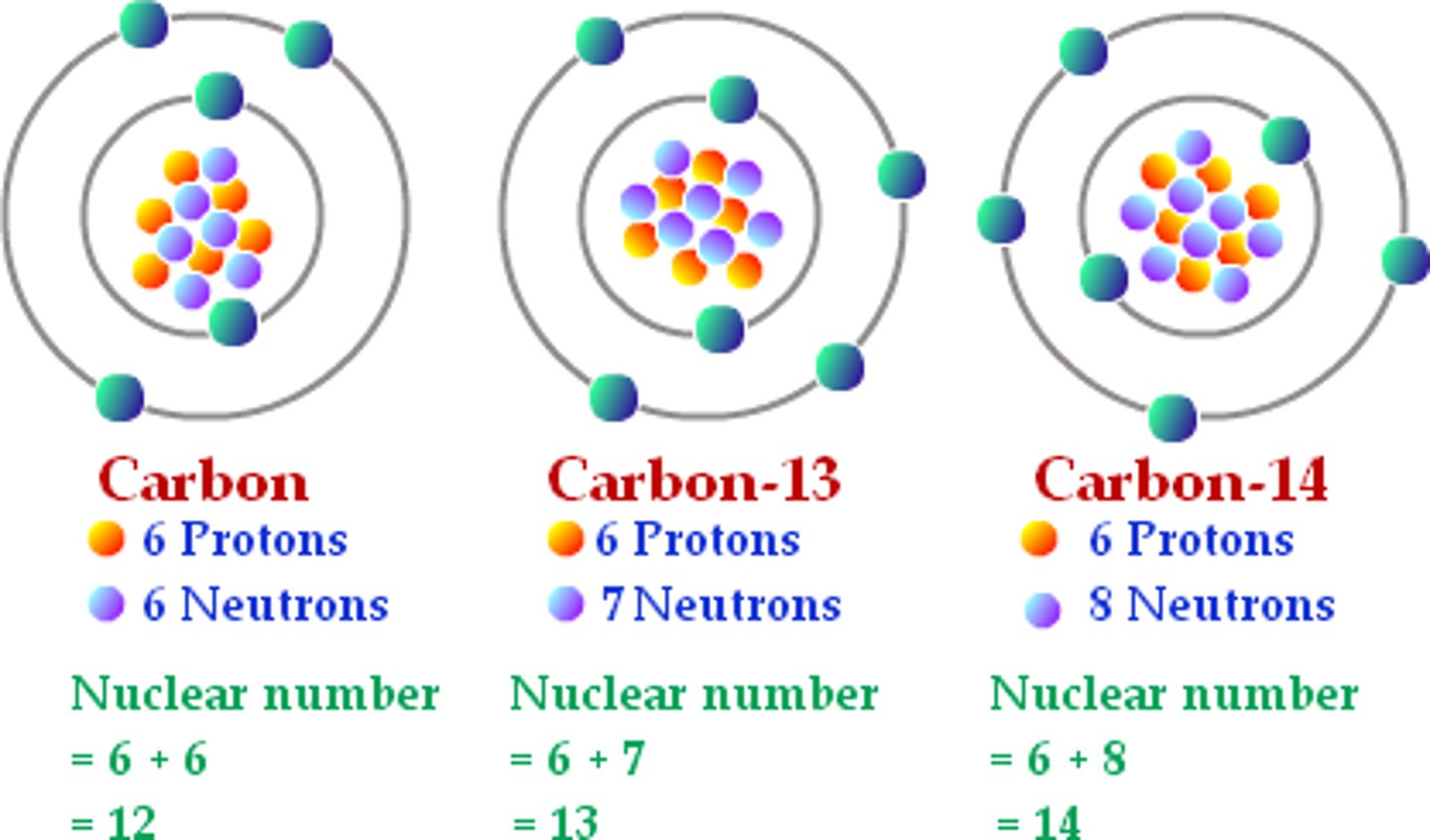
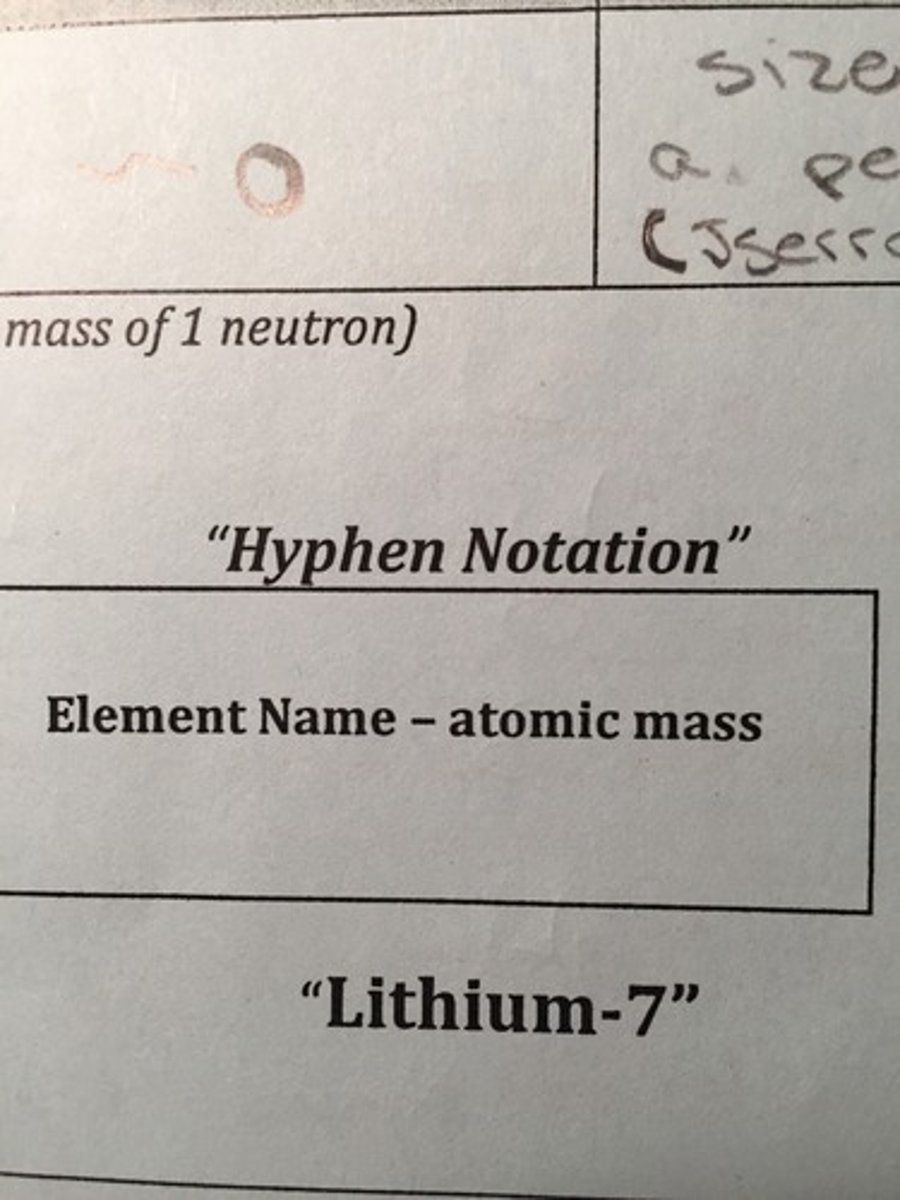
Carbon-14 is written in what type of notation?
Hyphen Notation
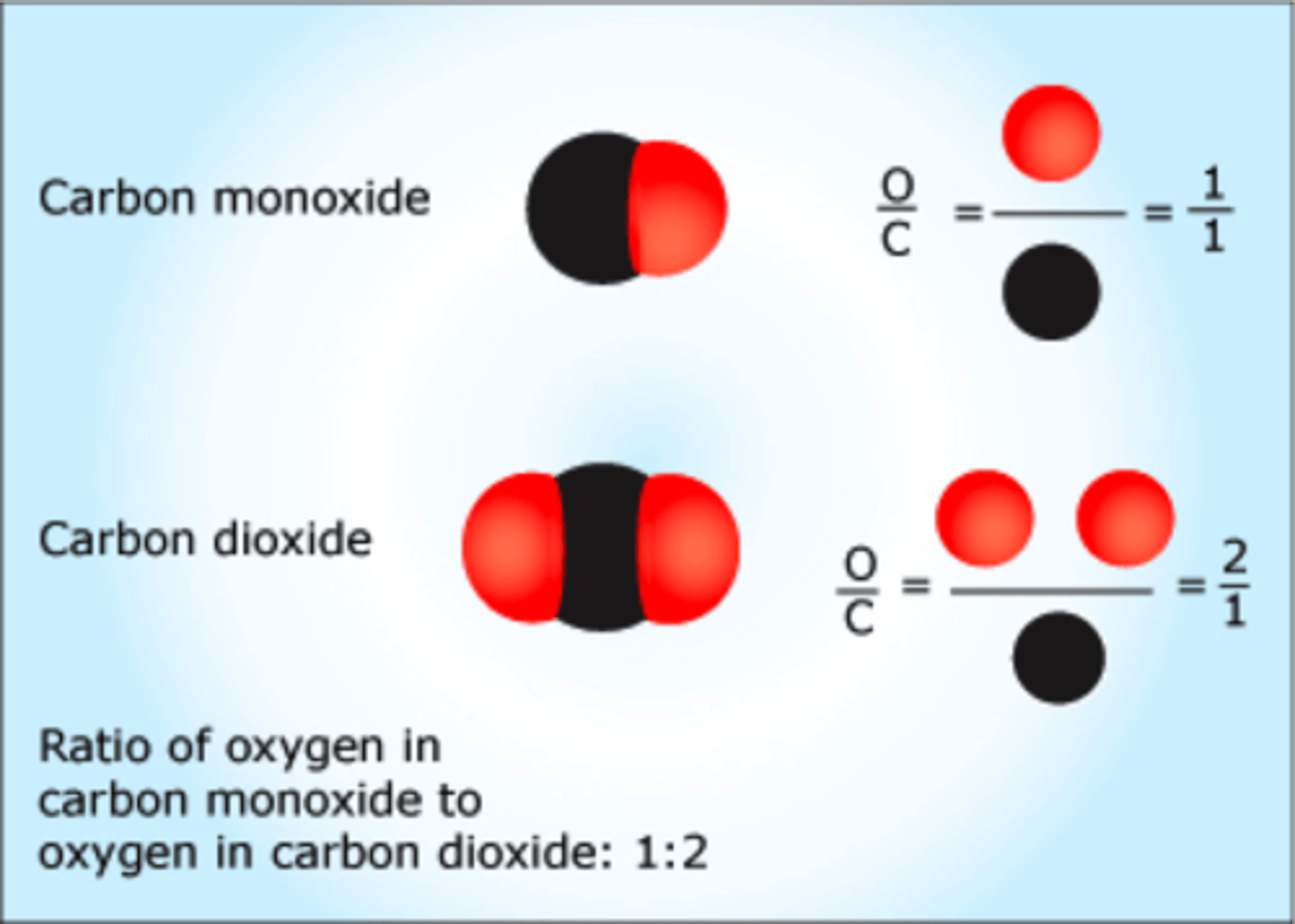
In the compound CuO (copper oxide), what is the ratio of copper to oxide?
1:1 (Because there is 1 carbon, and 1 oxygen together.)
In oxide of nitrogen, such as N2O, NO, NO2, and N2O3, atoms combine in small whole-number ratios. This evidence supports the law of:
Multiple proportions
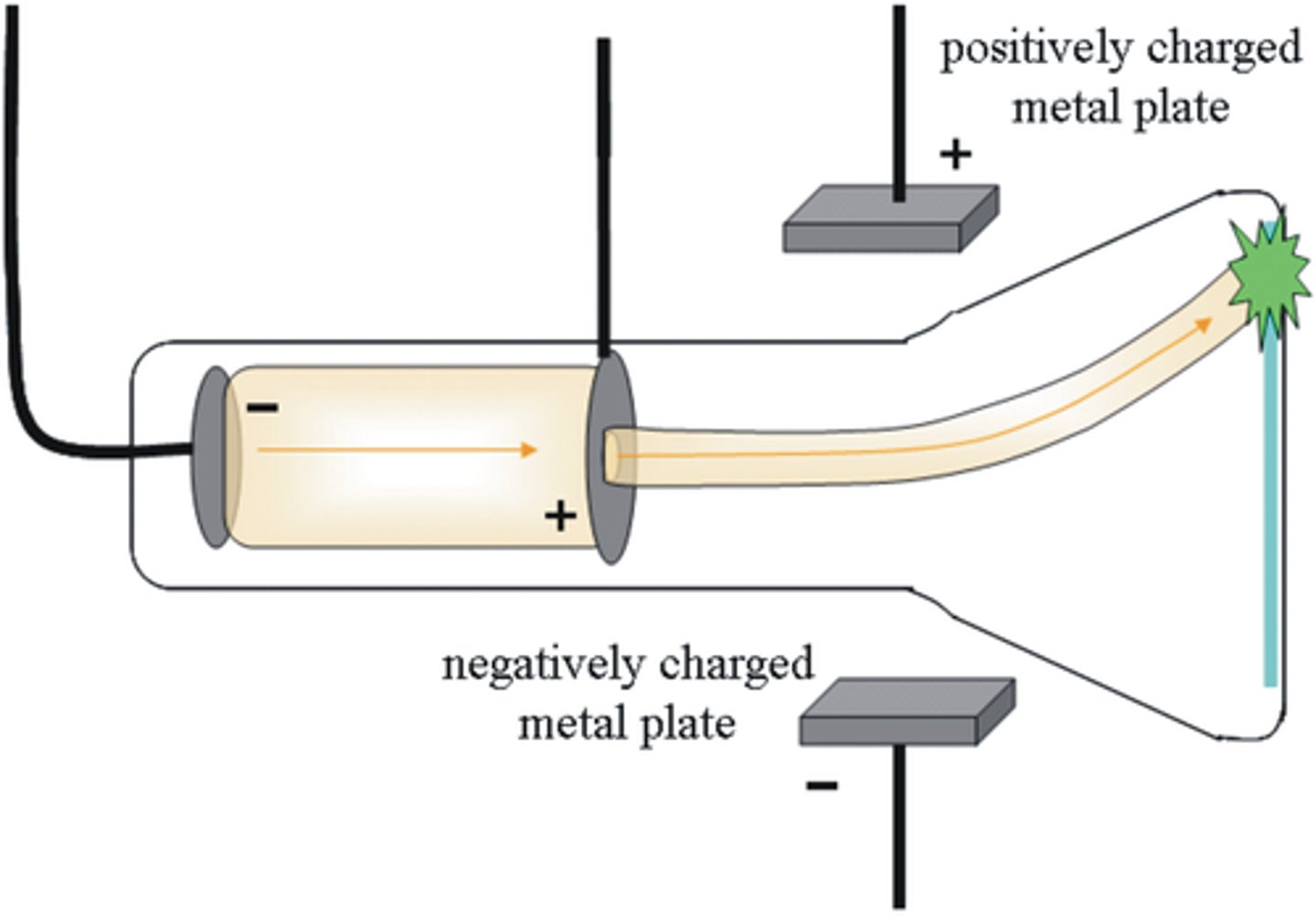
Cathode ray tube experiment:
Thomson
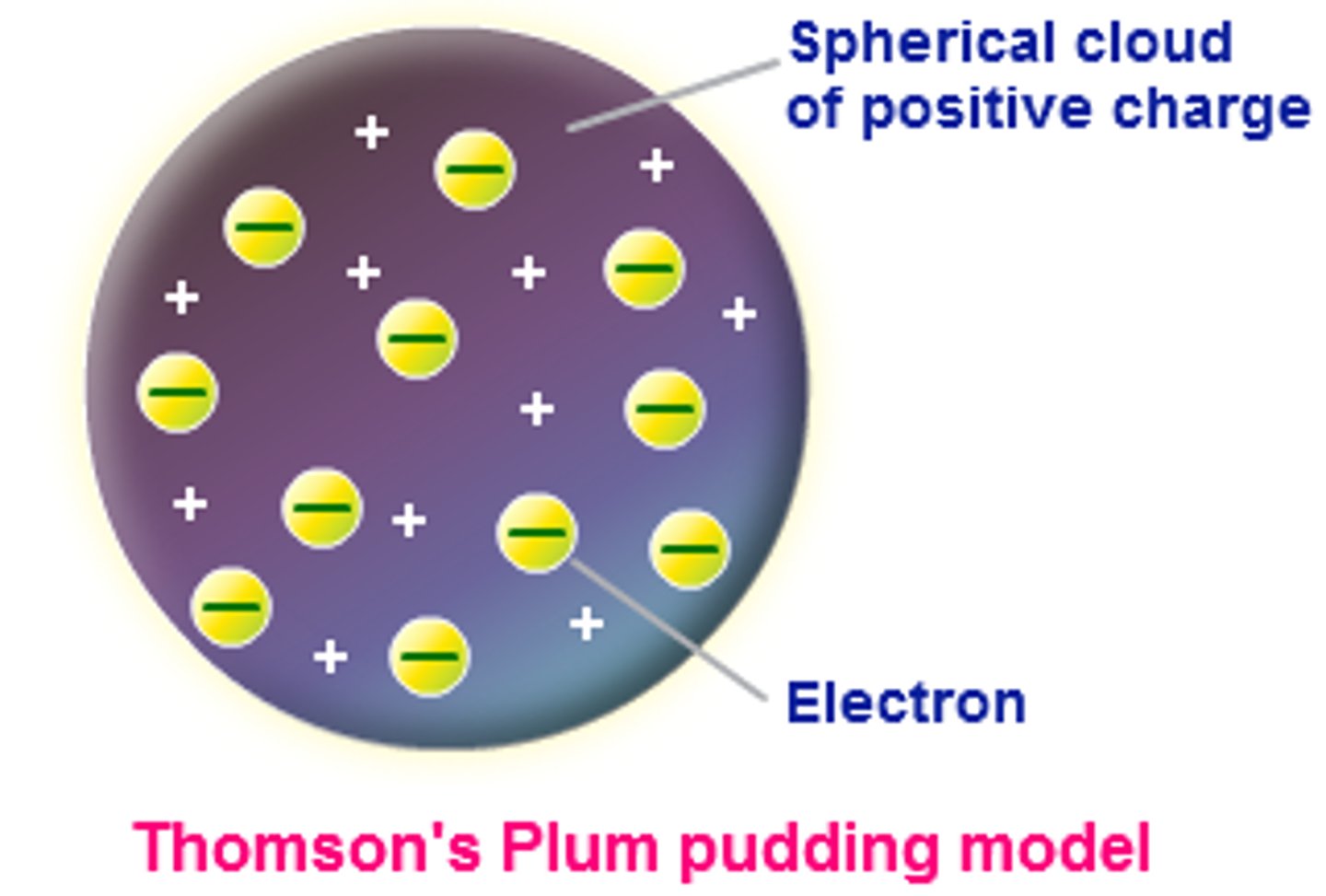
Plum Pudding Model:
Thomson
Published a 5 point Atomic Theory:
Dalton
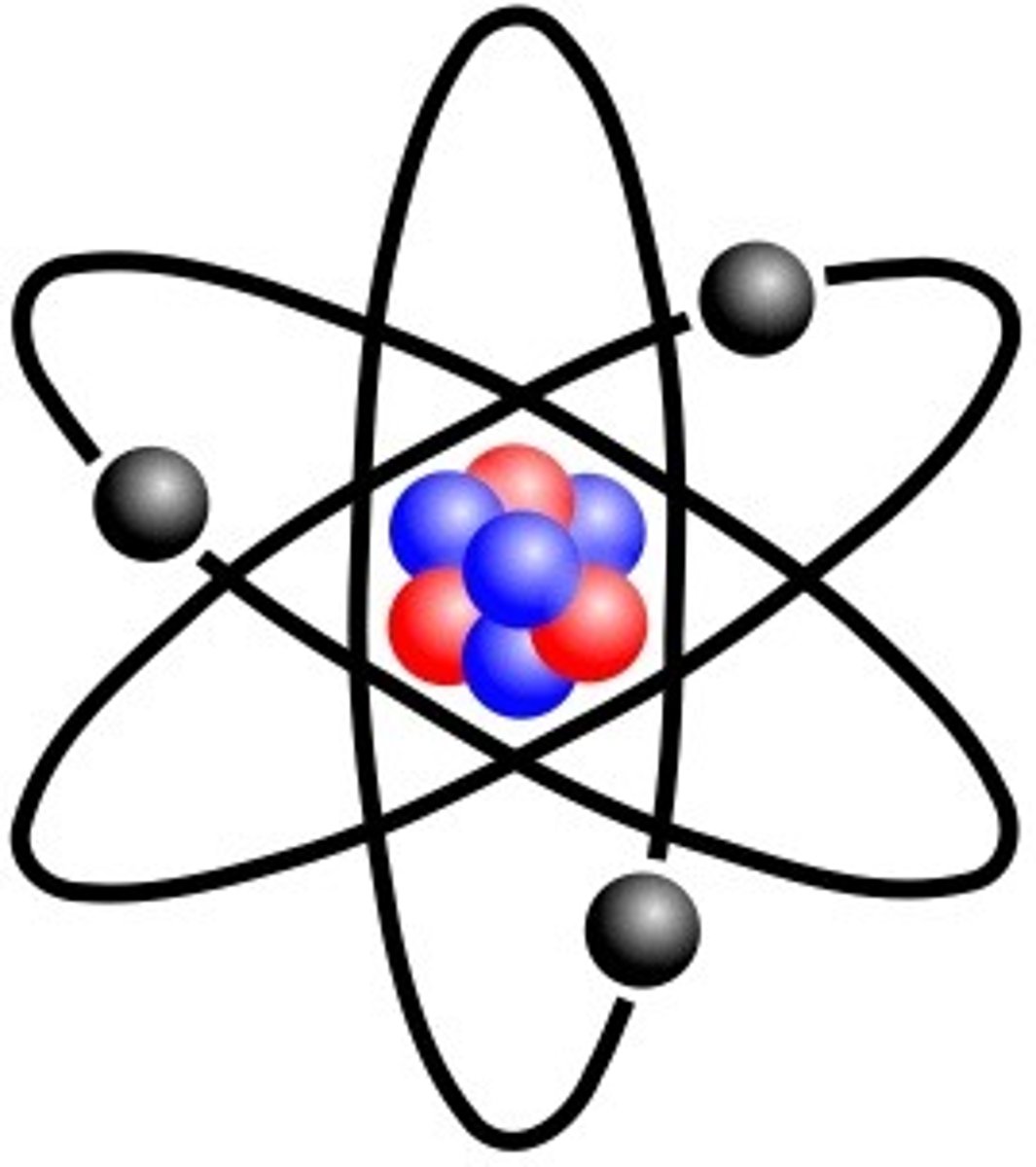
First came up with the idea of the atom:
Democritus
Discovered the positively charged protons in the nucleus:
Rutherford
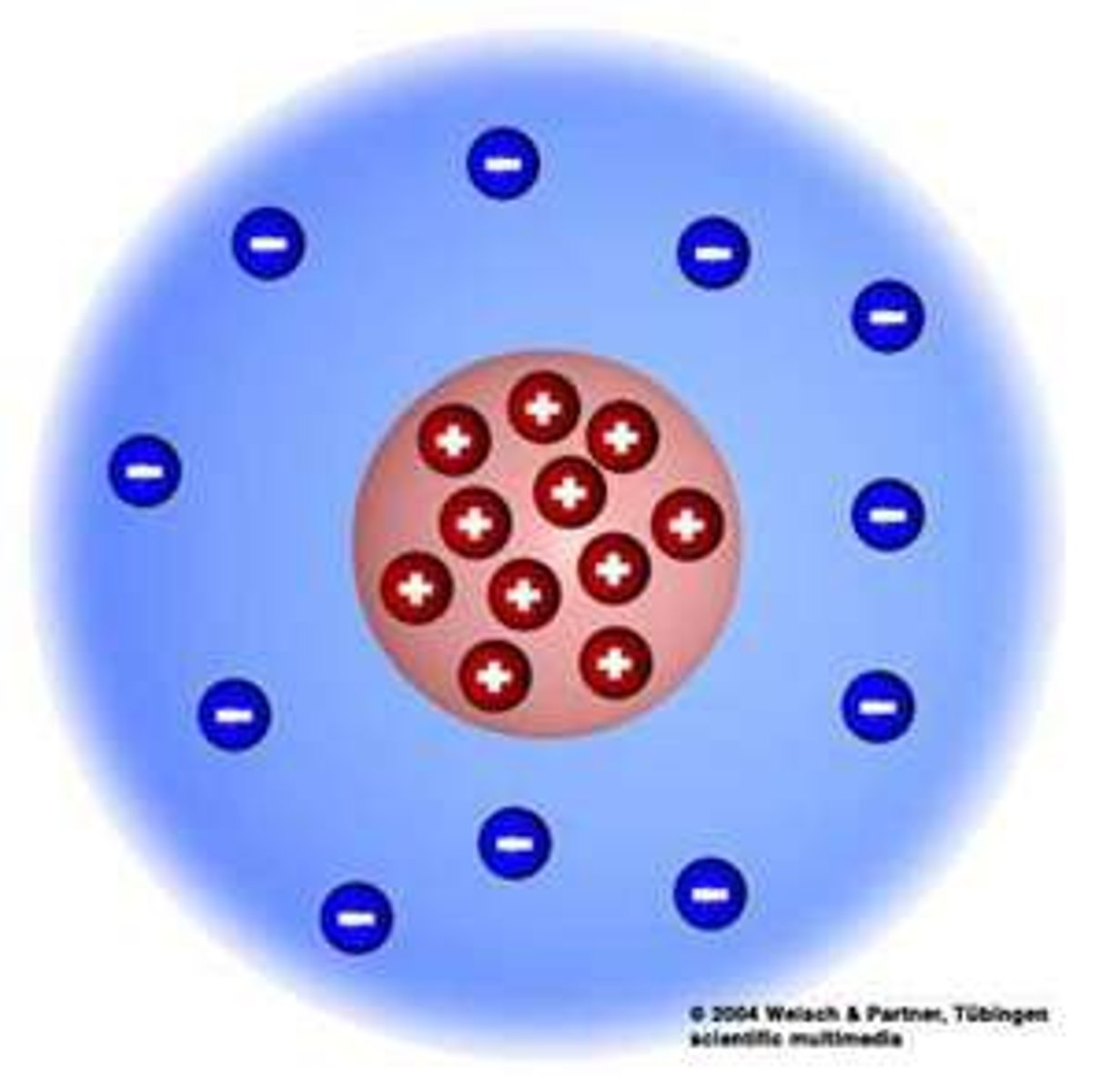
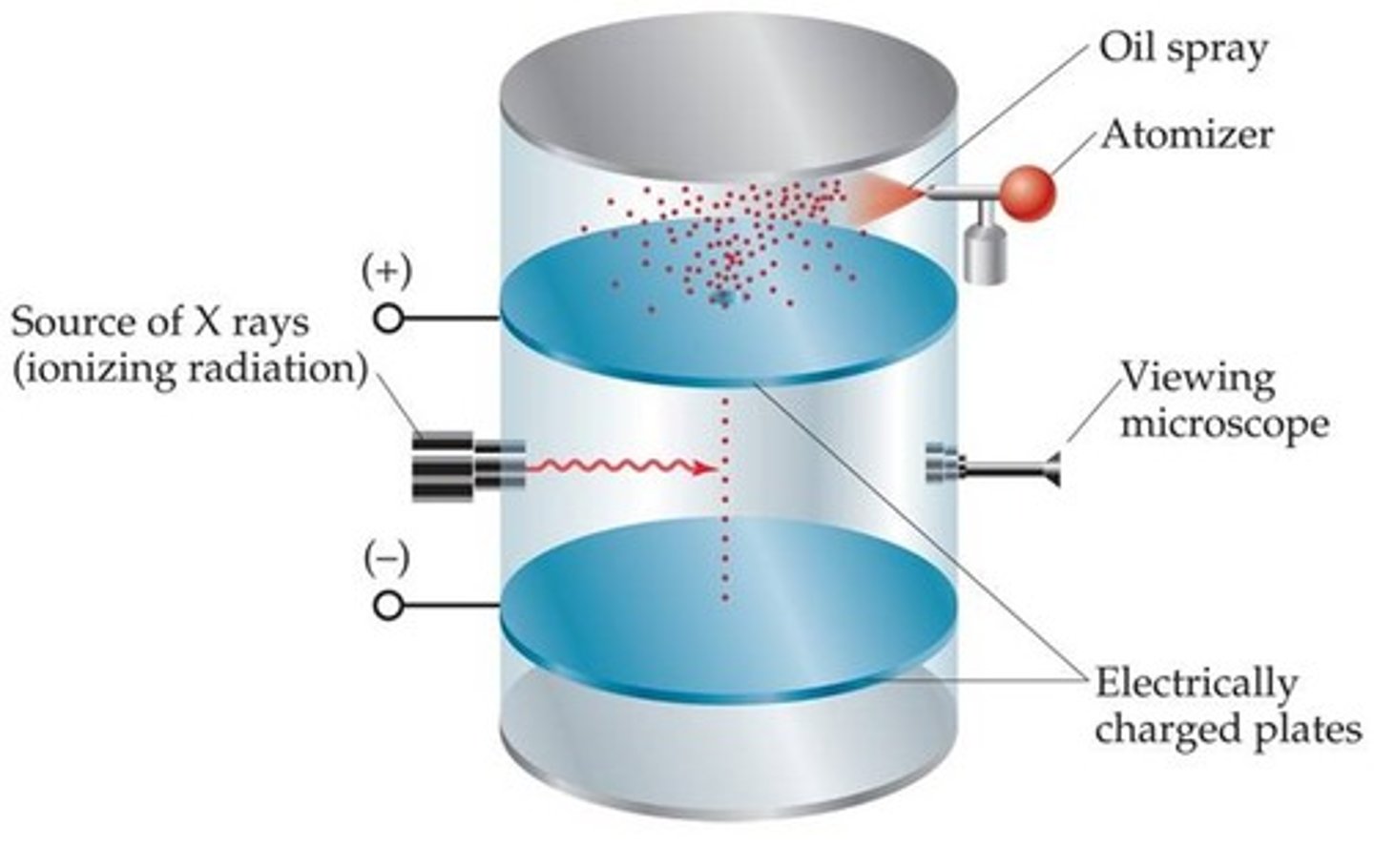
Oil drop experiment:
Millikan
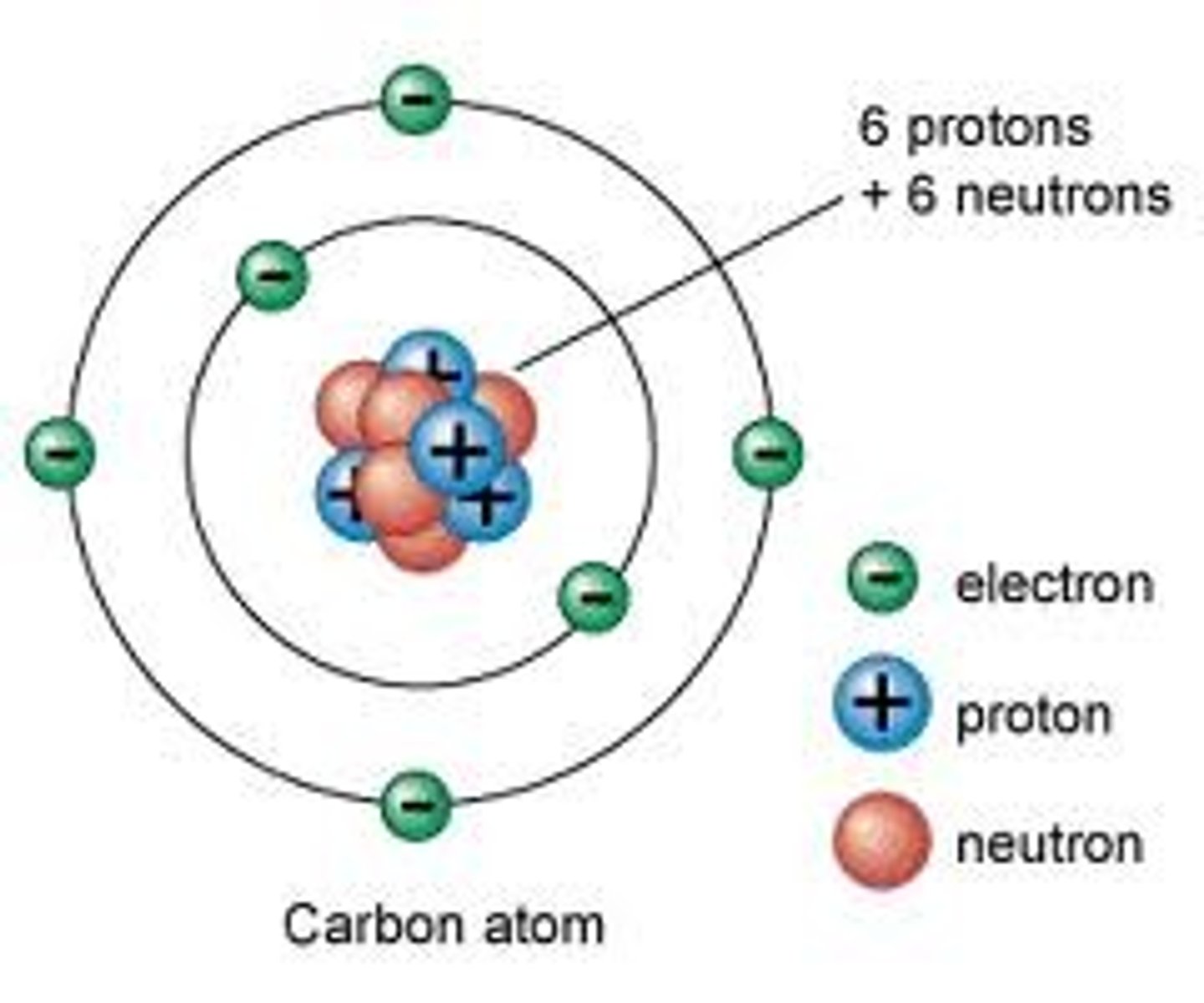
Discovered the electron:
Thomson
Discovered the neutron:
Chadwick
Gamma Decay
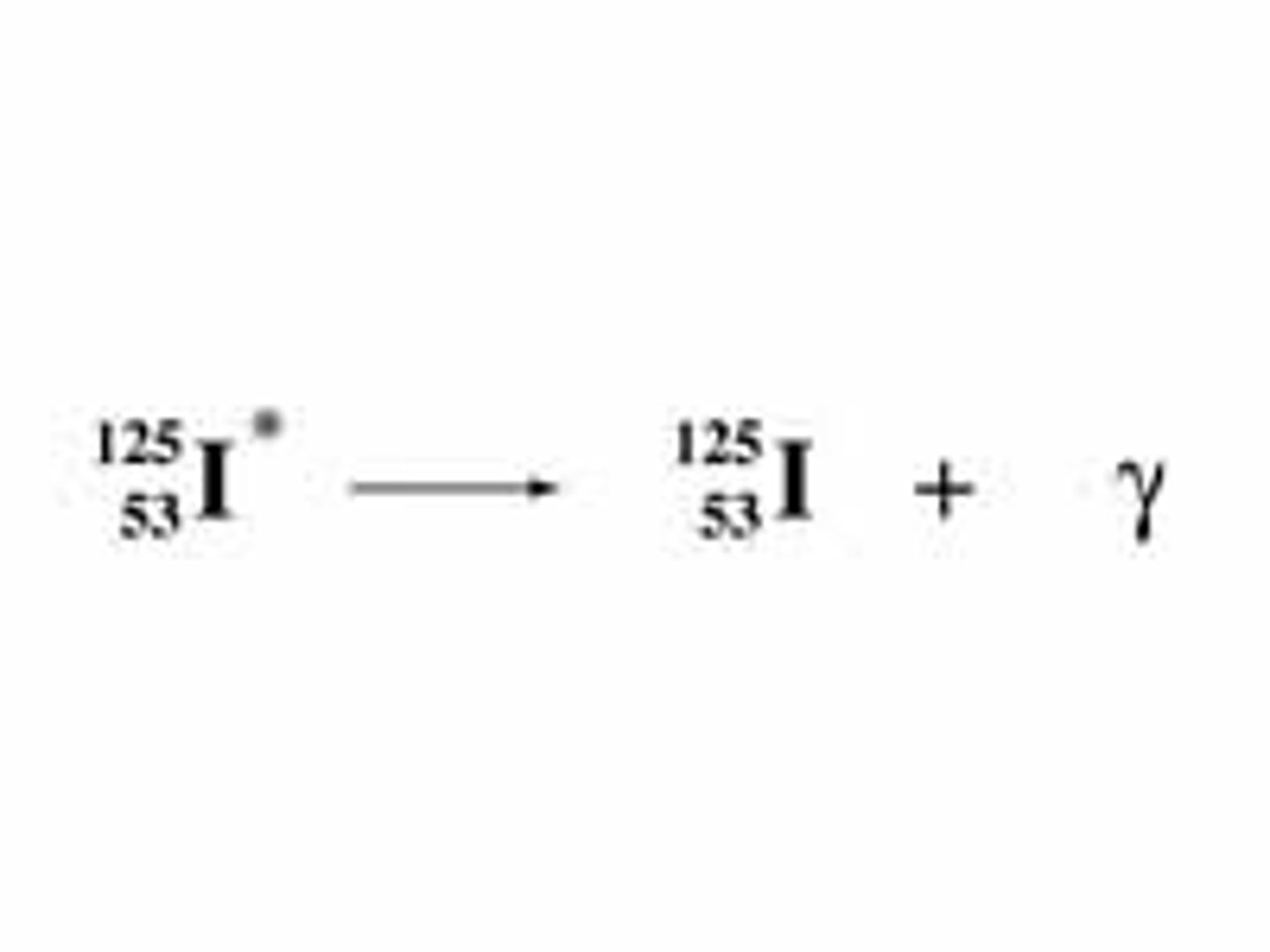
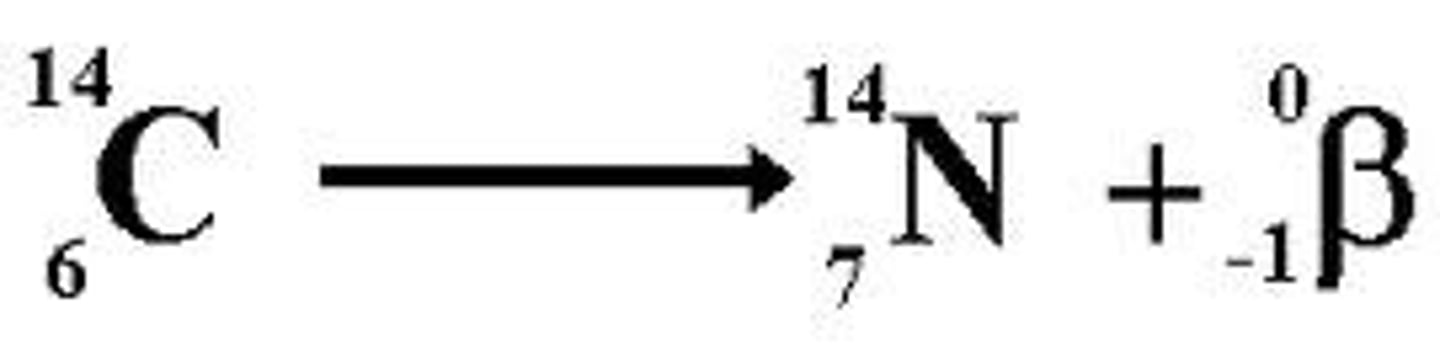
Beta Decay
Alpha Decay
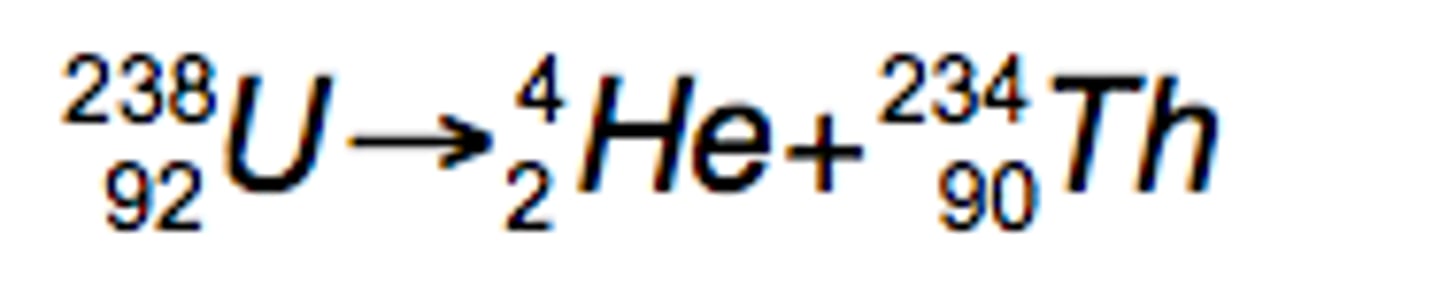
In _______ decay, the nucleus is too big so it spits out 2 neutrons and 2 protons to slim down.
Alpha
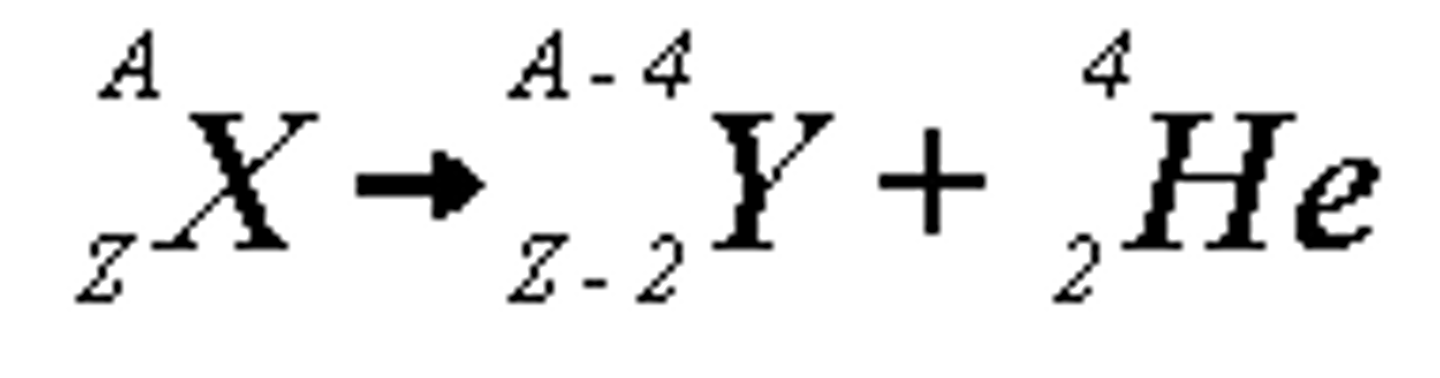
In _________ decay, there are too many neutrons and not enough protons in the nucleus, so a neutron turns into a proton.
Beta
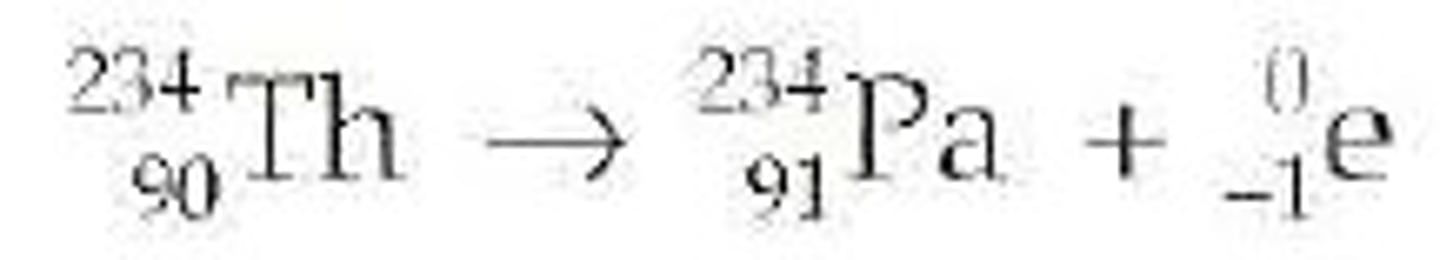
In _____________ decay, no particles (protons or neutrons) are released, so the photon carries no mass or charge.
Gamma
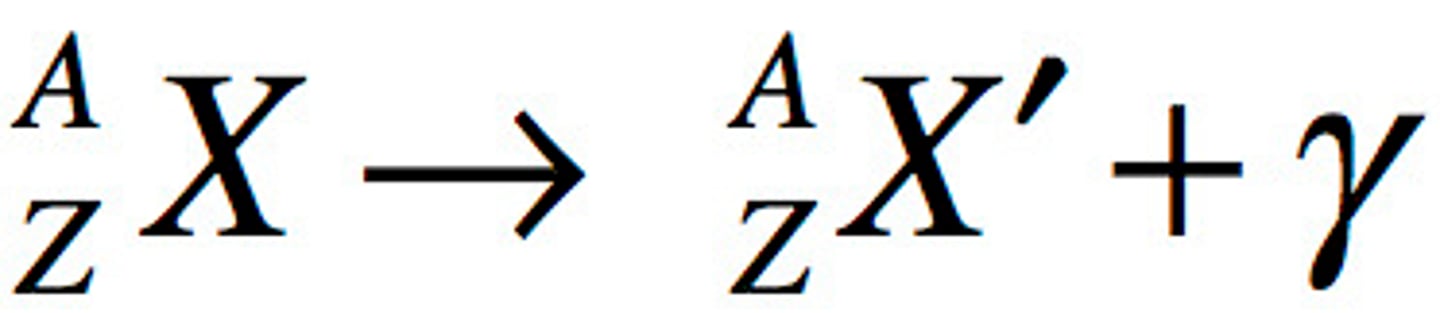
Magnesium has 3 stable isotopes. Calculate its average atomic mass, using the information below
Isotope - Magnesium-24, Magnesium-25, Magnesium-26
Mass - 23.985 amu, 24.986 amu, 25.983 amu
Abundance - 78.99%, 10.00%, 11.01%
You make the abundance a decimal by moving the point all the way to the left. You keep the mass the way that it is.
(M1)(A1) + (M2)(A2) + (M3)(A3) = Avg: ?
(23.985)(.7899) + (24.986)(.1000) + (25.983)(.1101) = Avg: ?
18.9457515 + 2.4986 + 2.8607283 = 24.3050798
Avg = 24. 305 = 24.31 amu
Avg = 24.305 = 24.31 amu
If you start with 1,000 g of Uranium, how much will be left after 33 days? t1/2 = 11 days (Hint: Find the # of half-lives.)
Start: 1000
You do how many times the 11 days goes into 33 by multiplying it by itself and a number until you get to 33. You then take half of what you started with (1000), and divide it by 2, and get an answer for the first day. You keep doing this until you make it all the way to 3 days, and come up with your final answer.
1/2n
1 = 11 1=500
2 = 22 2= 250
3 = 33 3=125
Your half lives are the numbers you use to figure out how many of them are in 11 days (then multiplied as the number gets bigger). What is left is all determined from taking half of what you started with, and putting it with the correct half life. (The solution you get)
The number of half-lives is 3, and the amount of Uranium that will be left is 125 g.
If you start with 500 g of Uranium, what percent will be left after 40 days? t1/2 = 10 days (Hint: Find the # of half-lives.)
Start: 500
You do how many times the 10 days goes into 40 by multiplying it by itself and a number until you get to 40. You then take half of what you started with (500), and divide it by 2, and get an answer for the first day. You keep doing this until you make it all the way to 4 days, and come up with your final answer.
1/2n
1 = 10 1 = 250
2 = 20 2 = 125
3 = 30 3 = 62.5
4 = 40 4 = 31.25
To find the percent, you always start with 100, and you divide it by 2 4 times, because of the number of half lives being 4. This will give you the correct answer to put in percent form.
100%/2 = 50/2 = 25/2 = 12.5/2 = 6.25
After 40 days, 6.25% of Uranium will be left. There are also 4 half lives.
This sublevel holds 10 electrons
Sublevel d
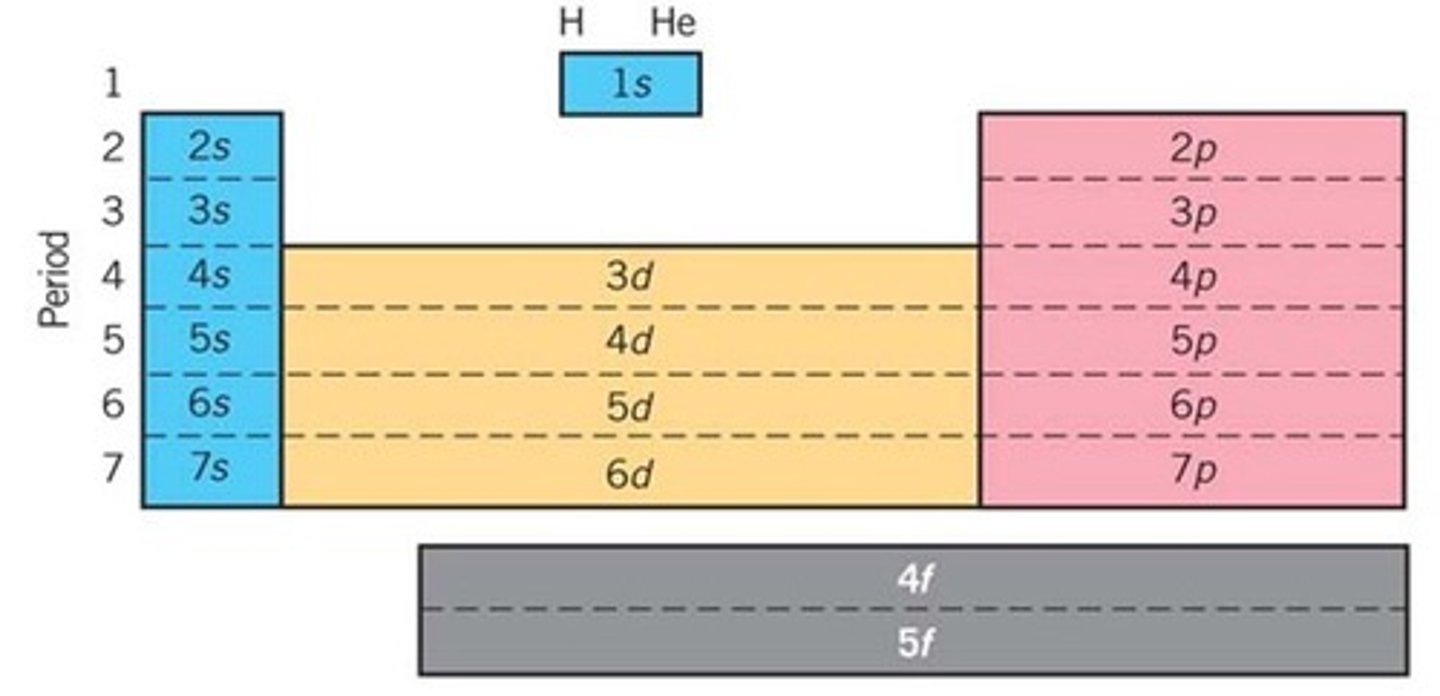
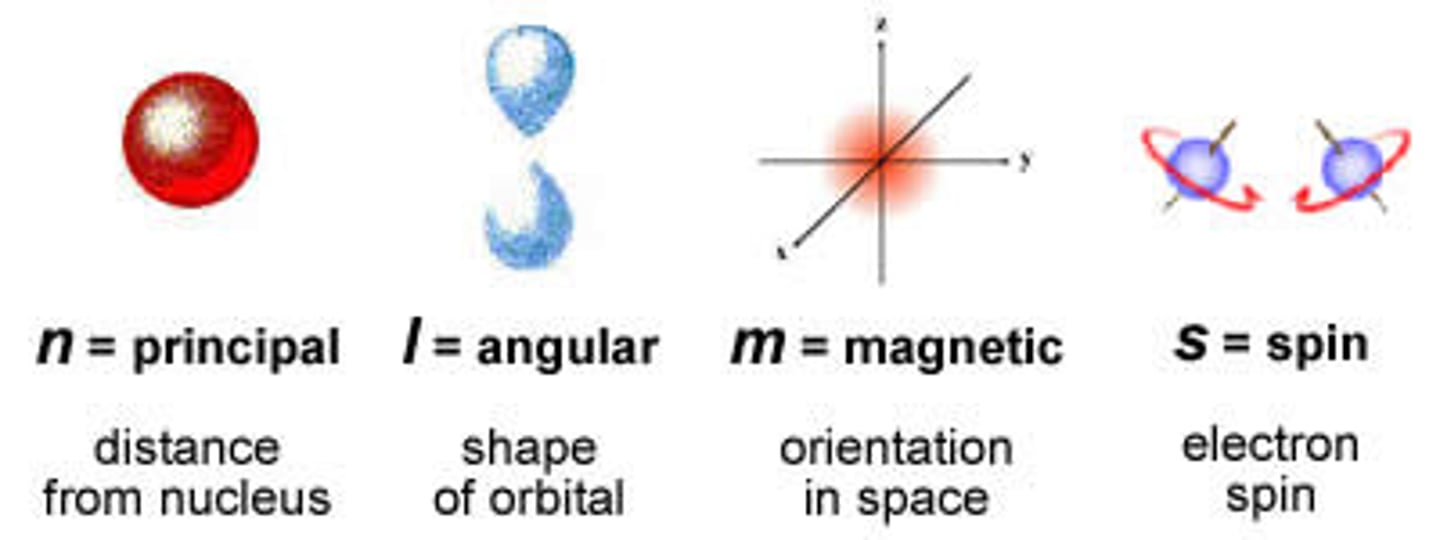
The way we describe the address of an individual electron are known as ________________ numbers.
Quantum